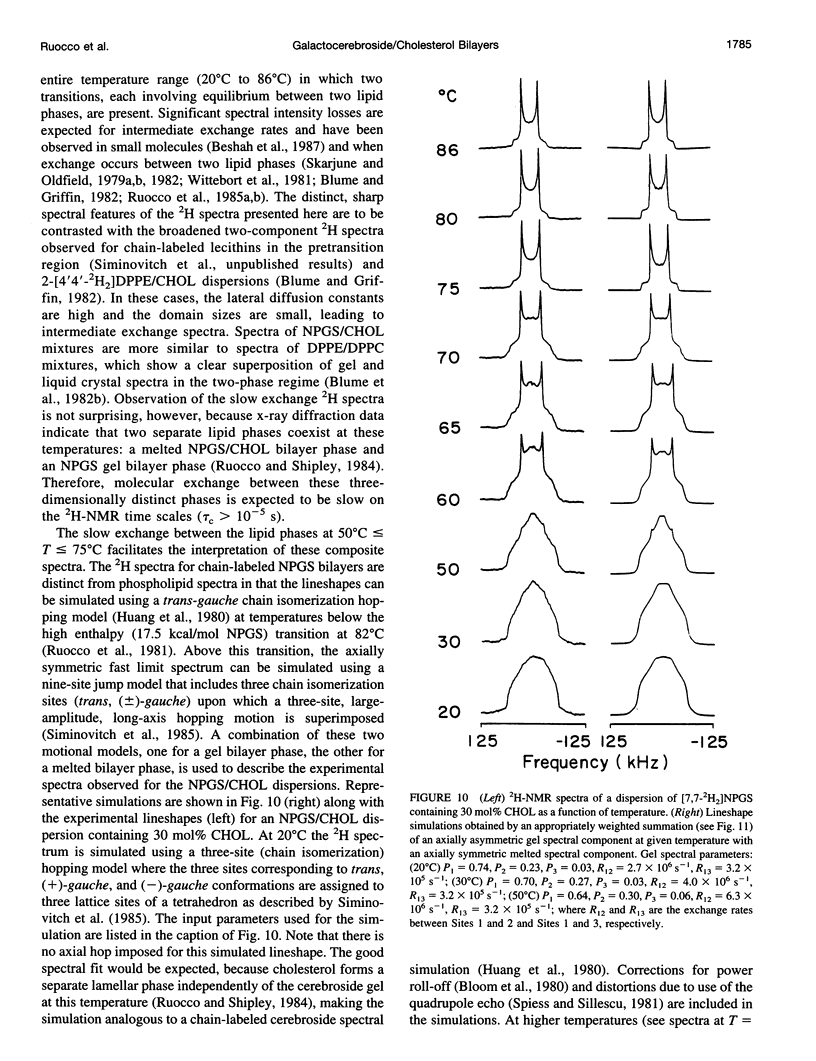
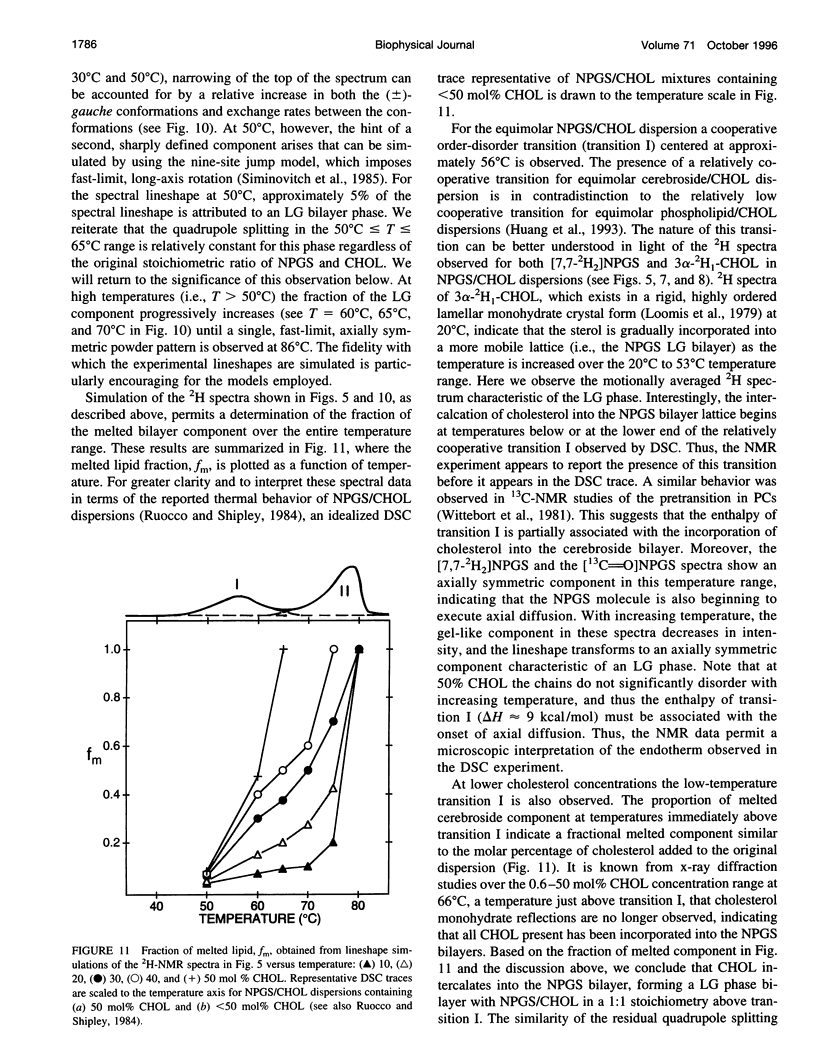
Abstract
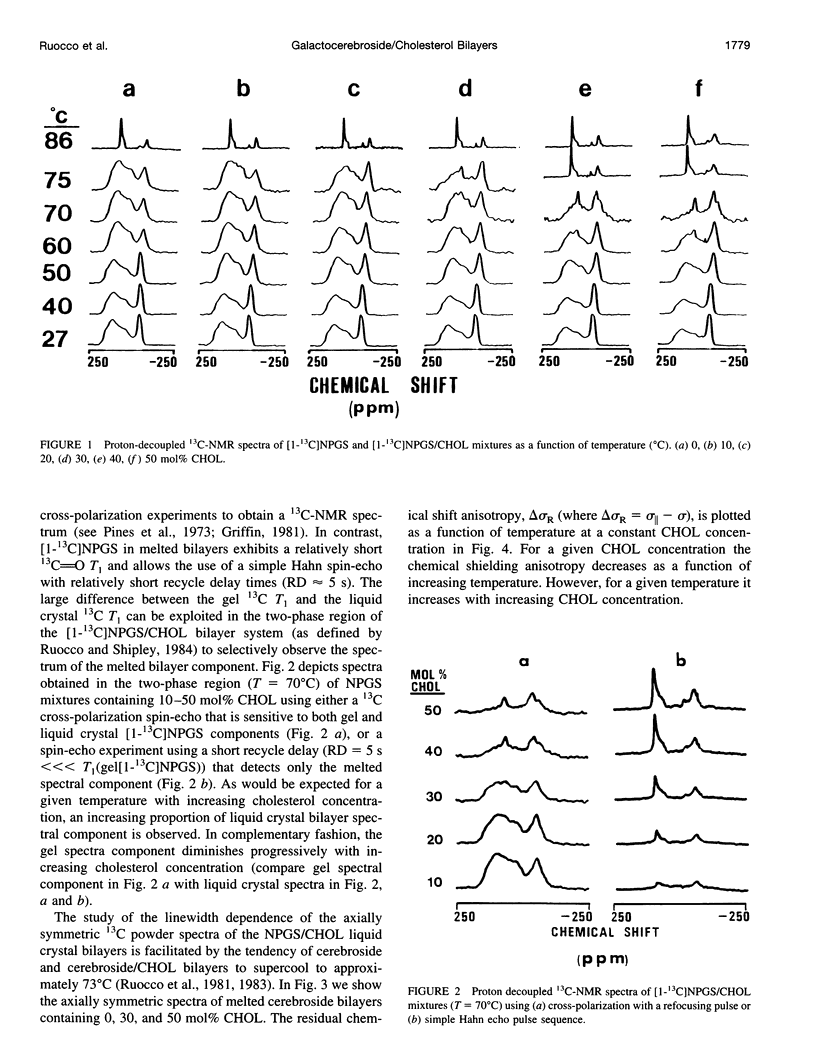
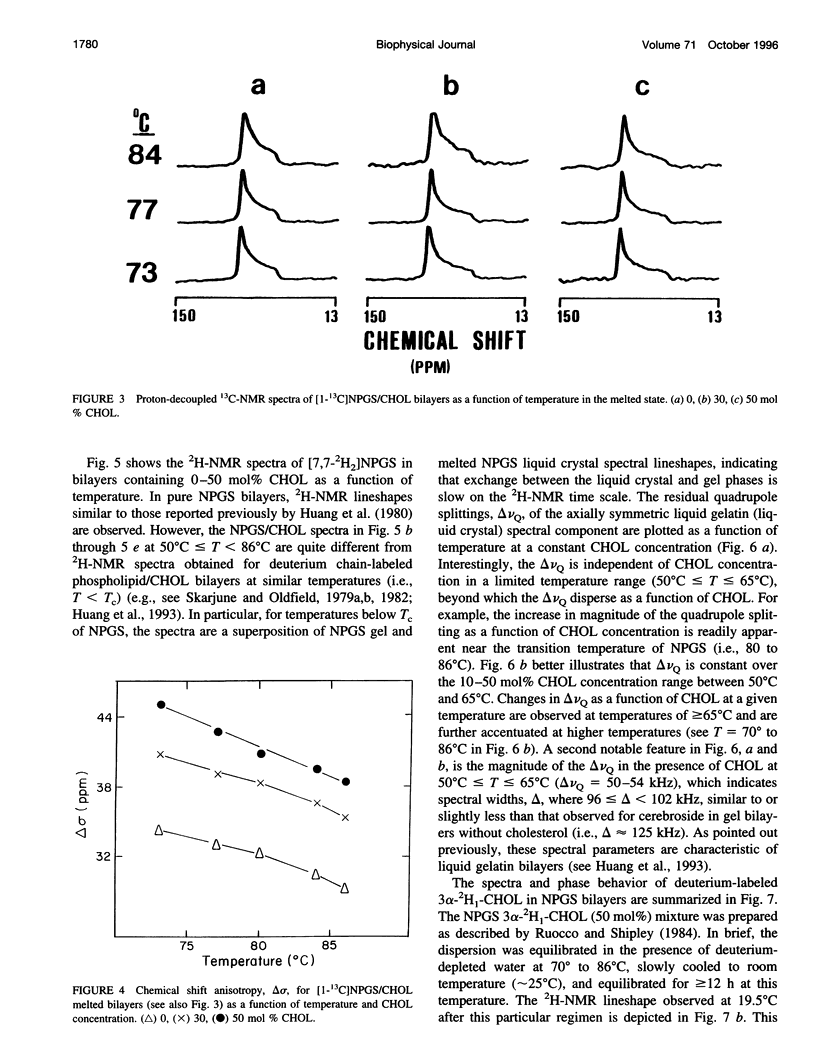
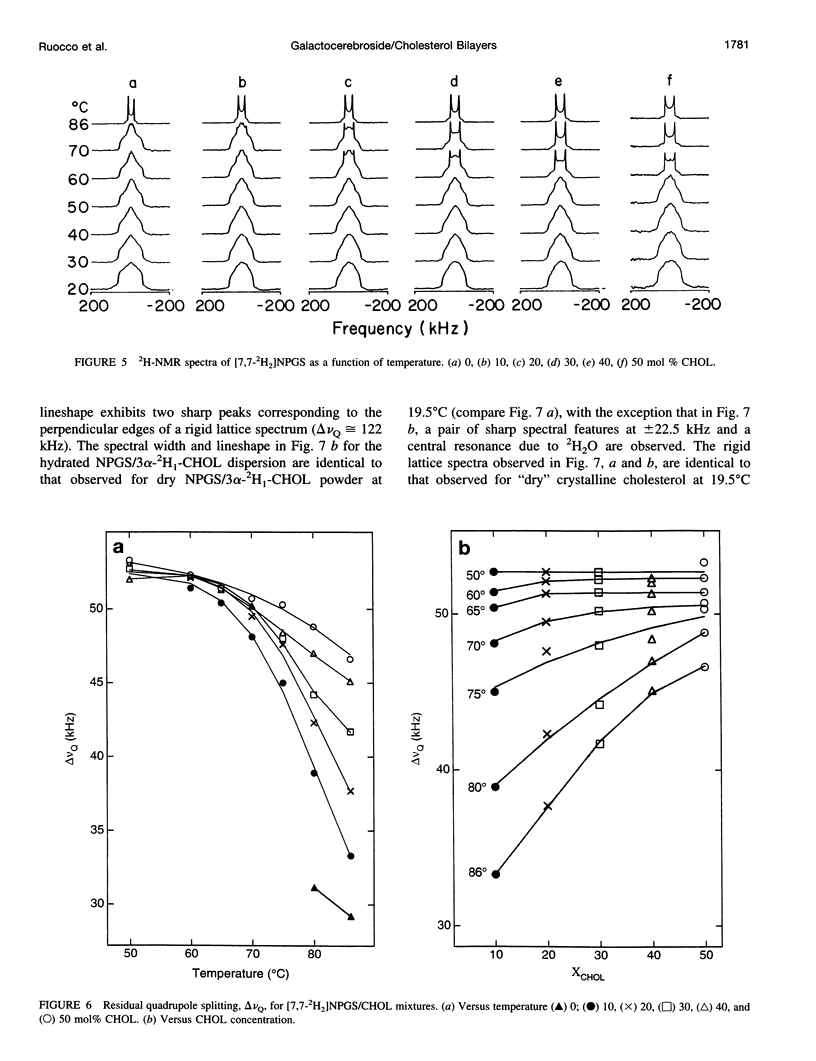
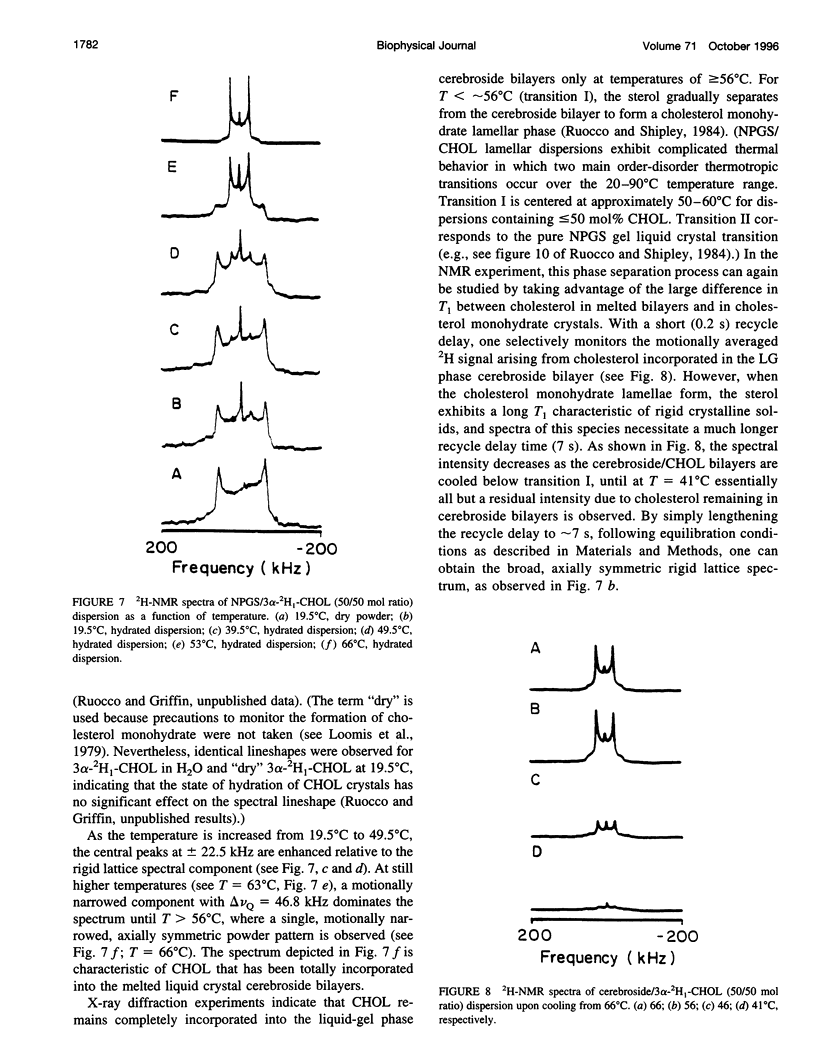
13C- and 2H-NMR experiments were used to examine the phase behavior and dynamic structures of N-palmitoylgalactosylsphingosine (NPGS) (cerebroside) and cholesterol (CHOL) in binary mixtures. 13C spectra of 13C=O-labeled and 2H spectra of [7,7-2H2] chain-labeled NPGS as well as 3 alpha-2H1 CHOL indicate that cerebroside and CHOL are immiscible in binary mixtures at temperatures less than 40 degrees C. In contrast, at 40 degrees C < t < or = T(C) (NPGS), up to 50 mol% CHOL can be incorporated into melted cerebroside bilayers. In addition, 13C and 2H spectra of melted NPGS/CHOL bilayers show a temperature and cholesterol concentration dependence. An analysis of spectra obtained from the melted 13C=O NPGS bilayer phase suggests that the planar NH-C=O group assumes an orientation tilted 40 degrees-55 degrees down from the bilayer interface. The similarity between the orientation of the amide group relative to the bilayer interface in melted bilayers and in the crystal structure of cerebroside suggests that the overall crystallographic conformation of cerebroside is preserved to a large degree in hydrated bilayers. Variation of temperature from 73 degrees to 86 degrees C and CHOL concentration from 0 to 51 mol% results in small changes in this general orientation of the amide group. 2H spectra of chain-labeled NPGS and labeled CHOL in NPGS/CHOL bilayer demonstrate that molecular exchange between the gel and liquid-gel (LG) phases is slow on the 2H time scale, and this facilitates the simulation of the two component 2H spectra of [7,7-2H2]NPGS/CHOL mixtures. Simulation parameters are used to quantitate the fractions of gel and LG cerebroside. The quadrupole splitting of [7,7-2H2]NPGS/CHOL mixtures and 2H simulations allows the LG phase bilayer fraction to be characterized as an equimolar mixture of cerebroside and CHOL.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham W., Downing D. T. Deuterium NMR investigation of polymorphism in stratum corneum lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 30;1068(2):189–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(91)90209-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Griffin R. G. Carbon-13 and deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance study of the interaction of cholesterol with phosphatidylethanolamine. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6230–6242. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Rice D. M., Wittebort R. J., Griffin R. G. Molecular dynamics and conformation in the gel and liquid-crystalline phases of phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6220–6230. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blume A., Wittebort R. J., Das Gupta S. K., Griffin R. G. Phase equilibria, molecular conformation, and dynamics in phosphatidylcholine/phosphatidylethanolamine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1982 Nov 23;21(24):6243–6253. doi: 10.1021/bi00267a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bologa-Sandru L., Zalc B., Herschkowitz N., Baumann N. Oligodendrocytes of jimpy mice express galactosylceramide: an immunofluorescence study on brain sections and dissociated brain cell cultures. Brain Res. 1981 Nov 30;225(2):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes A. W., Cherry R. J., Chapman D. Physical properties of lecithin-cerebroside bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Oct 12;249(1):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curatolo W. Thermal behavior of fractionated and unfractionated bovine brain cerebrosides. Biochemistry. 1982 Apr 13;21(8):1761–1764. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DasGupta S. K., Rice D. M., Griffin R. G. Synthesis of isotopically labeled saturated fatty acids. J Lipid Res. 1982 Jan;23(1):197–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florio E., Jarrell H., Fenske D. B., Barber K. R., Grant C. W. Glycosphingolipid interdigitation in phospholipid bilayers examined by deuterium NMR and EPR. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 27;1025(2):157–163. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin R. G. Solid state nuclear magnetic resonance of lipid bilayers. Methods Enzymol. 1981;72:108–174. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(81)72010-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton K. S., Jarrell H. C., Brière K. M., Grant C. W. Glycosphingolipid backbone conformation and behavior in cholesterol-containing phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 20;32(15):4022–4028. doi: 10.1021/bi00066a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang T. H., Lee C. W., Das Gupta S. K., Blume A., Griffin R. G. A 13C and 2H nuclear magnetic resonance study of phosphatidylcholine/cholesterol interactions: characterization of liquid-gel phases. Biochemistry. 1993 Dec 7;32(48):13277–13287. doi: 10.1021/bi00211a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson M., Johnston D. S., Chapman D. Differential scanning calorimetric and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopic investigations of cerebroside polymorphism. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 20;944(3):497–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90521-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D. S., Chapman D. A calorimetric study of the thermotropic behaviour of mixtures of brain cerebrosides with other brain lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Apr 22;939(3):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90108-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladbrooke B. D., Jenkinson T. J., Kamat V. B., Chapman D. Physical studies of myelin. I. Thermal analysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Sep 2;164(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(68)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson D., Karlsson D. A. Molecular arrangements in glycosphingolipids. Chem Phys Lipids. 1972 Mar;8(2):152–179. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(72)90027-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecuyer H., Dervichian D. G. Structure of aqueous mixtures of lecithin and cholesterol. J Mol Biol. 1969 Oct 14;45(1):39–57. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis C. R., Shipley G. G., Small D. M. The phase behavior of hydrated cholesterol. J Lipid Res. 1979 May;20(4):525–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T. Biochemistry of myelin. Adv Neurol. 1981;31:93–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quinn P. J., Sherman W. R. Monolayer characteristics and calcium adsorption to cerebroside and cerebroside sulphate oriented at the air-water interface. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jun 1;233(3):734–752. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90173-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENFELD R. S., FUKUSHIMA D. K., HELLMAN L., GALLAGHER T. F. The transformation of cholesterol to coprostanol. J Biol Chem. 1954 Nov;211(1):301–311. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Atkinson D., Small D. M., Skarjune R. P., Oldfield E., Shipley G. G. X-ray diffraction and calorimetric study of anhydrous and hydrated N-palmitoylgalactosylsphingosine (cerebroside). Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):5957–5966. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Makriyannis A., Siminovitch D. J., Griffin R. G. Deuterium NMR investigation of ether- and ester-linked phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1985 Aug 27;24(18):4844–4851. doi: 10.1021/bi00339a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Shipley G. G. Interaction of cholesterol with galactocerebroside and galactocerebroside-phosphatidylcholine bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1984 Dec;46(6):695–707. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84068-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Shipley G. G., Oldfield E. Galactocerebroside-phospholipid interactions in bilayer membranes. Biophys J. 1983 Jul;43(1):91–101. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84327-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Shipley G. G. Thermal and structural behavior of natural cerebroside 3-sulfate in bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jul 24;859(2):246–256. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90220-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruocco M. J., Siminovitch D. J., Griffin R. G. Comparative study of the gel phases of ether- and ester-linked phosphatidylcholines. Biochemistry. 1985 May 7;24(10):2406–2411. doi: 10.1021/bi00331a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siminovitch D. J., Ruocco M. J., Makriyannis A., Griffin R. G. The effect of cholesterol on lipid dynamics and packing in diether phosphatidylcholine bilayers. X-ray diffraction and 2H-NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 23;901(2):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarjune R., Oldfield E. Physical studies of cell surface and cell membrane structure. Determination of phospholipid head group organization by deuterium and phosphorus nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1979 Dec 25;18(26):5903–5909. doi: 10.1021/bi00593a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarjune R., Oldfield E. Physical studies of cell surface and cell membrane structure. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of deuterium-labelled N-hexadeconoylgalactosylceramides (cerebrosides). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Sep 21;556(2):208–218. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(79)90043-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skarjune R., Oldfield E. Physical studies of cell surface and cell membrane structure. Deuterium nuclear magnetic resonance studies of N-palmitoylglucosylceramide (cerebroside) head group structure. Biochemistry. 1982 Jun 22;21(13):3154–3160. doi: 10.1021/bi00256a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T., Utsumi H., Inoue K., Nojima S. Haptenic activity of galactosyl ceramide and its topographical distribution on liposomal membranes. I. Effect of cholesterol incorporation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jun 22;644(2):183–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(81)90374-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tardieu A., Luzzati V., Reman F. C. Structure and polymorphism of the hydrocarbon chains of lipids: a study of lecithin-water phases. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):711–733. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90303-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedmann T. S., Salmon A. Thermotropic phase properties of the hydroxyceramide/cholesterol system. Lipids. 1991 May;26(5):364–368. doi: 10.1007/BF02537200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittebort R. J., Blume A., Huang T. H., Das Gupta S. K., Griffin R. G. Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance investigations of phase transitions and phase equilibria in pure and mixed phospholipid bilayers. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 6;21(14):3487–3502. doi: 10.1021/bi00257a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittebort R. J., Schmidt C. F., Griffin R. G. Solid-state carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance of the lecithin gel to liquid-crystalline phase transition. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4223–4228. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


