Abstract
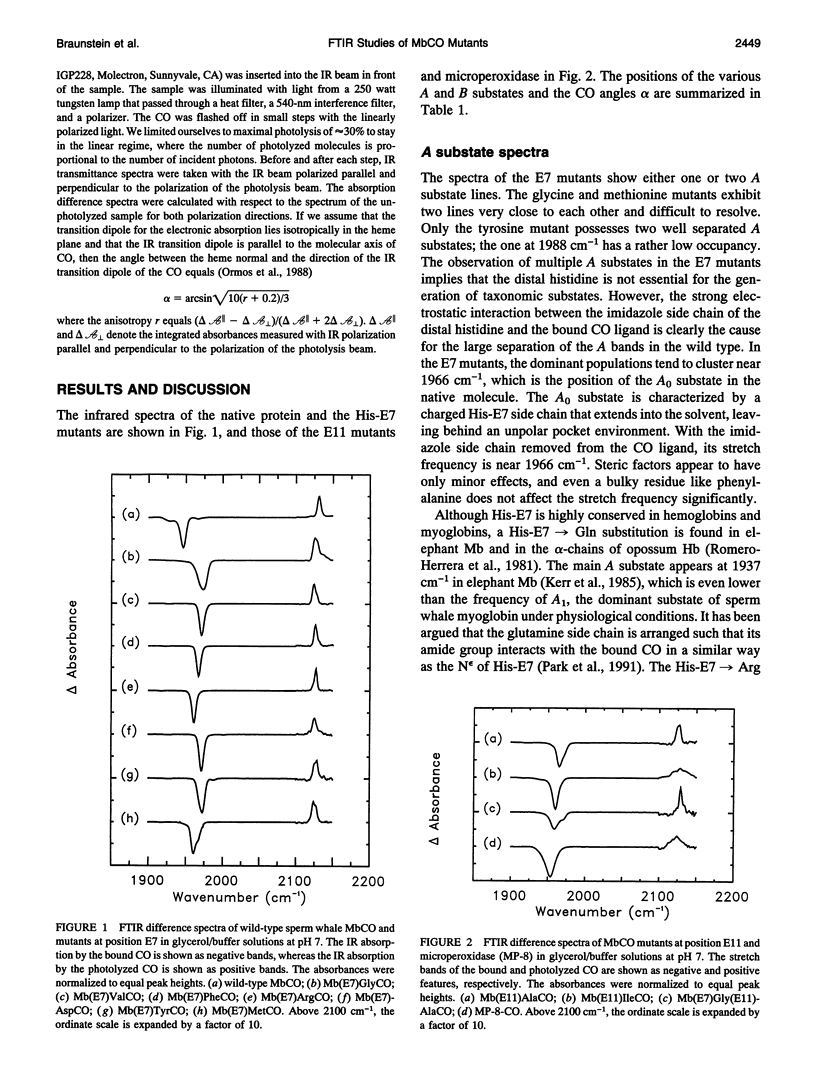
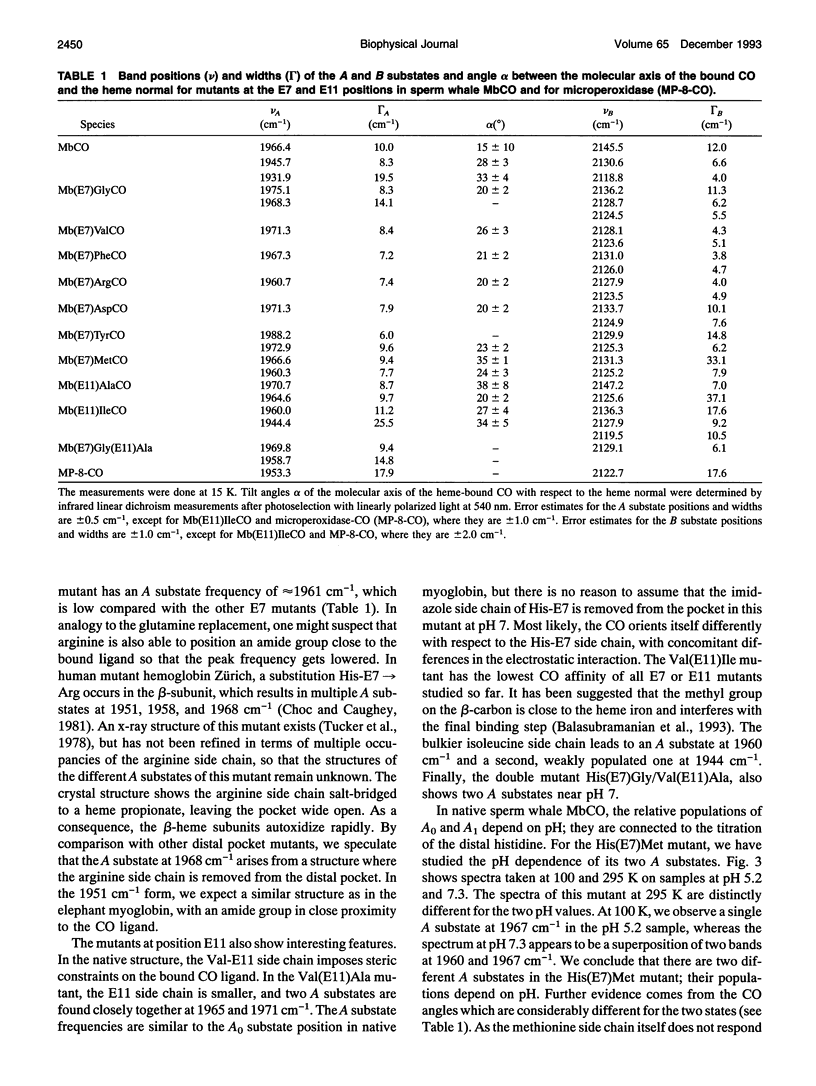
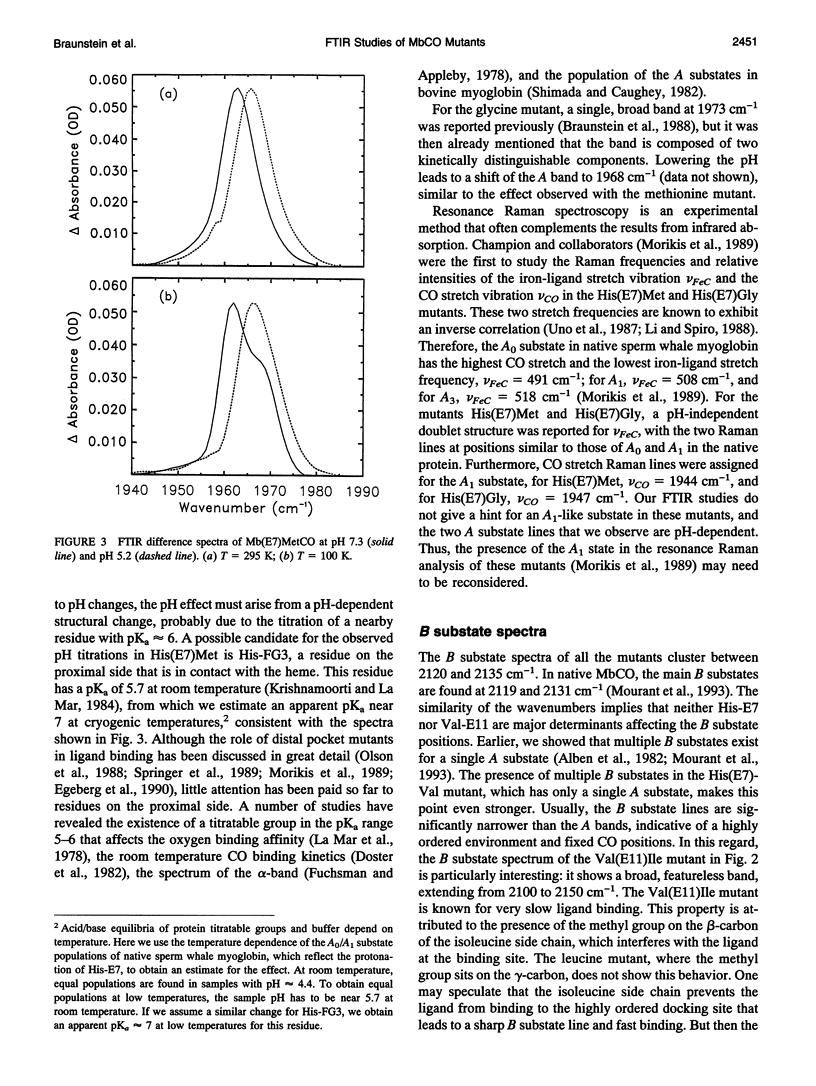
Fouier-transform infrared (FTIR) difference spectra of several His-E7 and Val-E11 mutants of sperm whale carbonmonoxymyoglobin were obtained by photodissociation at cryogenic temperatures. The IR absorption of the CO ligand shows characteristic features for each of the mutants, both in the ligand-bound (A) state and in the photodissociated (B) state. For most of the mutants, a single A substate band is observed, which points to the crucial role of the His-E7 residue in determining the A substrate spectrum of the bound CO in the native structure. The fact that some of the mutants show more than one stretch band of the bound CO indicates that the appearance of multiple A substates is not exclusively connected to the presence of His-E7. In all but one mutant, multiple stretch bands of the CO in the photodissociated state are observed; these B substates are thought to arise from discrete positions and/or orientations of the photodissociated ligand in the heme pocket. The red shifts of the B bands with respect to the free-gas frequency indicate weak binding in the heme pocket. The observation of similar red shifts in microperoxidase (MP-8), where there is no residue on the distal side, suggests that the photodissociated ligand is still associated with the heme iron. Photoselection experiments were performed to determine the orientation of the bound ligand with respect to the heme normal by photolyzing small fractions of the sample with linearly polarized light at 540 nm. The resulting linear dichroism in the CO stretch spectrum yielded angles alpha > 20 degrees between the CO molecular axis and the heme normal for all of the mutants. We conclude that the off-axis position of the CO ligand in the native structure does not arise from steric constraints imposed by the distal histidine. There is no clear correlation between the size of the distal residue and the alpha of the CO ligand.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberding N., Austin R. H., Beeson K. W., Chan S. S., Eisenstein L., Frauenfelder H., Nordlund T. M. Tunneling in ligand binding to heme proteins. Science. 1976 Jun 4;192(4243):1002–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.1273579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anfinrud P. A., Han C., Hochstrasser R. M. Direct observations of ligand dynamics in hemoglobin by subpicosecond infrared spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8387–8391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A., Berendzen J., Bowne S. F., Frauenfelder H., Iben I. E., Sauke T. B., Shyamsunder E., Young R. D. Protein states and proteinquakes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5000–5004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari A., Berendzen J., Braunstein D., Cowen B. R., Frauenfelder H., Hong M. K., Iben I. E., Johnson J. B., Ormos P., Sauke T. B. Rebinding and relaxation in the myoglobin pocket. Biophys Chem. 1987 May 9;26(2-3):337–355. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(87)80034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balasubramanian S., Lambright D. G., Marden M. C., Boxer S. G. CO recombination to human myoglobin mutants in glycerol-water solutions. Biochemistry. 1993 Mar 9;32(9):2202–2212. doi: 10.1021/bi00060a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein D., Ansari A., Berendzen J., Cowen B. R., Egeberg K. D., Frauenfelder H., Hong M. K., Ormos P., Sauke T. B., Scholl R. Ligand binding to synthetic mutant myoglobin (His-E7----Gly): role of the distal histidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8497–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown W. E., 3rd, Sutcliffe J. W., Pulsinelli P. D. Multiple internal reflectance infrared spectra of variably hydrated hemoglobin and myoglobin films: effects of globin hydration on ligand conformer dynamics and reactivity at the heme. Biochemistry. 1983 Jun 7;22(12):2914–2923. doi: 10.1021/bi00281a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carver T. E., Rohlfs R. J., Olson J. S., Gibson Q. H., Blackmore R. S., Springer B. A., Sligar S. G. Analysis of the kinetic barriers for ligand binding to sperm whale myoglobin using site-directed mutagenesis and laser photolysis techniques. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):20007–20020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chance B., Fischetti R., Powers L. Structure and kinetics of the photoproduct of carboxymyoglobin at low temperatures: an X-ray absorption study. Biochemistry. 1983 Aug 2;22(16):3820–3829. doi: 10.1021/bi00285a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choc M. G., Caughey W. S. Evidence from infrared and 13C NMR spectra for discrete rapidly interconverting conformers at the carbon monoxide binding sites of hemoglobins A and Zurich. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1831–1838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman J. P., Brauman J. I., Halbert T. R., Suslick K. S. Nature of O2 and CO binding to metalloporphyrins and heme proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3333–3337. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doster W., Beece D., Bowne S. F., DiIorio E. E., Eisenstein L., Frauenfelder H., Reinisch L., Shyamsunder E., Winterhalter K. H., Yue K. T. Control and pH dependence of ligand binding to heme proteins. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4831–4839. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egeberg K. D., Springer B. A., Sligar S. G., Carver T. E., Rohlfs R. J., Olson J. S. The role of Val68(E11) in ligand binding to sperm whale myoglobin. Site-directed mutagenesis of a synthetic gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11788–11795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiamingo F. G., Alben J. O. Structures of photolyzed carboxymyoglobin. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):7964–7970. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frauenfelder H., Sligar S. G., Wolynes P. G. The energy landscapes and motions of proteins. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1598–1603. doi: 10.1126/science.1749933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchsman W. H., Appleby C. A. CO and O2 complexes of soybean leghemoglobins: pH effects upon infrared and visible spectra. Comparisons with CO and O2 complexes of myoglobin and hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1309–1321. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong M. K., Braunstein D., Cowen B. R., Frauenfelder H., Iben I. E., Mourant J. R., Ormos P., Scholl R., Schulte A., Steinbach P. J. Conformational substates and motions in myoglobin. External influences on structure and dynamics. Biophys J. 1990 Aug;58(2):429–436. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82388-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr E. A., Yu N. T., Bartnicki D. E., Mizukami H. Resonance Raman studies of CO and O2 binding to elephant myoglobin (distal His(E7)----Gln). J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8360–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamoorthi R., La Mar G. N. Identification of the titrating group in the heme cavity of myoglobin. Evidence for the heme-protein pi-pi interaction. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 2;138(1):135–140. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07892.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuriyan J., Wilz S., Karplus M., Petsko G. A. X-ray structure and refinement of carbon-monoxy (Fe II)-myoglobin at 1.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 5;192(1):133–154. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90470-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Mar G. N., Budd D. L., Viscio D. B., Smith K. M., Langry K. C. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance characterization of heme disorder in hemoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5755–5759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makinen M. W., Houtchens R. A., Caughey W. S. Structure of carboxymyoglobin in crystals and in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6042–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell J. C., Caughey W. S. An infrared study of NO bonding to heme B and hemoglobin A. Evidence for inositol hexaphosphate induced cleavage of proximal histidine to iron bonds. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):388–396. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. N., Hansen P. A., Hochstrasser R. M. Iron-carbonyl bond geometries of carboxymyoglobin and carboxyhemoglobin in solution determined by picosecond time-resolved infrared spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5062–5066. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morikis D., Champion P. M., Springer B. A., Sligar S. G. Resonance raman investigations of site-directed mutants of myoglobin: effects of distal histidine replacement. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4791–4800. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mourant J. R., Braunstein D. P., Chu K., Frauenfelder H., Nienhaus G. U., Ormos P., Young R. D. Ligand binding to heme proteins: II. Transitions in the heme pocket of myoglobin. Biophys J. 1993 Oct;65(4):1496–1507. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81218-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson J. S., Mathews A. J., Rohlfs R. J., Springer B. A., Egeberg K. D., Sligar S. G., Tame J., Renaud J. P., Nagai K. The role of the distal histidine in myoglobin and haemoglobin. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):265–266. doi: 10.1038/336265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormos P., Braunstein D., Frauenfelder H., Hong M. K., Lin S. L., Sauke T. B., Young R. D. Orientation of carbon monoxide and structure-function relationship in carbonmonoxymyoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8492–8496. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park K. D., Guo K. M., Adebodun F., Chiu M. L., Sligar S. G., Oldfield E. Distal and proximal ligand interactions in heme proteins: correlations between C-O and Fe-C vibrational frequencies, oxygen-17 and carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance chemical shifts, and oxygen-17 nuclear quadrupole coupling constants in C17O- and 13CO-labeled species. Biochemistry. 1991 Mar 5;30(9):2333–2347. doi: 10.1021/bi00223a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Myoglobin and haemoglobin: role of distal residues in reactions with haem ligands. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Feb;14(2):42–44. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90039-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrich J. W., Lambry J. C., Kuczera K., Karplus M., Poyart C., Martin J. L. Ligand binding and protein relaxation in heme proteins: a room temperature analysis of NO geminate recombination. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3975–3987. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips G. N., Jr, Arduini R. M., Springer B. A., Sligar S. G. Crystal structure of myoglobin from a synthetic gene. Proteins. 1990;7(4):358–365. doi: 10.1002/prot.340070407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers L., Chance B., Chance M., Campbell B., Friedman J., Khalid S., Kumar C., Naqui A., Reddy K. S., Zhou Y. Kinetic, structural, and spectroscopic identification of geminate states of myoglobin: a ligand binding site on the reaction pathway. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 28;26(15):4785–4796. doi: 10.1021/bi00389a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohlfs R. J., Mathews A. J., Carver T. E., Olson J. S., Springer B. A., Egeberg K. D., Sligar S. G. The effects of amino acid substitution at position E7 (residue 64) on the kinetics of ligand binding to sperm whale myoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 25;265(6):3168–3176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero-Herrera A. E., Goodman M., Dene H., Bartnicki D. E., Mizukami H. An exceptional amino acid replacement on the distal side of the iron atom in proboscidean myoglobin. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(3):140–147. doi: 10.1007/BF01733907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Caughey W. S. Dynamic protein structures. Effects of pH on conformer stabilities at the ligand-binding site of bovine heart myoglobin carbonyl. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):11893–11900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer B. A., Egeberg K. D., Sligar S. G., Rohlfs R. J., Mathews A. J., Olson J. S. Discrimination between oxygen and carbon monoxide and inhibition of autooxidation by myoglobin. Site-directed mutagenesis of the distal histidine. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3057–3060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer B. A., Sligar S. G. High-level expression of sperm whale myoglobin in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8961–8965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach P. J., Ansari A., Berendzen J., Braunstein D., Chu K., Cowen B. R., Ehrenstein D., Frauenfelder H., Johnson J. B., Lamb D. C. Ligand binding to heme proteins: connection between dynamics and function. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3988–4001. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng T. Y., Huang H. W., Olah G. A. 5 K extended X-ray absorption fine structure and 40 K 10-s resolved extended X-ray absorption fine structure studies of photolyzed carboxymyoglobin. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8066–8072. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker P. W., Phillips S. E., Perutz M. F., Houtchens R., Caughey W. S. Structure of hemoglobins Zürich [His E7(63)beta replaced by Arg] and Sydney [Val E11(67)beta replaced by Ala] and role of the distal residues in ligand binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1076–1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno T., Nishimura Y., Tsuboi M., Makino R., Iizuka T., Ishimura Y. Two types of conformers with distinct Fe-C-O configuration in the ferrous CO complex of horseradish peroxidase. Resonance Raman and infarared spectroscopic studies with native and deuteroheme-substituted enzymes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4549–4556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


