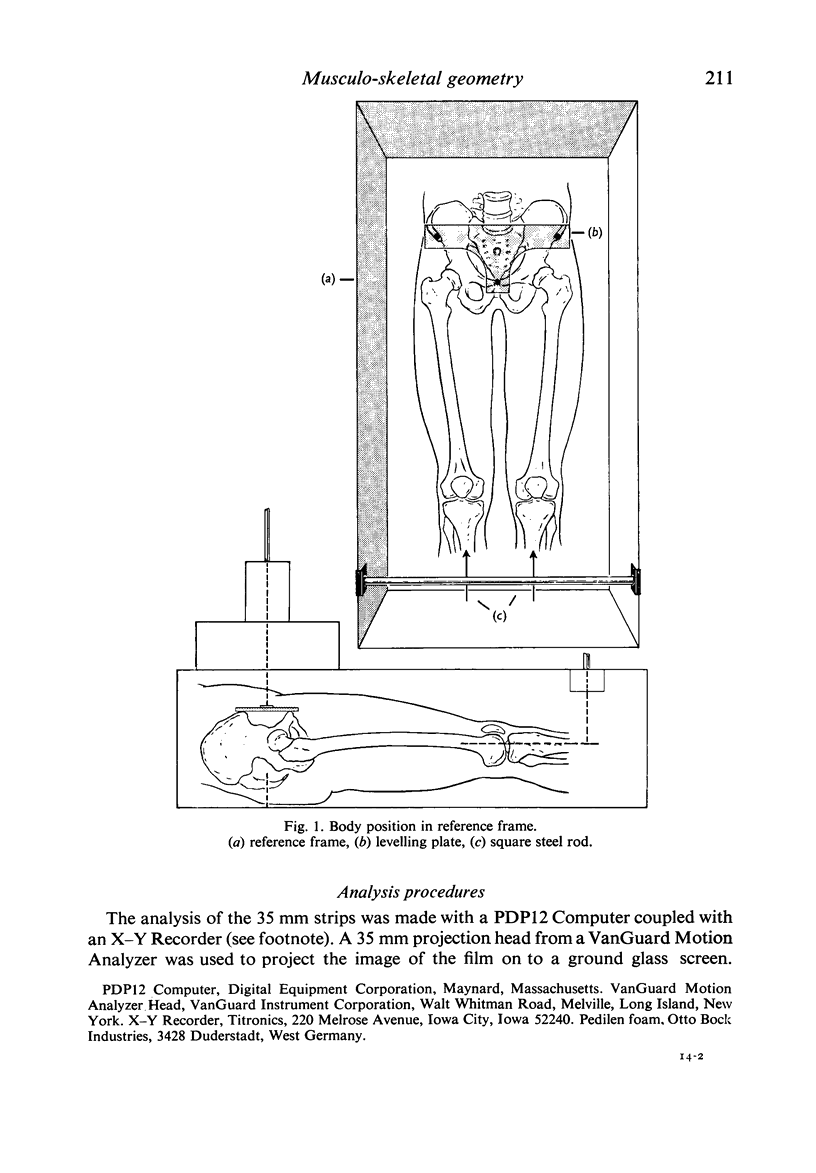
Abstract
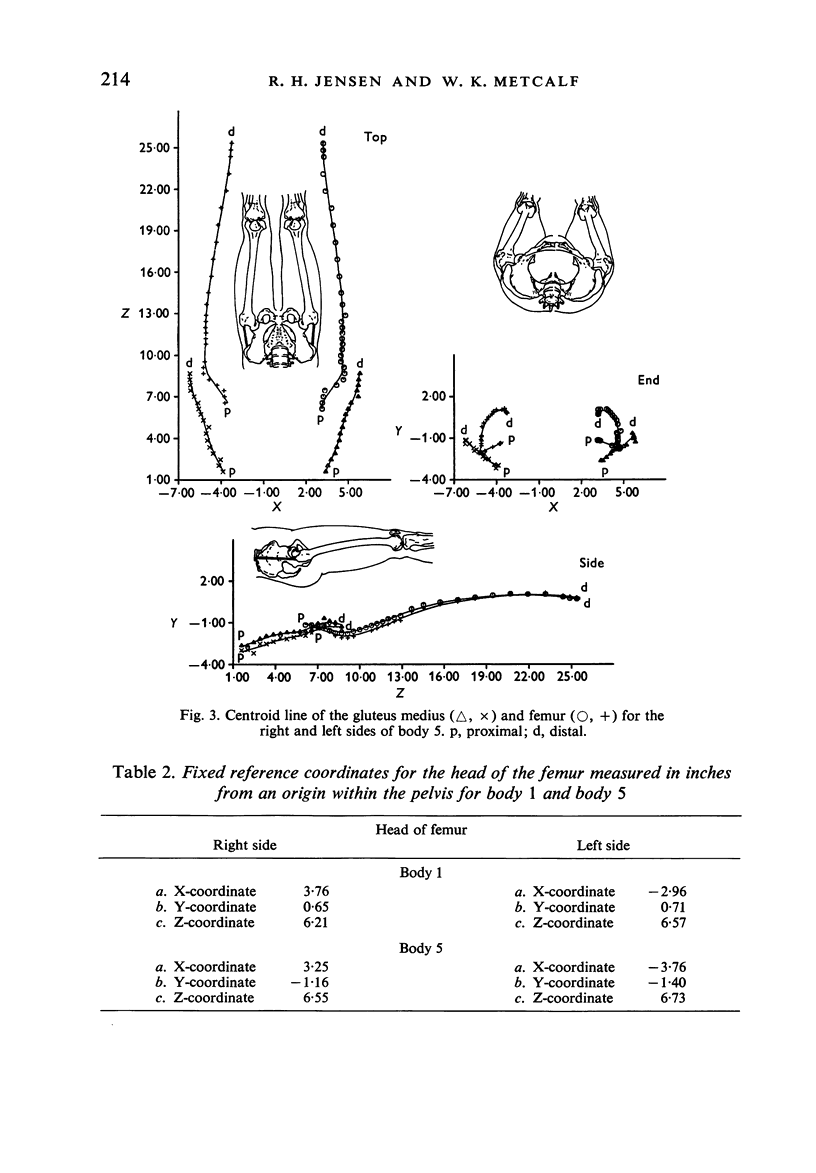
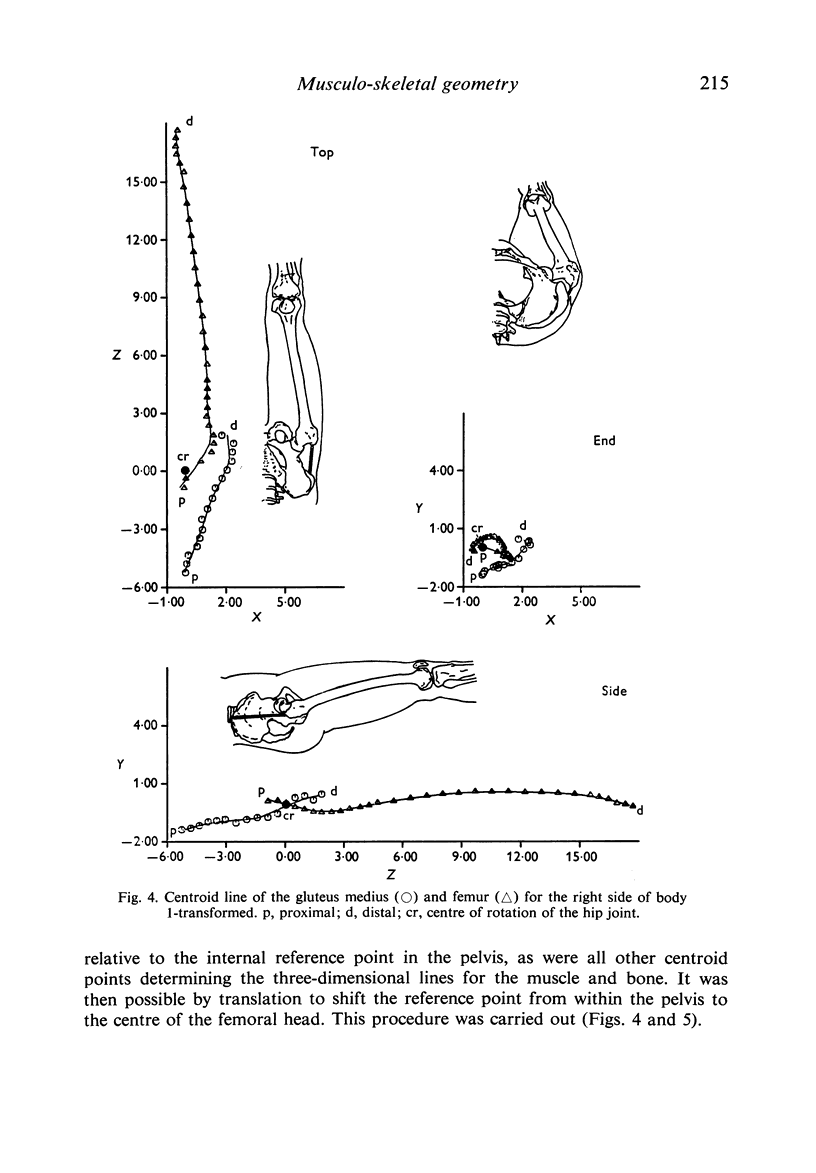
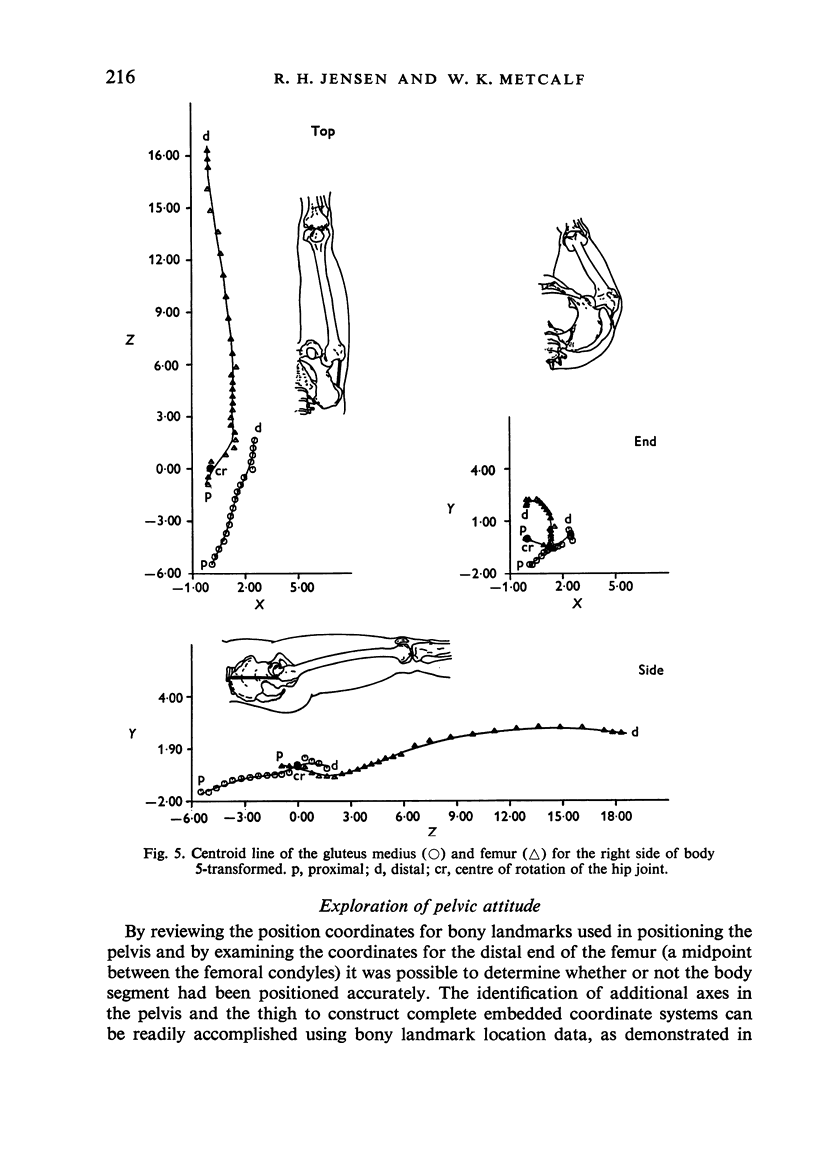
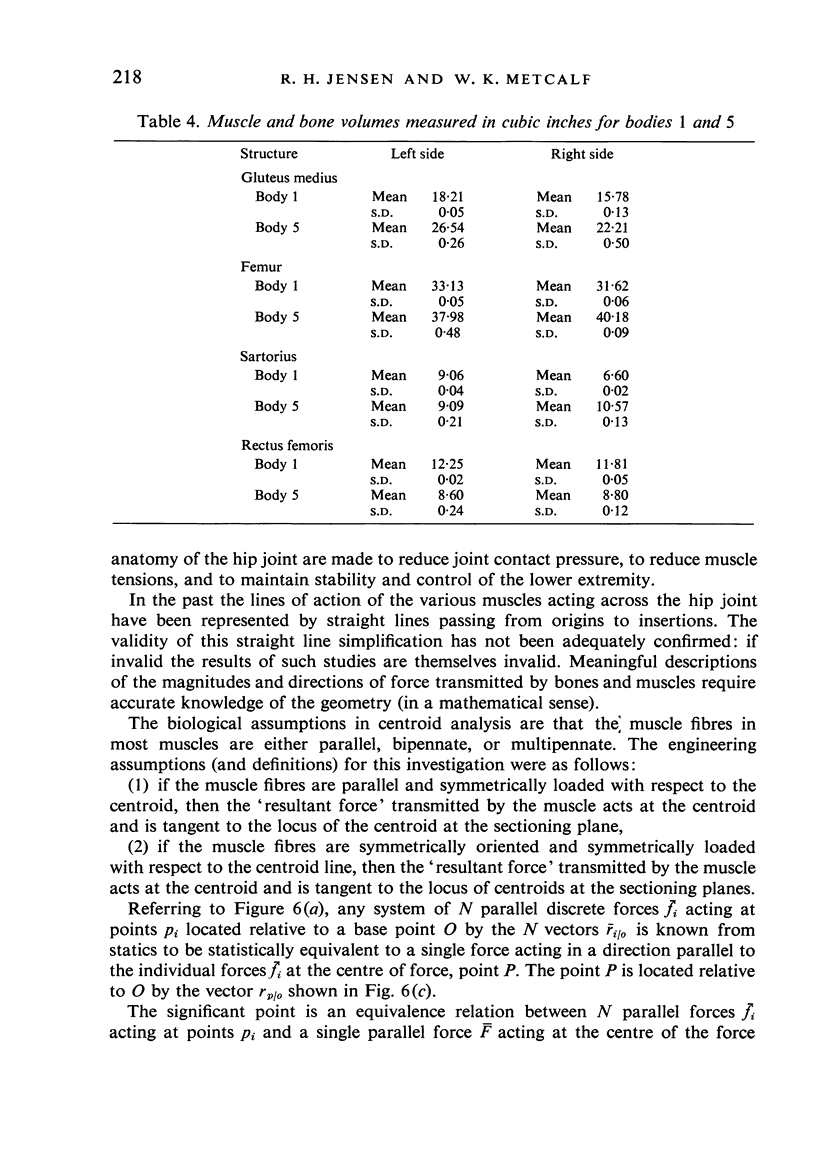
1. A systematized computer technique of centroid analysis has been developed to evaluate the precise geometric relationship between a muscle and a bone and it has been applied to the abductor mechanism of the human hip joint. 2. The validity of the traditional use of straight lines for displaying the line of action of a muscle is open to serious question, although in the case of the gluteus medius the straight line simplification is not unmeasurable. 3. The determination of the precise interactions of muscles and bones is of major importance in the consideration of various orthopaedic procedures.
Full text
PDF


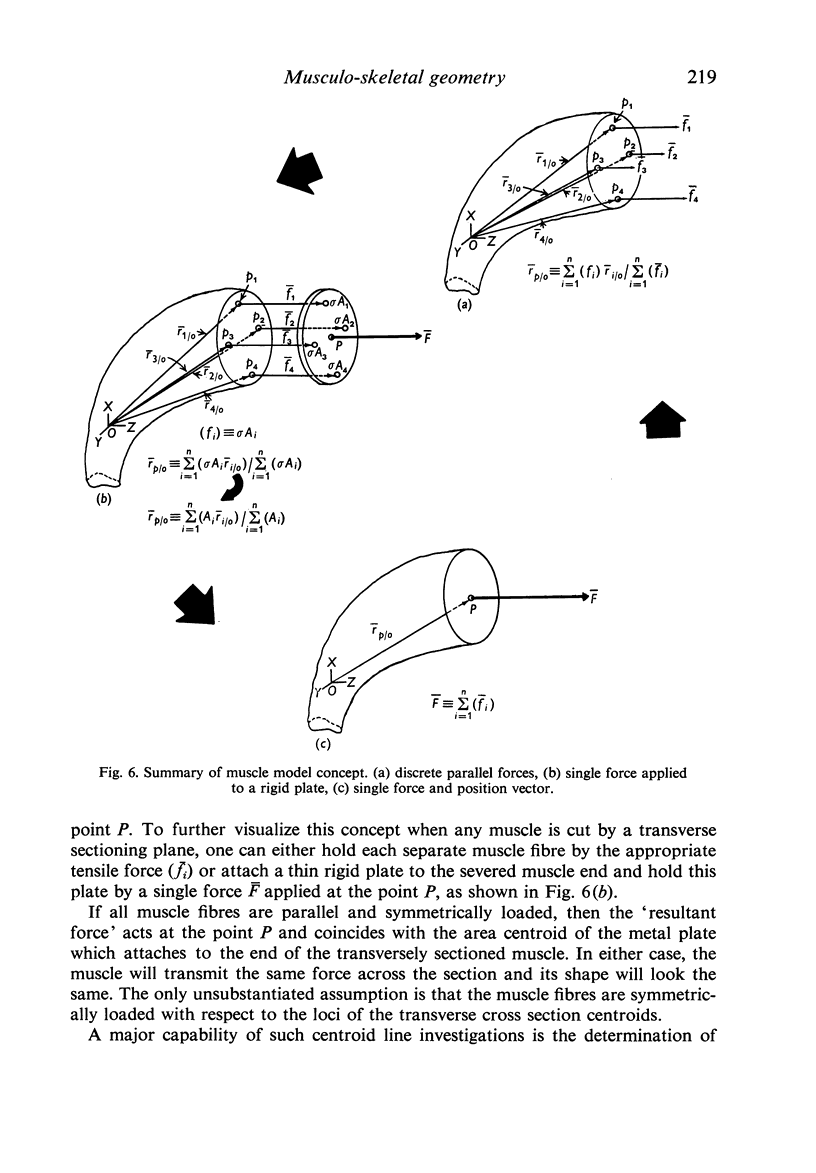


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Liu Y. K., Laborde J. M., Van Buskirk W. C. Inertial properties of a segmented cadaver trunk: their implications in acceleration injuries. Aerosp Med. 1971 Jun;42(6):650–657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERCHANT A. C. HIP ABDUCTOR MUSCLE FORCE; AN EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF THE INFLUENCE OF HIP POSITION WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO ROTATION. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1965 Apr;47:462–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeish R. D., Charnley J. Abduction forces in the one-legged stance. J Biomech. 1970 Mar;3(2):191–209. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(70)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. P. Biomechanics. The biomechanics of the hip-joint and its clinical relevance. Proc R Soc Med. 1966 Oct;59(10):943–948. doi: 10.1177/003591576605901009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]