Abstract
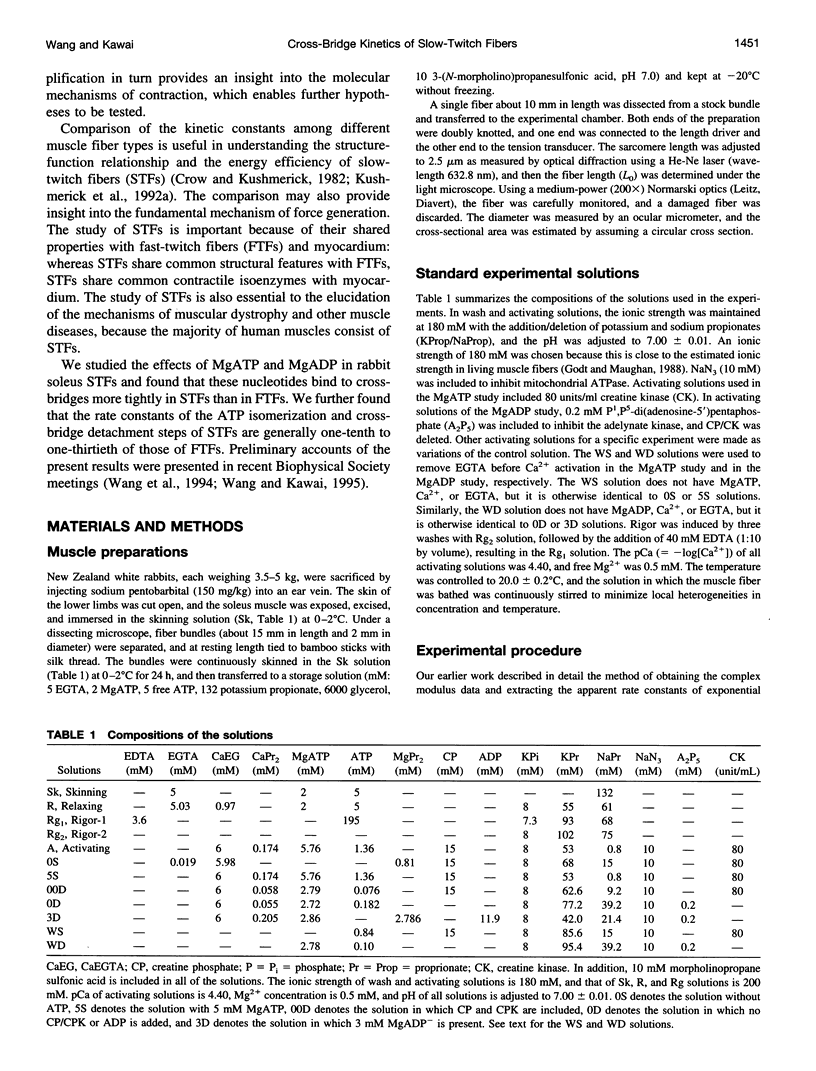
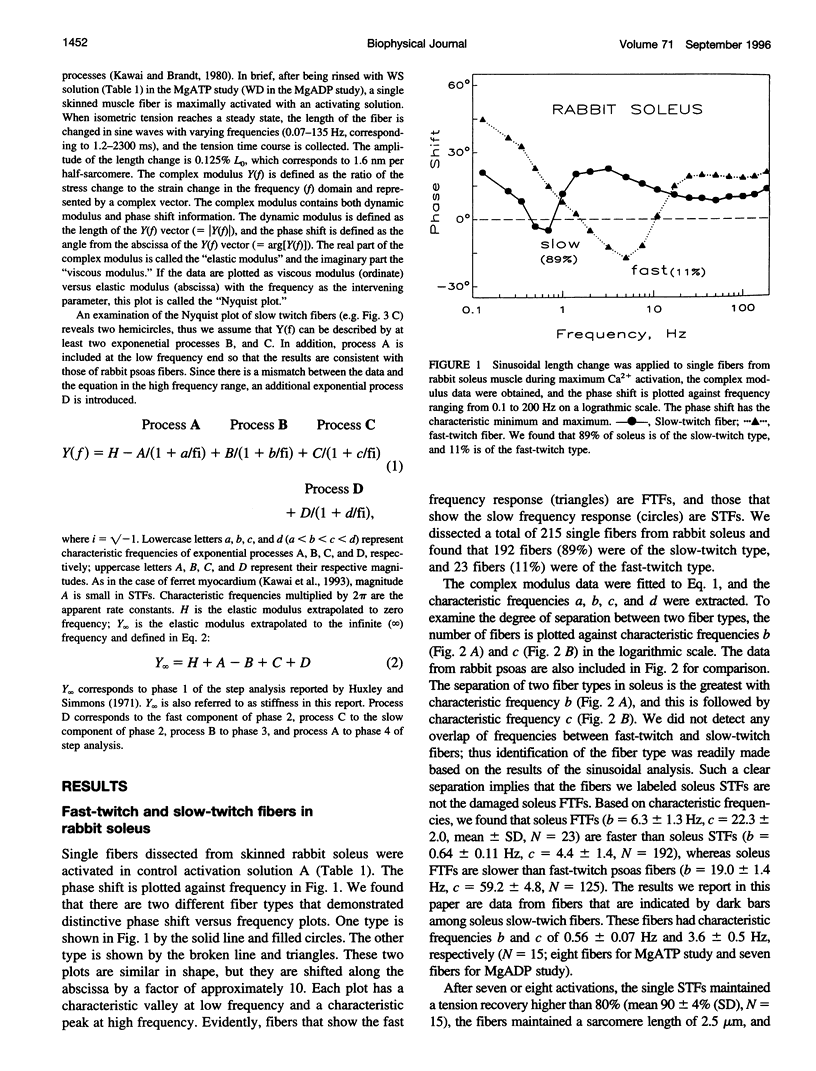
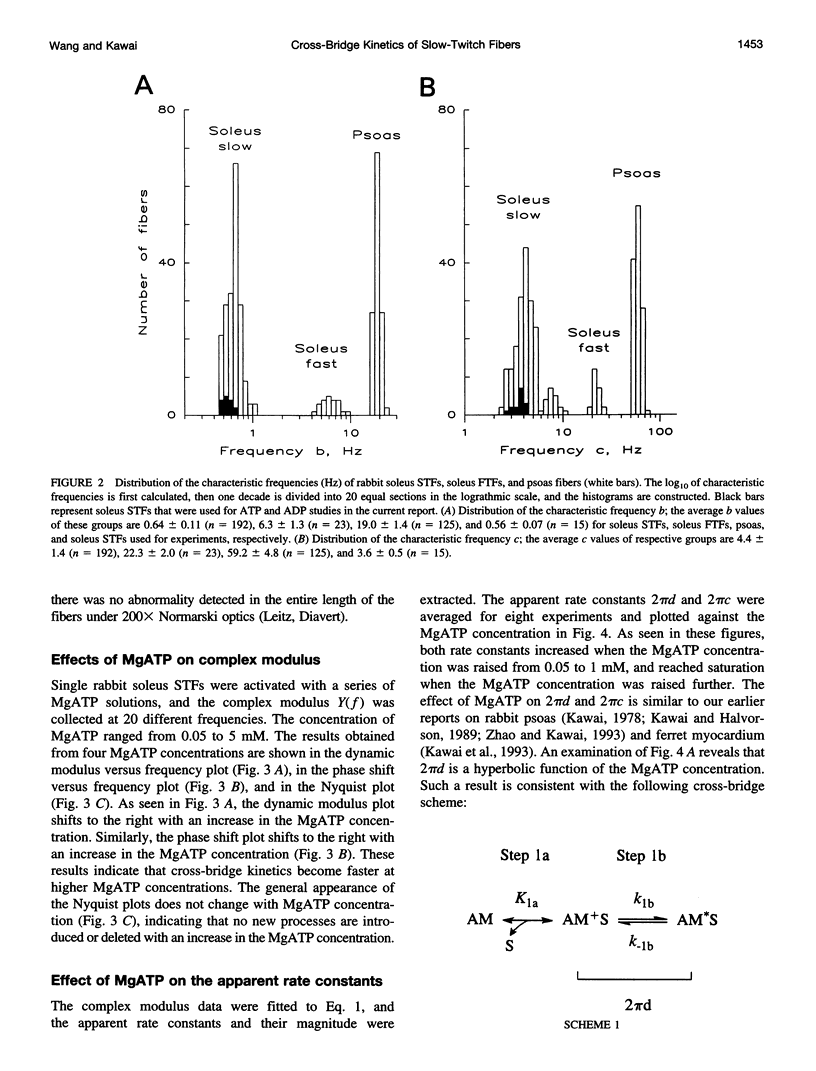
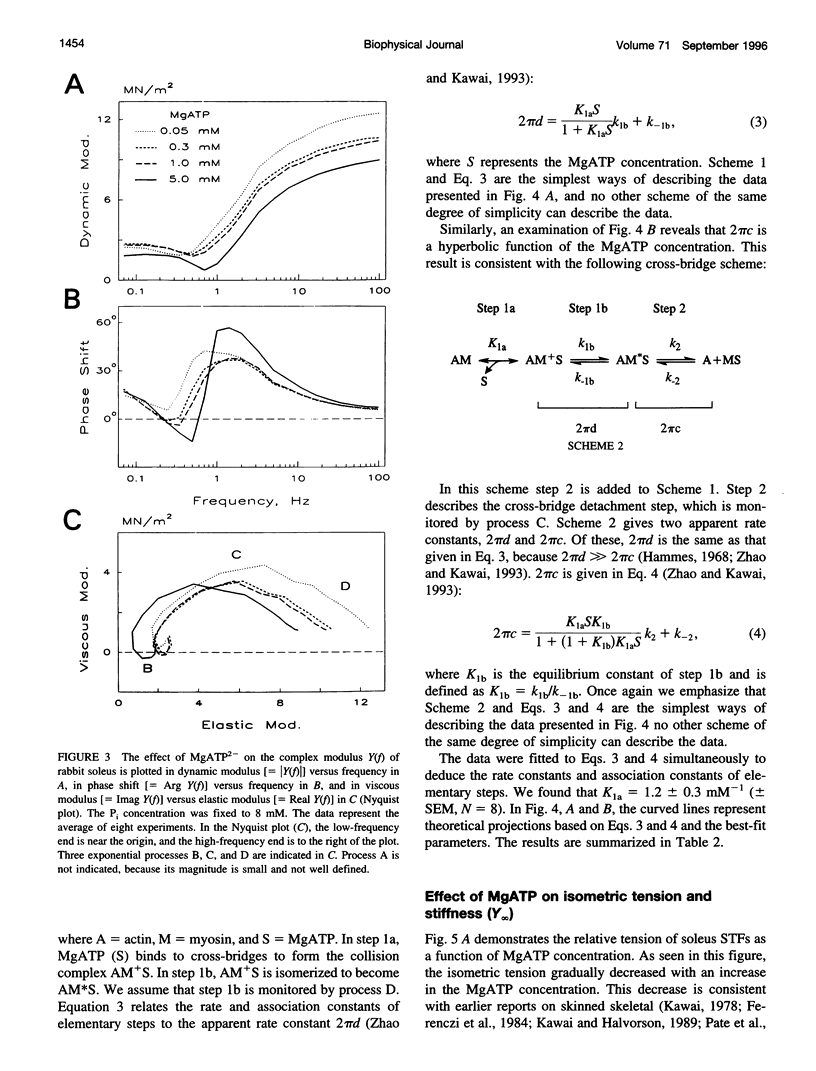
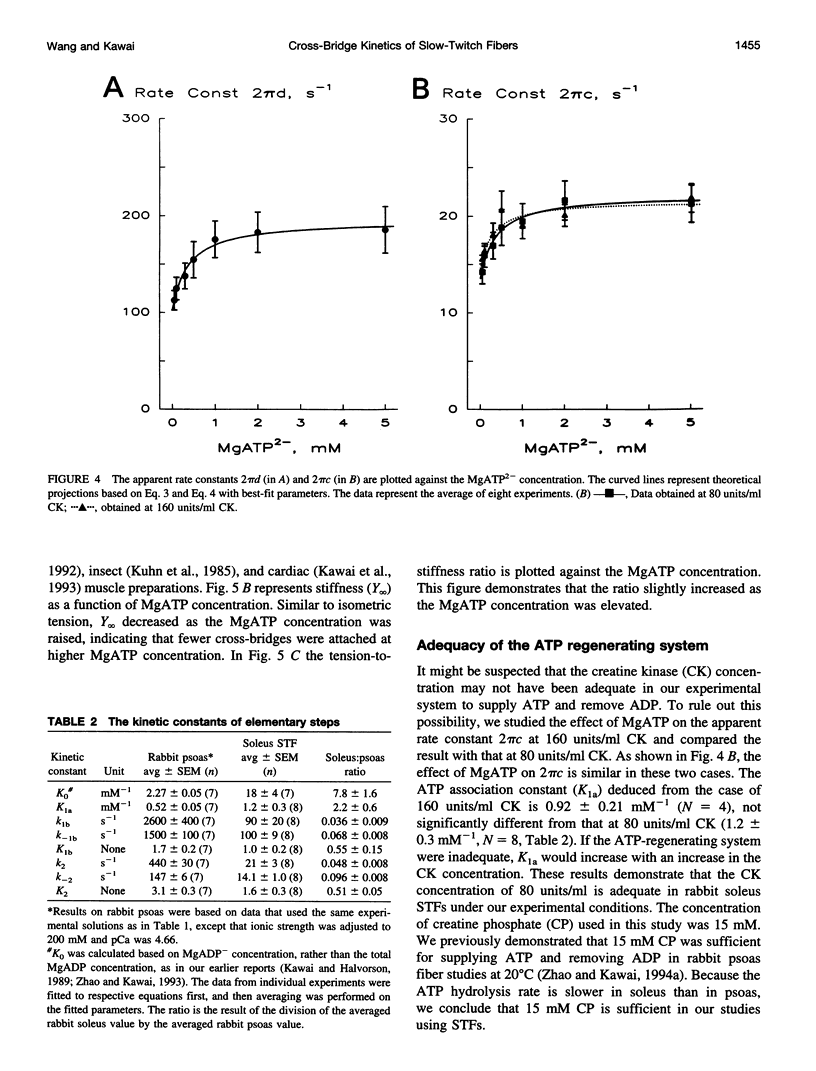
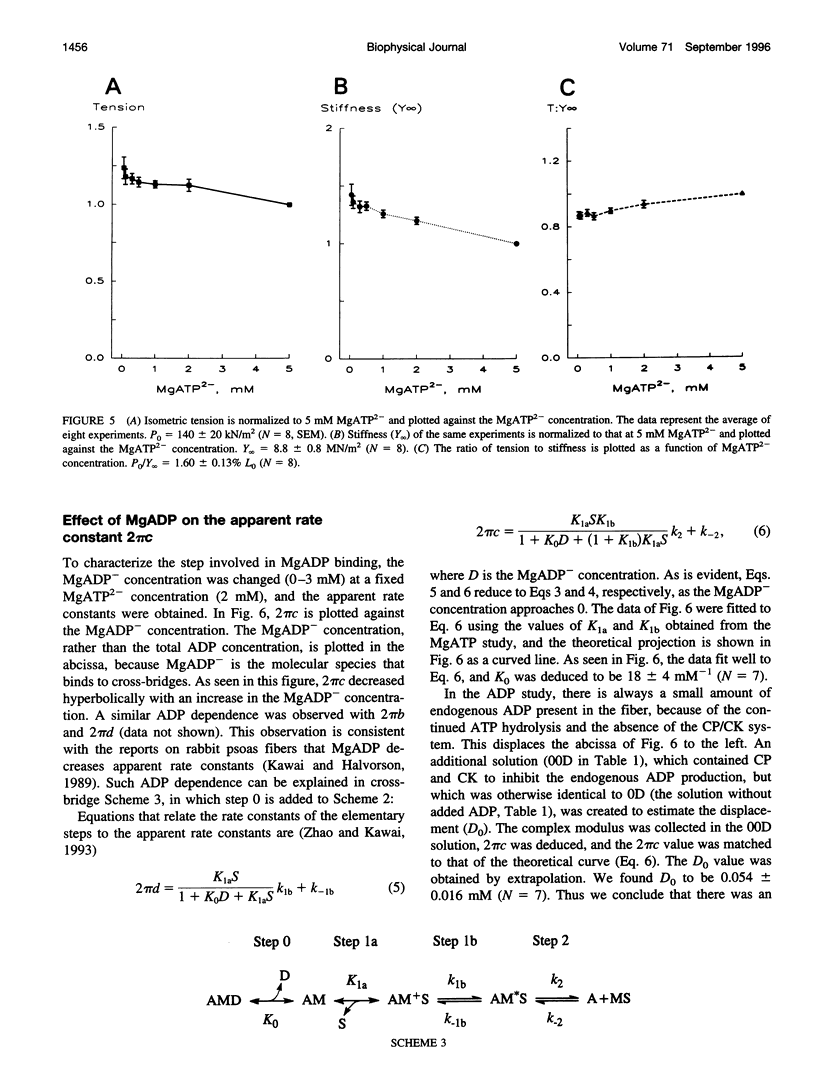
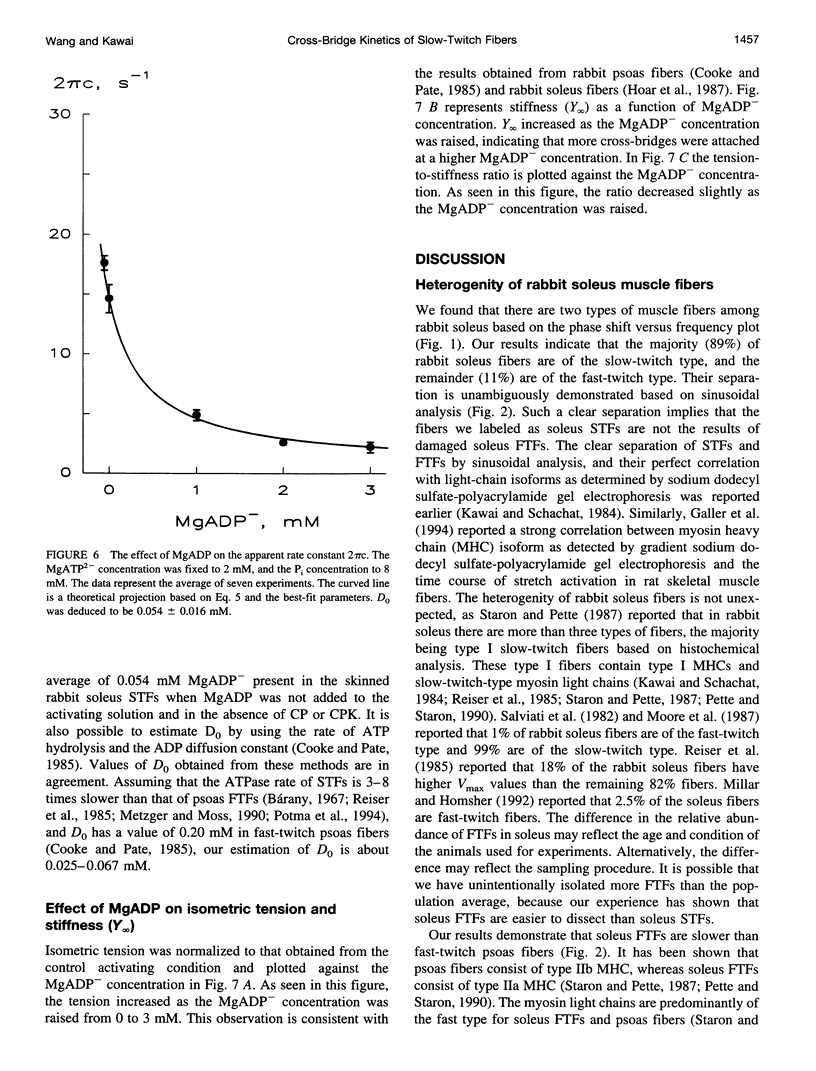
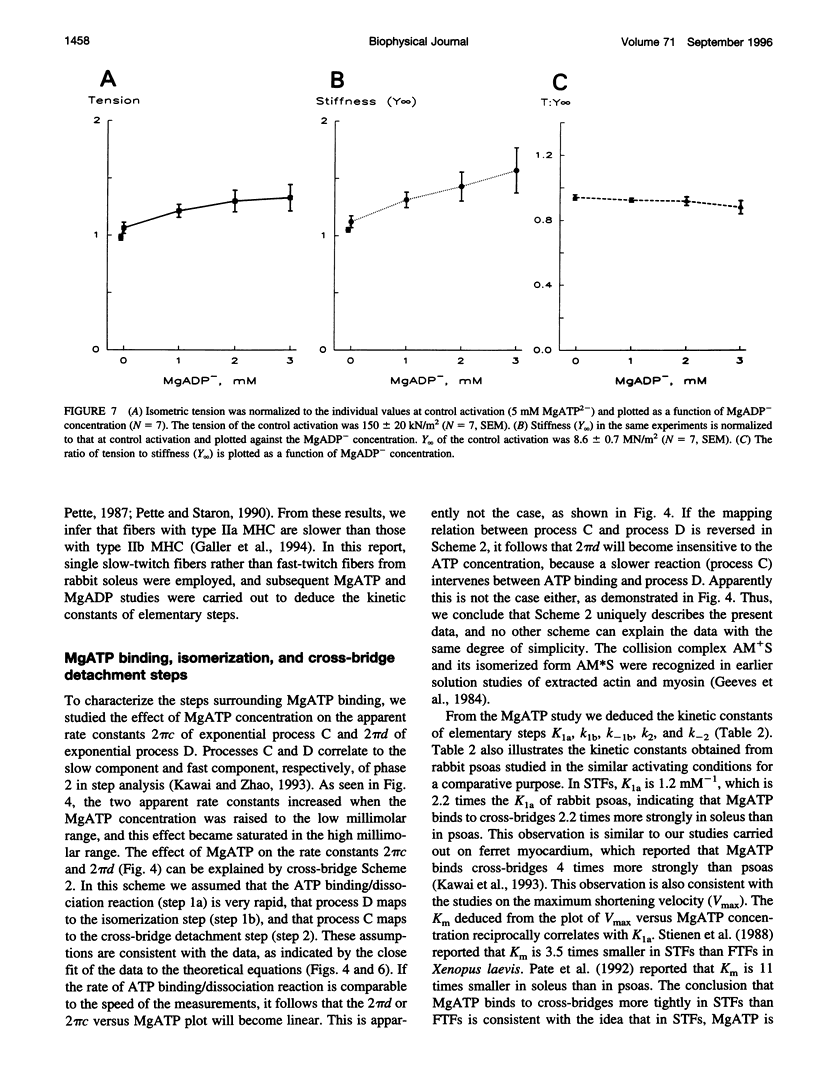
The elementary steps surrounding the nucleotide binding step in the cross-bridge cycle were investigated with sinusoidal analysis in rabbit soleus slow-twitch muscle fibers. The single-fiber preparations were activated at pCa 4.40, ionic strength 180 mM, 20 degrees C, and the effects of MgATP (S) and MgADP (D) concentrations on three exponential processes B, C, and D were studied. Our results demonstrate that all apparent (measured) rate constants increased and saturated hyperbolically as the MgATP concentration was increased. These results are consistent with the following cross-bridge scheme: [cross-bridge scheme: see text] where A = actin, M = myosin, S = MgATP, and D = MgADP. AM+S is a collision complex, and AM*S is its isomerized form. From our studies, we obtained K0 = 18 +/- 4 mM-1 (MgADP association constant, N = 7, average +/- sem), K1a = 1.2 +/- 0.3 mM-1 (MgATP association constant, N = 8 hereafter), k1b = 90 +/- 20 s-1 (rate constant of ATP isomerization), k-1b = 100 +/- 9 s-1 (rate constant of reverse isomerization), K1b = 1.0 +/- 0.2 (equilibrium constant of isomerization), k2 = 21 +/- 3 s-1 (rate constant of cross-bridge detachment), k-2 = 14.1 +/- 1.0 s-1 (rate constant of reversal of detachment), and K2 = 1.6 +/- 0.3 (equilibrium constant of detachment). K0 is 8 times and K1a is 2.2 times those in rabbit psoas, indicating that nucleotides bind to cross-bridges more tightly in soleus slow-twitch muscle fibers than in psoas fast-twitch muscle fibers. These results indicate that cross-bridges of slow-twitch fibers are more resistant to ATP depletion than those of fast-twitch fibers. The rate constants of ATP isomerization and cross-bridge detachment steps are, in general, one-tenth to one-thirtieth of those in psoas.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B., Schoenberg M., Chalovich J. M., Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Evidence for cross-bridge attachment in relaxed muscle at low ionic strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7288–7291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bárány M. ATPase activity of myosin correlated with speed of muscle shortening. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jul;50(6 Suppl):197–218. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.6.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Pate E. The effects of ADP and phosphate on the contraction of muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1985 Nov;48(5):789–798. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83837-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow M. T., Kushmerick M. J. Chemical energetics of slow- and fast-twitch muscles of the mouse. J Gen Physiol. 1982 Jan;79(1):147–166. doi: 10.1085/jgp.79.1.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Cross-bridge kinetics in the presence of MgADP investigated by photolysis of caged ATP in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:639–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A., Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. The dependence of force and shortening velocity on substrate concentration in skinned muscle fibres from Rana temporaria. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:519–543. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer M. W., Owen V. J., Lamb G. D., Stephenson D. G. Effects of creatine phosphate and P(i) on Ca2+ movements and tension development in rat skinned skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1995 Jan 1;482(Pt 1):123–140. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galler S., Schmitt T. L., Pette D. Stretch activation, unloaded shortening velocity, and myosin heavy chain isoforms of rat skeletal muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1994 Aug 1;478(Pt 3):513–521. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A., Goody R. S., Gutfreund H. Kinetics of acto-S1 interaction as a guide to a model for the crossbridge cycle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Aug;5(4):351–361. doi: 10.1007/BF00818255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godt R. E., Maughan D. W. On the composition of the cytosol of relaxed skeletal muscle of the frog. Am J Physiol. 1988 May;254(5 Pt 1):C591–C604. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1988.254.5.C591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene L. E., Eisenberg E. Dissociation of the actin.subfragment 1 complex by adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate, ADP, and PPi. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):543–548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammes G. G. Relaxation spectrometry of biological systems. Adv Protein Chem. 1968;23:1–57. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60399-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoar P. E., Mahoney C. W., Kerrick W. G. MgADP- increases maximum tension and Ca2+ sensitivity in skinned rabbit soleus fibers. Pflugers Arch. 1987 Sep;410(1-2):30–36. doi: 10.1007/BF00581892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. E., Adams P. H. ADP binds similarly to rigor muscle myofibrils and to actomyosin-subfragment one. FEBS Lett. 1984 Aug 20;174(1):11–14. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)81067-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Brandt P. W. Sinusoidal analysis: a high resolution method for correlating biochemical reactions with physiological processes in activated skeletal muscles of rabbit, frog and crayfish. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1980 Sep;1(3):279–303. doi: 10.1007/BF00711932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Role of MgATP and MgADP in the cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Study of a fast exponential process (C) Biophys J. 1989 Apr;55(4):595–603. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82857-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Halvorson H. R. Two step mechanism of phosphate release and the mechanism of force generation in chemically skinned fibers of rabbit psoas muscle. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):329–342. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82227-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M. Head rotation or dissociation? A study of exponential rate processes in chemically skinned rabbit muscle fibers when MgATP concentration is changed. Biophys J. 1978 Apr;22(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85473-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Saeki Y., Zhao Y. Crossbridge scheme and the kinetic constants of elementary steps deduced from chemically skinned papillary and trabecular muscles of the ferret. Circ Res. 1993 Jul;73(1):35–50. doi: 10.1161/01.res.73.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Schachat F. H. Differences in the transient response of fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Correlations between complex modulus and myosin light chains. Biophys J. 1984 Jun;45(6):1145–1151. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84262-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai M., Zhao Y. Cross-bridge scheme and force per cross-bridge state in skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):638–651. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81109-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kentish J. C., Stienen G. J. Differential effects of length on maximum force production and myofibrillar ATPase activity in rat skinned cardiac muscle. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 15;475(1):175–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhn H. J., Bletz C., Güth K., Rüegg J. C. The effect of MgATP on forming and breaking actin-myosin linkages in contracted skinned insect flight muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1985 Feb;6(1):5–27. doi: 10.1007/BF00712308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Meyer R. A., Brown T. R. Regulation of oxygen consumption in fast- and slow-twitch muscle. Am J Physiol. 1992 Sep;263(3 Pt 1):C598–C606. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.263.3.C598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushmerick M. J., Moerland T. S., Wiseman R. W. Mammalian skeletal muscle fibers distinguished by contents of phosphocreatine, ATP, and Pi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7521–7525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Y., Cooke R., Pate E. A model of stress relaxation in cross-bridge systems: effect of a series elastic element. Am J Physiol. 1993 Jul;265(1 Pt 1):C279–C288. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1993.265.1.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKinnon R., Gwathmey J. K., Allen P. D., Briggs G. M., Morgan J. P. Modulation by the thyroid state of intracellular calcium and contractility in ferret ventricular muscle. Circ Res. 1988 Dec;63(6):1080–1089. doi: 10.1161/01.res.63.6.1080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marston S. B., Taylor E. W. Comparison of the myosin and actomyosin ATPase mechanisms of the four types of vertebrate muscles. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 5;139(4):573–600. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland E. W., Kushmerick M. J., Moerland T. S. Activity of creatine kinase in a contracting mammalian muscle of uniform fiber type. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1912–1924. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80674-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Calcium-sensitive cross-bridge transitions in mammalian fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1088–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.2309121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. A., Brown T. R., Kushmerick M. J. Phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance of fast- and slow-twitch muscle. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C279–C287. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. Kinetics of force generation and phosphate release in skinned rabbit soleus muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1992 May;262(5 Pt 1):C1239–C1245. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.5.C1239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. E., Briggs M. M., Schachat F. H. Patterns of troponin T expression in mammalian fast, slow and promiscuous muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1987 Feb;8(1):13–22. doi: 10.1007/BF01767260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagesser A. S., van der Laarse W. J., Elzinga G. Metabolic changes with fatigue in different types of single muscle fibres of Xenopus laevis. J Physiol. 1992 Mar;448:511–523. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pate E., Lin M., Franks-Skiba K., Cooke R. Contraction of glycerinated rabbit slow-twitch muscle fibers as a function of MgATP concentration. Am J Physiol. 1992 Apr;262(4 Pt 1):C1039–C1046. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.4.C1039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potma E. J., van Graas I. A., Stienen G. J. Effects of pH on myofibrillar ATPase activity in fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers of the rabbit. Biophys J. 1994 Dec;67(6):2404–2410. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80727-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiser P. J., Moss R. L., Giulian G. G., Greaser M. L. Shortening velocity in single fibers from adult rabbit soleus muscles is correlated with myosin heavy chain composition. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9077–9080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salviati G., Betto R., Danieli Betto D. Polymorphism of myofibrillar proteins of rabbit skeletal-muscle fibres. An electrophoretic study of single fibres. Biochem J. 1982 Nov 1;207(2):261–272. doi: 10.1042/bj2070261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibata T., Hunter W. C., Yang A., Sagawa K. Dynamic stiffness measured in central segment of excised rabbit papillary muscles during barium contracture. Circ Res. 1987 May;60(5):756–769. doi: 10.1161/01.res.60.5.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemankowski R. F., Wiseman M. O., White H. D. ADP dissociation from actomyosin subfragment 1 is sufficiently slow to limit the unloaded shortening velocity in vertebrate muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):658–662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinha A. M., Friedman D. J., Nigro J. M., Jakovcic S., Rabinowitz M., Umeda P. K. Expression of rabbit ventricular alpha-myosin heavy chain messenger RNA sequences in atrial muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6674–6680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sleep J., Glyn H. Inhibition of myofibrillar and actomyosin subfragment 1 adenosinetriphosphatase by adenosine 5'-diphosphate, pyrophosphate, and adenyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate. Biochemistry. 1986 Mar 11;25(5):1149–1154. doi: 10.1021/bi00353a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staron R. S., Pette D. The multiplicity of combinations of myosin light chains and heavy chains in histochemically typed single fibres. Rabbit soleus muscle. Biochem J. 1987 May 1;243(3):687–693. doi: 10.1042/bj2430687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stienen G. J., van der Laarse W. J., Elzinga G. Dependency of the force-velocity relationships on Mg ATP in different types of muscle fibers from Xenopus laevis. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):849–855. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83165-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D., Taylor E. W. Energetics and mechanism of actomyosin adenosine triphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1976 Dec 28;15(26):5818–5826. doi: 10.1021/bi00671a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff M. R., McDonald K. S., Moss R. L. Rate of tension development in cardiac muscle varies with level of activator calcium. Circ Res. 1995 Jan;76(1):154–160. doi: 10.1161/01.res.76.1.154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. BDM affects nucleotide binding and force generation steps of the cross-bridge cycle in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1994 Feb;266(2 Pt 1):C437–C447. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1994.266.2.C437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. Kinetic and thermodynamic studies of the cross-bridge cycle in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1655–1668. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80638-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Y., Kawai M. The effect of the lattice spacing change on cross-bridge kinetics in chemically skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. II. Elementary steps affected by the spacing change. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):197–210. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81357-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


