Abstract
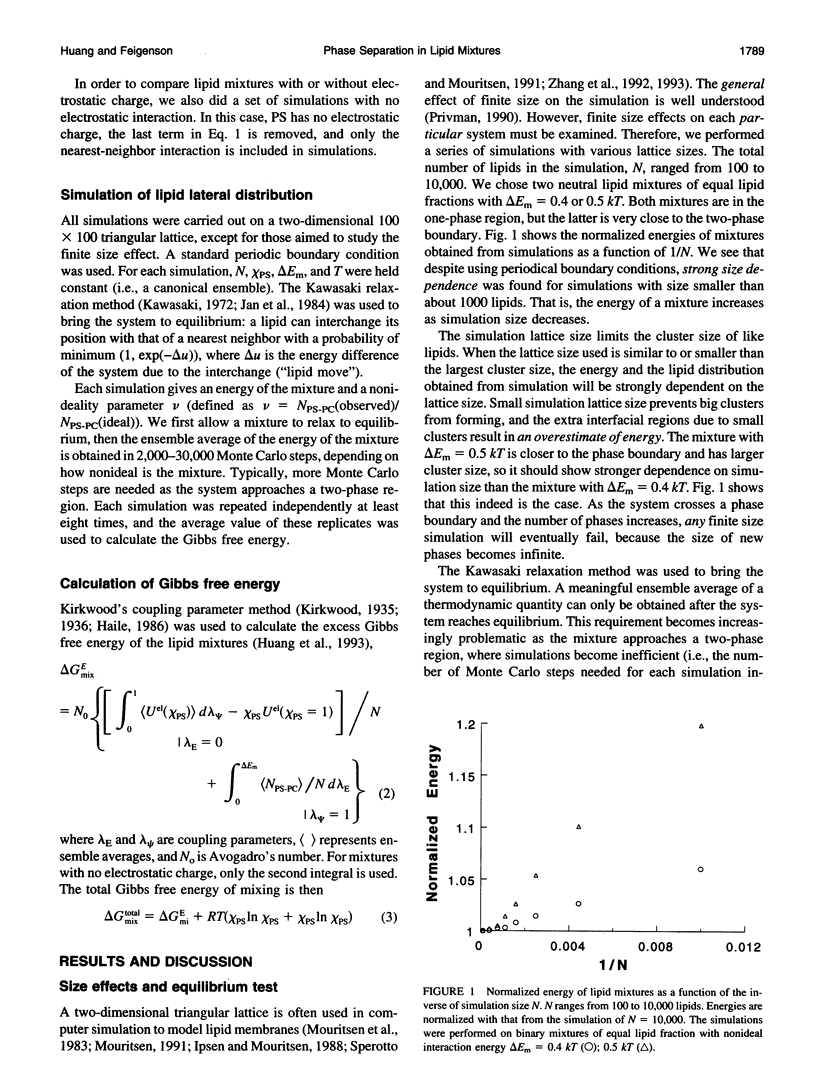
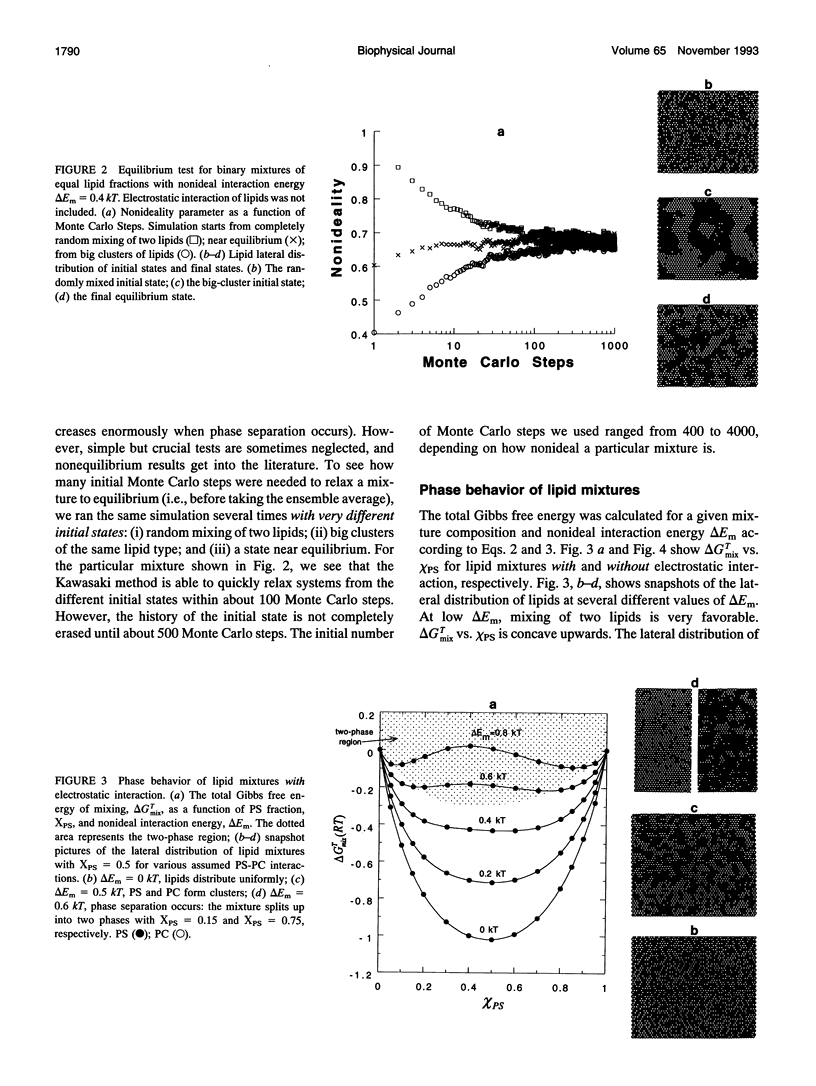
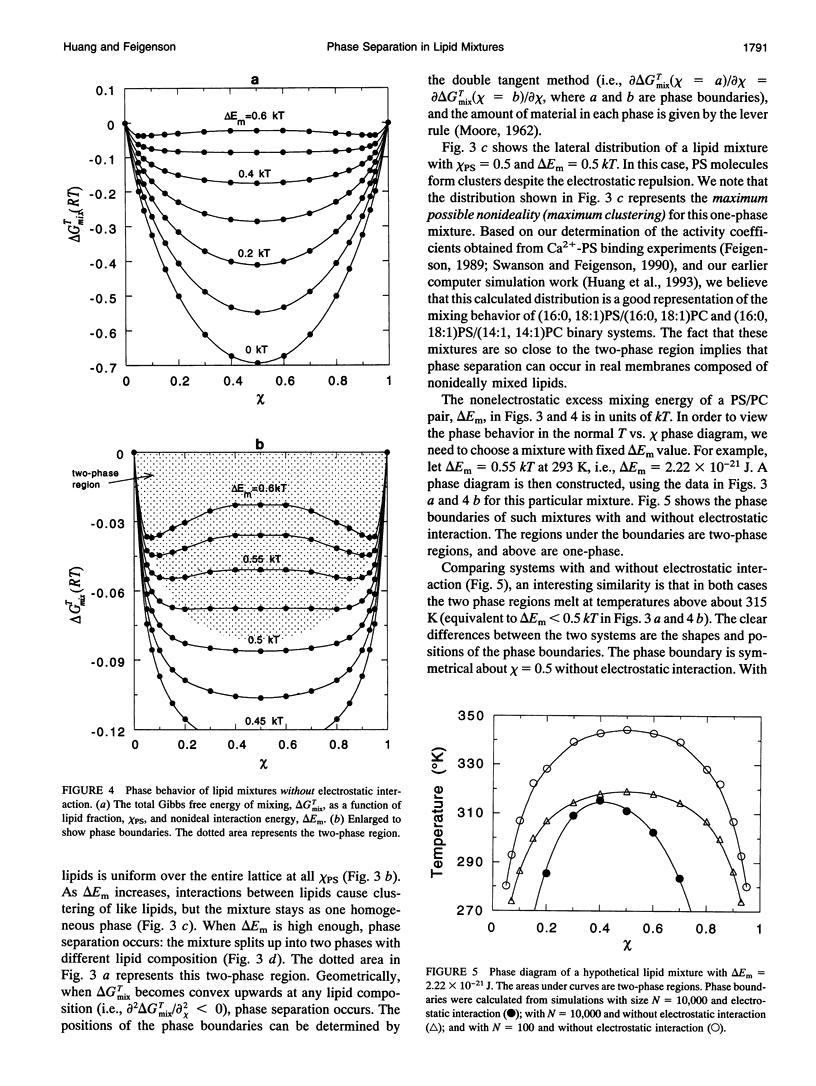
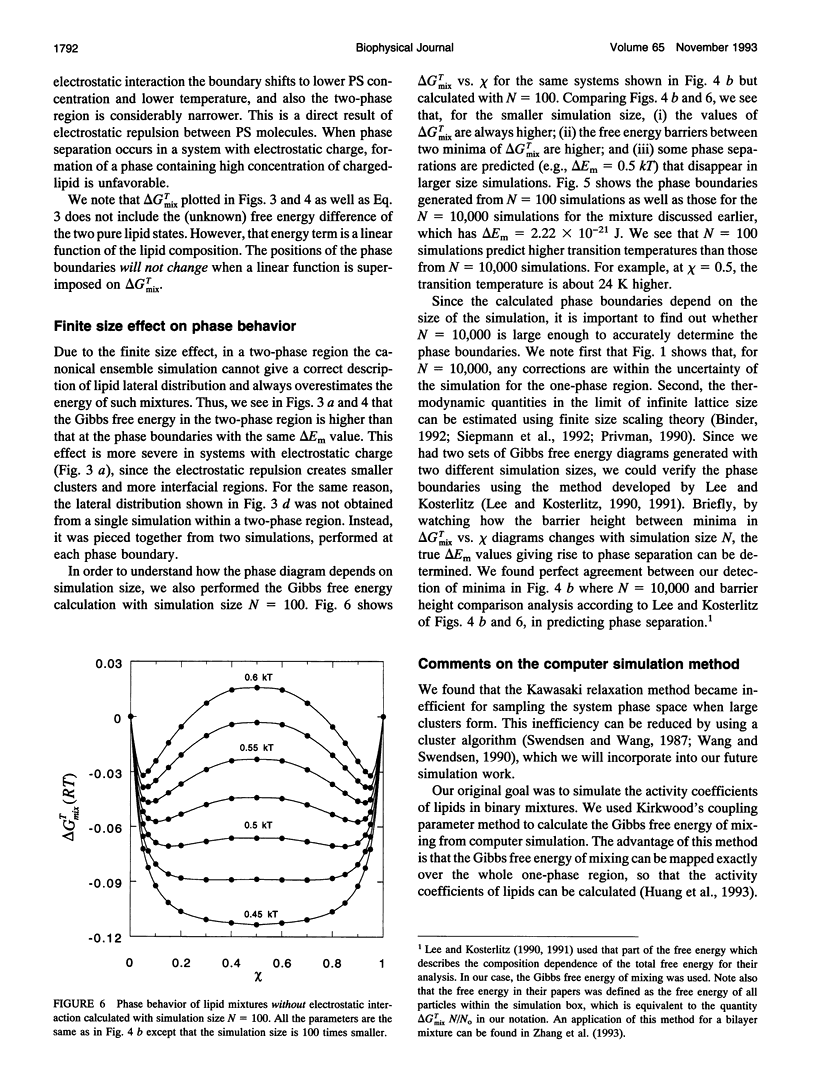
The nonideal mixing of phosphatidylserine (PS) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) binary lipid mixtures was studied by computer simulation based on a model wherein the excess energy of mixing is divided between an electrostatic term and one adjustable term delta Em that includes all other nonideal interactions. The lateral distribution of the lipids and the energy of the mixtures were obtained by using Kawasaki relaxation in a canonical ensemble. The Gibbs free energies were calculated by Kirkwood's coupling parameter method. The simulation results are strongly dependent on simulation size for sizes smaller than about 1000 lipids. Nonideal interaction between lipids can result in large scale separation of lipid phases of different composition at reasonable delta Em values as well as clustering of like lipids. In plots of total Gibbs free energy of mixing versus PS mole fraction in PS/PC, the boundaries of the two phase region could be accurately determined. The electrostatic interaction influences cluster size and shape, and also the composition of phases in the two-phase region.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Feigenson G. W. Calcium ion binding between lipid bilayers: the four-component system of phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylcholine, calcium chloride, and water. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):1270–1278. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J., Swanson J. E., Dibble A. R., Hinderliter A. K., Feigenson G. W. Nonideal mixing of phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylcholine in the fluid lamellar phase. Biophys J. 1993 Feb;64(2):413–425. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81382-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ipsen J. H., Mouritsen O. G. Modelling the phase equilibria in two-component membranes of phospholipids with different acyl-chain lengths. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 6;944(2):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jan N., Lookman T., Pink D. A. On computer simulation methods used to study models of two-component lipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1984 Jul 3;23(14):3227–3231. doi: 10.1021/bi00309a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnunen P. K. On the principles of functional ordering in biological membranes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 Mar;57(2-3):375–399. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90087-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. G. Lipid phase transitions and phase diagrams. II. Mictures involving lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Nov 14;472(3-4):285–344. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(77)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Kosterlitz JM. Finite-size scaling and Monte Carlo simulations of first-order phase transitions. Phys Rev B Condens Matter. 1991 Feb 1;43(4):3265–3277. doi: 10.1103/physrevb.43.3265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J, Kosterlitz JM. New numerical method to study phase transitions. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 Jul 9;65(2):137–140. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.65.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lookman T., Pink D. A., Grundke E. W., Zuckermann M. J., deVerteuil F. Phase separation in lipid bilayers containing integral proteins. Computer simulation studies. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5593–5601. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen O. G. Theoretical models of phospholipid phase transitions. Chem Phys Lipids. 1991 Mar;57(2-3):179–194. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(91)90075-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Wiener M. C. Structure of fully hydrated bilayer dispersions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Jul 7;942(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90268-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauvé R., Ohki S. Interactions of divalent cations with negatively charged membrane surfaces. I. Discrete charge potential. J Theor Biol. 1979 Nov 21;81(2):157–179. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(79)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperotto M. M., Mouritsen O. G. Mean-field and Monte Carlo simulation studies of the lateral distribution of proteins in membranes. Eur Biophys J. 1991;19(4):157–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00196342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. E., Feigenson G. W. Thermodynamics of mixing of phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine from measurements of high-affinity calcium binding. Biochemistry. 1990 Sep 11;29(36):8291–8297. doi: 10.1021/bi00488a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swendsen RH, Wang JS. Nonuniversal critical dynamics in Monte Carlo simulations. Phys Rev Lett. 1987 Jan 12;58(2):86–88. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.58.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z., Sperotto M. M., Zuckermann M. J., Mouritsen O. G. A microscopic model for lipid/protein bilayers with critical mixing. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 8;1147(1):154–160. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90326-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Laradji M, Guo H, Mouritsen OG, Zuckermann MJ. Phase behavior of pure lipid bilayers with mismatch interactions. Phys Rev A. 1992 May 15;45(10):7560–7567. doi: 10.1103/physreva.45.7560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


