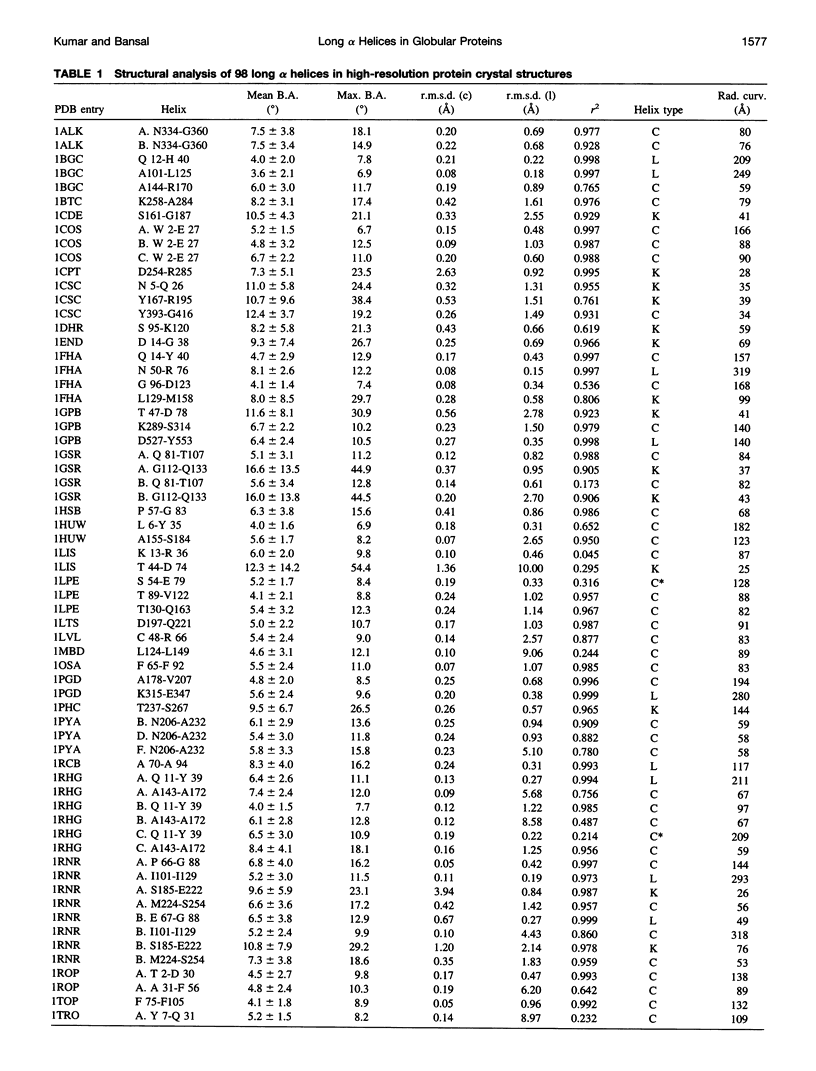
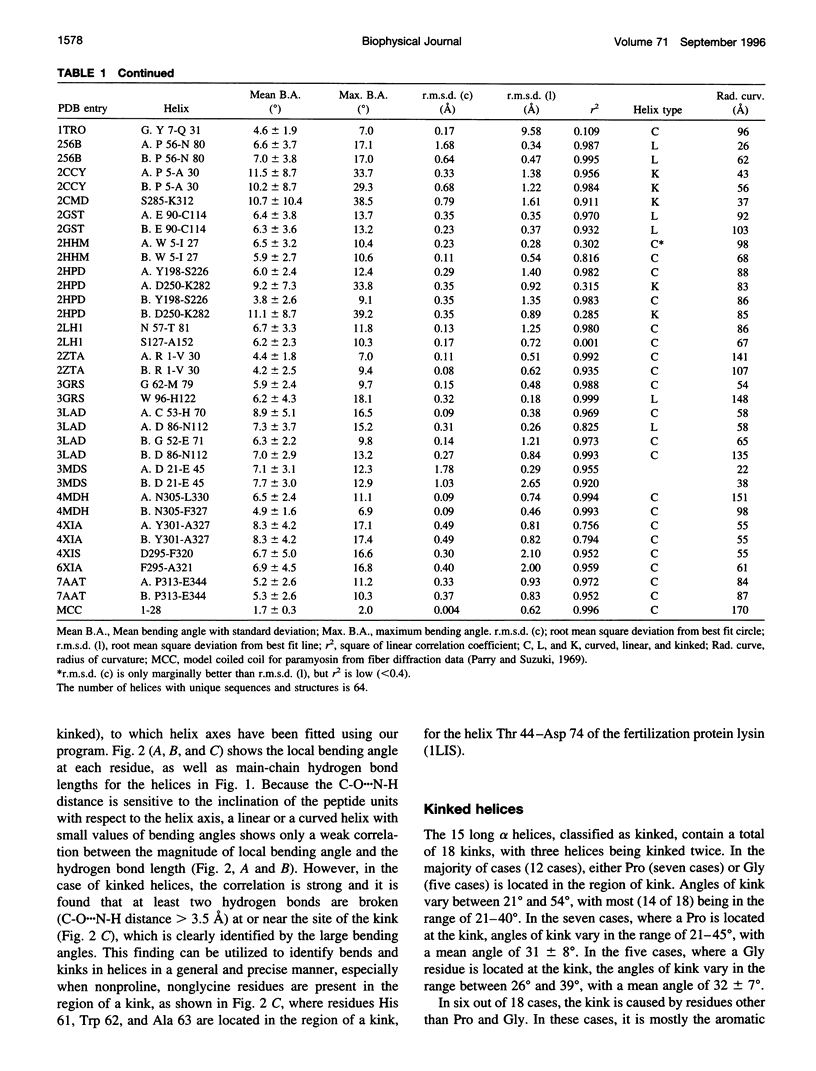
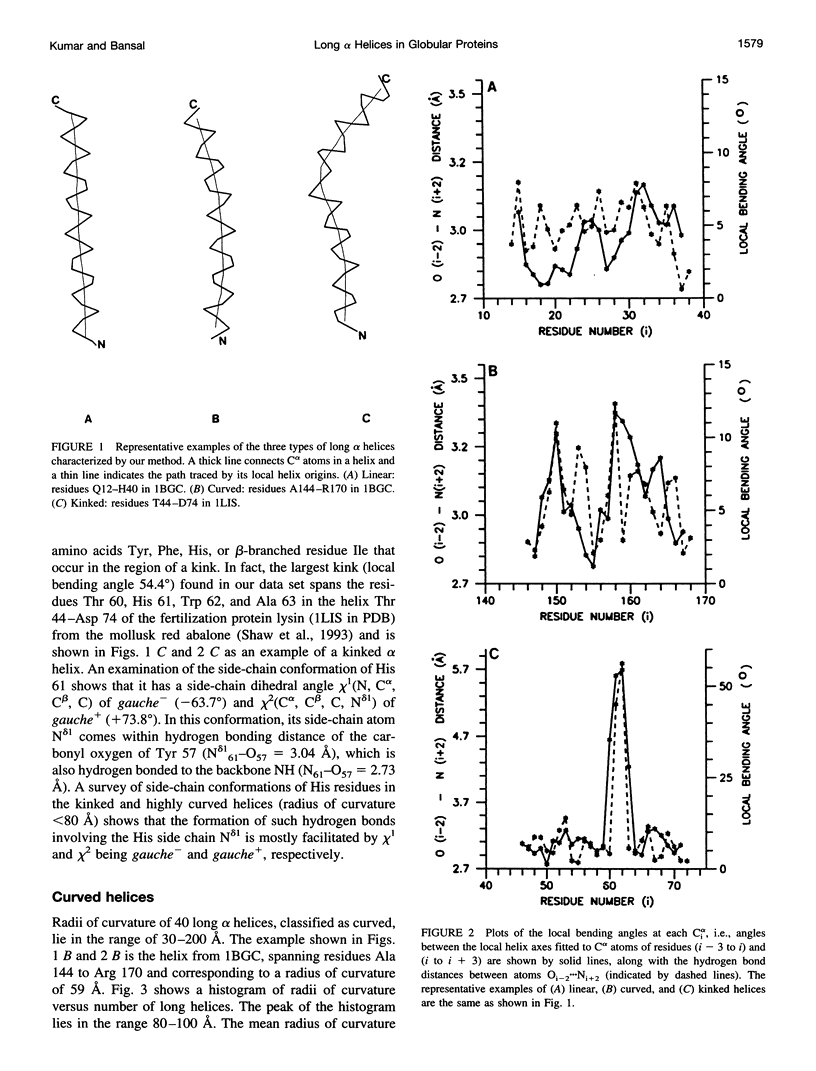
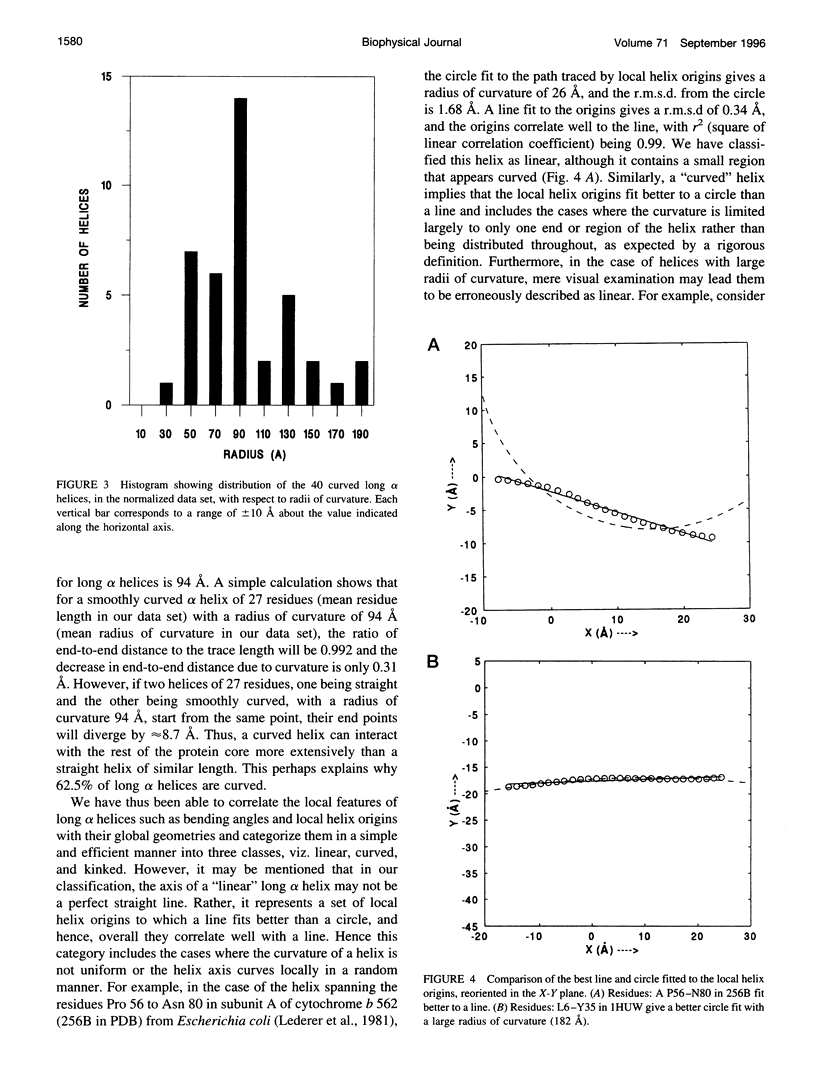
Abstract
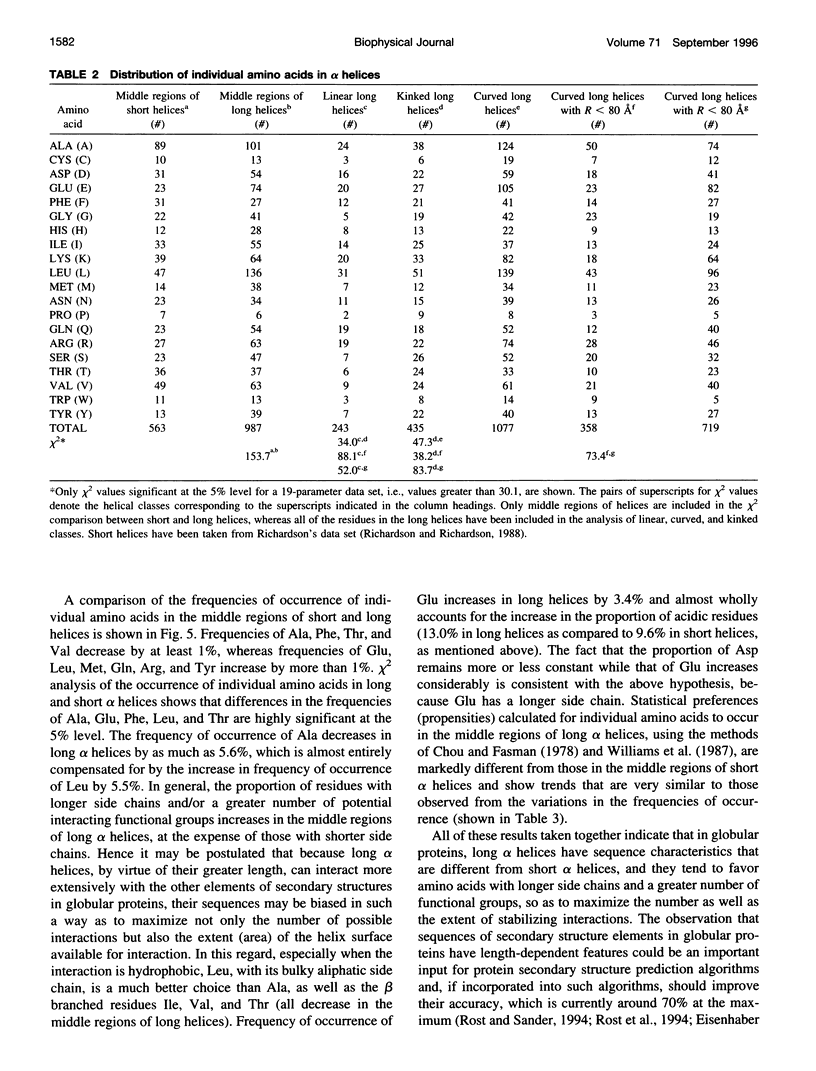
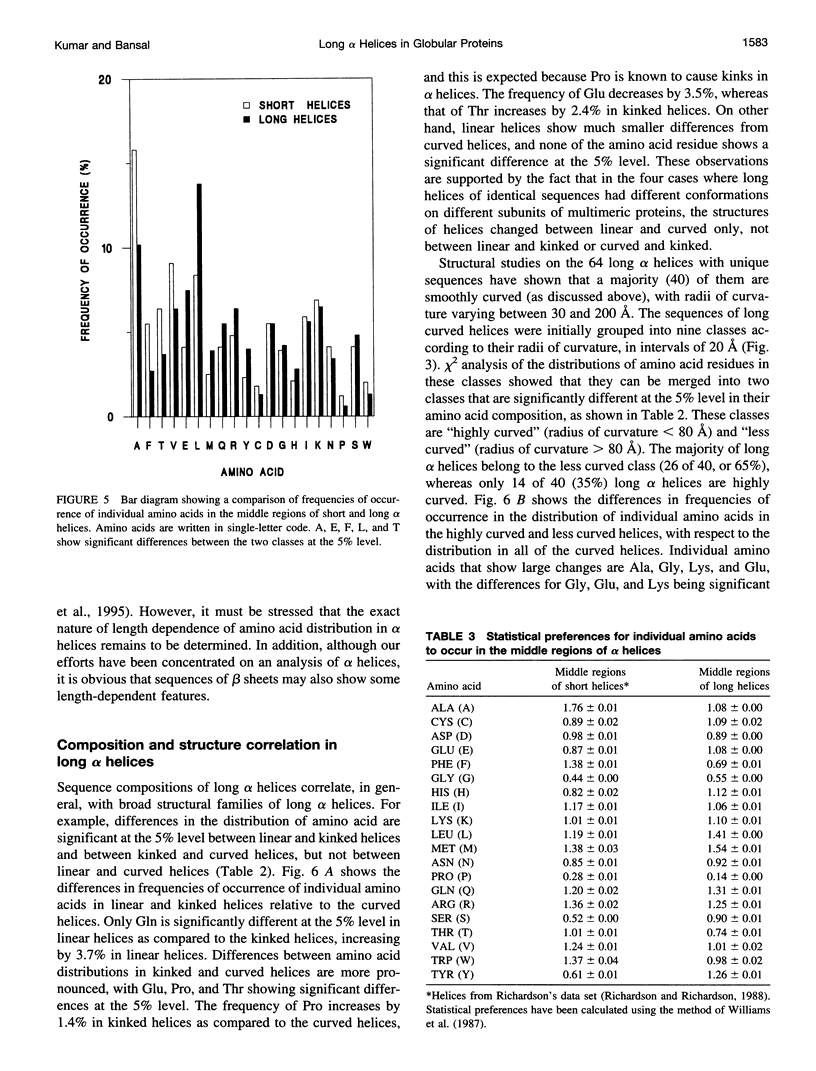
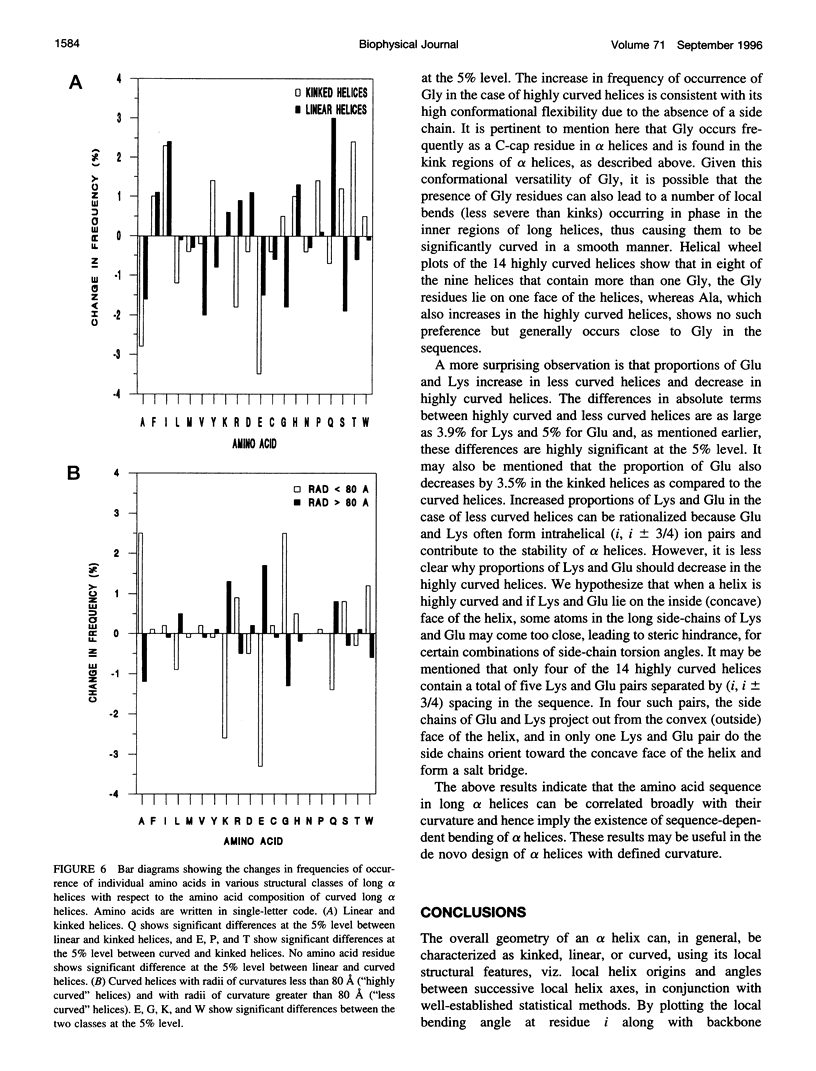
Elucidation of the detailed structural features and sequence requirements for alpha helices of various lengths could be very important in understanding secondary structure formation in proteins and, hence, in the protein folding mechanism. An algorithm to characterize the geometry of an alpha helix from its C(alpha) coordinates has been developed and used to analyze the structures of long alpha helices (number of residues > or = 25) found in globular proteins, the crystal structure coordinates of which are available from the Brookhaven Protein Data Bank. All long alpha helices can be unambiguously characterized as belonging to one of three classes: linear, curved, or kinked, with a majority being curved. Analysis of the sequences of these helices reveals that the long alpha helices have unique sequence characteristics that distinguish them from the short alpha helices in globular proteins. The distribution and statistical propensities of individual amino acids to occur in long alpha helices are different from those found in short alpha helices, with amino acids having longer side chains and/or having a greater number of functional groups occurring more frequently in these helices. The sequences of the long alpha helices can be correlated with their gross structural features, i.e., whether they are curved, linear, or kinked, and in case of the curved helices, with their curvature.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banner D. W., Kokkinidis M., Tsernoglou D. Structure of the ColE1 rop protein at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):657–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barlow D. J., Thornton J. M. Helix geometry in proteins. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 5;201(3):601–619. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90641-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blundell T., Barlow D., Borkakoti N., Thornton J. Solvent-induced distortions and the curvature of alpha-helices. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):281–283. doi: 10.1038/306281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti P., Bernard M., Rees D. C. Peptide-bond distortions and the curvature of alpha-helices. Biopolymers. 1986 Jun;25(6):1087–1093. doi: 10.1002/bip.360250609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of the secondary structure of proteins from their amino acid sequence. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1978;47:45–148. doi: 10.1002/9780470122921.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGrado W. F., Wasserman Z. R., Lear J. D. Protein design, a minimalist approach. Science. 1989 Feb 3;243(4891):622–628. doi: 10.1126/science.2464850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg D., Wilcox W., Eshita S. M., Pryciak P. M., Ho S. P., DeGrado W. F. The design, synthesis, and crystallization of an alpha-helical peptide. Proteins. 1986 Sep;1(1):16–22. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhaber F., Persson B., Argos P. Protein structure prediction: recognition of primary, secondary, and tertiary structural features from amino acid sequence. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1995;30(1):1–94. doi: 10.3109/10409239509085139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzel B. C., Weber P. C., Hardman K. D., Salemme F. R. Structure of ferricytochrome c' from Rhodospirillum molischianum at 1.67 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 5;186(3):627–643. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90135-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht M. H., Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C., Ogden R. C. De novo design, expression, and characterization of Felix: a four-helix bundle protein of native-like sequence. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):884–891. doi: 10.1126/science.2392678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill C. P., Osslund T. D., Eisenberg D. The structure of granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor and its relationship to other growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 1;90(11):5167–5171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.11.5167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobohm U., Scharf M., Schneider R., Sander C. Selection of representative protein data sets. Protein Sci. 1992 Mar;1(3):409–417. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560010313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hodges R. S., Semchuk P. D., Taneja A. K., Kay C. M., Parker J. M., Mant C. T. Protein design using model synthetic peptides. Pept Res. 1988 Sep-Oct;1(1):19–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus P. A., Schulz G. E. Refined structure of glutathione reductase at 1.54 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):701–729. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E. E., Wyckoff H. W. Reaction mechanism of alkaline phosphatase based on crystal structures. Two-metal ion catalysis. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):449–464. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90724-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson D. M., Artymiuk P. J., Yewdall S. J., Smith J. M., Livingstone J. C., Treffry A., Luzzago A., Levi S., Arosio P., Cesareni G. Solving the structure of human H ferritin by genetically engineering intermolecular crystal contacts. Nature. 1991 Feb 7;349(6309):541–544. doi: 10.1038/349541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederer F., Glatigny A., Bethge P. H., Bellamy H. D., Matthew F. S. Improvement of the 2.5 A resolution model of cytochrome b562 by redetermining the primary structure and using molecular graphics. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):427–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90185-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovejoy B., Choe S., Cascio D., McRorie D. K., DeGrado W. F., Eisenberg D. Crystal structure of a synthetic triple-stranded alpha-helical bundle. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1288–1293. doi: 10.1126/science.8446897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig M. L., Metzger A. L., Pattridge K. A., Stallings W. C. Manganese superoxide dismutase from Thermus thermophilus. A structural model refined at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1991 May 20;219(2):335–358. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90569-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaldon P., Argos P. Oligopeptide biases in protein sequences and their use in predicting protein coding regions in nucleotide sequences. Proteins. 1988;4(2):99–122. doi: 10.1002/prot.340040204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myszka D. G., Chaiken I. M. Design and characterization of an intramolecular antiparallel coiled coil peptide. Biochemistry. 1994 Mar 8;33(9):2363–2372. doi: 10.1021/bi00175a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Klemm J. D., Kim P. S., Alber T. X-ray structure of the GCN4 leucine zipper, a two-stranded, parallel coiled coil. Science. 1991 Oct 25;254(5031):539–544. doi: 10.1126/science.1948029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldfield T. J., Hubbard R. E. Analysis of C alpha geometry in protein structures. Proteins. 1994 Apr;18(4):324–337. doi: 10.1002/prot.340180404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAULING L., COREY R. B. Compound helical configurations of polypeptide chains: structure of proteins of the alpha-keratin type. Nature. 1953 Jan 10;171(4341):59–61. doi: 10.1038/171059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Finzel B. C., Gunsalus I. C., Wagner G. C., Kraut J. The 2.6-A crystal structure of Pseudomonas putida cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16122–16130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S., Richardson D. C. Amino acid preferences for specific locations at the ends of alpha helices. Science. 1988 Jun 17;240(4859):1648–1652. doi: 10.1126/science.3381086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rost B., Sander C., Schneider R. Redefining the goals of protein secondary structure prediction. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jan 7;235(1):13–26. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(05)80007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rost B., Sander C. Structure prediction of proteins--where are we now? Curr Opin Biotechnol. 1994 Aug;5(4):372–380. doi: 10.1016/0958-1669(94)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Satyshur K. A., Rao S. T., Pyzalska D., Drendel W., Greaser M., Sundaralingam M. Refined structure of chicken skeletal muscle troponin C in the two-calcium state at 2-A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1628–1647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A., McRee D. E., Vacquier V. D., Stout C. D. The crystal structure of lysin, a fertilization protein. Science. 1993 Dec 17;262(5141):1864–1867. doi: 10.1126/science.8266073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan R., Balasubramanian R., Rajan S. S. Some new methods and general results of analysis of protein crystallographic structural data. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 15;98(4):739–747. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sundaralingam M., Drendel W., Greaser M. Stabilization of the long central helix of troponin C by intrahelical salt bridges between charged amino acid side chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7944–7947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ultsch M. H., Somers W., Kossiakoff A. A., de Vos A. M. The crystal structure of affinity-matured human growth hormone at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994 Feb 11;236(1):286–299. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiegand G., Remington S., Deisenhofer J., Huber R. Crystal structure analysis and molecular model of a complex of citrate synthase with oxaloacetate and S-acetonyl-coenzyme A. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):205–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90373-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. W., Chang A., Juretić D., Loughran S. Secondary structure predictions and medium range interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 26;916(2):200–204. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90109-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C., Wardell M. R., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Agard D. A. Three-dimensional structure of the LDL receptor-binding domain of human apolipoprotein E. Science. 1991 Jun 28;252(5014):1817–1822. doi: 10.1126/science.2063194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


