Abstract
To test the hypothesis that water pores in a lipid membrane mediate the proton transport, molecular dynamic simulations of a phospholipid membrane, in which the formation of a water pore is induced, are reported. The probability density of such a pore in the membrane was obtained from the free energy of formation of the pore, which was computed from the average force needed to constrain the pore in the membrane. It was found that the free energy of a single file of water molecules spanning the bilayer is 108(+/-10) kJ/mol. From unconstrained molecular dynamic simulations it was further deduced that the nature of the pore is very transient, with a mean lifetime of a few picoseconds. The orientations of water molecules within the pore were also studied, and the spontaneous translocation of a turning defect was observed. The combined data allowed a permeability coefficient for proton permeation across the membrane to be computed, assuming that a suitable orientation of the water molecules in the pore allows protons to permeate the membrane relatively fast by means of a wirelike conductance mechanism. The computed value fits the experimental data only if it is assumed that the entry of the proton into the pore is not rate limiting.
Full text
PDF




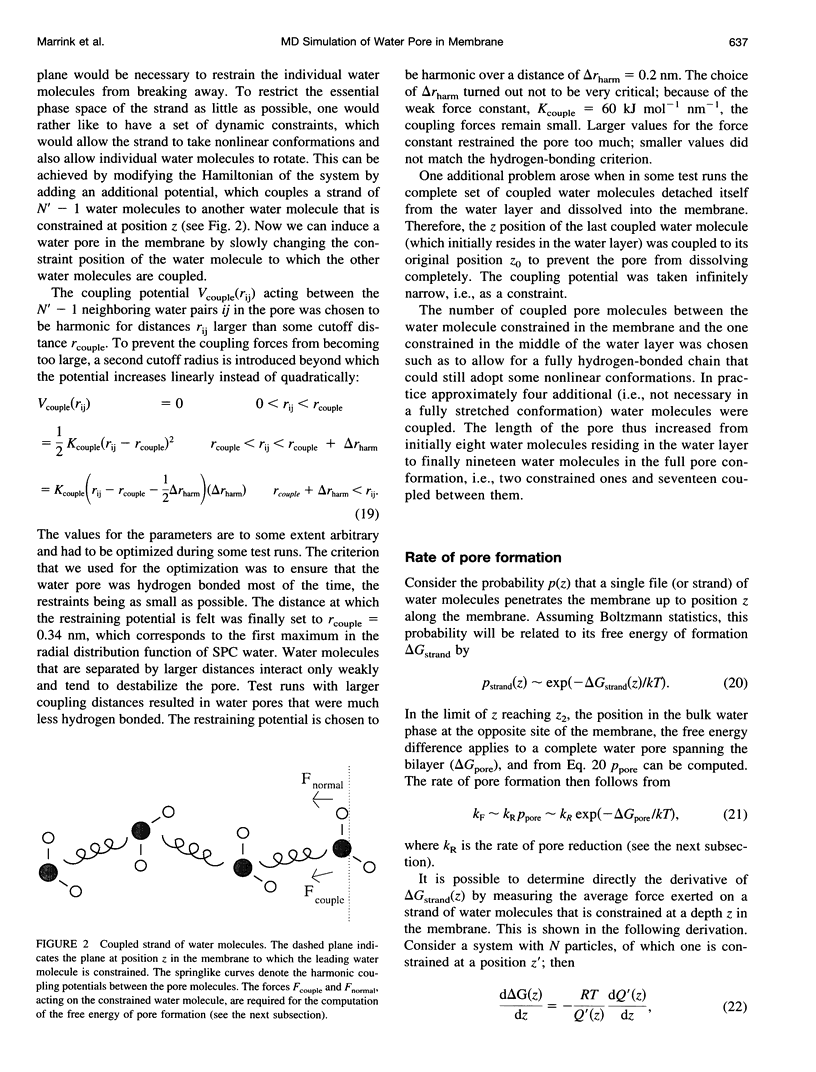


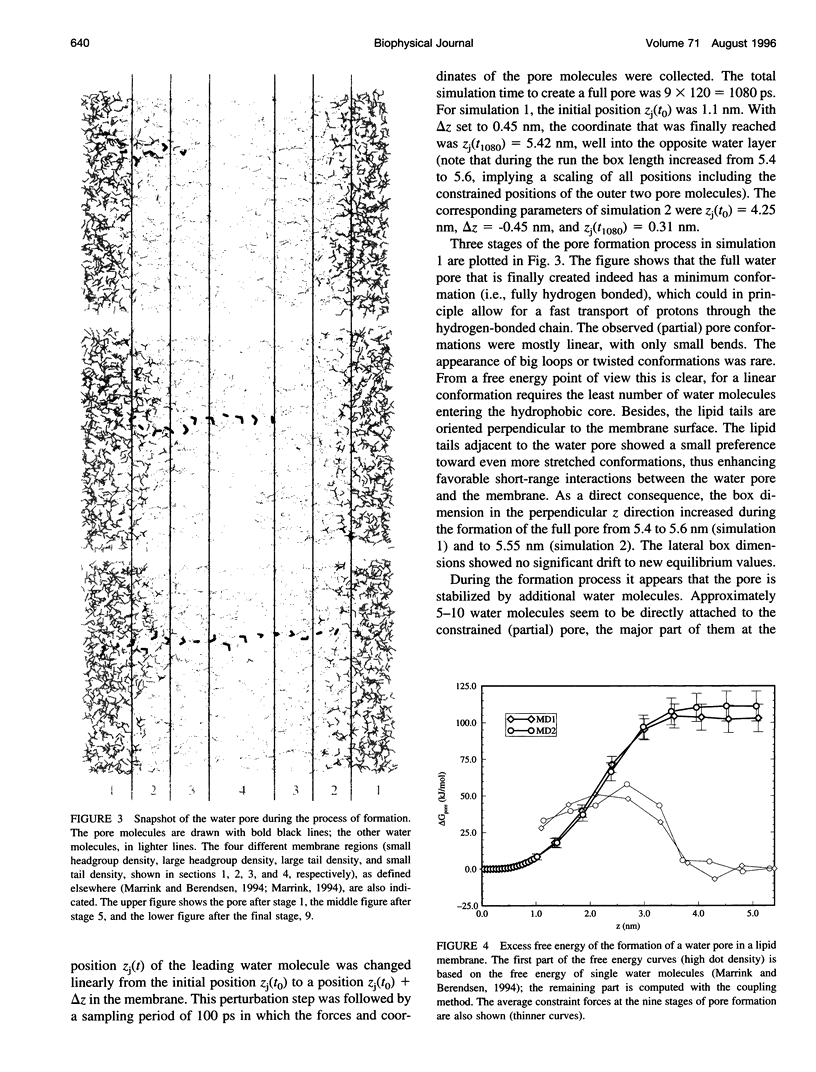




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benz R., McLaughlin S. The molecular mechanism of action of the proton ionophore FCCP (carbonylcyanide p-trifluoromethoxyphenylhydrazone). Biophys J. 1983 Mar;41(3):381–398. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84449-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiso D. S., Hubbell W. L. Electrogenic H+/OH- movement across phospholipid vesicles measured by spin-labeled hydrophobic ions. Biophys J. 1983 Oct;44(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84276-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Bramhall J. Permeability of lipid bilayers to water and ionic solutes. Chem Phys Lipids. 1986 Jun-Jul;40(2-4):167–188. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(86)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton flux mechanisms in model and biological membranes. J Membr Biol. 1989 Feb;107(2):91–103. doi: 10.1007/BF01871715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W., Nichols J. W. Proton-hydroxide permeability of liposomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):165–168. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deamer D. W. Proton permeation of lipid bilayers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):457–479. doi: 10.1007/BF00770030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egberts E., Marrink S. J., Berendsen H. J. Molecular dynamics simulation of a phospholipid membrane. Eur Biophys J. 1994;22(6):423–436. doi: 10.1007/BF00180163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elamrani K., Blume A. Effect of the lipid phase transition on the kinetics of H+/OH- diffusion across phosphatidic acid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 5;727(1):22–30. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90364-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. The membrane dipole potential in a total membrane potential model. Applications to hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83664-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Proton conductance through phospholipid bilayers: water wires or weak acids? J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):427–442. doi: 10.1007/BF00770028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Proton/hydroxide conductance and permeability through phospholipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6443–6446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J. Proton/hydroxide conductance through lipid bilayer membranes. J Membr Biol. 1984;82(1):105–112. doi: 10.1007/BF01870737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutknecht J., Walter A. Transport of protons and hydrochloric acid through lipid bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Feb 20;641(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90582-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauser H., Oldani D., Phillips M. C. Mechanism of ion escape from phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylserine single bilayer vesicles. Biochemistry. 1973 Oct 23;12(22):4507–4517. doi: 10.1021/bi00746a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueller P., Rudin D. O. Action potential phenomena in experimental bimolecular lipid membranes. Nature. 1967 Feb 11;213(5076):603–604. doi: 10.1038/213603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Morowitz H. J. Molecular mechanisms for proton transport in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F. Theory of passive proton conductance in lipid bilayers. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1987 Oct;19(5):413–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00770027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Deamer D. W. Net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes measured by an acid-base titration technique. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols J. W., Hill M. W., Bangham A. D., Deamer D. W. Measurement of net proton-hydroxyl permeability of large unilamellar liposomes with the fluorescent pH probe, 9-aminoacridine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 13;596(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki Y., Tanford C. Proton and hydroxide ion permeability of phospholipid vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4324–4328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsegian A. Energy of an ion crossing a low dielectric membrane: solutions to four relevant electrostatic problems. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):844–846. doi: 10.1038/221844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paula S., Volkov A. G., Van Hoek A. N., Haines T. H., Deamer D. W. Permeation of protons, potassium ions, and small polar molecules through phospholipid bilayers as a function of membrane thickness. Biophys J. 1996 Jan;70(1):339–348. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79575-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins W. R., Cafiso D. S. An electrical and structural characterization of H+/OH- currents in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1986 Apr 22;25(8):2270–2276. doi: 10.1021/bi00356a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]