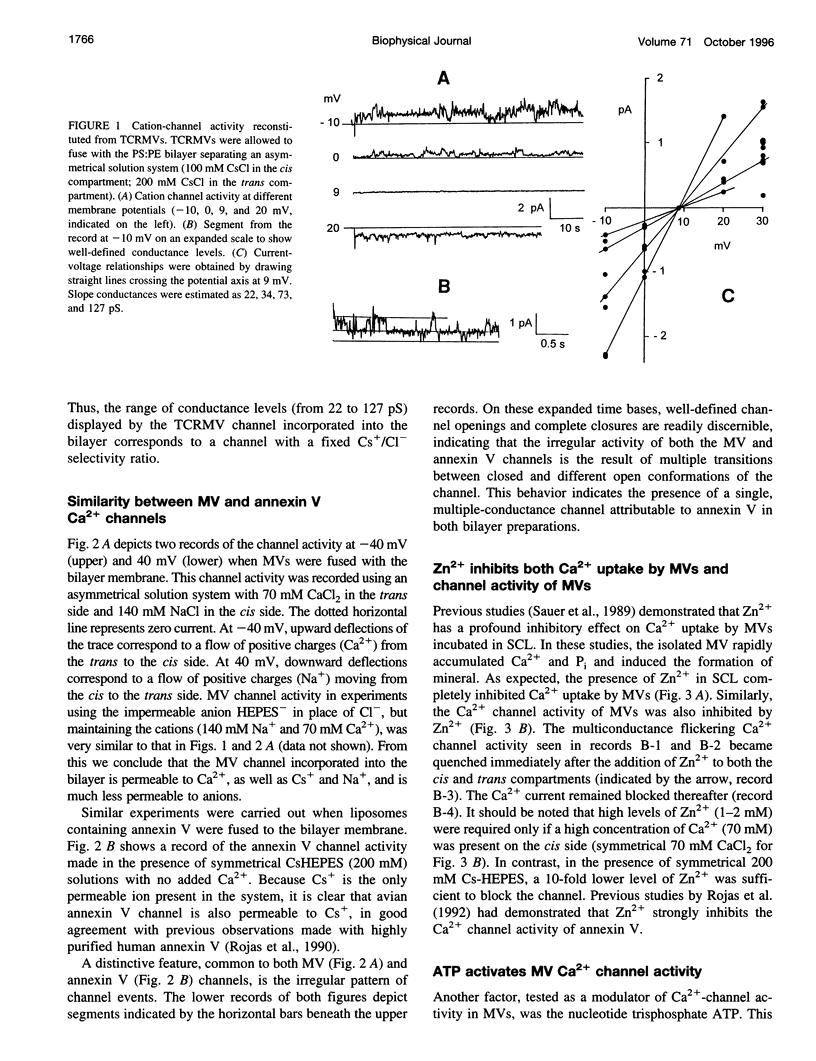
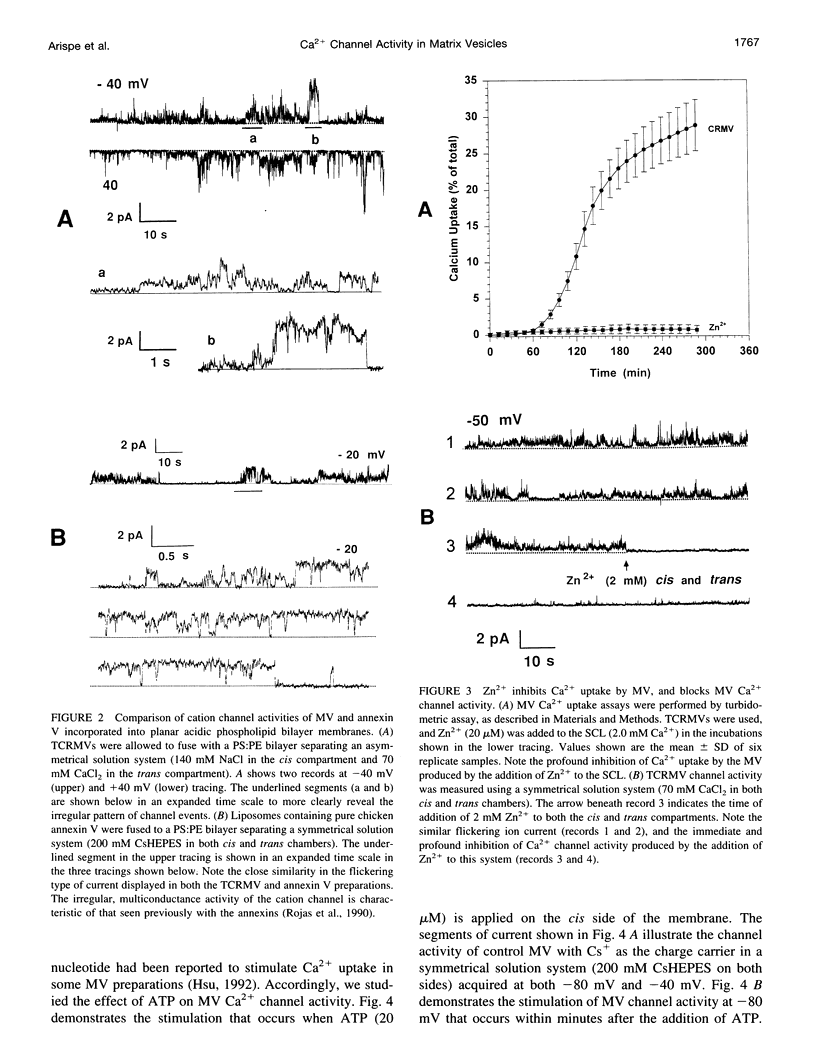
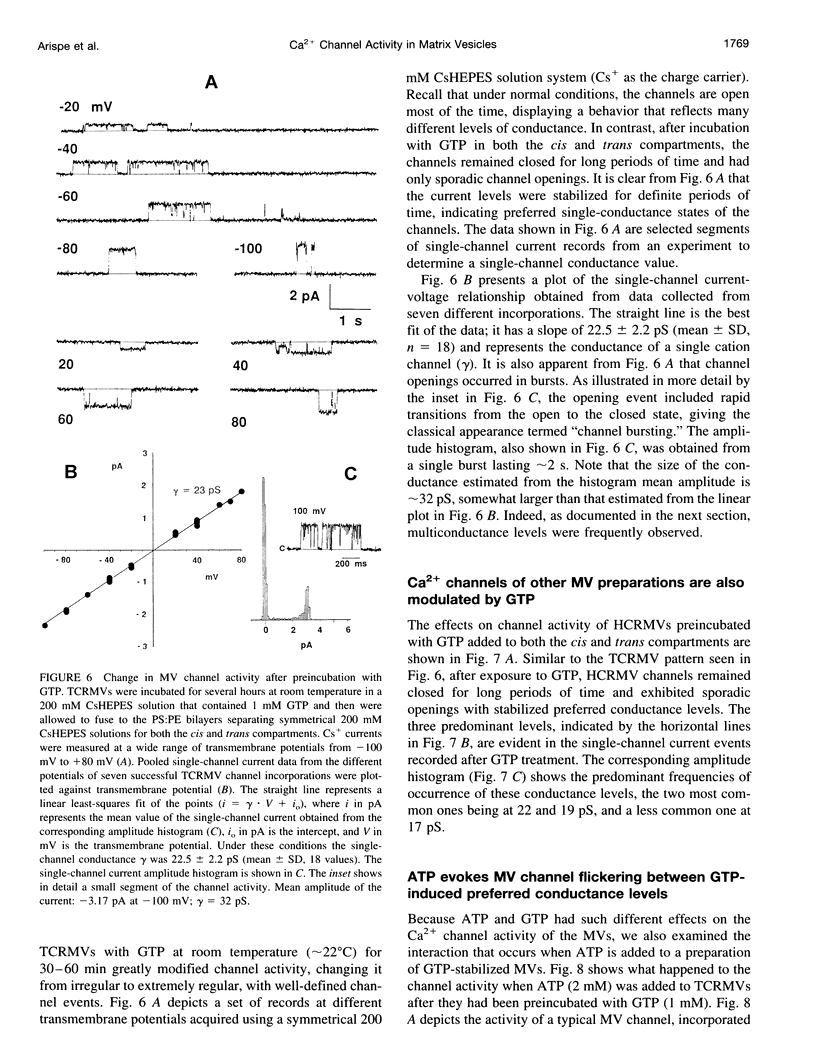
Abstract
Matrix vesicles (MVs), structures that accumulate Ca2+ during the initiation of mineral formation in growing bone, are rich in annexin V. When MVs are fused with planar phospholipid bilayers, a multiconductance Ca2+ channel is formed, with activity essentially identical to that observed when annexin V is delivered to the bilayer with phosphatidylserine liposomes. Ca2+ currents through this channel, from either MV or annexin V liposomes, are blocked by Zn2+, as is Ca2+ uptake by MV incubated in synthetic cartilage lymph. Blockage by Zn2+ was most effective when applied to the side containing the MV or liposomes. ATP and GTP differentially modulated the activity of this channel: ATP increased the amplitude of the current and the number of conductance states; GTP dramatically reduced the number of events and conductance states, leading to well-defined Ca2+ channel activity from either MV or the annexin V liposomes. In the distinctive effects of ATP, GTP, and Zn2+ on the Ca2+ channel activity observed in both the MV and the liposome systems, the common factor was the presence of annexin V. From this we conclude that Ca2+ entry into MV results from the presence of annexin V in these membrane-enclosed structures.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. C. Vesicles associated with calcification in the matrix of epiphyseal cartilage. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):59–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arispe N., Pollard H. B., Rojas E. Calcium-independent K(+)-selective channel from chromaffin granule membranes. J Membr Biol. 1992 Nov;130(2):191–202. doi: 10.1007/BF00231896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendes R., Voges D., Demange P., Huber R., Burger A. Structure-function analysis of the ion channel selectivity filter in human annexin V. Science. 1993 Oct 15;262(5132):427–430. doi: 10.1126/science.7692599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bewley M. C., Boustead C. M., Walker J. H., Waller D. A., Huber R. Structure of chicken annexin V at 2.25-A resolution. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 20;32(15):3923–3929. doi: 10.1021/bi00066a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonucci E. Fine structure and histochemistry of "calcifying globules" in epiphyseal cartilage. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;103(2):192–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00337312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brecević L., Füredi-Milhofer H. Precipitation of calcium phosphates from electrolyte solutions. II. The formation and transformation of the precipitates. Calcif Tissue Res. 1972;10(1):82–90. doi: 10.1007/BF02012538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger A., Voges D., Demange P., Perez C. R., Huber R., Berendes R. Structural and electrophysiological analysis of annexin V mutants. Mutagenesis of human annexin V, an in vitro voltage-gated calcium channel, provides information about the structural features of the ion pathway, the voltage sensor and the ion selectivity filter. J Mol Biol. 1994 Apr 8;237(4):479–499. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao X., Genge B. R., Wu L. N., Buzzi W. R., Showman R. M., Wuthier R. E. Characterization, cloning and expression of the 67-kDA annexin from chicken growth plate cartilage matrix vesicles. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Dec 15;197(2):556–561. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.2515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conklin B. R., Bourne H. R. Structural elements of G alpha subunits that interact with G beta gamma, receptors, and effectors. Cell. 1993 May 21;73(4):631–641. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90245-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demange P., Voges D., Benz J., Liemann S., Göttig P., Berendes R., Burger A., Huber R. Annexin V: the key to understanding ion selectivity and voltage regulation? Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genge B. R., Cao X., Wu L. N., Buzzi W. R., Showman R. W., Arsenault A. L., Ishikawa Y., Wuthier R. E. Establishment of the primary structure of the major lipid-dependent Ca2+ binding proteins of chicken growth plate cartilage matrix vesicles: identity with anchorin CII (annexin V) and annexin II. J Bone Miner Res. 1992 Jul;7(7):807–819. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650070710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genge B. R., Sauer G. R., Wu L. N., McLean F. M., Wuthier R. E. Correlation between loss of alkaline phosphatase activity and accumulation of calcium during matrix vesicle-mediated mineralization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18513–18519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genge B. R., Wu L. N., Adkisson H. D., 4th, Wuthier R. E. Matrix vesicle annexins exhibit proteolipid-like properties. Selective partitioning into lipophilic solvents under acidic conditions. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10678–10685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genge B. R., Wu L. N., Wuthier R. E. Differential fractionation of matrix vesicle proteins. Further characterization of the acidic phospholipid-dependent Ca2(+)-binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4703–4710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genge B. R., Wu L. N., Wuthier R. E. Identification of phospholipid-dependent calcium-binding proteins as constituents of matrix vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10917–10921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu H. H. Further studies on ATP-mediated Ca deposition by isolated matrix vesicles. Bone Miner. 1992 May;17(2):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(92)90751-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Römisch J., Paques E. P. The crystal and molecular structure of human annexin V, an anticoagulant protein that binds to calcium and membranes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3867–3874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07605.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch T., Ishikawa Y., Mwale F., Wuthier R. E. Roles of the nucleational core complex and collagens (types II and X) in calcification of growth plate cartilage matrix vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1994 Aug 5;269(31):20103–20109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch T., Wuthier R. E. Stimulation of calcification of growth plate cartilage matrix vesicles by binding to type II and X collagens. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 15;269(15):11462–11469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean F. M., Keller P. J., Genge B. R., Walters S. A., Wuthier R. E. Disposition of preformed mineral in matrix vesicles. Internal localization and association with alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10481–10488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollenhauer J., Bee J. A., Lizarbe M. A., von der Mark K. Role of anchorin CII, a 31,000-mol-wt membrane protein, in the interaction of chondrocytes with type II collagen. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1572–1579. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollenhauer J., von der Mark K. Isolation and characterization of a collagen-binding glycoprotein from chondrocyte membranes. EMBO J. 1983;2(1):45–50. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01378.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollesello P., de Bernard B., Grandolfo M., Paoletti S., Vittur F., Kvam B. J. Energy state of chondrocytes assessed by 31P-NMR studies of preosseous cartilage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Oct 15;180(1):216–222. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(05)81279-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynal P., Pollard H. B. Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium- and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 5;1197(1):63–93. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(94)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Register T. C., Warner G. P., Wuthier R. E. Effect of L- and D-tetramisole on 32Pi and 45Ca uptake and mineralization by matrix vesicle-enriched fractions from chicken epiphyseal cartilage. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 25;259(2):922–928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Arispe N., Haigler H. T., Burns A. L., Pollard H. B. Identification of annexins as calcium channels in biological membranes. Bone Miner. 1992 May;17(2):214–218. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(92)90739-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojas E., Pollard H. B., Haigler H. T., Parra C., Burns A. L. Calcium-activated endonexin II forms calcium channels across acidic phospholipid bilayer membranes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21207–21215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer G. R., Adkisson H. D., Genge B. R., Wuthier R. E. Regulatory effect of endogenous zinc and inhibitory action of toxic metal ions on calcium accumulation by matrix vesicles in vitro. Bone Miner. 1989 Nov;7(3):233–244. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(89)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer G. R., Wuthier R. E. Influence of trace metal ions on matrix vesicle calcification. Bone Miner. 1992 May;17(2):284–289. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(92)90752-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valhmu W. B., Wu L. N., Wuthier R. E. Effects of Ca/Pi ratio, Ca2+ x Pi ion product, and pH of incubation fluid on accumulation of 45Ca2+ by matrix vesicles in vitro. Bone Miner. 1990 Mar;8(3):195–209. doi: 10.1016/0169-6009(90)90105-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. N., Genge B. R., Lloyd G. C., Wuthier R. E. Collagen-binding proteins in collagenase-released matrix vesicles from cartilage. Interaction between matrix vesicle proteins and different types of collagen. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 15;266(2):1195–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. N., Sauer G. R., Genge B. R., Wuthier R. E. Induction of mineral deposition by primary cultures of chicken growth plate chondrocytes in ascorbate-containing media. Evidence of an association between matrix vesicles and collagen. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):21346–21355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. N., Yoshimori T., Genge B. R., Sauer G. R., Kirsch T., Ishikawa Y., Wuthier R. E. Characterization of the nucleational core complex responsible for mineral induction by growth plate cartilage matrix vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 25;268(33):25084–25094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuthier R. E. Involvement of cellular metabolism of calcium and phosphate in calcification of avian growth plate cartilage. J Nutr. 1993 Feb;123(2 Suppl):301–309. doi: 10.1093/jn/123.suppl_2.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]