Abstract
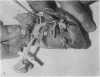
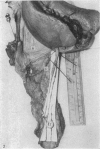
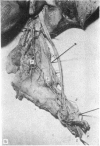
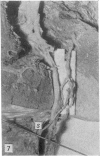
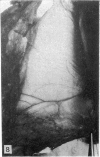
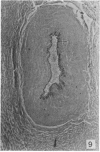
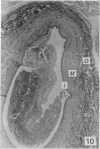
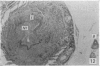
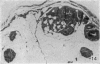
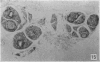
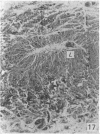
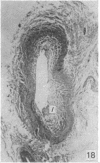
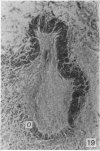
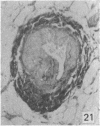
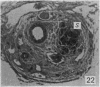
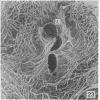
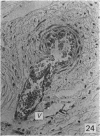
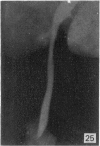
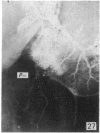
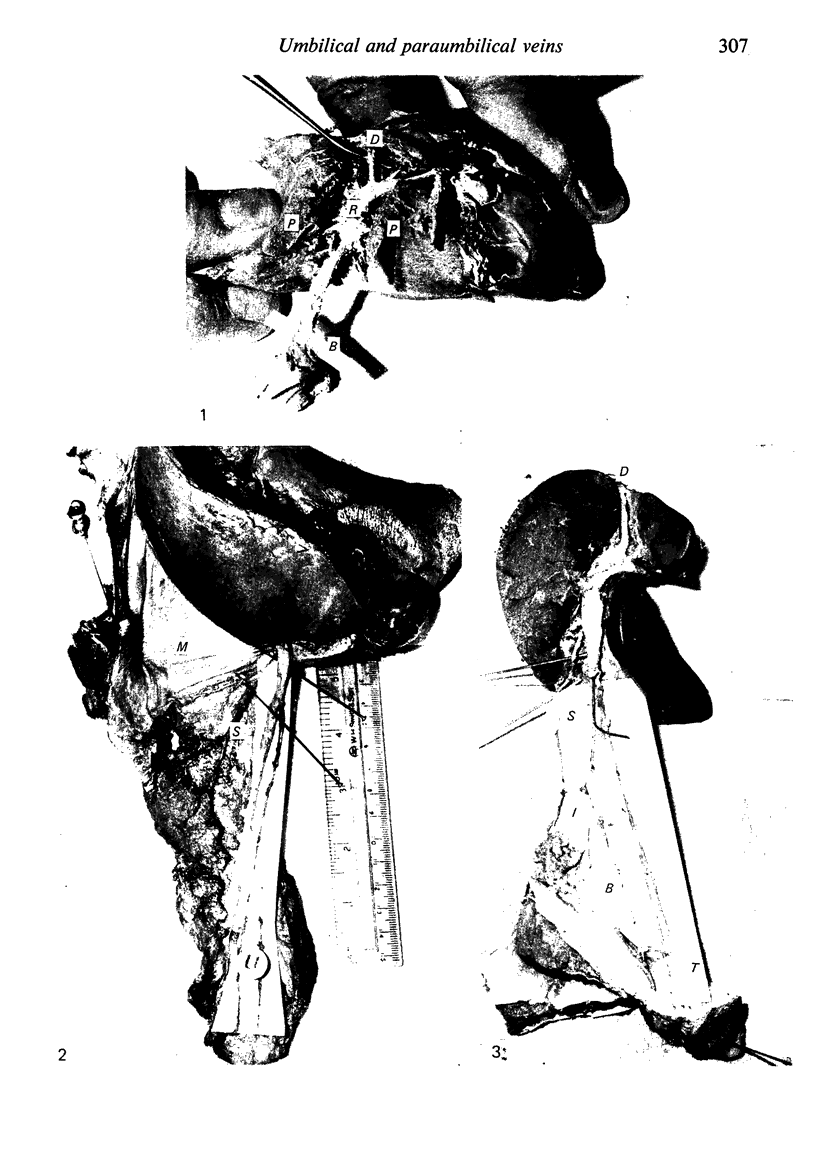
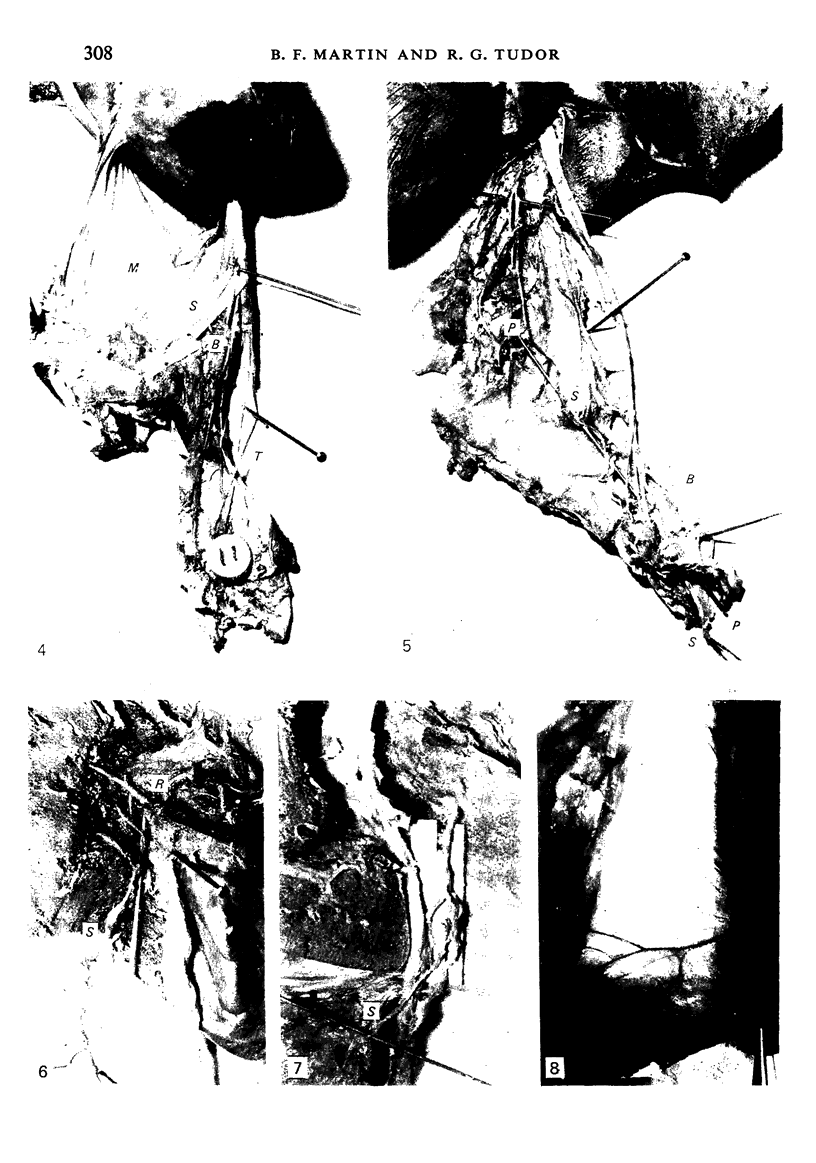
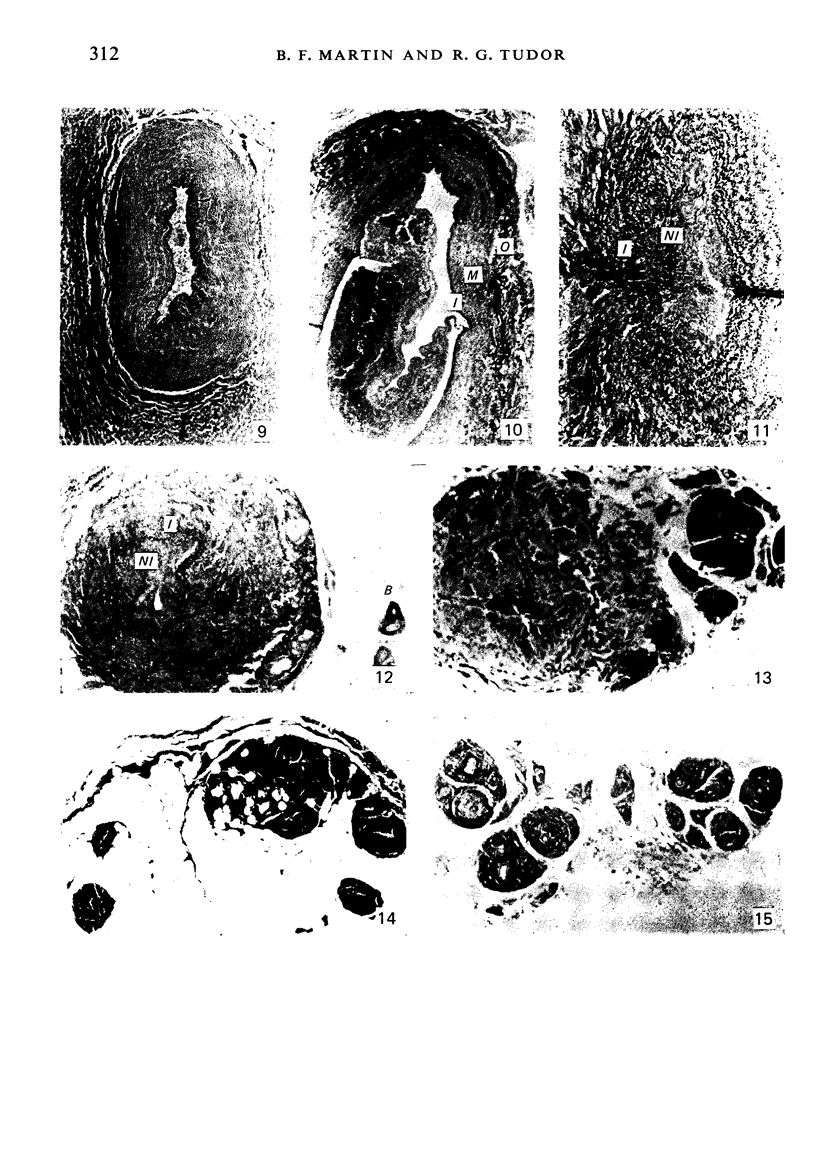
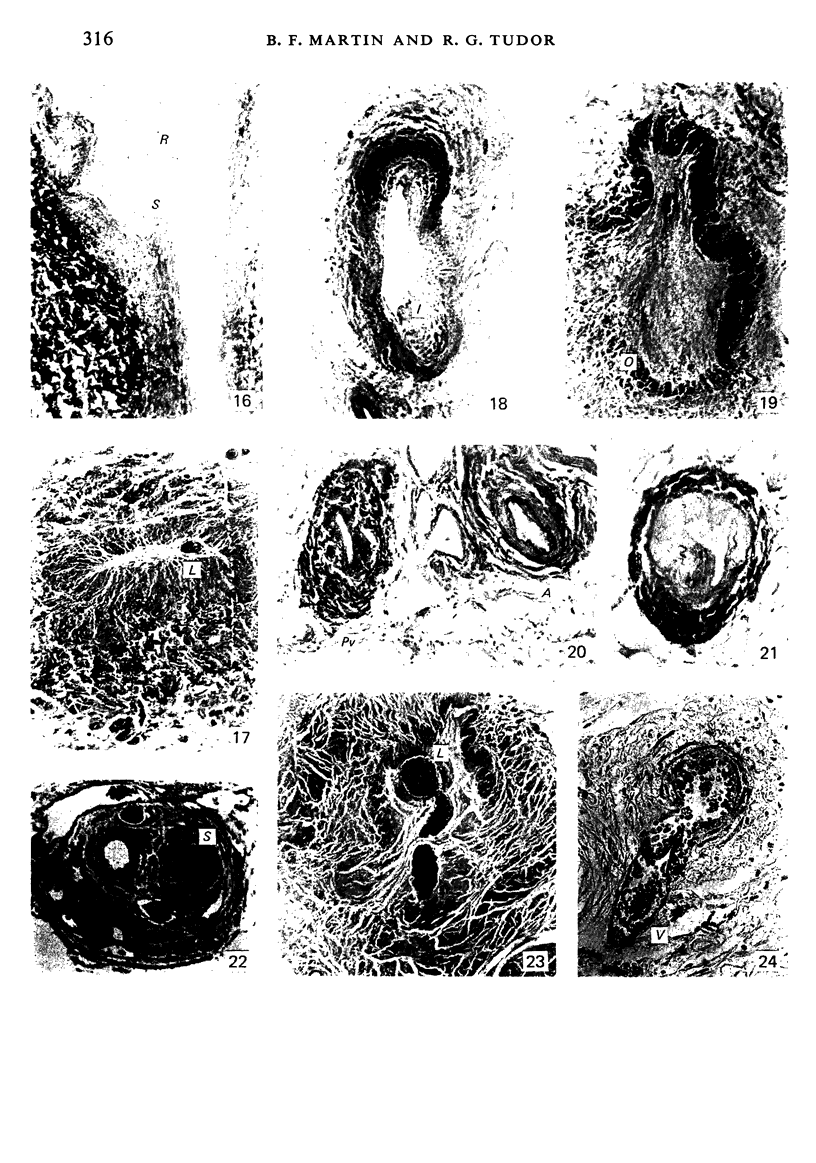
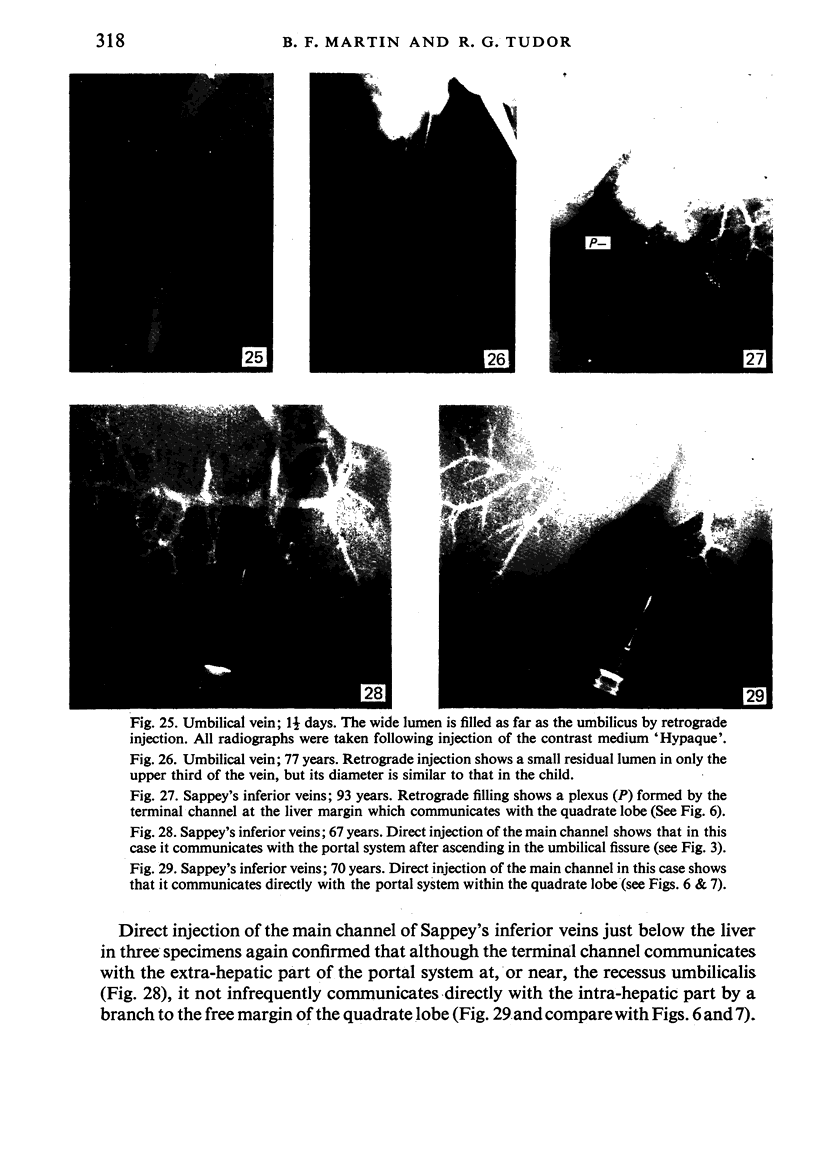
During its transit through the umbilicus structural changes occur in the thick wall of the extra-abdominal segment of the umbilical vein whereby the components of the intra-abdominal segment acquire an essentially longitudinal direction and become arranged in fibro-elastic and fibro-muscular zones. The vein lumen becomes largely obliterated by asymmetrical proliferation of loose subendothelial conective tissue. The latter forms a new inner zone within which a small segment of the lumen persists in an eccentric position. This residual lumen transmits blood to the portal system from paraumbilical and systemic sources, and is retained in the upper part of the vein, even in old age. A similar process of lumen closure is observed in the ductus venosus. In early childhood the lower third of the vein undergoes breakdown, with fatty infiltration, resulting in its complete division into vascular fibro-elastic strands, and in old age some breakdown occurs in the outermost part of the wall of the upper two thirds. The paraumbilical veins are thick-walled and of similar structure to the umbilical vein. Together they constitute an accessory portal system which is confined between the layers of the falciform ligament and is in communication with the veins of the ventral abdominal wall. The constituents form an ascending series, namely, Burow's veins, the umbilical vein, and Sappey's inferior and superior veins. The main channel of Sappey's inferior veins may be the remnant of the right umbilical vein since it communicates with the right rectus sheath and often communicates directly with the portal system within the right lobe of the liver. The results are of significance in relation to clinical usage of the umbilical vein.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BUTLER H. Gastro-oesophageal haemorrhage in hepatic cirrhosis. Thorax. 1952 Jun;7(2):159–166. doi: 10.1136/thx.7.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTLER H. Post-natal changes in the intra-abdominal umbilical vein. Arch Dis Child. 1954 Oct;29(147):427–435. doi: 10.1136/adc.29.147.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braastad F. W., Condon R. E., Gyorkey F. The umbilical vein. Surgical anatomy in the normal adult. Arch Surg. 1967 Dec;95(6):948–955. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1967.01330180096018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EDWARDS E. A. Functional anatomy of the porta-systemic communications. AMA Arch Intern Med. 1951 Aug;88(2):137–154. doi: 10.1001/archinte.1951.03810080005002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardy K. J., Nye D. H. The anatomy of the umbilical vein. Aust N Z J Surg. 1969 Nov;39(2):127–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.1969.tb05574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillier K., Karim S. M. Effects of prostaglandins E1, E2, F1-alpha, F2-alpha on isolated human umbilical and placental blood vessels. J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 1968 Jun;75(6):667–673. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.1968.tb00178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitterman J. A., Phibbs R. H., Tooley W. H. Catheterization of umbilical vessels in newborn infants. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1970 Nov;17(4):895–912. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)32486-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krahn V. Lage der Blutgefässe im Lig. teres hepatis und Darstellung der Besonderheiten des Baues der Chorda venae umbilicalis. Anat Anz. 1974;136(4):378–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larroche J. C. Umbilical catheterization: its complications. Anatomical study. Biol Neonate. 1970;16(1):101–116. doi: 10.1159/000240264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer W. W., Lind J. Postnatal changes in the portal circulation. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Dec;41(220):606–612. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.220.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer W. W., Lind J. The ductus venosus and the mechanism of its closure. Arch Dis Child. 1966 Dec;41(220):597–605. doi: 10.1136/adc.41.220.597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moinian M., Meyer W. W., Lind J. Diameters of umbilical cord vessels and the weight of the cord in relation to clamping time. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1969 Oct 15;105(4):604–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piccone V. A., LeVeen H. H. Transumbilical portal decompression. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1967 Jul;125(1):66–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ram M. D., Didolkar M. S. Clinical anatomy of the obliterated umbilical vein. Am J Surg. 1973 Feb;125(2):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(73)90027-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]