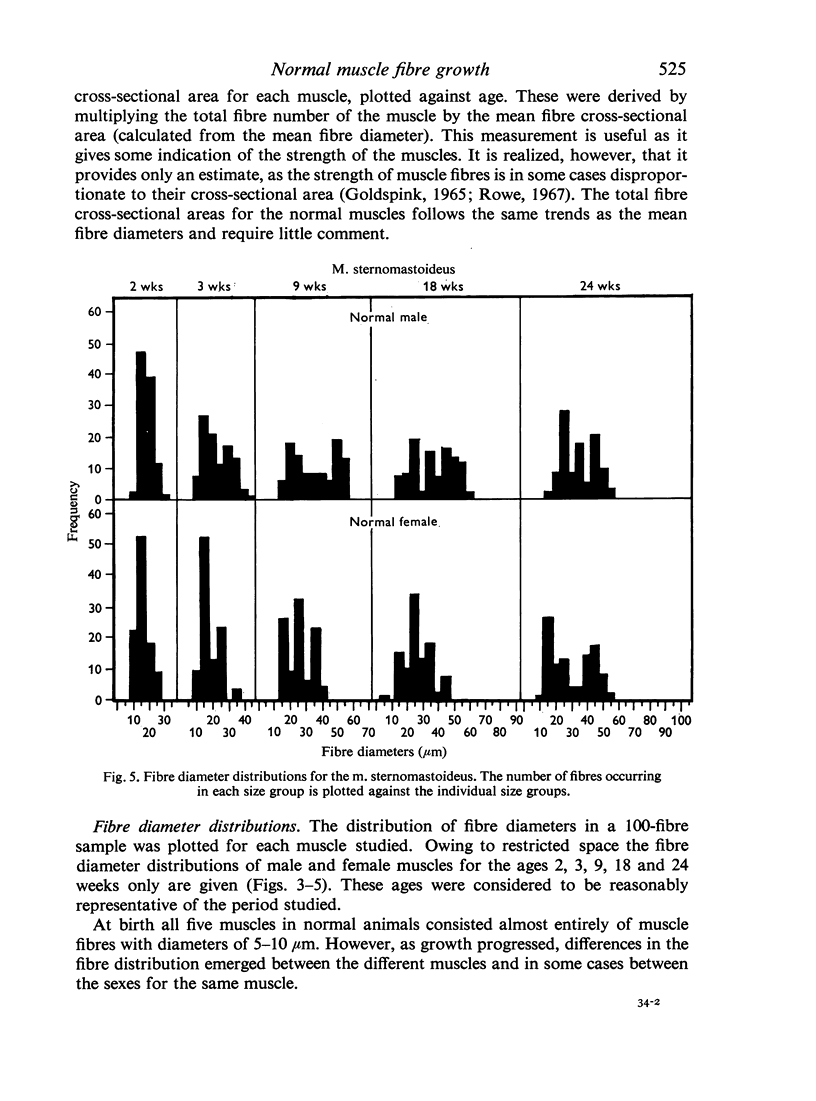
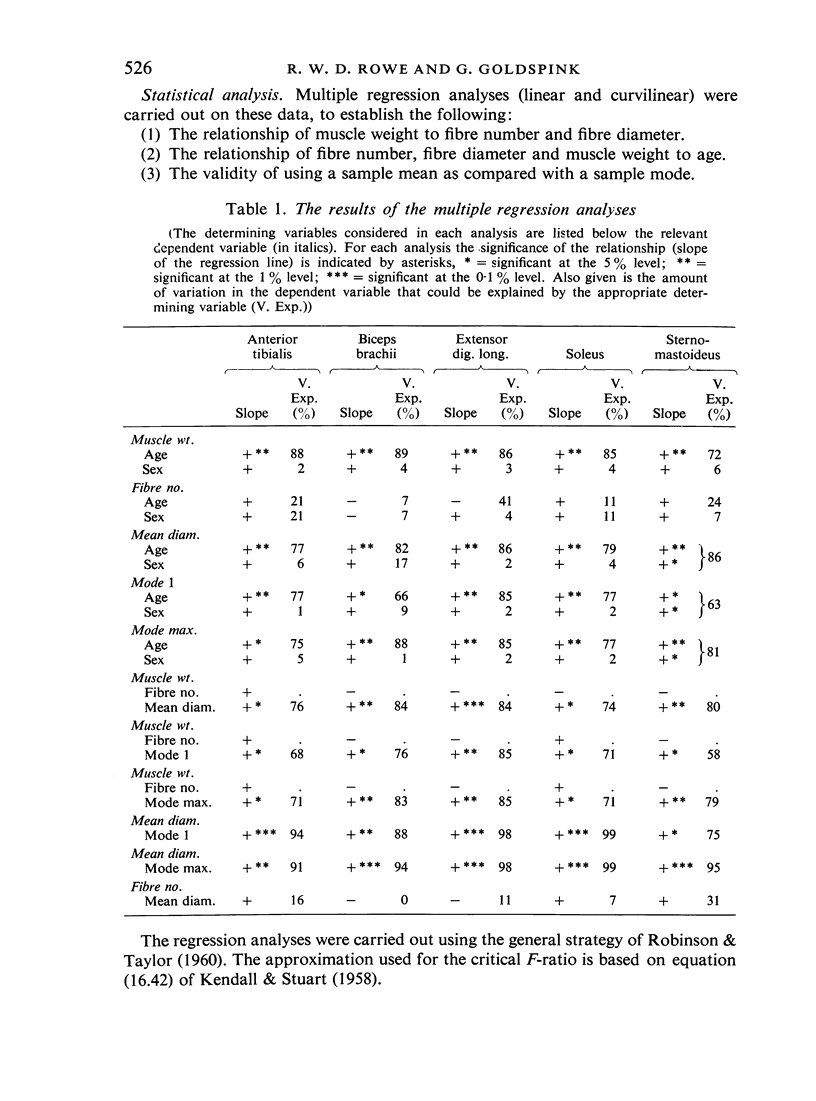
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Differentiation of fast and slow muscles in the cat hind limb. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:399–416. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIAKULAS J. J., PAULY J. E. A STUDY OF POSTNATAL GROWTH OF SKELETAL MUSCLE IN THE RAT. Anat Rec. 1965 May;152:55–61. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091520107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLOSE R. DYNAMIC PROPERTIES OF FAST AND SLOW SKELETAL MUSCLES OF THE RAT DURING DEVELOPMENT. J Physiol. 1964 Sep;173:74–95. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1964.sp007444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREESE R., D'SILVA J. L., HASHISH S. E. Inulin space and fibre size of stimulated rat muscle. J Physiol. 1955 Mar 28;127(3):525–532. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSPINK G. CYTOLOGICAL BASIS OF DECREASE IN MUSCLE STRENGTH DURING STARVATION. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jul;209:100–104. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.1.100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSPINK G. Fixation of muscle. Nature. 1961 Dec 30;192:1305–1306. doi: 10.1038/1921305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDSPINK G. THE COMBINED EFFECTS OF EXERCISE AND REDUCED FOOD INTAKE ON SKELETAL MUSCLE FIBERS. J Cell Physiol. 1964 Apr;63:209–216. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030630211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldspink G. An attempt at estimating extrafiber fluid in small skeletal muscles by a simple physical method. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1966 Sep;44(5):765–775. doi: 10.1139/y66-095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROMANUL F. C. ENZYMES IN MUSCLE. I. HISTOCHEMICAL STUDIES OF ENZYMES IN INDIVIDUAL MUSCLE FIBERS. Arch Neurol. 1964 Oct;11:355–358. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1964.00460220017003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe R. W., Goldspink G. Surgically induced hypertrophy in skeletal muscles of the laboratory mouse. Anat Rec. 1968 May;161(1):69–75. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091610107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN J. M., PADYKULA H. A. Histochemical classification of individual skeletal muscle fibers of the rat. Am J Anat. 1962 Mar;110:103–123. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001100203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


