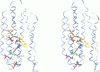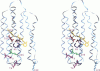Abstract
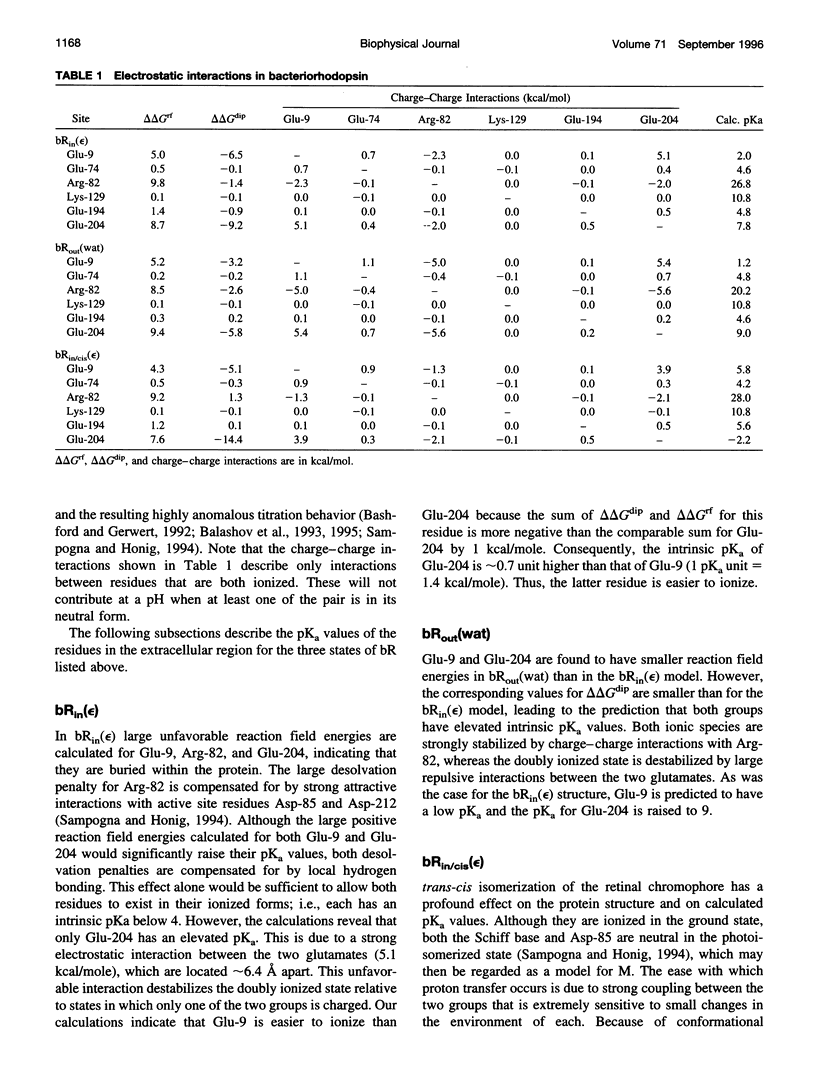
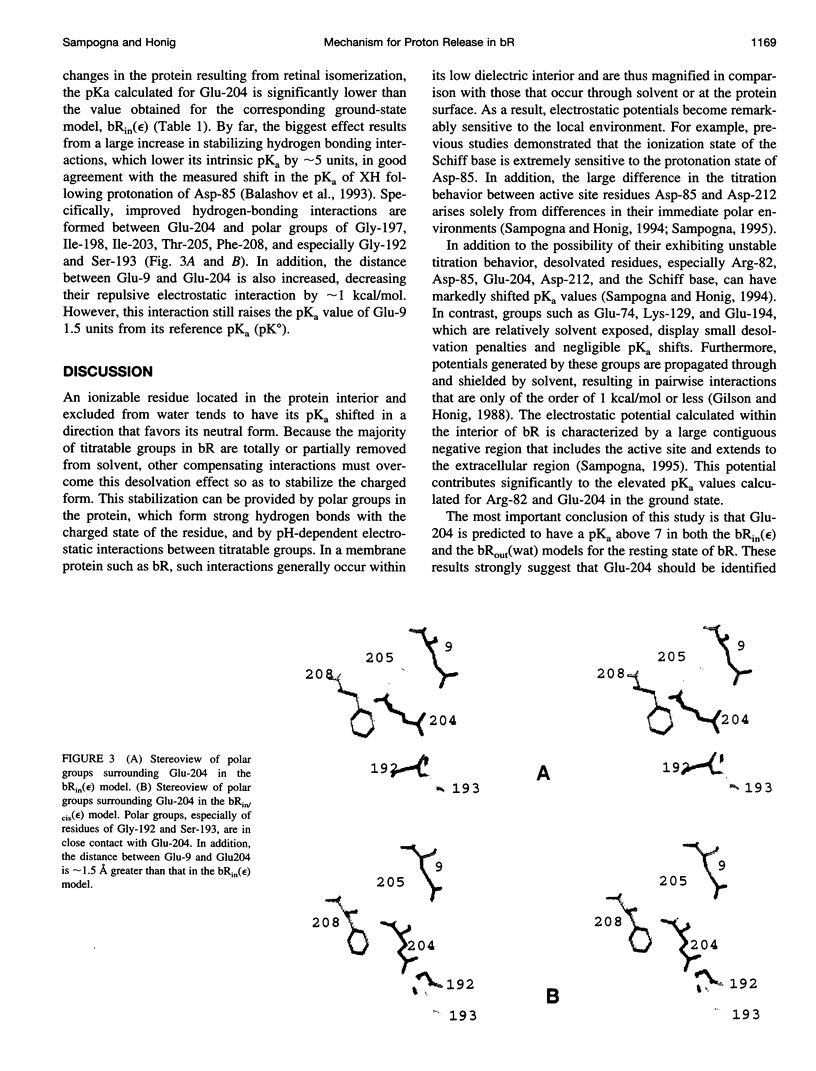
The pKa values of ionizable groups that lie between the active site region of bacteriorhodopsin (bR) and the extracellular surface of the protein are reported. Glu-204 is found to have an elevated pKa in the resting state of bR, suggesting that it corresponds to the proton-releasing group in bR. Its elevated pKa is predicted to be due in part to strong repulsive interactions with Glu-9. Following trans-cis isomerization of the retinal chromophore and the transfer of a proton to Asp-85, polar groups on the protein are able to interact more strongly with the ionized state of Glu-204, leading to a substantial reduction of its pKa. This suggests a general mechanism for proton release in which isomerization and subsequent charge separation initially produce a new electrostatic balance in the active site of bR. Here it is proposed that those events in turn drives a conformational change in the protein in which the ionized state of Glu-204 can be stabilized through interactions with groups that were previously inaccessible. Whether these groups should be identified with polar moieties in the protein, bound waters, or Arg-82 is an important mechanistic question whose elucidation will require further study.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balashov S. P., Govindjee R., Ebrey T. G. Redshift of the purple membrane absorption band and the deprotonation of tyrosine residues at high pH: Origin of the parallel photocycles of trans-bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1991 Aug;60(2):475–490. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82074-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balashov S. P., Govindjee R., Imasheva E. S., Misra S., Ebrey T. G., Feng Y., Crouch R. K., Menick D. R. The two pKa's of aspartate-85 and control of thermal isomerization and proton release in the arginine-82 to lysine mutant of bacteriorhodopsin. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 11;34(27):8820–8834. doi: 10.1021/bi00027a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashford D., Gerwert K. Electrostatic calculations of the pKa values of ionizable groups in bacteriorhodopsin. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 20;224(2):473–486. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)91009-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Bousché O., Rothschild K. J. Protein dynamics in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle: submillisecond Fourier transform infrared spectra of the L, M, and N photointermediates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Souvignier G., Hess B. Simultaneous monitoring of light-induced changes in protein side-group protonation, chromophore isomerization, and backbone motion of bacteriorhodopsin by time-resolved Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec 15;87(24):9774–9778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson M. K., Honig B. H. Energetics of charge-charge interactions in proteins. Proteins. 1988;3(1):32–52. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindjee R., Misra S., Balashov S. P., Ebrey T. G., Crouch R. K., Menick D. R. Arginine-82 regulates the pKa of the group responsible for the light-driven proton release in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1996 Aug;71(2):1011–1023. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79302-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagler A. T., Huler E., Lifson S. Energy functions for peptides and proteins. I. Derivation of a consistent force field including the hydrogen bond from amide crystals. J Am Chem Soc. 1974 Aug 21;96(17):5319–5327. doi: 10.1021/ja00824a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanamoto J. H., Dupuis P., El-Sayed M. A. On the protein (tyrosine)-chromophore (protonated Schiff base) coupling in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7083–7087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Baldwin J. M., Ceska T. A., Zemlin F., Beckmann E., Downing K. H. Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):899–929. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80271-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B., Ebrey T., Callender R. H., Dinur U., Ottolenghi M. Photoisomerization, energy storage, and charge separation: a model for light energy transduction in visual pigments and bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2503–2507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey W., Logunov I., Schulten K., Sheves M. Molecular dynamics study of bacteriorhodopsin and artificial pigments. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 29;33(12):3668–3678. doi: 10.1021/bi00178a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. Proton translocation mechanism and energetics in the light-driven pump bacteriorhodopsin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 7;1183(2):241–261. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(93)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathies R. A., Lin S. W., Ames J. B., Pollard W. T. From femtoseconds to biology: mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin's light-driven proton pump. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:491–518. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls A., Sharp K. A., Honig B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins. 1991;11(4):281–296. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., He Y. W., Sonar S., Marti T., Khorana H. G. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants. Evidence that Thr-46 and Thr-89 form part of a transient network of hydrogen bonds. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1615–1622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sampogna R. V., Honig B. Environmental effects on the protonation states of active site residues in bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1994 May;66(5):1341–1352. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80925-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souvignier G., Gerwert K. Proton uptake mechanism of bacteriorhodopsin as determined by time-resolved stroboscopic-FTIR-spectroscopy. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1393–1405. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81722-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tavan P., Schulten K., Oesterhelt D. The effect of protonation and electrical interactions on the stereochemistry of retinal schiff bases. Biophys J. 1985 Mar;47(3):415–430. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83933-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang A. S., Gunner M. R., Sampogna R., Sharp K., Honig B. On the calculation of pKas in proteins. Proteins. 1993 Mar;15(3):252–265. doi: 10.1002/prot.340150304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimányi L., Váró G., Chang M., Ni B., Needleman R., Lanyi J. K. Pathways of proton release in the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biochemistry. 1992 Sep 15;31(36):8535–8543. doi: 10.1021/bi00151a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]