Abstract
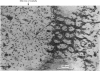
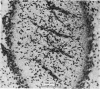
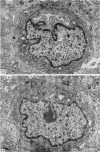
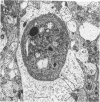
The development of the blood vascular system of the human fetal brain was examined by both light and electron microscopy. By light microscopy the brains of human embryos and fetuses ranging in size from 8.5 to 70 mm crown-rump length have been studied in serial sections, usually of the whole embryo or fetus. In the smallest specimens the whole brain was encapsulated by a very dense vascular plexus. From this, perforating offshoots passed to or from the substance of the brain, while other connexions were effected with neighbouring arterial and venous channels. These latter vessels were never more mature than capillaries, and their status only recognizable by their location and ultimately by their connexions with the heart. The neopallial part of the cerebral hemisphere was later than all other parts of the brain in receiving vessels perforating its substances. There is some evidence, however, that the cellular basis of a blood vascular supply was present in this part of the brain before lumina and blood cells appeared. The cerebral cortex of fetuses ranging from 50 to 100 mm crown-rump length was examined. Both the extrinsic and intrinsic vessels of the cortex were never more mature than capillaries; occasionally a capillary was seen to penetrate the cortex from the surrounding pial investment. Within the developing cerebral cortex blind ending solid endothelial sprouts were identified, as well as 'seamless' capillaries.
Full text
PDF
















Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsopp G., Gamble H. J. An electron microscopic study of the pericytes of the developing capillaries in human fetal brain and muscle. J Anat. 1979 Jan;128(Pt 1):155–168. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer K. F., Vester G. Das elektronenmikroskopische Bild der Hirnkapillaren menschlicher Feten. Fortschr Neurol Psychiatr Grenzgeb. 1970 Jun;38(6):269–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caley D. W., Maxwell D. S. Development of the blood vessels and extracellular spaces during postnatal maturation of rat cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1970 Jan;138(1):31–47. doi: 10.1002/cne.901380104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHL V. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF CAPILLARIES IN CEREBRAL TISSUE OF HUMAN EMBRYOS; A PRELIMINARY REPORT. Dan Med Bull. 1963 Oct;10:196–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLILAN L. A. The arterial blood supply of the human spinal cord. J Comp Neurol. 1958 Aug;110(1):75–103. doi: 10.1002/cne.901100104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauw J. J., Berger B., Escourolle R. Ultrastructural observations on human cerebral capillaries in organ culture. Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Nov 7;163(2):133–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00221722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauw J., Berger B., Escourolle R. Electron microscopic study of the developing capillaries of human brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1975;31(3):229–242. doi: 10.1007/BF00684562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T. The development of the human amygdala during early embryonic life. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Jan;132(1):135–165. doi: 10.1002/cne.901320108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISCH B. Electron microscopy of the capillary wall. II. The filiform processes of the endothelium. Exp Med Surg. 1957;15(1):89–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Povlishock J. T., Martinez A. J., Moossy J. The fine structure of blood vessels of the telencephalic germinal matrix in the human fetus. Am J Anat. 1977 Aug;149(4):439–452. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001490402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON K. C., JARETT L., FINKE E. H. Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol. 1960 Nov;35:313–323. doi: 10.3109/10520296009114754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRONG L. H. THE EARLY EMBRYONIC PATTERN OF INTERNAL VASCULARIZATION OF THE MAMMALIAN CEREBRAL CORTEX. J Comp Neurol. 1964 Aug;123:121–138. doi: 10.1002/cne.901230111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westergaard E. The fine structure of nerve fibers and endings in the lateral cerebral ventricles of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1972 Mar;144(3):345–354. doi: 10.1002/cne.901440306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J. R., Bär T. 'Seamless' endothelia in brain capillaries during development of the rat's cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1972 Jun 8;41(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90613-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff J. R., Moritz A., Güldner F. H. 'Seamless' endothelia within fenestrated capillaries of duodenal villi (rat). Angiologica. 1972;9(1):11–14. doi: 10.1159/000157910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]