Abstract
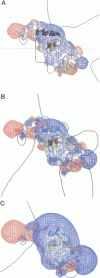
The electrostatic properties of cytochrome f (cyt f), a member of the cytochrome b6f complex and reaction partner with plastocyanin (PC) in photosynthetic electron transport, are qualitatively studied with the goal of determining the mechanism of electron transfer between cyt f and PC. A crystal structure for cyt f was analyzed with the software package GRASP, revealing a large region of positive potential generated by a patch of positively charged residues (including K58, K65, K66, K122, K185, K187, and R209) and reinforced by the iron center of the heme. This positive field attracts the negative charges of the two acidic patches on the mobile electron carrier PC. Three docked complexes are obtained for the two proteins, based on electrostatic or hydrophobic interactions or both and on steric fits by manual docking methods. The first of these three complexes shows strong electrostatic interactions between K187 on cyt f and D44 on PC and between E59 on PC and K58 on cyt f. Two other manually docked complexes are proposed, implicating H87 on PC as the electron-accepting site from the iron center of cyt f through Y1. The second complex maintains the D44/K187 cross-link (but not the E59/K58 link) while increasing hydrophobic interactions between PC and cyt f. Hydrophobic interactions are increased still further in the third complex, whereas the link between K187 on cyt f and D44 on PC is broken. The proposed reaction mechanism, therefore, involves an initial electrostatic docking complex that gives rise to a nonpolar attraction between the regions surrounding H87 on PC and Y1 on cyt f, providing for an electron-transfer active complex.
Full text
PDF












Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson G. P., Sanderson D. G., Lee C. H., Durell S., Anderson L. B., Gross E. L. The effect of ethylenediamine chemical modification of plastocyanin on the rate of cytochrome f oxidation and P-700+ reduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Dec 17;894(3):386–398. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(87)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagby S., Driscoll P. C., Harvey T. S., Hill H. A. High-resolution solution structure of reduced parsley plastocyanin. Biochemistry. 1994 May 31;33(21):6611–6622. doi: 10.1021/bi00187a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cookson D. J., Hayes M. T., Wright P. E. NMR study of the interaction of plastocyanin with chromium(II) analogues of inorganic electron transfer reagents. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Jun 10;591(1):162–176. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90230-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. E., Madura J. D., Sines J., Luty B. A., Allison S. A., McCammon J. A. Diffusion-controlled enzymatic reactions. Methods Enzymol. 1991;202:473–497. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)02024-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durell S. R., Labanowski J. K., Gross E. L. Modeling of the electrostatic potential field of plastocyanin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Mar;277(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90575-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. C., Rochford R. J., Packman L. C. Proteolytic removal of the C-terminal transmembrane region of cytochrome f during extraction from turnip and charlock leaves generates a water-soluble monomeric form of the protein. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jul 15;223(2):481–488. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19016.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E. L., Curtiss A., Durell S. R., White D. Chemical modification of spinach plastocyanin using 4-chloro-3,5-dinitrobenzoic acid: characterization of four singly-modified forms. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Mar 15;1016(1):107–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(90)90012-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E. L., Curtiss A. The interaction of nitrotyrosine-83 plastocyanin with cytochromes f and c: pH dependence and the effect of an additional negative charge on plastocyanin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 22;1056(2):166–172. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss J. M., Bartunik H. D., Freeman H. C. Accuracy and precision in protein structure analysis: restrained least-squares refinement of the structure of poplar plastocyanin at 1.33 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr B. 1992 Dec 1;48(Pt 6):790–811. doi: 10.1107/s0108768192004270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guss J. M., Freeman H. C. Structure of oxidized poplar plastocyanin at 1.6 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 15;169(2):521–563. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harvey S. C. Treatment of electrostatic effects in macromolecular modeling. Proteins. 1989;5(1):78–92. doi: 10.1002/prot.340050109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauska G., Nitschke W., Herrmann R. G. Amino acid identities in the three redox center-carrying polypeptides of cytochrome bc1/b6f complexes. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1988 Apr;20(2):211–228. doi: 10.1007/BF00768395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He S., Modi S., Bendall D. S., Gray J. C. The surface-exposed tyrosine residue Tyr83 of pea plastocyanin is involved in both binding and electron transfer reactions with cytochrome f. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):4011–4016. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04976.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janin J., Chothia C. The structure of protein-protein recognition sites. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16027–16030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez S. E., Huang D., Szczepaniak A., Cramer W. A., Smith J. L. Crystal structure of chloroplast cytochrome f reveals a novel cytochrome fold and unexpected heme ligation. Structure. 1994 Feb 15;2(2):95–105. doi: 10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B. Electrostatic effects in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:387–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Gurd F. R. Calculation of electrostatic interactions in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:413–436. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30019-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modi S., Nordling M., Lundberg L. G., Hansson O., Bendall D. S. Reactivity of cytochromes c and f with mutant forms of spinach plastocyanin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Aug 28;1102(1):85–90. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(92)90068-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morand L. Z., Frame M. K., Colvert K. K., Johnson D. A., Krogmann D. W., Davis D. J. Plastocyanin cytochrome f interaction. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8039–8047. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niwa S., Ishikawa H., Nikai S., Takabe T. Electron transfer reactions between cytochrome f and plastocyanin from Brassica komatsuna. J Biochem. 1980 Oct;88(4):1177–1183. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northrup S. H., Boles J. O., Reynolds J. C. Brownian dynamics of cytochrome c and cytochrome c peroxidase association. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):67–70. doi: 10.1126/science.2838904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Rottenberg H., Avron M. The dependence of photophosphorylation in chloroplasts on delta pH and external pH. FEBS Lett. 1974 Nov 1;48(1):32–36. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)81055-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qin L., Kostić N. M. Importance of protein rearrangement in the electron-transfer reaction between the physiological partners cytochrome f and plastocyanin. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 15;32(23):6073–6080. doi: 10.1021/bi00074a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M. Areas, volumes, packing and protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1977;6:151–176. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.06.060177.001055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose G. D., Wolfenden R. Hydrogen bonding, hydrophobicity, packing, and protein folding. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1993;22:381–415. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.22.060193.002121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Grunwald T. Determination of pH in chloroplasts. 3. Ammonium uptake as a measure of pH in chloroplasts and sub-chloroplast particles. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Jan 31;25(1):71–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01668.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Honig B. Electrostatic interactions in macromolecules: theory and applications. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:301–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp K. A., Nicholls A., Fine R. F., Honig B. Reconciling the magnitude of the microscopic and macroscopic hydrophobic effects. Science. 1991 Apr 5;252(5002):106–109. doi: 10.1126/science.2011744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Ishikawa H. Kinetic studies on a cross-linked complex between plastocyanin cytochrome f. J Biochem. 1989 Jan;105(1):98–102. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Ishikawa H., Niwa S., Tanaka Y. Electron transfer reactions of chemically modified plastocyanin with P700 and cytochrome f. Importance of local charges. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):385–393. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Niwa S., Ishikawa H., Takenaka K. Electron transfer reactions of cytochrome f from Brassica komatsuna with hexacyanoferrate. J Biochem. 1980 Oct;88(4):1167–1176. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takabe T., Takenaka K., Kawamura H., Beppu Y. Charges on proteins and distances of electron transfer in metalloprotein redox reactions. J Biochem. 1986 Mar;99(3):833–840. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takenaka K., Takabe T. Importance of local positive charges on cytochrome f for electron transfer to plastocyanin and potassium ferricyanide. J Biochem. 1984 Dec;96(6):1813–1821. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warshel A., Aqvist J. Electrostatic energy and macromolecular function. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:267–298. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.001411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins J. A., Cusanovich M. A., Meyer T. E., Tollin G. A "parallel plate" electrostatic model for bimolecular rate constants applied to electron transfer proteins. Protein Sci. 1994 Nov;3(11):2104–2114. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelle R. B., Park N. S., Ichiye T. Molecular dynamics simulations of rubredoxin from Clostridium pasteurianum: changes in structure and electrostatic potential during redox reactions. Proteins. 1995 Jun;22(2):154–167. doi: 10.1002/prot.340220208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]