Abstract
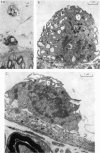
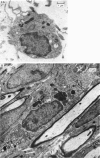
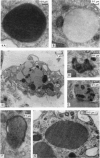
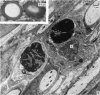
In immature rats active macrophages were frequently seen projecting into the subarachnoid space from the surface of the leptomeninges. They also occurred between the layers of the pia and within the nerve roots. They were most frequent during the first two weeks after birth, which is a period of rapid neural growth and myelination in ventral roots. In contrast, they were much fewer at later stages. The ultrastructural characteristics of these cells are described. It is suggested that these cells take part in tissue growth and remodelling by the removal of material which degenerates or becomes redundant during development. For example, they may ingest effete leptomeningeal cells or fragments of them. Those within the ventral roots may phagocytose abnormal Schwann cells, or the myelin of sheaths which have failed to develop normally. It is also suggested that macrophages may be involved in the excavation of the subarachnoid space. Another possible function in which they may be involved is the ingestion of material, possibly of a protein nature, from the cerebrospinal fluid.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berthold C. H. A comparative morphological study of the developing node-paranode region in lumbar spinal roots. II. Light microscopy after osmiumtetroxide-alpha-naphthylamine (OTAN)-staining. Neurobiology. 1974;4(3):117–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthold C. H., Skoglund S. Postnatal development of feline paranodal myelin-sheath segments. II. Electron microscopy. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1968;73(3-4):127–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr I. Some aspects of the fine structure of the reticulo-endothelial system; the cells which clear colloids from the blood stream. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1968;89(3):355–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00319246. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr I. The fine structure of the mammalian lymphoreticular system. Int Rev Cytol. 1970;27:283–348. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61249-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Low F. N. Scanning electron microscopy of the subarachnoid space in the dog. I. Spinal cord levels. J Comp Neurol. 1974 Feb 15;153(4):325–368. doi: 10.1002/cne.901530402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. A numerical study of cervical and thoracic ventral nerve roots. J Anat. 1974 Sep;118(Pt 1):127–142. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. A quantitative study of anterior root fibres during early myelination. II. Longitudinal variation in sheath thickness and axon circumference. J Anat. 1973 Sep;115(Pt 3):421–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. A quantitative study of anterior root fibres during early myelination. J Anat. 1972 May;112(Pt 1):99–124. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraher J. P. Probable glial islands in a rat spinal nerve root--a longitudinal study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1974 Aug;33(4):552–560. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197408000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friend D. S., Farquhar M. G. Functions of coated vesicles during protein absorption in the rat vas deferens. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):357–376. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller F. R., Haller C., Low F. N. The fine structure of cellular layers and connective tissue space at spinal nerve root attachments in the rat. Am J Anat. 1972 Jan;133(1):109–123. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001330107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haller F. R., Low F. N. The fine structure of the peripheral nerve root sheath in the subarachnoid space in the rat and other laboratory animals. Am J Anat. 1971 May;131(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001310102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Himango W. A., Low F. N. The fine structure of a lateral recess of the subarachnoid space in the rat. Anat Rec. 1971 Sep;171(1):1–19. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLATZO I., MIQUEL J., FERRIS P. J., PROKOP J. D., SMITH D. E. OBSERVATIONS ON THE PASSAGE OF THE FLUORESCEIN LABELED SERUM PROTEINS (FLSP) FROM THE CEREBROSPINAL FLUID. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1964 Jan;23:18–35. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196401000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCabe J. S., Low F. N. The subarachnoid angle: an area of transition in peripheral nerve. Anat Rec. 1969 May;164(1):15–33. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091640102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. A., Bainton D. F., Farquhar M. G. Differentiation of monocytes. Origin, nature, and fate of their azurophil granules. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):498–515. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., SCHULTZ R. L. Electron microscopy of rat cranial meninges. Am J Anat. 1958 Mar;102(2):301–321. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001020207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTH T. F., PORTER K. R. YOLK PROTEIN UPTAKE IN THE OOCYTE OF THE MOSQUITO AEDES AEGYPTI. L. J Cell Biol. 1964 Feb;20:313–332. doi: 10.1083/jcb.20.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHANTHAVEERAPPA T. R., HOPE J., BOURNE G. H. Electron microscopic demonstration of the perineural epithelium in rat peripheral nerve. Acta Anat (Basel) 1963;52:193–201. doi: 10.1159/000142351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggener J. D., Beggs J. The membranous coverings of neural tissues: an electron microscopy study. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1967 Jul;26(3):412–426. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196707000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. L., Hall S. M. Chronic Wallerian degeneration--an in vivo and ultrastructural study. J Anat. 1971 Sep;109(Pt 3):487–503. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Furth R. Origin and kinetics of monocytes and macrophages. Semin Hematol. 1970 Apr;7(2):125–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]