Abstract
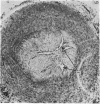
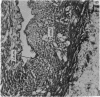
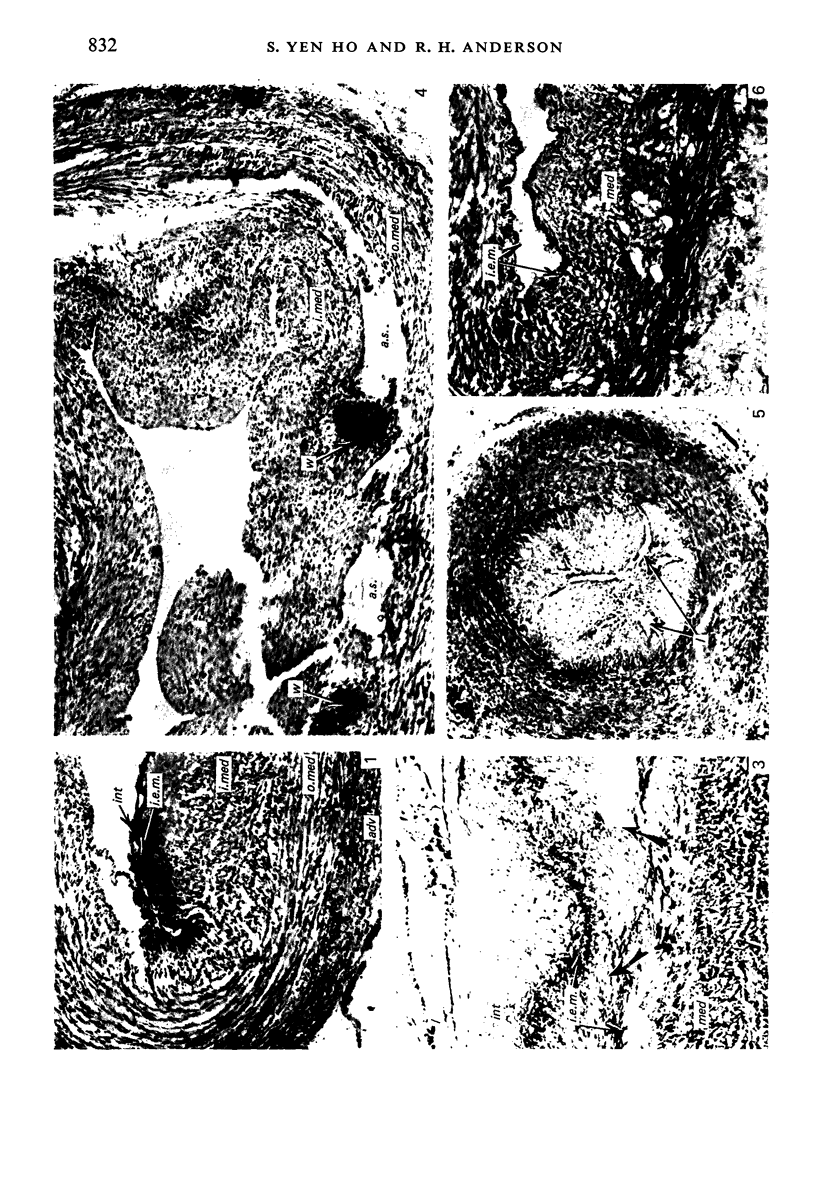
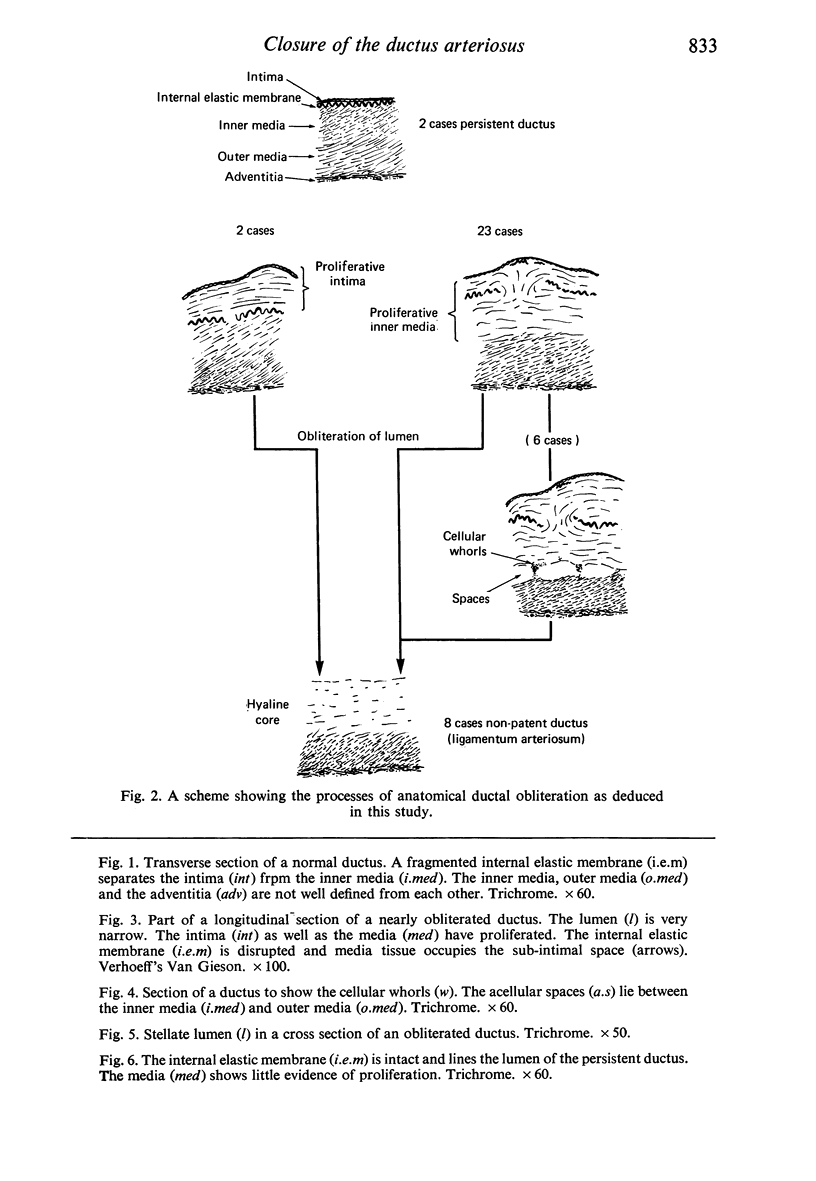
The process of anatomical ductal obliteration appears to be gradual and to involve proliferation of intima and media (mainly the latter) producing mounds, mucoid-filled spaces and fragmentation of the internal elastic membrane. Dissociation of the inner media may also be involved. The persistent ductus can be recognized histologically, and its clinical significance is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Broccoli F., Carinci P. Histological and histochemical analysis of the obliteration processes of ductus arteriosus Botalli. Acta Anat (Basel) 1973;85(1):69–83. doi: 10.1159/000143982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANESINO V. L., REYNOLDS S. R., REHMAN I. H. Comparative histological structure of the human ductus arteriosus according to topography, age, and degree of constriction. Anat Rec. 1955 Apr;121(4):801–829. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091210408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desligneres S., Larroche J. C. Ductus arteriosus. I. Anatomical and histological study of its development during the second half of gestation and its closure after birth. II. Histological study of a few cases of patent ductus arteriosus in infancy. Biol Neonate. 1970;16(5):278–296. doi: 10.1159/000240286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fay J. E., Travill A. The "valve" of the ductus arteriosus--an enigma. Can Med Assoc J. 1967 Jul 8;97(2):78–80. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gittenberger-de Groot A. C. Persistent ductus arteriosus: most probably a primary congenital malformation. Br Heart J. 1977 Jun;39(6):610–618. doi: 10.1136/hrt.39.6.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörnblad P. Y. Embryological observations of the ductus arteriosus in the guinea-pig, rabbit, rat and mouse. Studies on closure of the ductus arteriosus. IV. Acta Physiol Scand. 1969 May-Jun;76(1):49–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1969.tb04450.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jager B. V., Wollenman O. J. An Anatomical Study of the Closure of the Ductus Arteriosus. Am J Pathol. 1942 Jul;18(4):595–613. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M., Barrow M. V., Wheat M. W., Jr An ultrastructural evaluation of the closure of the ductus arteriosus in rats. Surgery. 1969 Nov;66(5):891–898. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato M., Aikawa E., Uchiyama Y. Studies on the obliteration of the ductus arteriosus in rat embryos. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1971;133(1):54–72. doi: 10.1007/BF00523510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A., Ho S. Y., Anderson R. H. Histological study of the cardiac conducting system as a routine procedure. Med Lab Sci. 1977 Jul;34(3):223–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]