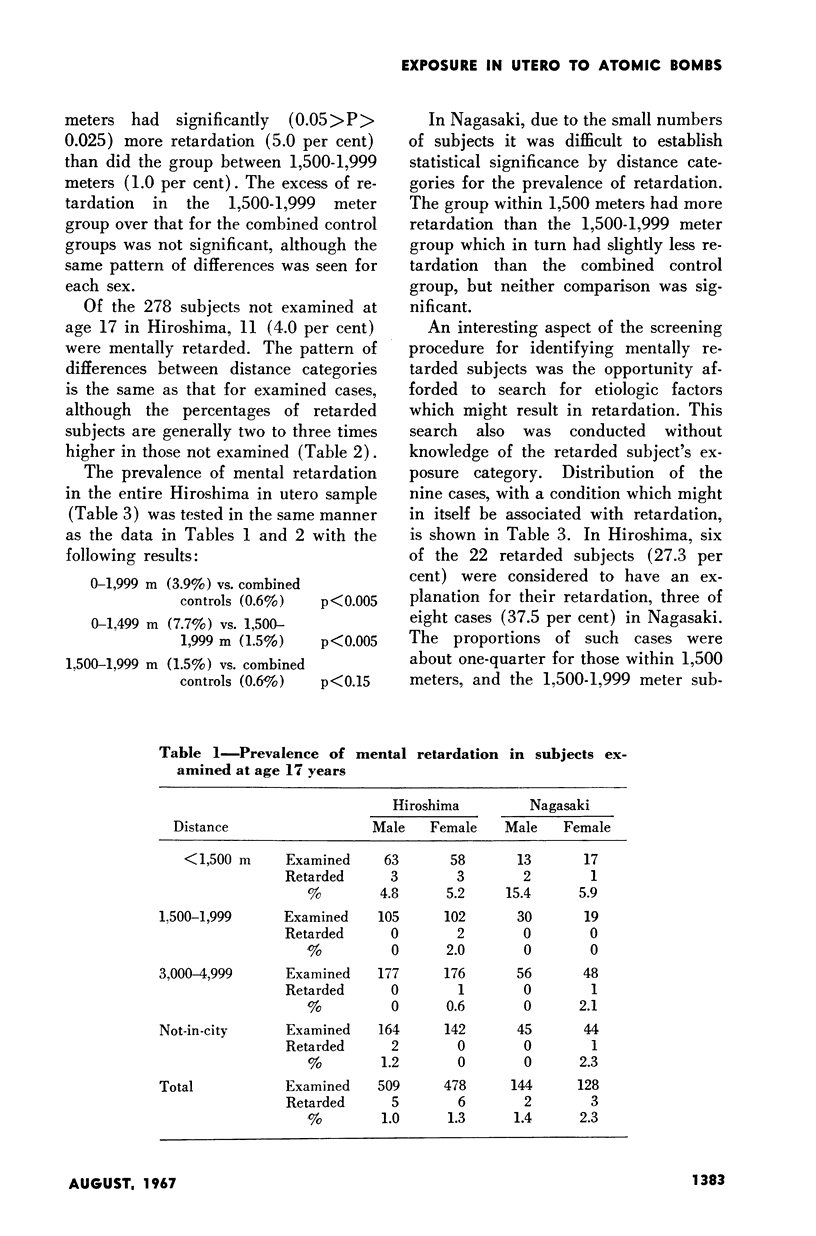
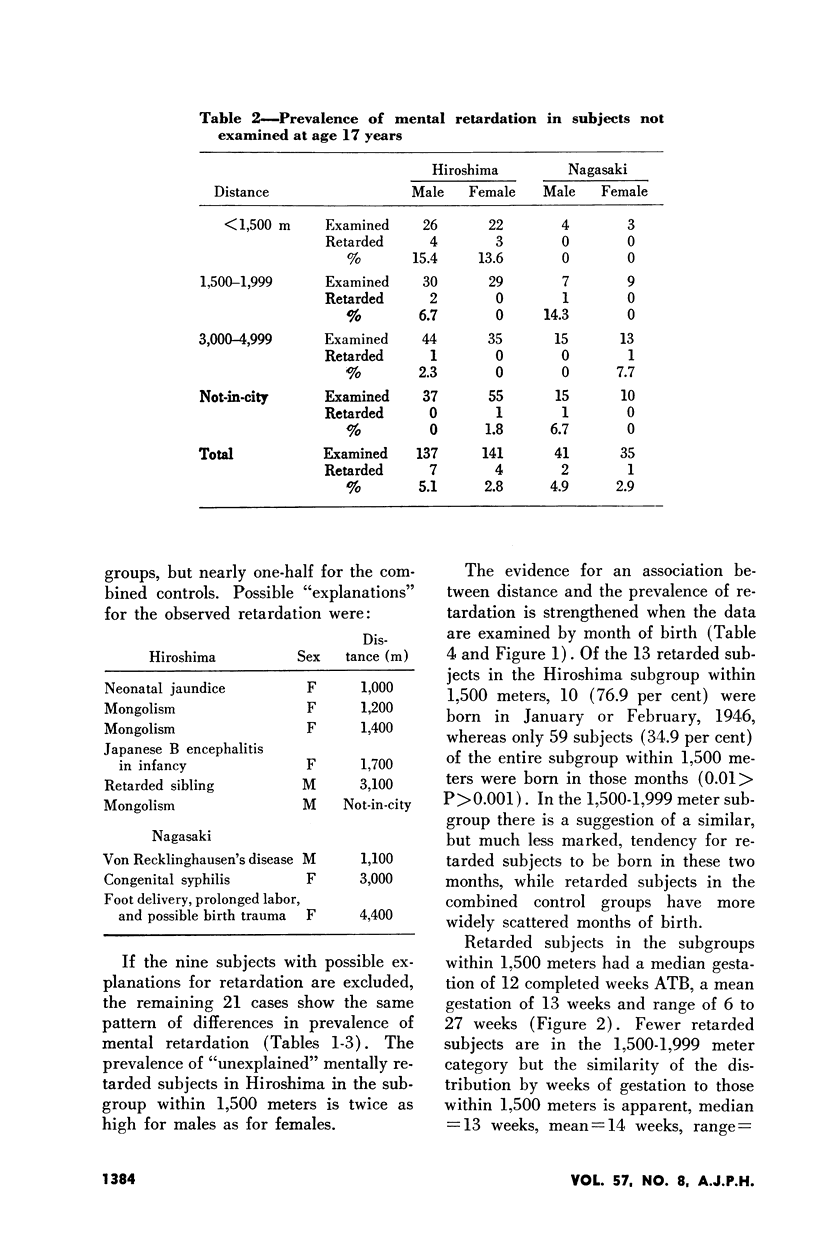
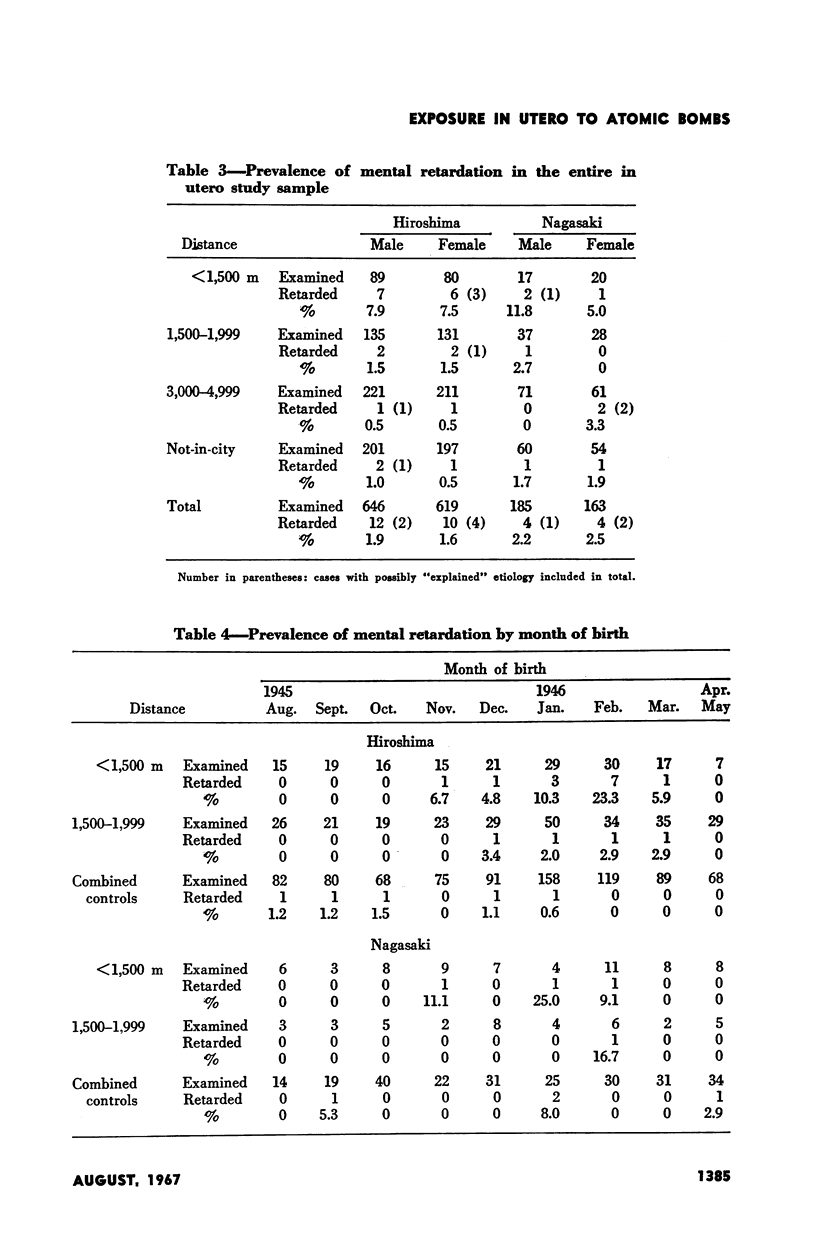
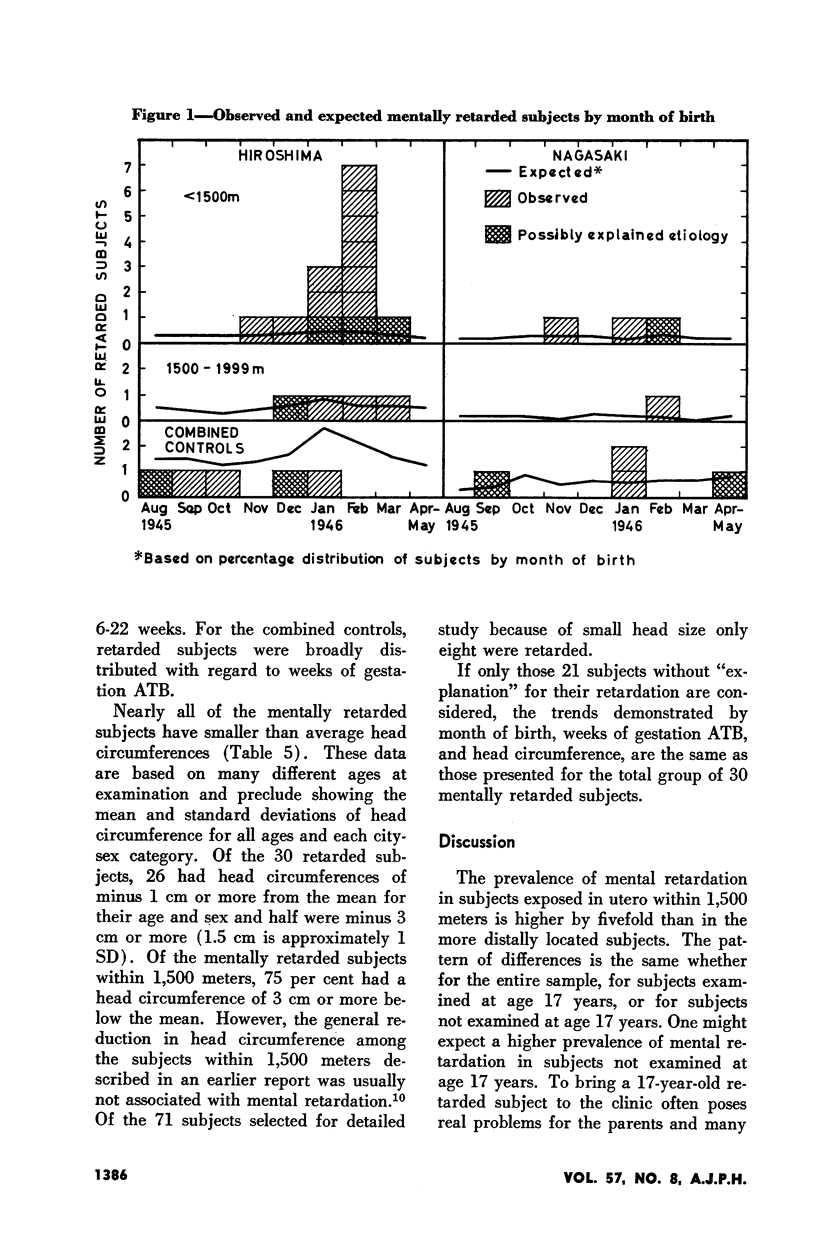
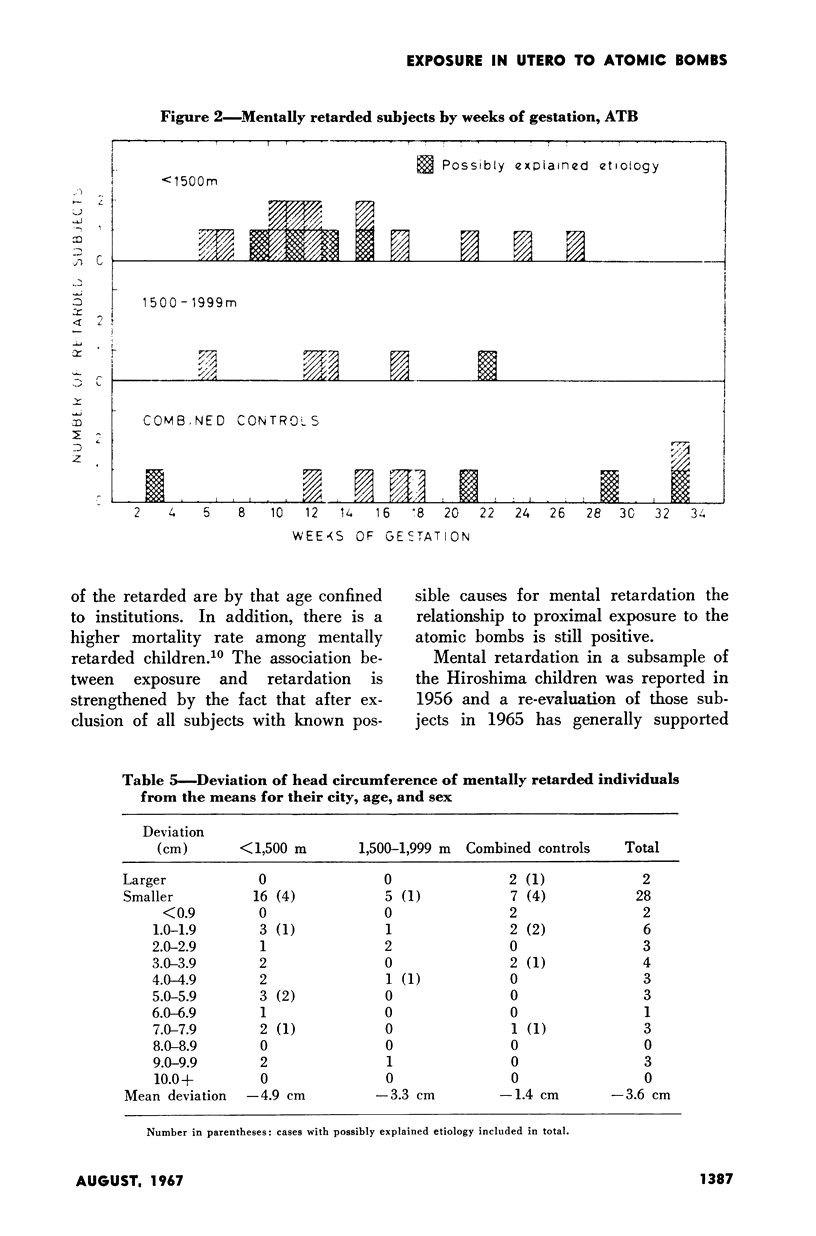
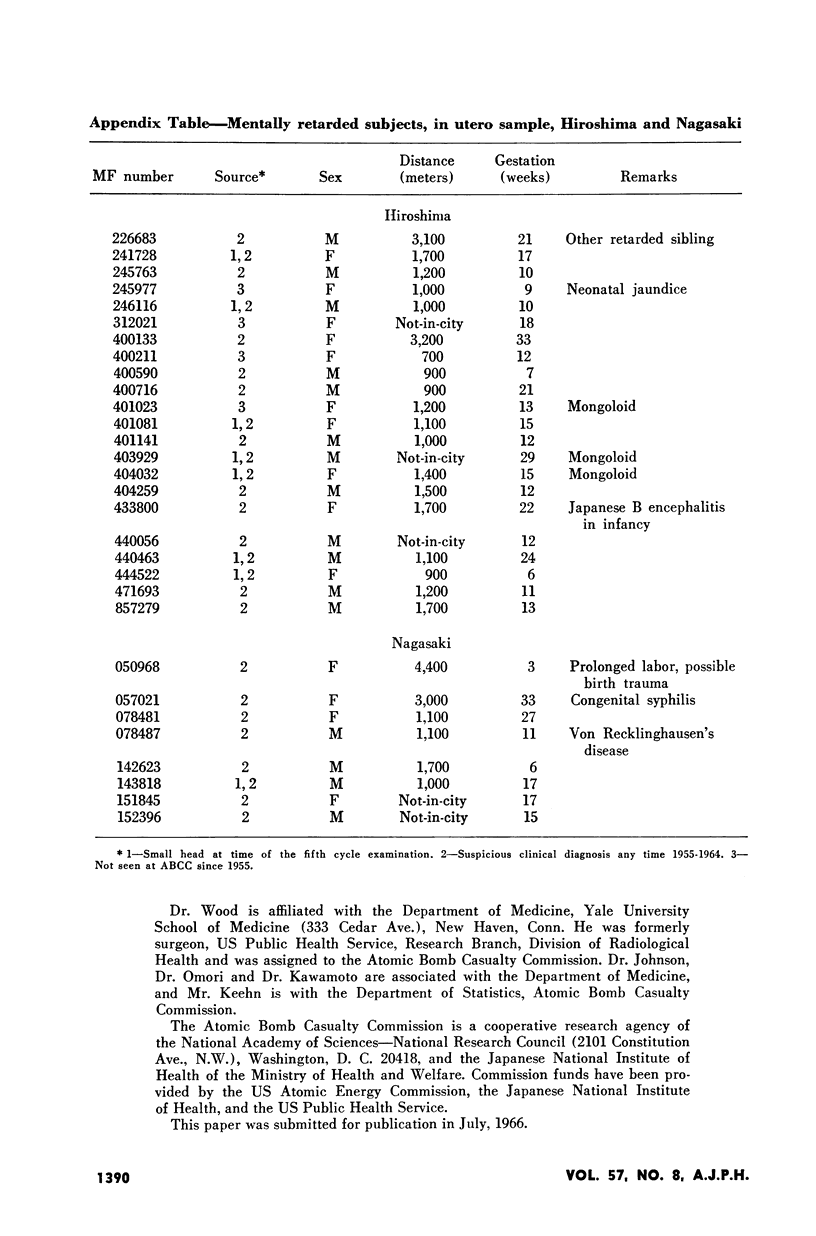
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARAKAWA E. T. Radiation dosimetry in Hiroshima and Nagasaki atomic-bomb survivors. N Engl J Med. 1960 Sep 8;263:488–493. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196009082631005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURROW G. N., HAMILTON H. B., HRUBEC Z., AMAMOTO K., MATSUNAGA F., BRILL A. B. STUDY OF ADOLESCENTS EXPOSED IN UTERO TO THE ATOMIC BOMB, NAGASAKI, JAPAN. I. GENERAL ASPECTS: CLINICAL AND LABORATORY DATA. Yale J Biol Med. 1964 Jun;36:430–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amato C. J., Hicks S. P. Effects of low levels of ionizing radiation on the developing cerebral cortex of the rat. Neurology. 1965 Dec;15(12):1104–1116. doi: 10.1212/wnl.15.12.1104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKS S. P., D'AMATO C. J., LOWE M. J. The development of the mammalian nervous system. I. Malformations of the brain, especially the cerebral cortex, induced in rats by radiation. II. Some mechanisms of the malformations of the cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1959 Dec;113:435–469. doi: 10.1002/cne.901130306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKS S. P. Effects of ionizing radiation on the adult and embryonic nervous system. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1953;32:439–462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER R. W. Delayed effects occurring within the first decade after exposure of young individuals to the Hiroshima atomic bomb. Pediatrics. 1956 Jul;18(1):1–18. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLUMMER G. Anomalies occurring in children exposed in utero to the atomic bomb in Hiroshima. Pediatrics. 1952 Dec;10(6):687–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REKERS P. E. Induced pregnancy in a mammalian host following severe total body x-irradiation. J Lab Clin Med. 1951 Mar;37(3):331–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUGH R. X-irradiation effects on the human fetus. J Pediatr. 1958 May;52(5):531–538. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(58)80030-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. W., Johnson K. G., Omori Y. In utero exposure to the Hiroshima atomic bomb. An evaluation of head size and mental retardation: twenty years later. Pediatrics. 1967 Mar;39(3):385–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. W., Keehn R. J., Kawamoto S., Johnson K. G. The growth and development of children exposed in utero to the atomic bombs in Hiroshima and Nagasaki. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1967 Aug;57(8):1374–1380. doi: 10.2105/ajph.57.8.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YAMAZAKI J. N., WRIGHT S. W., WRIGHT P. M. Outcome of pregnancy in women exposed to the atomic bomb in Nagasaki. AMA Am J Dis Child. 1954 Apr;87(4):448–463. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1954.02050090436004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



