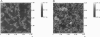Abstract
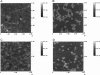
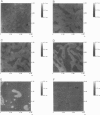
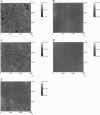
The lipids found in the bilayers of the stratum corneum fulfill the vital barrier role of mammalian bodies. The main classes of lipids found in stratum corneum are ceramides, cholesterol, and free fatty acids. For an investigation of their phase behavior, mixed Langmuir-Blodgett monolayers of these lipids were prepared. Atomic force microscopy was used to investigate the structure of the monolayers as a function of the monolayer composition. Three different types of ceramide were used: ceramide extracted from pigskin, a commercially available ceramide with several fatty acid chain lengths, and two synthetic ceramides that have only one fatty acid chain length. In pigskin ceramide-cholesterol mixed monolayers phase separation was observed. This phase separation was also found for the commercially available type III Sigma ceramide-cholesterol mixed monolayers with molar ratios ranging from 1:0.1 to 1:1. These monolayers separated into two phases, one composed of the long fatty acid chain fraction of Sigma ceramide III and the other of the short fatty acid chain fraction of Sigma ceramide III mixed with cholesterol. Mixtures with a higher cholesterol content consisted of only one phase. These observations were confirmed by the results obtained with synthetic ceramides, which have only one fatty acid chain length. The synthetic ceramide with a palmitic acid (16:0) chain mixed with cholesterol, and the synthetic ceramide with a lignoceric acid (24:0) chain did not. Free fatty acids showed a preference to mix with one of these phases, depending on their fatty acid chain lengths. The results of this investigation suggest that the model system used in this study is in good agreement with those of other studies concerning the phase behavior of the stratum corneum lipids. By varying the composition of the monolayers one can study the role of each lipid class in detail.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouwstra J. A., Gooris G. S., Bras W., Downing D. T. Lipid organization in pig stratum corneum. J Lipid Res. 1995 Apr;36(4):685–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwstra J. A., Gooris G. S., Cheng K., Weerheim A., Bras W., Ponec M. Phase behavior of isolated skin lipids. J Lipid Res. 1996 May;37(5):999–1011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwstra J. A., Gooris G. S., van der Spek J. A., Bras W. Structural investigations of human stratum corneum by small-angle X-ray scattering. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Dec;97(6):1005–1012. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12492217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwstra J. A., Gooris G. S., van der Spek J. A., Lavrijsen S., Bras W. The lipid and protein structure of mouse stratum corneum: a wide and small angle diffraction study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 May 13;1212(2):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)90252-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach A. S., Goodman T., Stolinski C., Gross M. Freeze-fracture replication of cells of stratum corneum of human epidermis. J Anat. 1973 Jan;114(Pt 1):65–81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demel R. A., De Kruyff B. The function of sterols in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Oct 26;457(2):109–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(76)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias P. M. Epidermal lipids, barrier function, and desquamation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jun;80 (Suppl):44s–49s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfgren H., Pascher I. Molecular arrangements of sphingolipids. The monolayer behaviour of ceramides. Chem Phys Lipids. 1977 Dec;20(4):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(77)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott D. T., Turner J. E. Mesophase formation by ceramides and cholesterol: a model for stratum corneum lipid packing? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 22;1147(2):273–276. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurer N. Y., Elias P. M. The biochemistry and function of stratum corneum lipids. Adv Lipid Res. 1991;24:27–56. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-024924-4.50006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wertz P. W., Downing D. T. Ceramides of pig epidermis: structure determination. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jun;24(6):759–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White S. H., Mirejovsky D., King G. I. Structure of lamellar lipid domains and corneocyte envelopes of murine stratum corneum. An X-ray diffraction study. Biochemistry. 1988 May 17;27(10):3725–3732. doi: 10.1021/bi00410a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]