Abstract
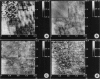
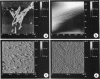
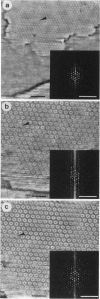
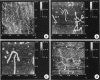
Scanning force microscopy allows imaging of biological molecules in their native state in buffer solution. To this end samples have to be fixed to a flat solid support so that they cannot be displaced by the scanning tip. Here we describe a method to achieve the covalent binding of biological samples to glass surfaces. Coverslips were chemically modified with the photoactivatable cross-linker N-5-azido-2-nitrobenzoyloxysuccinimide. Samples are squeezed between derivatized coverslips and then cross-linked to the glass surface by irradiation with ultraviolet light. Such samples can be imaged repeatedly by the scanning force microscope without loss of image quality, whereas identical but not immobilized samples are pushed away by the stylus.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebersold R. H., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Electroblotting onto activated glass. High efficiency preparation of proteins from analytical sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels for direct sequence analysis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4229–4238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aplin J. D., Hughes R. C., Jaffe C. L., Sharon N. Reversible cross-linking of cellular components of adherent fibroblasts to fibronectin and lectin-coated substrata. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Aug;134(2):488–494. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90453-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumeister W., Barth M., Hegerl R., Guckenberger R., Hahn M., Saxton W. O. Three-dimensional structure of the regular surface layer (HPI layer) of Deinococcus radiodurans. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 20;187(2):241–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90231-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt H. J., Downing K. H., Hansma P. K. Imaging the membrane protein bacteriorhodopsin with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1473–1480. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82492-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake B., Prater C. B., Weisenhorn A. L., Gould S. A., Albrecht T. R., Quate C. F., Cannell D. S., Hansma H. G., Hansma P. K. Imaging crystals, polymers, and processes in water with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1989 Mar 24;243(4898):1586–1589. doi: 10.1126/science.2928794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H., Moudrianakis E. N. The compaction of DNA helices into either continuous supercoils or folded-fiber rods and toroids. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):295–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90198-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A., Baumeister W., Saxton W. O. Mass mapping of a protein complex with the scanning transmission electron microscope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):4050–4054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.4050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A., Hoenger A., Hefti A., Henn C., Ford R. C., Kistler J., Zulauf M. Assembly of 2-D membrane protein crystals: dynamics, crystal order, and fidelity of structure analysis by electron microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Nov-Dec;109(3):219–234. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Vesenka J., Siegerist C., Kelderman G., Morrett H., Sinsheimer R. L., Elings V., Bustamante C., Hansma P. K. Reproducible imaging and dissection of plasmid DNA under liquid with the atomic force microscope. Science. 1992 May 22;256(5060):1180–1184. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5060.1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitlinger E., Peter M., Häner M., Lustig A., Aebi U., Nigg E. A. Expression of chicken lamin B2 in Escherichia coli: characterization of its structure, assembly, and molecular interactions. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(3):485–495. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.3.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendry R. M., Herrmann J. E. Immobilization of antibodies on nylon for use in enzyme-linked immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(3-4):285–296. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90255-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Sosinsky G. E., Revel J. P., Hansma P. K. Structure of the extracellular surface of the gap junction by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):149–163. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81074-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson B. S., Branton D. Plasma membrane: rapid isolation and exposure of the cytoplasmic surface by use of positively charged beads. Science. 1977 Jan 21;195(4275):302–304. doi: 10.1126/science.831278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeng T. W., Crowther R. A., Stubbs G., Chiu W. Visualization of alpha-helices in tobacco mosaic virus by cryo-electron microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jan 5;205(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90379-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. V., Roberts M. F., Dennis E. A., Allison W. S. Photoactivated heterobifunctional cross-linking reagents which demonstrate the aggregation state of phospholipase A2. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5650–5654. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyubchenko Y. L., Oden P. I., Lampner D., Lindsay S. M., Dunker K. A. Atomic force microscopy of DNA and bacteriophage in air, water and propanol: the role of adhesion forces. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1117–1123. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machleidt W., Wachter E. New supports in solid-phase sequencing. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:263–277. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47031-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manne S., Hansma P. K., Massie J., Elings V. B., Gewirth A. A. Atomic-resolution electrochemistry with the atomic force microscope: copper deposition on gold. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):183–186. doi: 10.1126/science.251.4990.183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Stubbs G. Structure of tobacco mosaic virus at 3.6 A resolution: implications for assembly. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3952490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quash G., Roch A. M., Niveleau A., Grange J., Keolouangkhot T., Huppert J. The preparation of latex particles with covalently bound polyamines, IgG and measles agglutinins and their use in visual agglutination tests. J Immunol Methods. 1978;22(1-2):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radmacher M., Tillmann R. W., Gaub H. E. Imaging viscoelasticity by force modulation with the atomic force microscope. Biophys J. 1993 Mar;64(3):735–742. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81433-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson P. J., Dunnill P., Lilly M. D. Porous glass as a solid support for immobilisation or affinity chromatography of enzymes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Sep 22;242(3):659–661. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(71)90160-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarin V. K., Kent S. B., Tam J. P., Merrifield R. B. Quantitative monitoring of solid-phase peptide synthesis by the ninhydrin reaction. Anal Biochem. 1981 Oct;117(1):147–157. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90704-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaiu W. L., Larson D. D., Vesenka J., Henderson E. Atomic force microscopy of oriented linear DNA molecules labeled with 5nm gold spheres. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jan 11;21(1):99–103. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. J., Capaldi R. A., Muchmore D., Dahlquist F. Cross-linking of ubiquinone cytochrome c reductase (complex III) with periodate-cleavable bifunctional reagents. Biochemistry. 1978 Sep 5;17(18):3719–3723. doi: 10.1021/bi00611a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemmer A., Engel A. Imaging biological macromolecules by STM: quantitative interpretation of topographs. Ultramicroscopy. 1990 Dec;34(3):129–140. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(90)90067-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemmer A., Hefti A., Aebi U., Engel A. Scanning tunneling and transmission electron microscopy on identical areas of biological specimens. Ultramicroscopy. 1989 Jul-Aug;30(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(89)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven A. C., Couture E., Aebi U., Showe M. K. Structure of T4 polyheads. II. A pathway of polyhead transformation as a model for T4 capsid maturation. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 5;106(1):187–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90307-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. Intermediate filaments: structure, assembly and molecular interactions. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;2(1):91–100. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(05)80037-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unwin P. N., Klug A. Electron microscopy of the stacked disk aggregate of tobacco mosaic virus protein. I. Three-dimensional image reconstruction. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 25;87(4):641–656. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90075-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesenka J., Guthold M., Tang C. L., Keller D., Delaine E., Bustamante C. Substrate preparation for reliable imaging of DNA molecules with the scanning force microscope. Ultramicroscopy. 1992 Jul;42-44(Pt B):1243–1249. doi: 10.1016/0304-3991(92)90430-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wachter E., Machleidt W., Hofner H., Otto J. Aminopropyl glass and its p-phenylene diisothiocyanate derivative, a new support in solid-phase Edman degradation of peptides and proteins. FEBS Lett. 1973 Sep 1;35(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z. H., Hartmann T., Baumeister W., Guckenberger R. Thickness determination of biological samples with a zeta-calibrated scanning tunneling microscope. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9343–9347. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weetall H. H. Covalent coupling methods for inorganic support materials. Methods Enzymol. 1976;44:134–148. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(76)44012-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisenhorn A. L., Drake B., Prater C. B., Gould S. A., Hansma P. K., Ohnesorge F., Egger M., Heyn S. P., Gaub H. E. Immobilized proteins in buffer imaged at molecular resolution by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Nov;58(5):1251–1258. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82465-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegräbe W., Nonnenmacher M., Guckenberger R., Wolter O. Atomic force microscopy of a hydrated bacterial surface protein. J Microsc. 1991 Jul;163(Pt 1):79–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1991.tb03161.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Tamm L. K., Tillack T. W., Shao Z. New approach for atomic force microscopy of membrane proteins. The imaging of cholera toxin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):286–290. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zenhausern F., Adrian M., ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Emch R., Jobin M., Taborelli M., Descouts P. Imaging of DNA by scanning force microscopy. J Struct Biol. 1992 Jan-Feb;108(1):69–73. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(92)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]