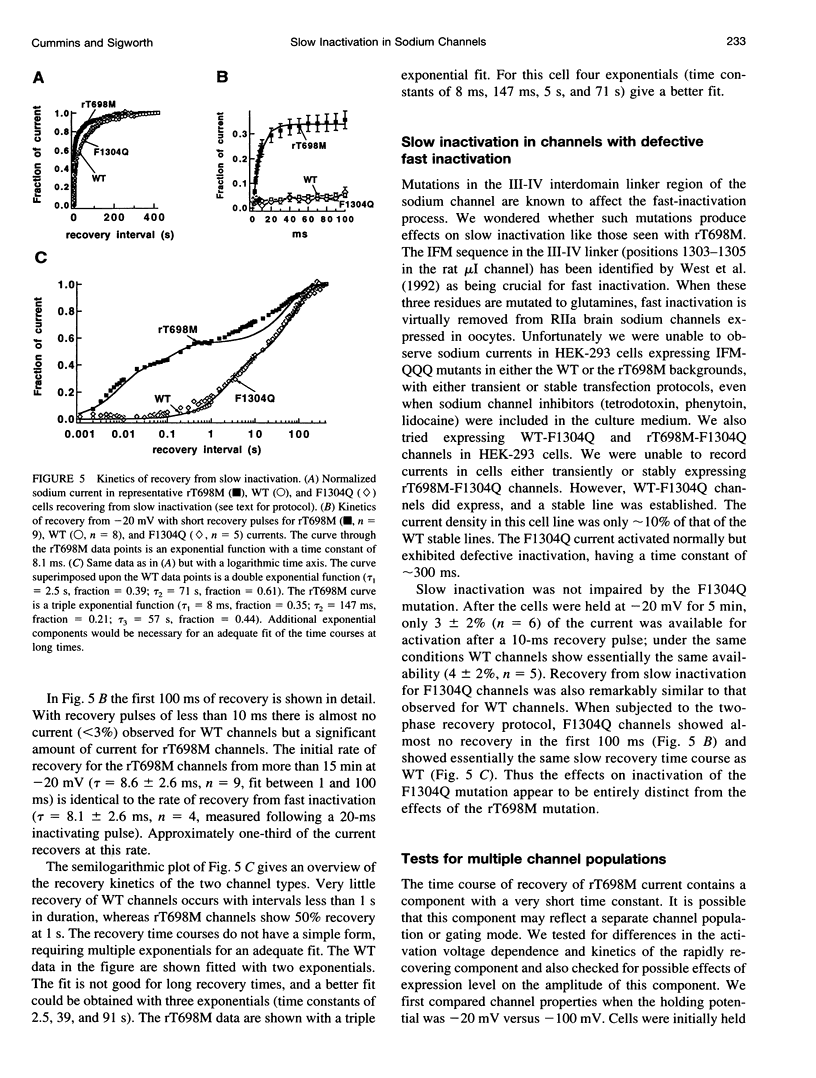
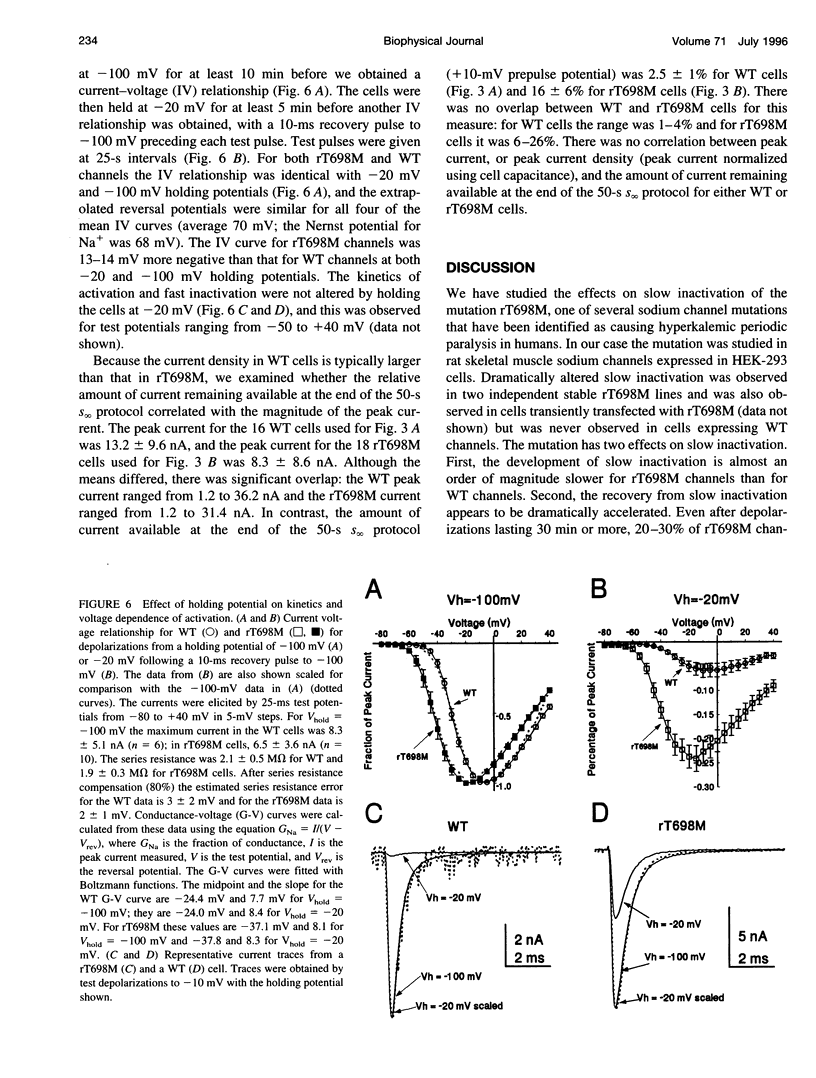
Abstract
Hyperkalemic periodic paralysis (HyperPP) is a disorder in which current through Na+ channels causes a prolonged depolarization of skeletal muscle fibers, resulting in membrane inexcitability and muscle paralysis. Although HyperPP mutations can enhance persistent sodium currents, unaltered slow inactivation would effectively eliminate any sustained currents through the mutant channels. We now report that rat skeletal muscle channels containing the mutation T698M, which corresponds to the human T704M HyperPP mutation, recover very quickly from prolonged depolarizations. Even after holding at -20 mV for 20 min, approximately 25% of the maximal sodium current is available subsequent to a 10-ms hyperpolarization (-100 mV). Under the same conditions, recovery is less than 3% in wild-type channels and in the F1304Q mutant, which has impaired fast inactivation. This effect of the T698M mutation on slow inactivation, in combination with its effects on activation, is expected to result in persistent currents such as that seen in HyperPP muscle.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almers W., Stanfield P. R., Stühmer W. Slow changes in currents through sodium channels in frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:253–271. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barchi R. L. Molecular pathology of the skeletal muscle sodium channel. Annu Rev Physiol. 1995;57:355–385. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.57.030195.002035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon S. C., Strittmatter S. M. Functional expression of sodium channel mutations identified in families with periodic paralysis. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):317–326. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90321-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chahine M., George A. L., Jr, Zhou M., Ji S., Sun W., Barchi R. L., Horn R. Sodium channel mutations in paramyotonia congenita uncouple inactivation from activation. Neuron. 1994 Feb;12(2):281–294. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummins T. R., Zhou J., Sigworth F. J., Ukomadu C., Stephan M., Ptácek L. J., Agnew W. S. Functional consequences of a Na+ channel mutation causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Neuron. 1993 Apr;10(4):667–678. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90168-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fahlke C., Rüdel R. Giga-seal formation alters properties of sodium channels of human myoballs. Pflugers Arch. 1992 Mar;420(3-4):248–254. doi: 10.1007/BF00374454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. The dual effect of membrane potential on sodium conductance in the giant axon of Loligo. J Physiol. 1952 Apr;116(4):497–506. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch G. E., Anderson M. F. Sodium channel kinetics in normal and denervated rabbit muscle membrane. Muscle Nerve. 1986 Oct;9(8):738–747. doi: 10.1002/mus.880090810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korge B. P., Gan S. Q., McBride O. W., Mischke D., Steinert P. M. Extensive size polymorphism of the human keratin 10 chain resides in the C-terminal V2 subdomain due to variable numbers and sizes of glycine loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Feb 1;89(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Küther G., Ricker K., Grafe P., Ballanyi K., Rüdel R. Adynamia episodica hereditaria with myotonia: a non-inactivating sodium current and the effect of extracellular pH. Muscle Nerve. 1987 May;10(4):363–374. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R., Ricker K., Lorković H., Dengler R., Hopf H. C. Two cases of adynamia episodica hereditaria: in vitro investigation of muscle cell membrane and contraction parameters. Muscle Nerve. 1983 Feb;6(2):113–121. doi: 10.1002/mus.880060206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptácek L. J., George A. L., Jr, Griggs R. C., Tawil R., Kallen R. G., Barchi R. L., Robertson M., Leppert M. F. Identification of a mutation in the gene causing hyperkalemic periodic paralysis. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):1021–1027. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90374-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricker K., Camacho L. M., Grafe P., Lehmann-Horn F., Rüdel R. Adynamia episodica hereditaria: what causes the weakness? Muscle Nerve. 1989 Nov;12(11):883–891. doi: 10.1002/mus.880121103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben P. C., Starkus J. G., Rayner M. D. Steady-state availability of sodium channels. Interactions between activation and slow inactivation. Biophys J. 1992 Apr;61(4):941–955. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81901-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudy B. Slow inactivation of the sodium conductance in squid giant axons. Pronase resistance. J Physiol. 1978 Oct;283:1–21. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Comparison between slow sodium channel inactivation in rat slow- and fast-twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:339–348. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L. Slow Na+ channel inactivation must be disrupted to evoke prolonged depolarization-induced paralysis. Biophys J. 1994 Feb;66(2 Pt 1):542–542. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80807-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruff R. L., Whittlesey D. Na+ current densities and voltage dependence in human intercostal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1992 Dec;458:85–97. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Lehmann-Horn F. Membrane changes in cells from myotonia patients. Physiol Rev. 1985 Apr;65(2):310–356. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1985.65.2.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüdel R., Ricker K., Lehmann-Horn F. Genotype-phenotype correlations in human skeletal muscle sodium channel diseases. Arch Neurol. 1993 Nov;50(11):1241–1248. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1993.00540110113011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncini L., Stühmer W. Slow sodium channel inactivation in rat fast-twitch muscle. J Physiol. 1987 Feb;383:327–337. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1987.sp016411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streib E. W. AAEE minimonograph #27: differential diagnosis of myotonic syndromes. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Sep;10(7):603–615. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ukomadu C., Zhou J., Sigworth F. J., Agnew W. S. muI Na+ channels expressed transiently in human embryonic kidney cells: biochemical and biophysical properties. Neuron. 1992 Apr;8(4):663–676. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90088-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



