Abstract
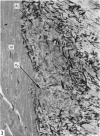
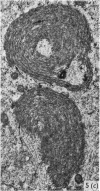
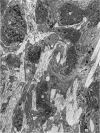
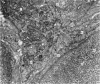
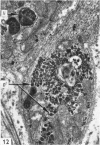
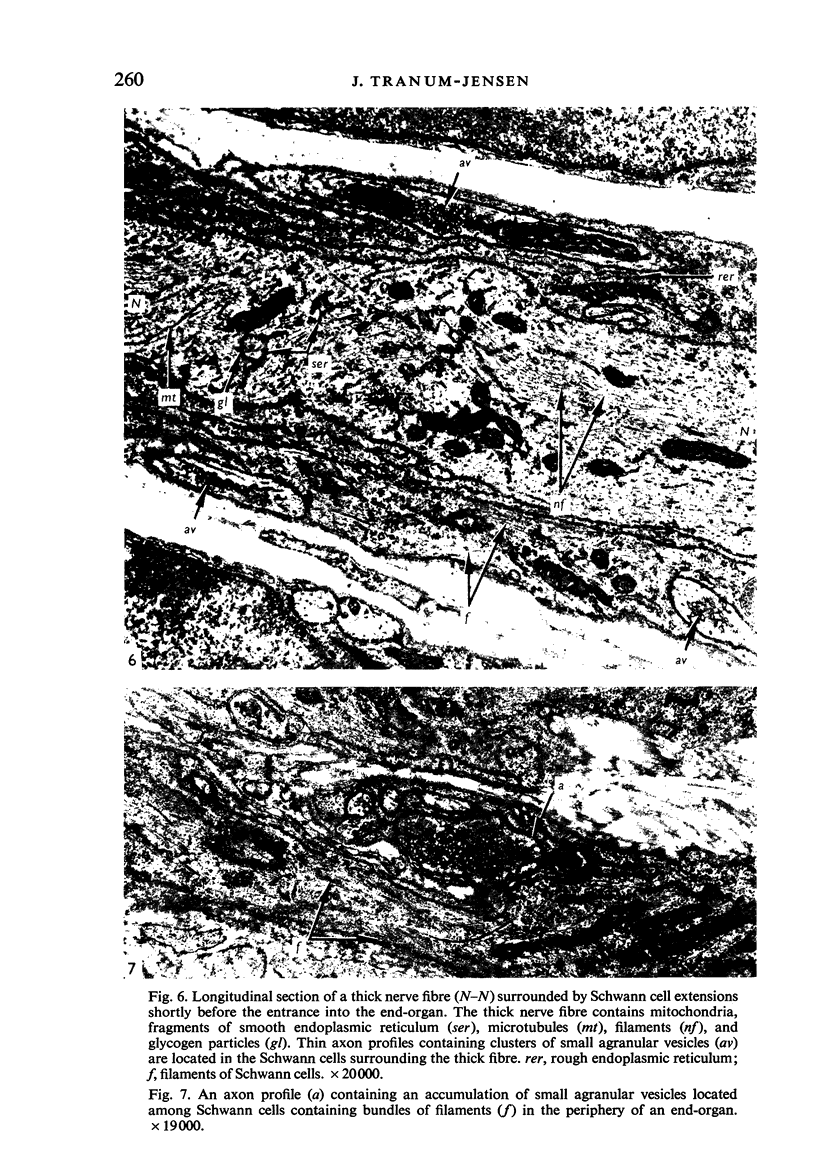
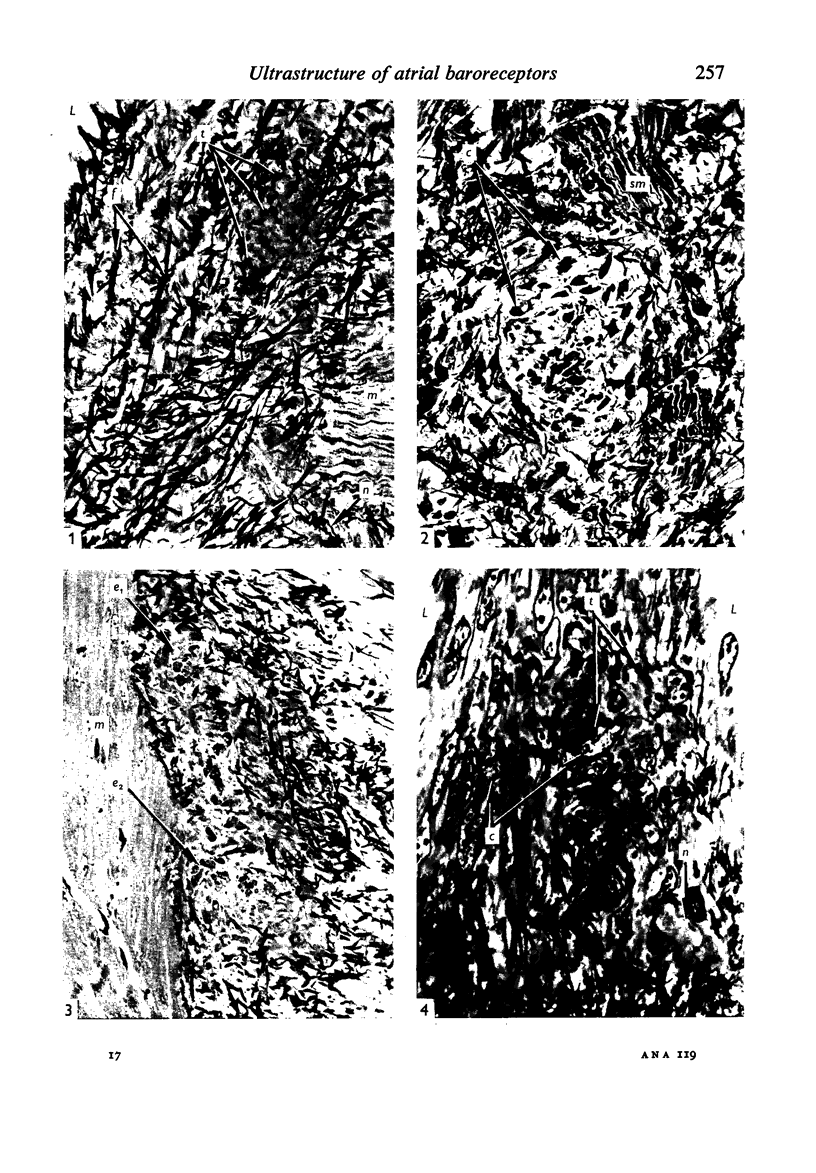
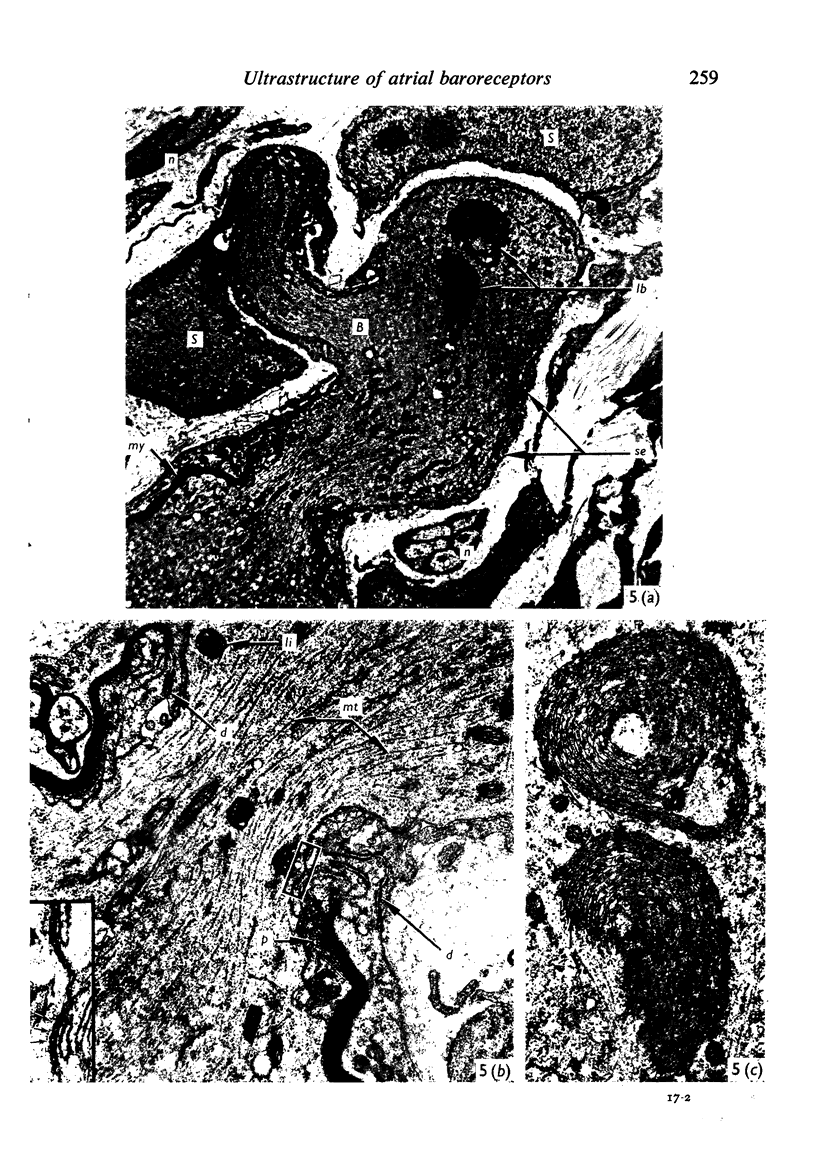
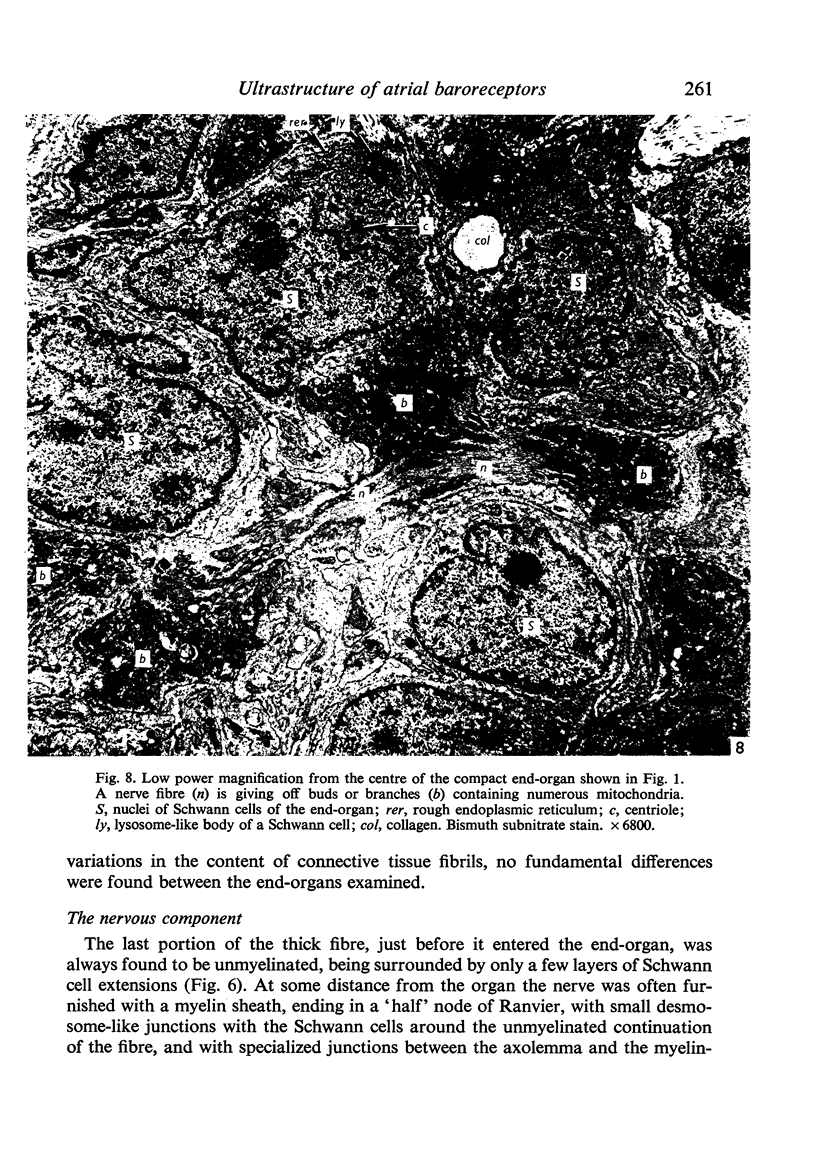
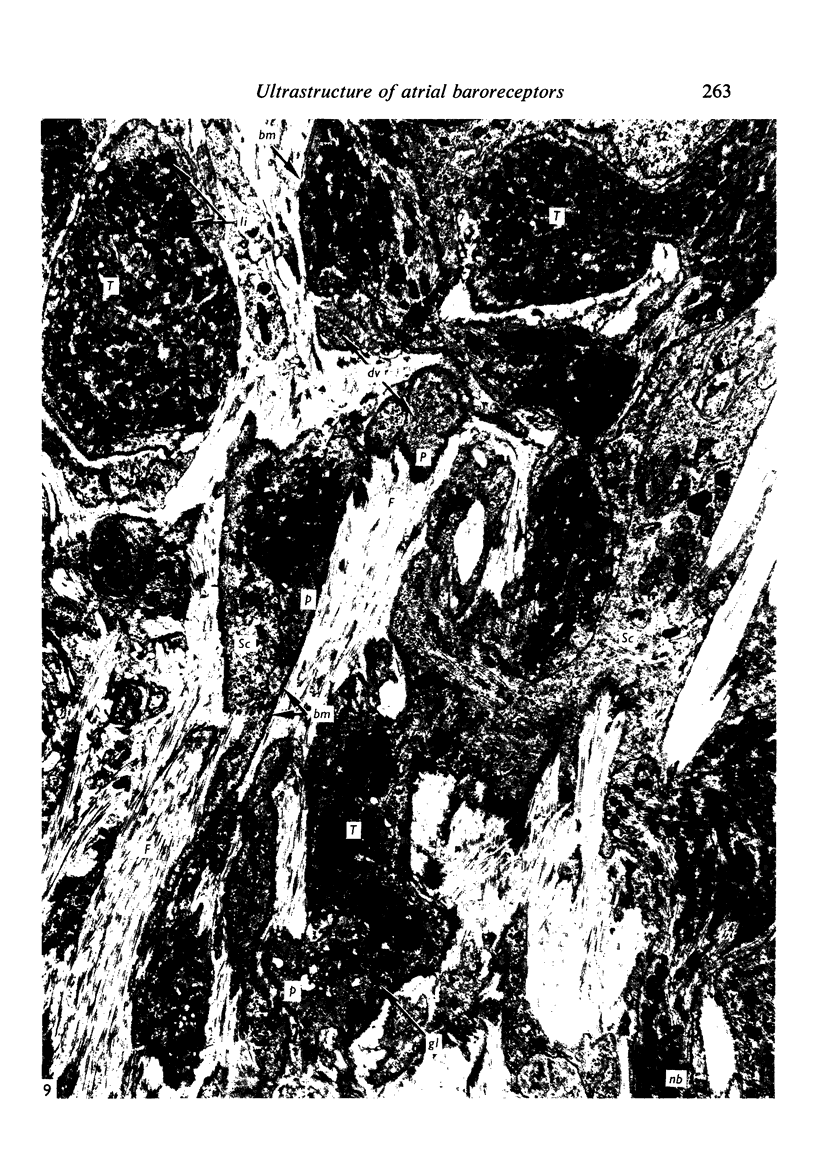
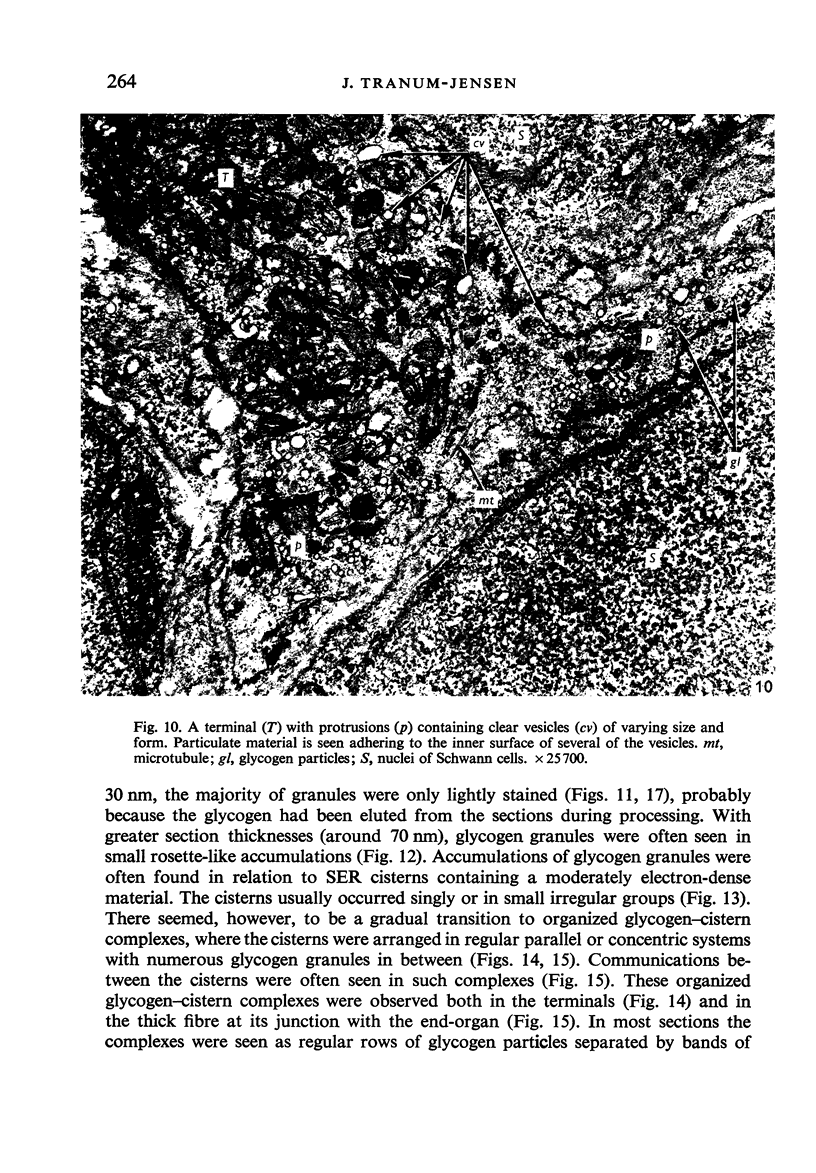
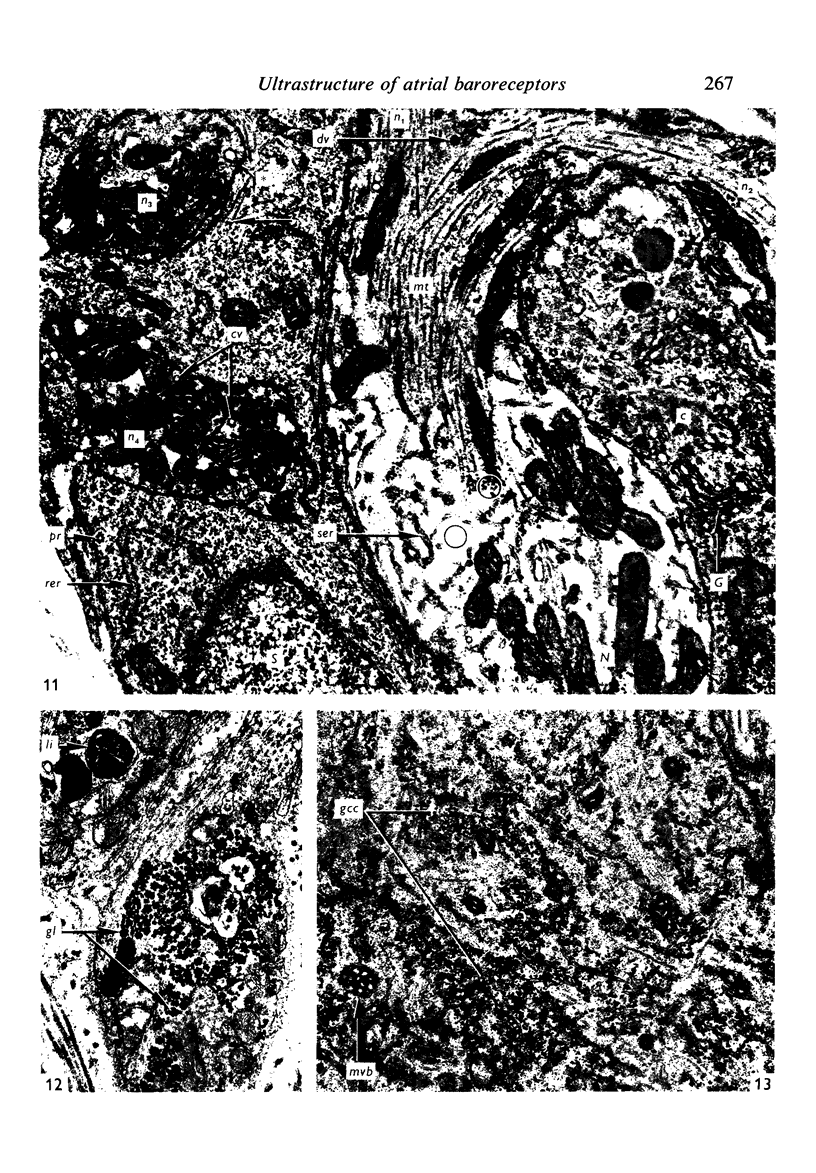
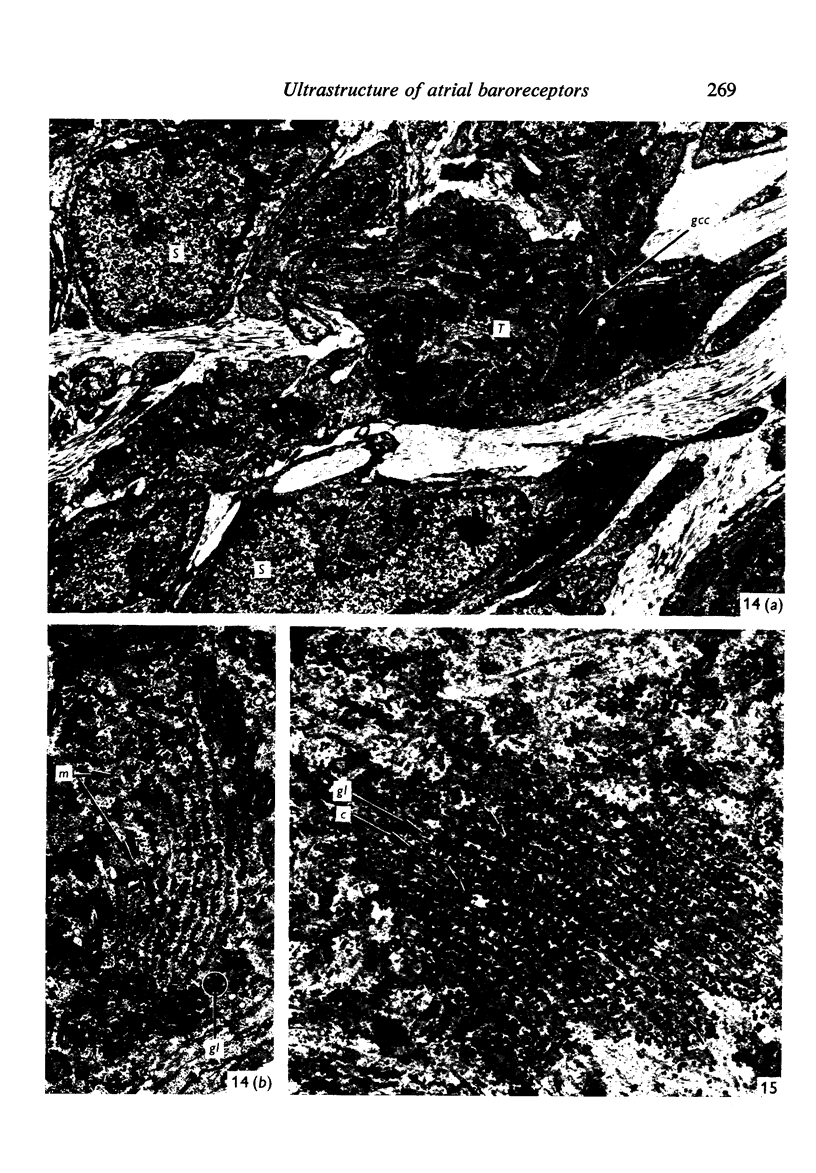
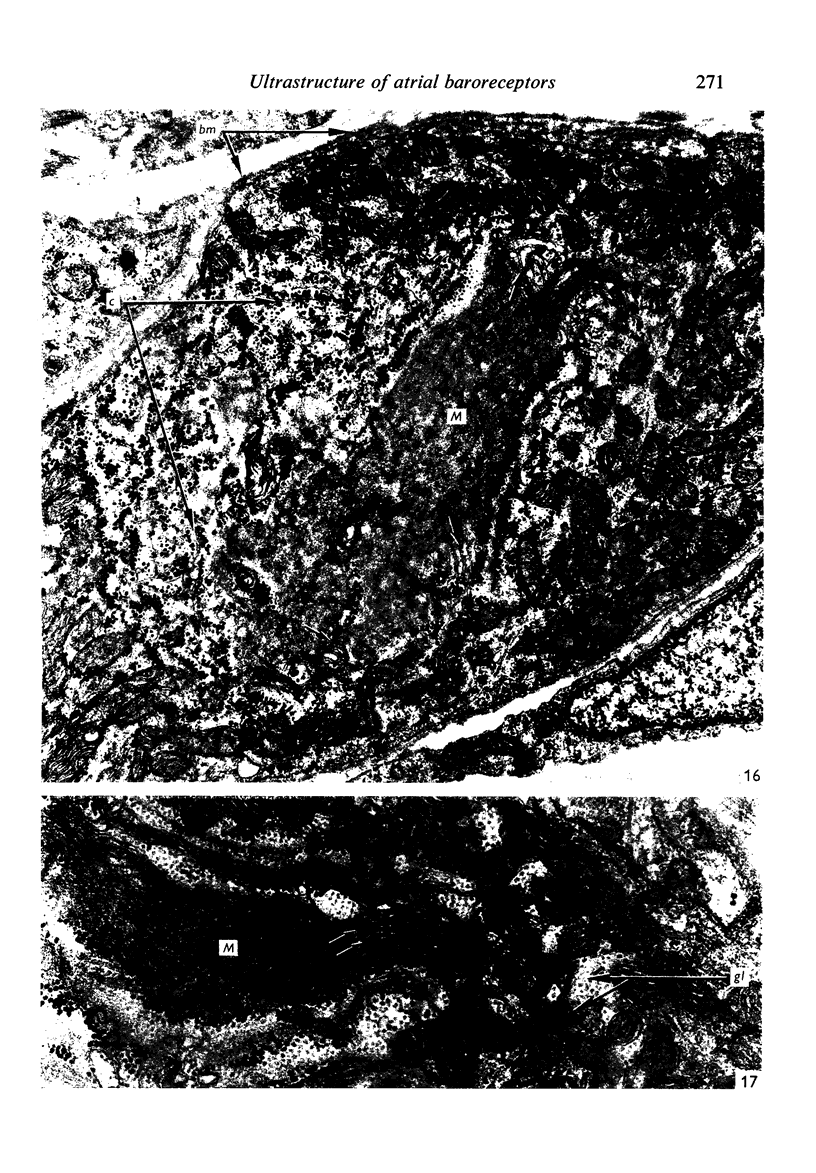
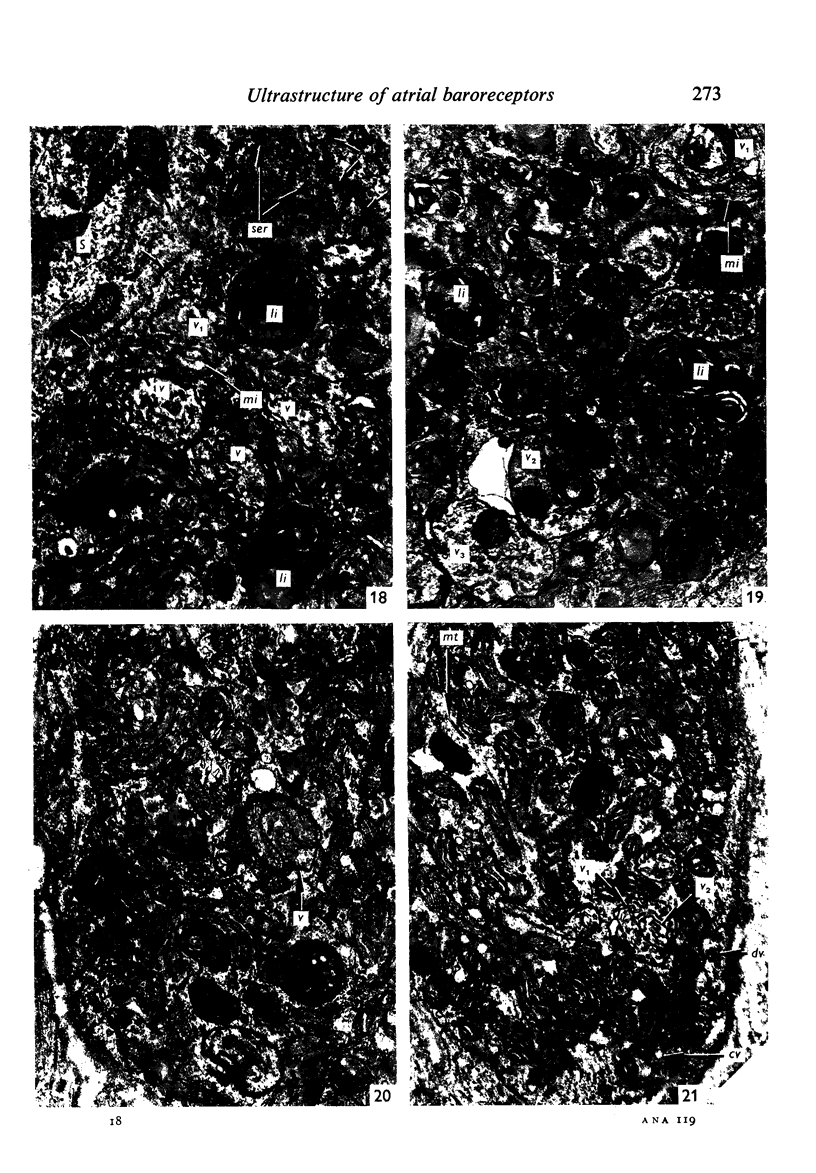
Light and electron microscopical studies on pig hearts have confirmed the presence in the right and the left atrial endocardium of distinct circumscribed, unencapsulated end-organs (baroreceptors) associated with 4-9 mum thick nerve fibres. The myelin sheath terminates before the entrance of the nerve into the end-organ. The regular presence of thin axon profiles containing clusters of small agranular vesicles, both around the thick nerve fibre and in the periphery of the end-organs, suggests a double innervation. The thick fibre arborizes inside an aggregate of Schwann-like cells to form a large number of terminals which are considered to be the mechano-sensitive receptors of the organ. In addition to the nervous structures and the Schwann-like cells the organs contain a varying number of connective tissue fibrils. The terminals are covered by a basement membrane but are partly or completely devoid of Schwann cell covering. Most of the space inside the terminals is occupied by tightly packed mitochondria. Glycogen granules are regularly present, sometimes abundant. SER occurs widely, frequently forming complexes with glycogen granules. These complexes may be highly organized as parallel or concentric structures, suggesting a close connection between SER and glycogen metabolism in the terminals. The terminals are regularly furnished with small protrusions containing numerous 30-100 nm clear vesicles which resemble pinocytotic vesicles. In addition, a few 80 nm dense-cored vesicles are found. The occurrence of numerous cyto-segresomes and lipofuscin-like bodies suggests a lively turnover of organelles in the terminals.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brunk U., Ericsson J. L. Electron microscopical studies on rat brain neurons. Localization of acid phosphatase and mode of formation of lipofuscin bodies. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Jan;38(1):1–15. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAUNA N., ROSS L. L. The fine structure of Meissner's touch corpuscles of human fingers. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Oct;8:467–482. doi: 10.1083/jcb.8.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAUNA N. The mode of termination of the sensory nerves and its significance. J Comp Neurol. 1959 Oct;113:169–209. doi: 10.1002/cne.901130202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHABAROWA A. J. [Afferent innervation of the heart]. Z Mikrosk Anat Forsch. 1960;66:236–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLERIDGE H. M., COLERIDGE J. C., KIDD C. CARDIAC RECEPTORS IN THE DOG, WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO TWO TYPES OF AFFERENT ENDING IN THE VENTRICULAR WALL. J Physiol. 1964 Nov;174:323–339. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLERIDGE J. C., HEMINGWAY A., HOLMES R. L., LINDEN R. J. The location of atrial receptors in the dog: a physiological and histological study. J Physiol. 1957 Apr 3;136(1):174–197. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardell R. R., Jr Action of metabolic hormones on the fine structure of rat liver cells. I. Effects of fasting on the ultrastructure of hepatocytes. Am J Anat. 1971 May;131(1):21–53. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001310103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T. Fine structure of the baroreceptor nerve terminals in the carotid sinus of the dog. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1972;21(2):139–148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiba T., Yamauchi A. On the fine structure of the nerve terminals in the human myocardium. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;108(3):324–338. doi: 10.1007/BF00336523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe A., Ragab A. H. Studies on the fine structure of the capsular region of tortoise muscle spindles. J Anat. 1970 Sep;107(Pt 2):257–269. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman D. E. The transducer action of mechanoreceptor membranes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1965;30:59–68. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1965.030.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLMES R. L. Structures in the atrial endocardium of the dog which stain with methylene blue, and the effects of unilateral vagotomy. J Anat. 1957 Apr;91(2):259–266. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen E., Wittkowski W. Licht- und elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchungen zur Innervation der Piagefässe. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969;95(3):429–444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanker J. S., Dixon A. D., Moore H. G., 3rd Cytochrome oxidase activity of mitochondria in sensory nerve endings of mouse palatal rugae. J Anat. 1973 Oct;116(Pt 1):93–102. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNOCHE H., SCHMITT G. BEITRAG ZUR KENNTNIS DES NERVENGEWEBES IN DER WAND DES SINUS CAROTICUS. I. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1964 Jun 12;63:22–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kappagoda C. T., Linden R. J., Snow H. M. The effect of stretching the superior vena caval-right atrial junction on right atrial receptors in the dog. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(3):875–887. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon D. N. The fine structure of the equatorial regions of developing muscle spindles in the rat. J Neurocytol. 1972 Sep;1(2):189–210. doi: 10.1007/BF01099184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MERRILLEES N. C. The fine structure of muscle spindles in the lumbrical muscles of the rat. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jul;7:725–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.4.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER M. R., KASAHARA M. STUDIES ON THE NERVE ENDINGS IN THE HEART. Am J Anat. 1964 Sep;115:217–233. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrillees N. C. The nervous environment of individual smooth muscle cells of the guinea pig vas deferens. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):794–817. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K., Oura C., Pallie W. Fine structure of Pacinian corpuscles in the mesentery of the cat. J Cell Biol. 1969 Dec;43(3):539–552. doi: 10.1083/jcb.43.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., QUILLIAM T. A. Electron microscopy of the pacinian corpuscle. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1957 May 25;3(3):331–342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.3.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pannese E. Unusual membrane-particle complexes within nerve cells of the spinal ganglia. J Ultrastruct Res. 1969 Nov;29(3):334–342. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(69)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit A. Ultrastructure de la rétine de l'oeil pariétal d'un Lacertilien, Anguis fragilis. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;92(1):70–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees P. M. Observations on the fine structure and distribution of presumptive baroreceptor nerves at the carotid sinus. J Comp Neurol. 1967 Dec;131(4):517–548. doi: 10.1002/cne.901310409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson K. C. Electron microscopic identification of autonomic nerve endings. Nature. 1966 May 14;210(5037):756–756. doi: 10.1038/210756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoultz T. W., Swett J. E. The fine structure of the Golgi tendon organ. J Neurocytol. 1972 Jul;1(1):1–26. doi: 10.1007/BF01098642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer P. S., Schaumburg H. H. An ultrastructural study of the inner core of the Pacinian corpuscle. J Neurocytol. 1973 Jun;2(2):217–235. doi: 10.1007/BF01474721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unsicker K. Fine structure and innervation of the avian adrenal gland. 3. Non-cholinergic nerve fibers. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1973 Dec 21;145(4):557–575. doi: 10.1007/BF00306724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerker R. B., Kirkpatrick J. B. Neuronal microtubules, neurofilaments, and microfilaments. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;33:45–75. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]