Abstract
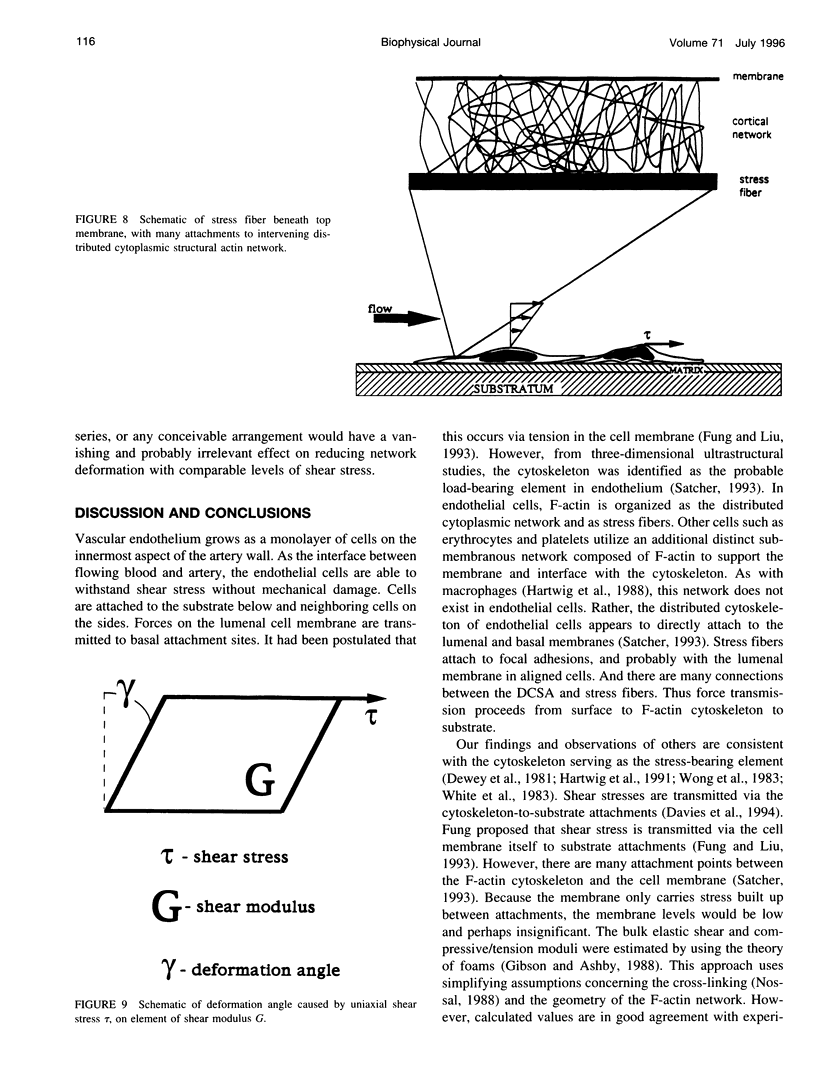
Current modeling of endothelial cell mechanics does not account for the network of F-actin that permeates the cytoplasm. This network, the distributed cytoplasmic structural actin (DCSA), extends from apical to basal membranes, with frequent attachments. Stress fibers are intercalated within the network, with similar frequent attachments. The microscopic structure of the DCSA resembles a foam, so that the mechanical properties can be estimated with analogy to these well-studied systems. The moduli of shear and elastic deformations are estimated to be on the order of 10(5) dynes/cm2. This prediction agrees with experimental measurements of the properties of cytoplasm and endothelial cells reported elsewhere. Stress fibers can potentially increase the modulus by a factor of 2-10, depending on whether they act in series or parallel to the network in transmitting surface forces. The deformations produced by physiological flow fields are of insufficient magnitude to disrupt cell-to-cell or DCSA cross-linkages. The questions raised by this paradox, and the ramifications of implicating the previously unreported DCSA as the primary force transmission element are discussed.
Full text
PDF

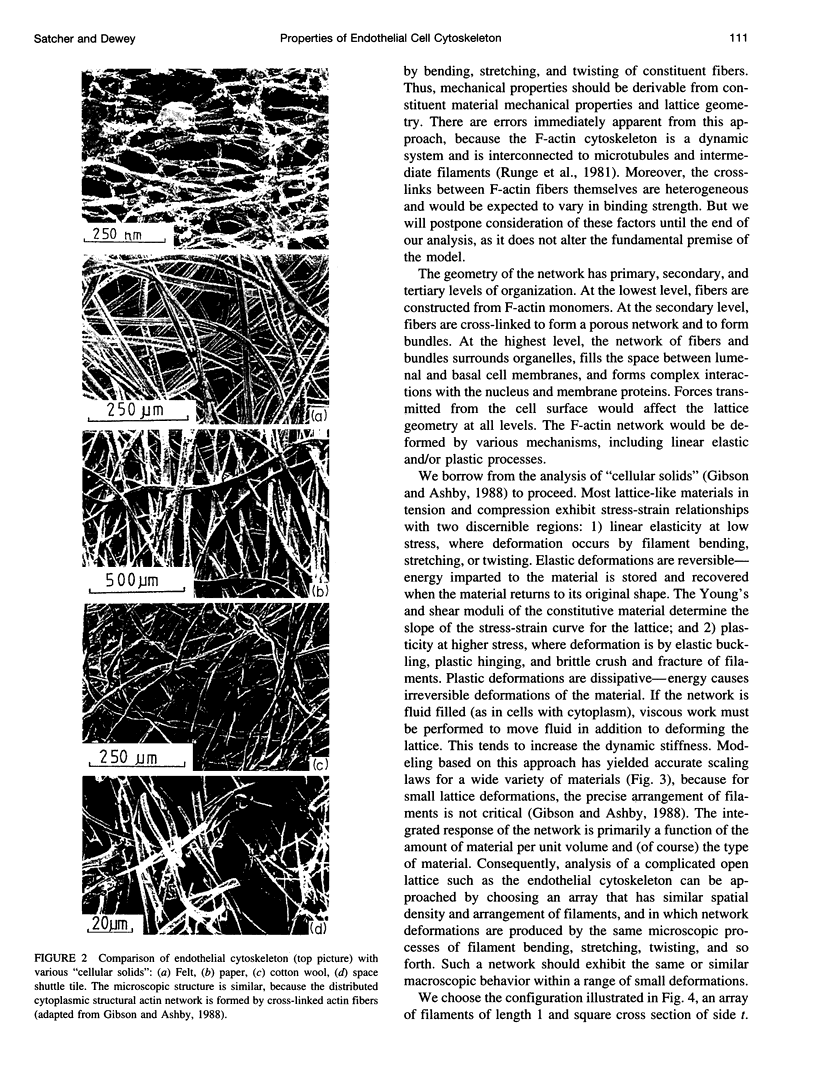
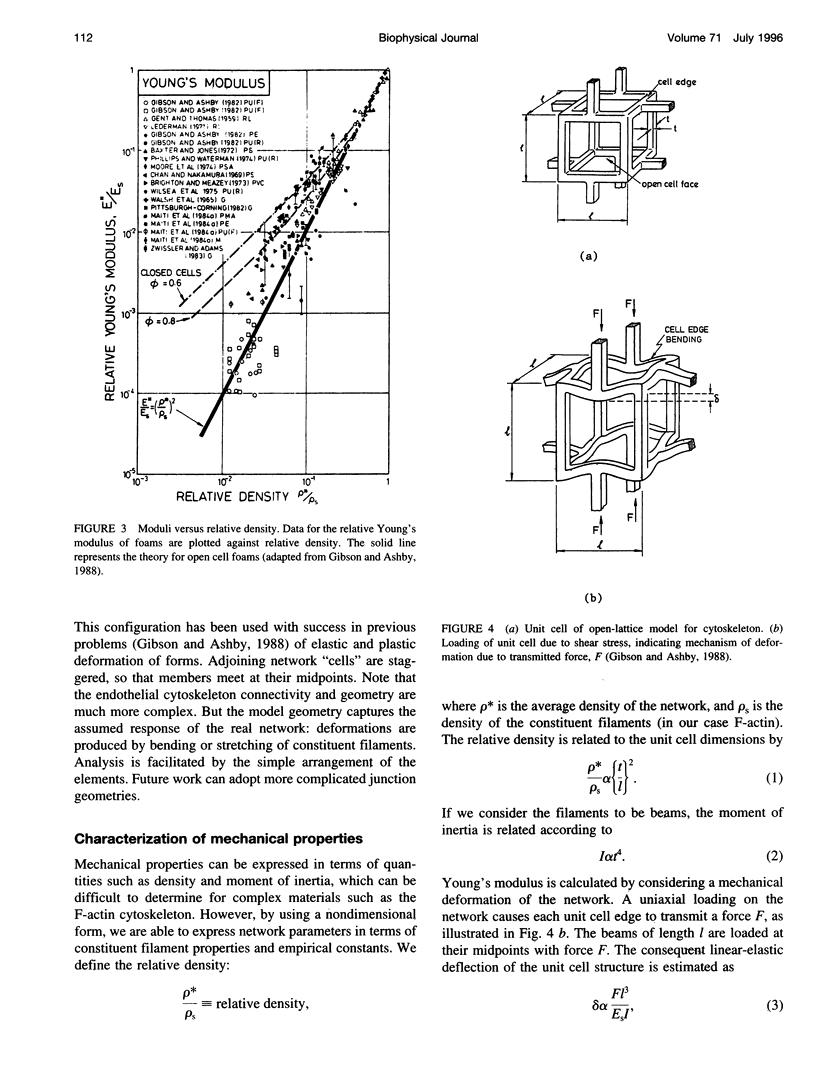

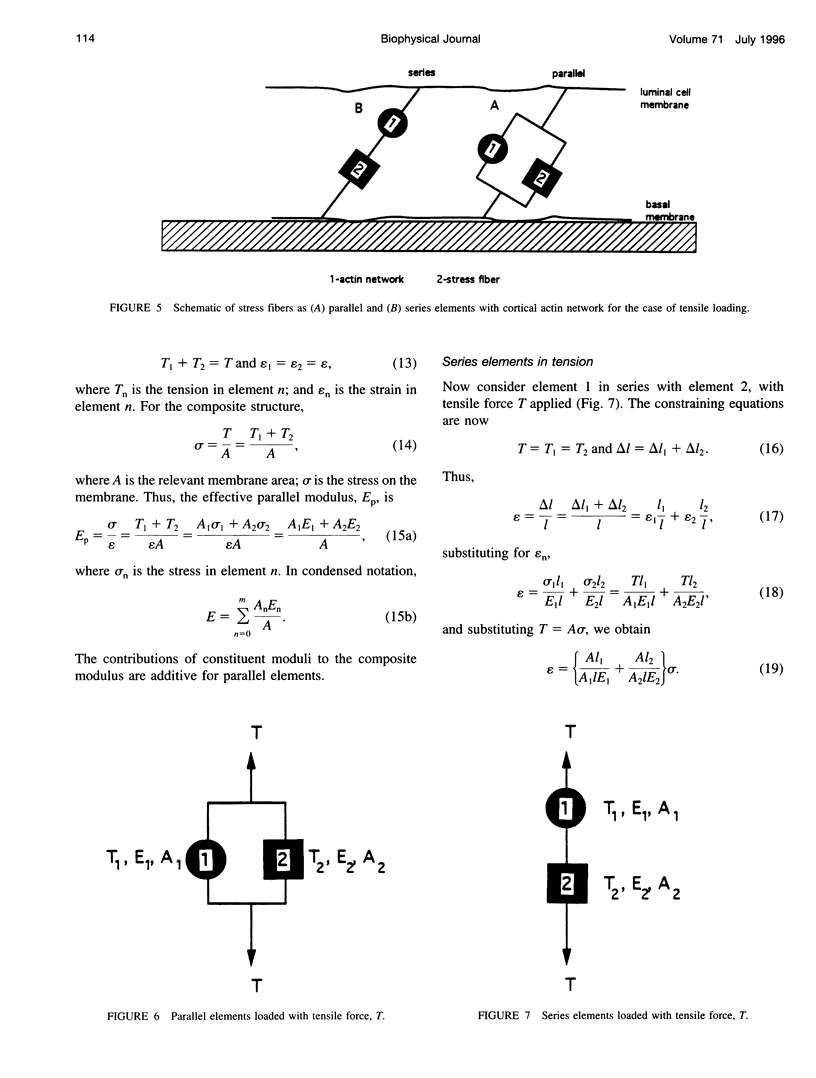



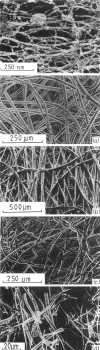
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams D. S. Mechanisms of cell shape change: the cytomechanics of cellular response to chemical environment and mechanical loading. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):83–93. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buxbaum R. E., Dennerll T., Weiss S., Heidemann S. R. F-actin and microtubule suspensions as indeterminate fluids. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1511–1514. doi: 10.1126/science.2881354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortese J. D., Frieden C. Microheterogeneity of actin gels formed under controlled linear shear. J Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;107(4):1477–1487. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.4.1477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F. Flow-mediated endothelial mechanotransduction. Physiol Rev. 1995 Jul;75(3):519–560. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1995.75.3.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Remuzzi A., Gordon E. J., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Turbulent fluid shear stress induces vascular endothelial cell turnover in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2114–2117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. F., Robotewskyj A., Griem M. L. Quantitative studies of endothelial cell adhesion. Directional remodeling of focal adhesion sites in response to flow forces. J Clin Invest. 1994 May;93(5):2031–2038. doi: 10.1172/JCI117197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewey C. F., Jr, Bussolari S. R., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Davies P. F. The dynamic response of vascular endothelial cells to fluid shear stress. J Biomech Eng. 1981 Aug;103(3):177–185. doi: 10.1115/1.3138276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettenson D. S., Gotlieb A. I. Centrosomes, microtubules, and microfilaments in the reendothelialization and remodeling of double-sided in vitro wounds. Lab Invest. 1992 Jun;66(6):722–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. E. Linkage of a membrane skeleton to integral membrane glycoproteins in human platelets. Identification of one of the glycoproteins as glycoprotein Ib. J Clin Invest. 1985 Oct;76(4):1673–1683. doi: 10.1172/JCI112153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C., Liu S. Q. Elementary mechanics of the endothelium of blood vessels. J Biomech Eng. 1993 Feb;115(1):1–12. doi: 10.1115/1.2895465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorlin J. B., Yamin R., Egan S., Stewart M., Stossel T. P., Kwiatkowski D. J., Hartwig J. H. Human endothelial actin-binding protein (ABP-280, nonmuscle filamin): a molecular leaf spring. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1089–1105. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottlieb A. I., Langille B. L., Wong M. K., Kim D. W. Structure and function of the endothelial cytoskeleton. Lab Invest. 1991 Aug;65(2):123–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Chambers K. A., Stossel T. P. Association of gelsolin with actin filaments and cell membranes of macrophages and platelets. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):467–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Zaner K. S., Stossel T. P. Nonideality of volume flows and phase transitions of F-actin solutions in response to osmotic stress. Biophys J. 1987 May;51(5):745–753. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83401-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Euteneuer U., Traub P., Schliwa M. Viscoelastic properties of vimentin compared with other filamentous biopolymer networks. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):155–160. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janmey P. A., Hvidt S., Käs J., Lerche D., Maggs A., Sackmann E., Schliwa M., Stossel T. P. The mechanical properties of actin gels. Elastic modulus and filament motions. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 23;269(51):32503–32513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerst A., Chmielewski C., Livesay C., Buxbaum R. E., Heidemann S. R. Liquid crystal domains and thixotropy of filamentous actin suspensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4241–4245. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishino A., Yanagida T. Force measurements by micromanipulation of a single actin filament by glass needles. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):74–76. doi: 10.1038/334074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolodney M. S., Wysolmerski R. B. Isometric contraction by fibroblasts and endothelial cells in tissue culture: a quantitative study. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):73–82. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E., Birchmeier W. Stress fiber sarcomeres of fibroblasts are contractile. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90365-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levesque M. J., Liepsch D., Moravec S., Nerem R. M. Correlation of endothelial cell shape and wall shear stress in a stenosed dog aorta. Arteriosclerosis. 1986 Mar-Apr;6(2):220–229. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.6.2.220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lux S. E. Dissecting the red cell membrane skeleton. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):426–429. doi: 10.1038/281426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal R. On the elasticity of cytoskeletal networks. Biophys J. 1988 Mar;53(3):349–359. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83112-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa F. Actin-actin bond strength and the conformational change of F-actin. Biorheology. 1977;14(1):11–19. doi: 10.3233/bir-1977-14102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnick N., Collins T., Atkinson W., Bonthron D. T., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Platelet-derived growth factor B chain promoter contains a cis-acting fluid shear-stress-responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 May 15;90(10):4591–4595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.10.4591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Runge M. S., Laue T. M., Yphantis D. A., Lifsics M. R., Saito A., Altin M., Reinke K., Williams R. C., Jr ATP-induced formation of an associated complex between microtubules and neurofilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1431–1435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs F. Mechanical transduction in biological systems. Crit Rev Biomed Eng. 1988;16(2):141–169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satcher R. L., Jr, Bussolari S. R., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Dewey C. F., Jr The distribution of fluid forces on model arterial endothelium using computational fluid dynamics. J Biomech Eng. 1992 Aug;114(3):309–316. doi: 10.1115/1.2891388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato M., Levesque M. J., Nerem R. M. An application of the micropipette technique to the measurement of the mechanical properties of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells. J Biomech Eng. 1987 Feb;109(1):27–34. doi: 10.1115/1.3138638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen J., Luscinskas F. W., Connolly A., Dewey C. F., Jr, Gimbrone M. A., Jr Fluid shear stress modulates cytosolic free calcium in vascular endothelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1992 Feb;262(2 Pt 1):C384–C390. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.2.C384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Yamazaki M., Ito T. Osmoelastic coupling in biological structures: formation of parallel bundles of actin filaments in a crystalline-like structure caused by osmotic stress. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6513–6518. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theret D. P., Levesque M. J., Sato M., Nerem R. M., Wheeler L. T. The application of a homogeneous half-space model in the analysis of endothelial cell micropipette measurements. J Biomech Eng. 1988 Aug;110(3):190–199. doi: 10.1115/1.3108430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Butler J. P., Ingber D. E. Mechanotransduction across the cell surface and through the cytoskeleton. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1124–1127. doi: 10.1126/science.7684161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Ingber D. E. Control of cytoskeletal mechanics by extracellular matrix, cell shape, and mechanical tension. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2181–2189. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)81014-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White G. E., Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Fujiwara K. Factors influencing the expression of stress fibers in vascular endothelial cells in situ. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):416–424. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]