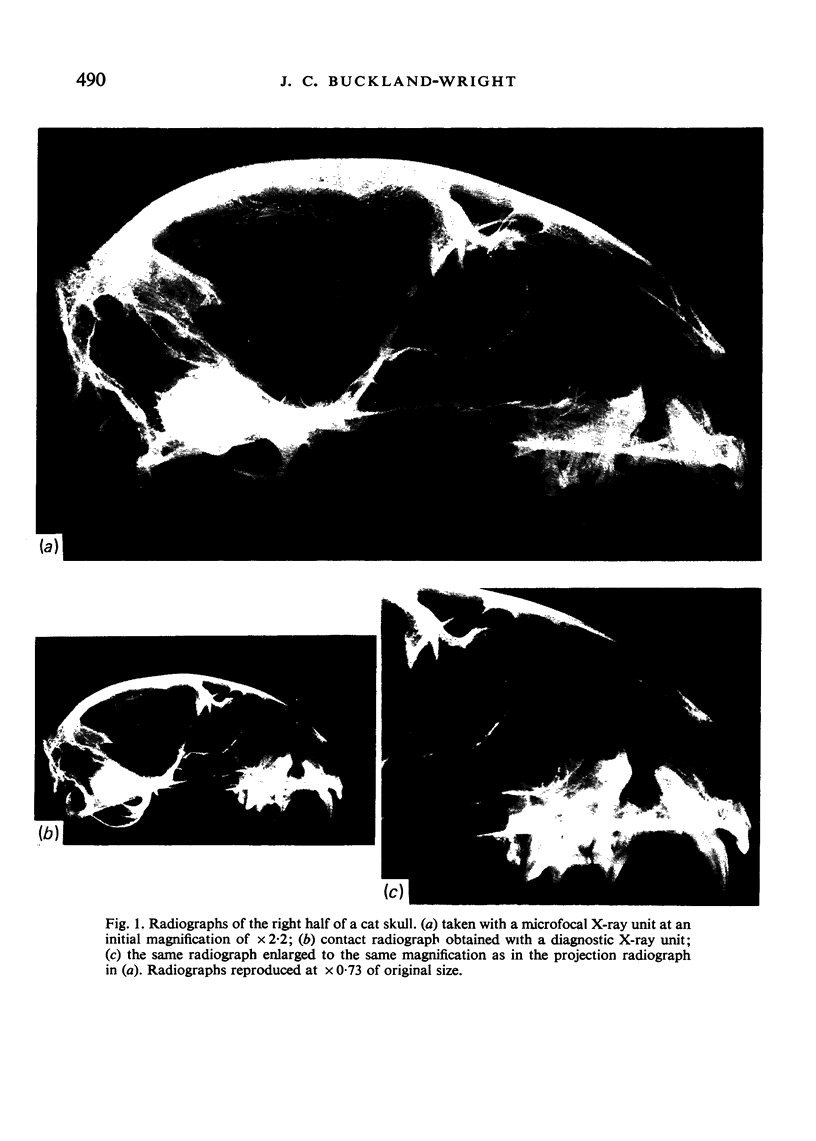
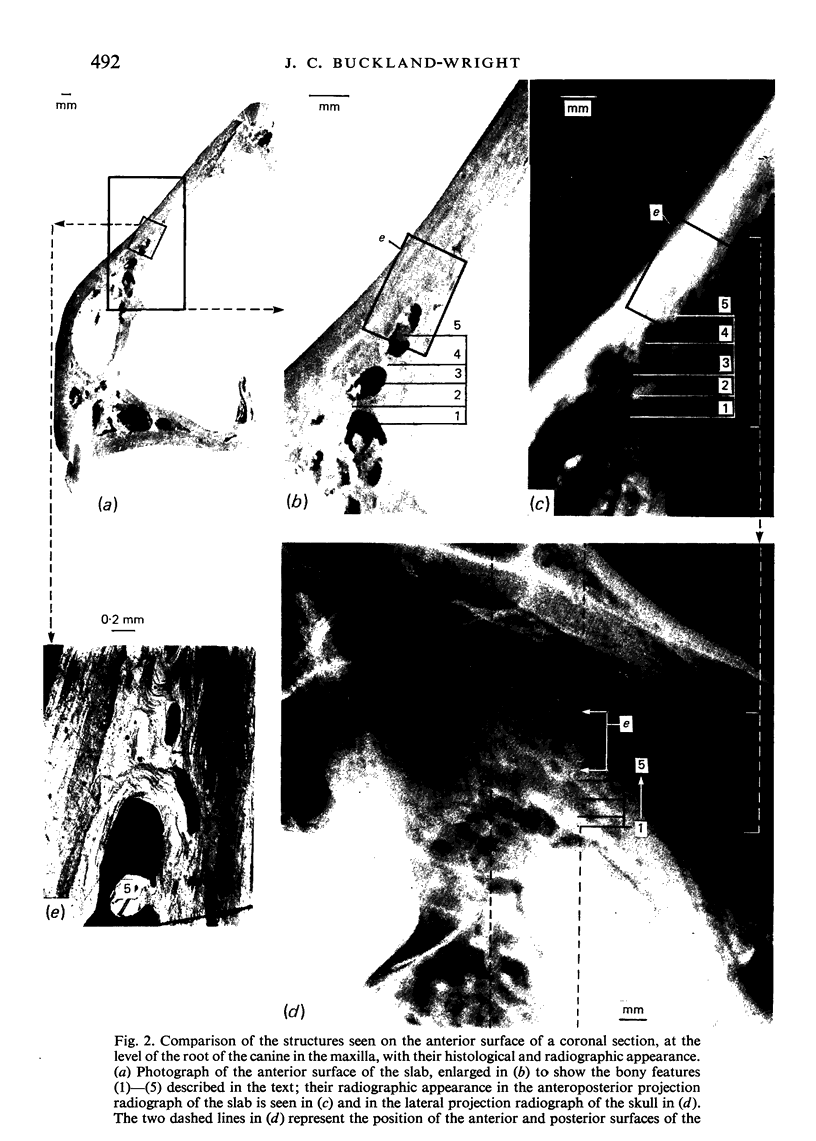
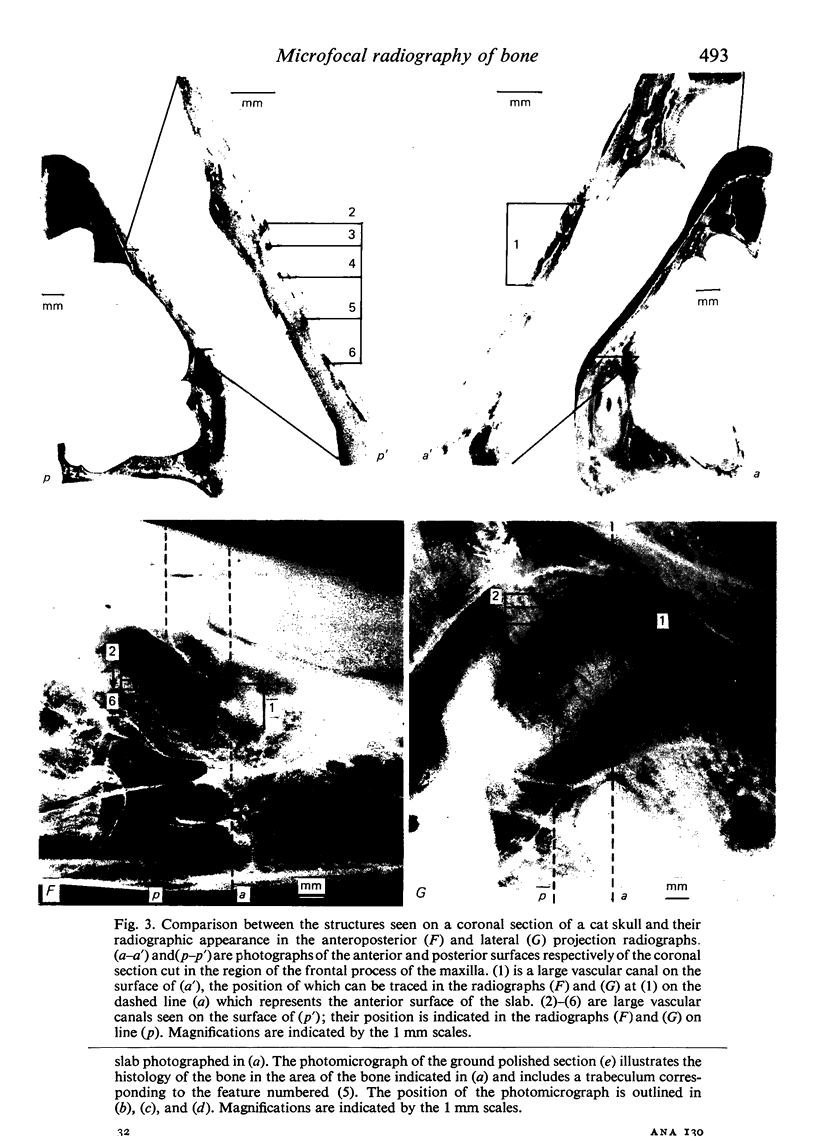
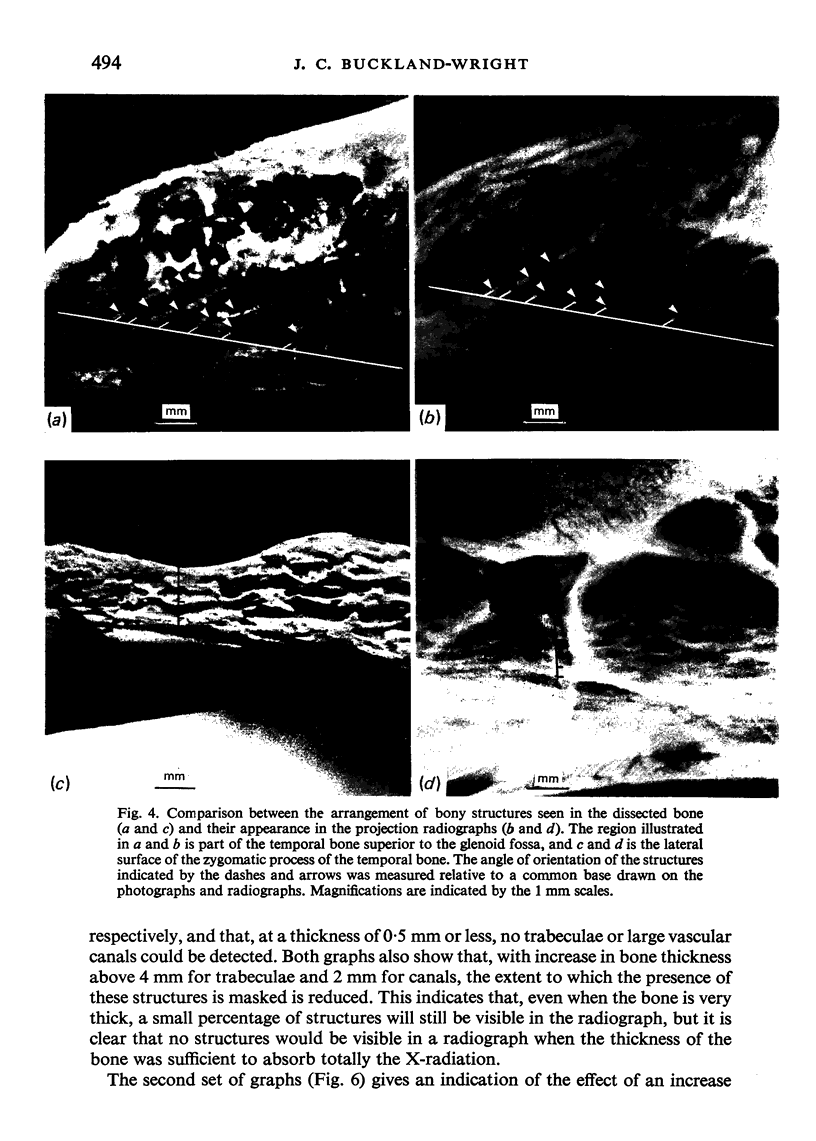
Abstract
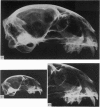
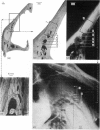
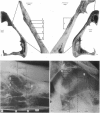
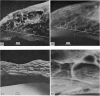
The relatively low resolution in the radiographs produced by clinical X-ray machines has led to the rejection, by a number of investigators, of this machine as a method of examining the detailed structural organisation of bone. In the recently developed microfocal X-ray unit a fine beam of electrons is focussed onto the side of a water cooled target. Stereo-projection radiographs of specimens can be produced at magnifications of x 1-100 and a theoretical resolution to the diamter of the X-ray source (5-10 micrometer). The application of stereo-projection radiography to the study of cat skulls revealed details of structure not readily visible with conventional X-ray techniques. Using three different methods, the shadow images of trabeculae and vascular canals seen in the radiographs were closely correlated with the structures observed in the coronal sections and dissected regions of the cat skulls. The smallest structures recorded from the radiographs had a diameter of 60 micrometer. The effect of the depth of bone and of overlapping trabeculae and large vascular canals on the number of osseous structures recorded in the radiographs of five cat skulls was assessed. The results showed that 50% of the trabeculae and large vascular canals were no longer visible at a bone depth of 4 and 1x5 mm respectively and when superimposed by twelve and two structures respectively.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARDRAN G. M. Bone destruction not demonstrable by radiography. Br J Radiol. 1951 Feb;24(278):107–109. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-24-278-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland-Wright J. C. Bone structure and the patterns of force transmission in the cat skull (felis catus). J Morphol. 1978 Jan;155(1):35–61. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051550104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland-Wright J. C. The micro-focal x-ray unit and its application to bio-medical research. Experientia. 1976 Dec 15;32(12):1613–1616. doi: 10.1007/BF01924484. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckland-Wright J. C. The micro-focal x-ray unit: a demonstration of its potential. Med Biol Illus. 1977 Nov;27(4):163–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDMAN H. M., MILLSAP J. S., BRENMAN H. S. Origin of registration of the architectural pattern, the lamina dura, and the alveolar crest in the dental radiograph. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1957 Jul;10(7):749–758. doi: 10.1016/s0030-4220(57)80070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]