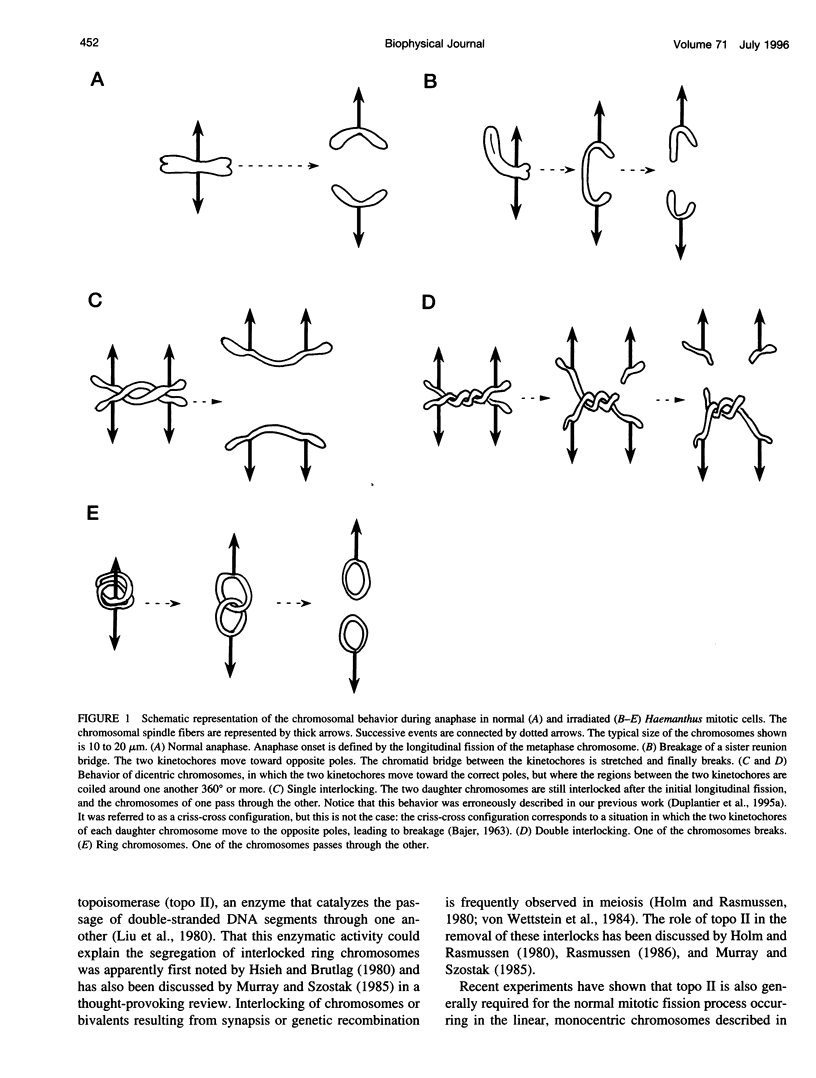
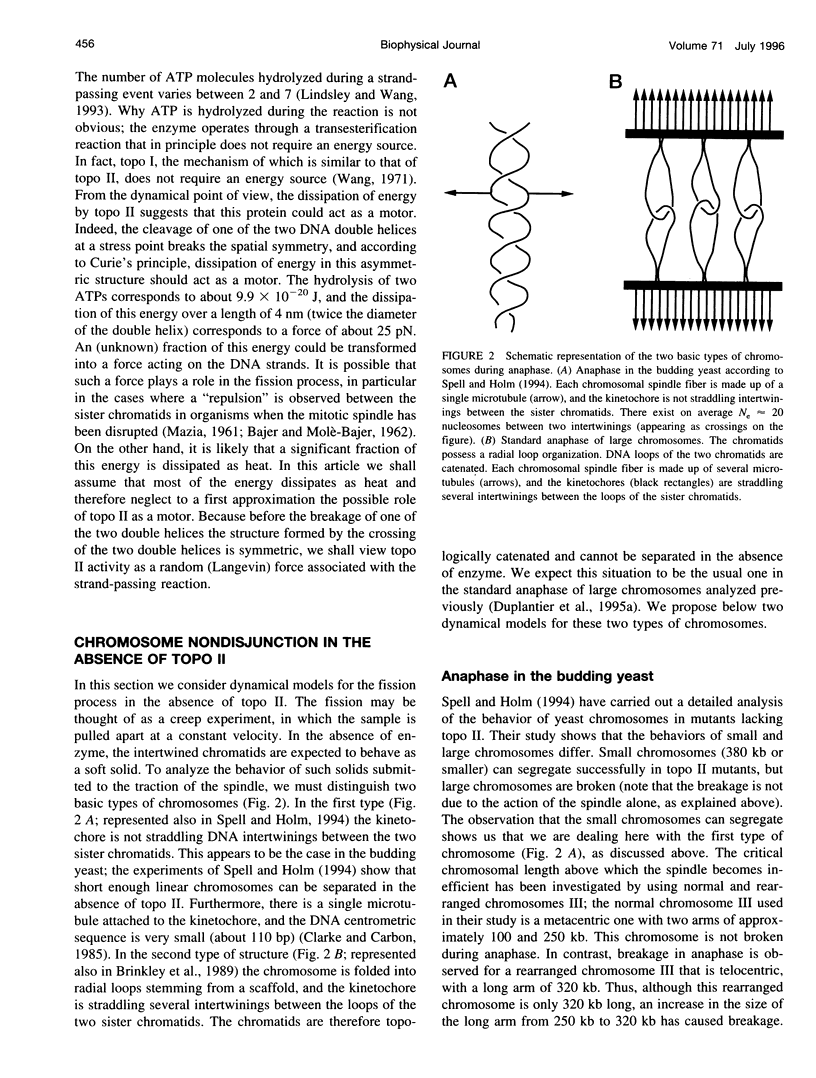
Abstract
In the course of anaphase, the chromosomal DNA is submitted to the traction of the spindle. Several physical problems are associated with this action. In particular, the sister chromatids are generally topologically intertwined at the onset of anaphase, and the removal of the intertwinings results from a coupling between the enzymatic action of type II DNA topoisomerases and the force exerted by the spindle. We propose a physical analysis of some of these problems: 1) We compare the maximum force the spindle can produce with the force required to break a DNA molecule, and define the conditions compatible with biological safety during anaphase. 2) We show that the behavior of the sister chromatids in the absence of type II DNA topoisomerases can be described by two distinct models: a chain pullout model accounts for the experimental observations made in the budding yeast, and a model of the mechanical rupture of rubbers accounts for the nondisjunction in standard cases. 3) Using the fluctuation-dissipation theorem, we introduce an effective protein friction associated with the strand-passing activity of type II DNA topoisomerases. We show that this friction can be used to describe the situation in which one chromosome passes entirely through another one. Possible experiments that could test these theoretical analyses are discussed.
Full text
PDF












Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander S. P., Rieder C. L. Chromosome motion during attachment to the vertebrate spindle: initial saltatory-like behavior of chromosomes and quantitative analysis of force production by nascent kinetochore fibers. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):805–815. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAJER A. CINE-MICROGRAPHIC STUDIES ON DICENTRIC CHROMOSOMES. Chromosoma. 1964 Dec 10;15:630–651. doi: 10.1007/BF00319996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beere H. M., Chresta C. M., Alejo-Herberg A., Skladanowski A., Dive C., Larsen A. K., Hickman J. A. Investigation of the mechanism of higher order chromatin fragmentation observed in drug-induced apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol. 1995 May;47(5):986–996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensimon D, Simon AJ, Croquette V, V, Bensimon A. Stretching DNA with a receding meniscus: Experiments and models. Phys Rev Lett. 1995 Jun 5;74(23):4754–4757. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.74.4754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bicknell G. R., Snowden R. T., Cohen G. M. Formation of high molecular mass DNA fragments is a marker of apoptosis in the human leukaemic cell line, U937. J Cell Sci. 1994 Sep;107(Pt 9):2483–2489. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.9.2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bortner C. D., Oldenburg N. B., Cidlowski J. A. The role of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol. 1995 Jan;5(1):21–26. doi: 10.1016/s0962-8924(00)88932-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. G., Sun X. M., Cohen G. M. Dexamethasone-induced apoptosis involves cleavage of DNA to large fragments prior to internucleosomal fragmentation. J Biol Chem. 1993 Feb 15;268(5):3037–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchenau P., Saumweber H., Arndt-Jovin D. J. Consequences of topoisomerase II inhibition in early embryogenesis of Drosophila revealed by in vivo confocal laser scanning microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1993 Apr;104(Pt 4):1175–1185. doi: 10.1242/jcs.104.4.1175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke D. J., Johnson R. T., Downes C. S. Topoisomerase II inhibition prevents anaphase chromatid segregation in mammalian cells independently of the generation of DNA strand breaks. J Cell Sci. 1993 Jun;105(Pt 2):563–569. doi: 10.1242/jcs.105.2.563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. The structure and function of yeast centromeres. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:29–55. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cluzel P., Lebrun A., Heller C., Lavery R., Viovy J. L., Chatenay D., Caron F. DNA: an extensible molecule. Science. 1996 Feb 9;271(5250):792–794. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5250.792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. M., Sun X. M., Fearnhead H., MacFarlane M., Brown D. G., Snowden R. T., Dinsdale D. Formation of large molecular weight fragments of DNA is a key committed step of apoptosis in thymocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Jul 15;153(2):507–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downes C. S., Mullinger A. M., Johnson R. T. Inhibitors of DNA topoisomerase II prevent chromatid separation in mammalian cells but do not prevent exit from mitosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):8895–8899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.8895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duplantier B., Jannink G., Sikorav J. L. Anaphase chromatid motion: involvement of type II DNA topoisomerases. Biophys J. 1995 Oct;69(4):1596–1605. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80032-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filipski J., Leblanc J., Youdale T., Sikorska M., Walker P. R. Periodicity of DNA folding in higher order chromatin structures. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1319–1327. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08241.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funabiki H., Hagan I., Uzawa S., Yanagida M. Cell cycle-dependent specific positioning and clustering of centromeres and telomeres in fission yeast. J Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;121(5):961–976. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.5.961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G. J. Cell cycle progression and chromosome segregation in mammalian cells cultured in the presence of the topoisomerase II inhibitors ICRF-187 [(+)-1,2-bis(3,5-dioxopiperazinyl-1-yl)propane; ADR-529] and ICRF-159 (Razoxane). Cancer Res. 1994 Feb 15;54(4):1042–1048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guacci V., Hogan E., Koshland D. Chromosome condensation and sister chromatid pairing in budding yeast. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):517–530. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C. Coming undone: how to untangle a chromosome. Cell. 1994 Jul 1;77(7):955–957. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90433-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Goto T., Wang J. C., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II is required at the time of mitosis in yeast. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):553–563. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80028-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holm C., Stearns T., Botstein D. DNA topoisomerase II must act at mitosis to prevent nondisjunction and chromosome breakage. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):159–168. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh T., Brutlag D. ATP-dependent DNA topoisonmerase from D. melanogaster reversibly catenates duplex DNA rings. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen C. G. Dynamics of spindle microtubule organization: kinetochore fiber microtubules of plant endosperm. J Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;92(2):540–558. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagarkova M. A., Iarovaia O. V., Razin S. V. Large-scale fragmentation of mammalian DNA in the course of apoptosis proceeds via excision of chromosomal DNA loops and their oligomers. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 1;270(35):20239–20241. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.35.20239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X., Nicklas R. B. Mitotic forces control a cell-cycle checkpoint. Nature. 1995 Feb 16;373(6515):630–632. doi: 10.1038/373630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang H., Wright W. H., Cheng S., He W., Berns M. W. Micromanipulation of chromosomes in PTK2 cells using laser microsurgery (optical scalpel) in combination with laser-induced optical force (optical tweezers). Exp Cell Res. 1993 Jan;204(1):110–120. doi: 10.1006/excr.1993.1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindsley J. E., Wang J. C. On the coupling between ATP usage and DNA transport by yeast DNA topoisomerase II. J Biol Chem. 1993 Apr 15;268(11):8096–8104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F., Liu C. C., Alberts B. M. Type II DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that can unknot a topologically knotted DNA molecule via a reversible double-strand break. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):697–707. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki W. Y., Orr-Weaver T. L. Sister-chromatid cohesion in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:167–187. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami S., Yanagida M., Niwa O. A large circular minichromosome of Schizosaccharomyces pombe requires a high dose of type II DNA topoisomerase for its stabilization. Mol Gen Genet. 1995 Mar 20;246(6):671–679. doi: 10.1007/BF00290712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NICKLAS R. B. CHROMOSOME VELOCITY DURING MITOSIS AS A FUNCTION OF CHROMOSOME SIZE AND POSITION. J Cell Biol. 1965 Apr;25:SUPPL–SUPPL:135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.25.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. G., Kastan M. B. DNA strand breaks: the DNA template alterations that trigger p53-dependent DNA damage response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1815–1823. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas R. B. Measurements of the force produced by the mitotic spindle in anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;97(2):542–548. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.2.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicklas R. B. The forces that move chromosomes in mitosis. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:431–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oberhammer F., Wilson J. W., Dive C., Morris I. D., Hickman J. A., Wakeling A. E., Walker P. R., Sikorska M. Apoptotic death in epithelial cells: cleavage of DNA to 300 and/or 50 kb fragments prior to or in the absence of internucleosomal fragmentation. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3679–3684. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06042.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olvera de la Cruz M, Deutsch JM, Edwards SF. Electrophoresis in strong fields. Phys Rev A Gen Phys. 1986 Mar;33(3):2047–2055. doi: 10.1103/physreva.33.2047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheroff N., Shelton E. R., Brutlag D. L. DNA topoisomerase II from Drosophila melanogaster. Relaxation of supercoiled DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9536–9543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer R. E., Koval M., Koshland D. The dynamics of chromosome movement in the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3355–3366. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins T. T., Smith D. E., Chu S. Direct observation of tube-like motion of a single polymer chain. Science. 1994 May 6;264(5160):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.8171335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS O. C., BOYER P. D. CHEMICAL MECHANISM OF SONIC, ACID, ALKALINE AND ENZYMIC DEGRADATION OF DNA. J Mol Biol. 1965 Feb;11:327–340. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rieder C. L. The formation, structure, and composition of the mammalian kinetochore and kinetochore fiber. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;79:1–58. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose D., Holm C. Meiosis-specific arrest revealed in DNA topoisomerase II mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3445–3455. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitoh Y., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure: bands arise from a differential folding path of the highly AT-rich scaffold. Cell. 1994 Feb 25;76(4):609–622. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90502-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimoto K, Tawada K. Extended time correlation of in vitro motility by motor protein. Phys Rev Lett. 1995 Jul 3;75(1):180–183. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamu C. E., Murray A. W. Sister chromatid separation in frog egg extracts requires DNA topoisomerase II activity during anaphase. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(5):921–934. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.5.921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorav J. L., Jannink G. Kinetics of chromosome condensation in the presence of topoisomerases: a phantom chain model. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):827–837. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80859-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Cui Y., Bustamante C. Overstretching B-DNA: the elastic response of individual double-stranded and single-stranded DNA molecules. Science. 1996 Feb 9;271(5250):795–799. doi: 10.1126/science.271.5250.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spell R. M., Holm C. Nature and distribution of chromosomal intertwinings in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Feb;14(2):1465–1476. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.2.1465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundin O., Varshavsky A. Arrest of segregation leads to accumulation of highly intertwined catenated dimers: dissection of the final stages of SV40 DNA replication. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):659–669. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90173-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawada K., Sekimoto K. Protein friction exerted by motor enzymes through a weak-binding interaction. J Theor Biol. 1991 May 21;150(2):193–200. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80331-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Ohkura H., Adachi Y., Morino K., Shiozaki K., Yanagida M. DNA topoisomerase II is required for condensation and separation of mitotic chromosomes in S. pombe. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):917–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90518-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uemura T., Tanagida M. Mitotic spindle pulls but fails to separate chromosomes in type II DNA topoisomerase mutants: uncoordinated mitosis. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1003–1010. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04315.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale R. D., Soll D. R., Gibbons I. R. One-dimensional diffusion of microtubules bound to flagellar dynein. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90614-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viovy J. L., Duke T. Solid friction and polymer relaxation in gel electrophoresis. Science. 1994 Apr 1;264(5155):112–113. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5155.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. D., CRICK F. H. The structure of DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1953;18:123–131. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1953.018.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. R., Smith C., Youdale T., Leblanc J., Whitfield J. F., Sikorska M. Topoisomerase II-reactive chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis in thymocytes. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 15;51(4):1078–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and an Escherichia coli protein omega. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz D. Direct measurement of the transport properties of a single DNA molecule. Phys Rev Lett. 1995 Sep 18;75(12):2436–2439. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.75.2436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Engh G., Sachs R., Trask B. J. Estimating genomic distance from DNA sequence location in cell nuclei by a random walk model. Science. 1992 Sep 4;257(5075):1410–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.1388286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Wettstein D., Rasmussen S. W., Holm P. B. The synaptonemal complex in genetic segregation. Annu Rev Genet. 1984;18:331–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.18.120184.001555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


