Abstract
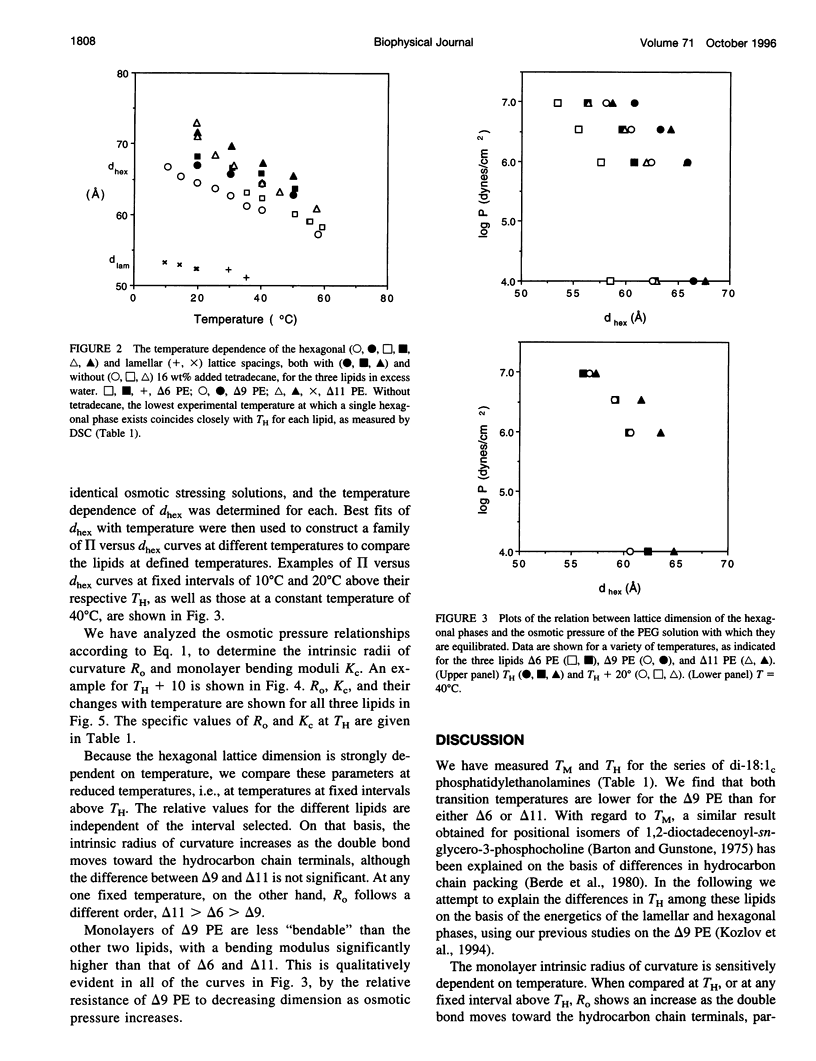
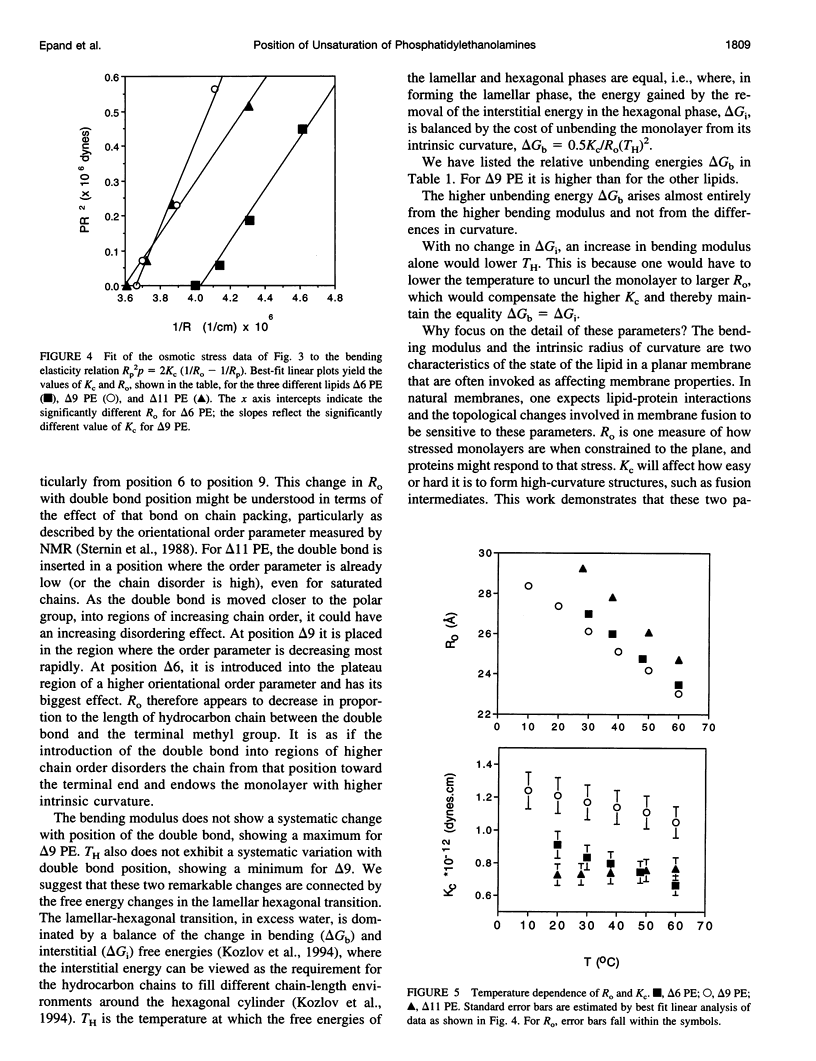
The bilayer-to-hexagonal phase transition temperatures (T(H)) of di-18:1(C) phosphatidylethanolamine with double bonds at positions 6, 9, and 11 are 37 degrees C, 8 degrees C, and 28 degrees C, respectively, as measured by differential scanning calorimetry and x-ray diffraction. Thus T(H) exhibits a minimum when the C=C is around position 9, similar to what has been found for the gel-to-liquid crystalline phase transition temperature in other lipids. Factors that may contribute to the dependence of T(H) on double bond position were studied by x-ray diffraction of the hexagonal phases in the presence and absence of added alkane, with or without the osmotic stress of polyethylene glycol, and over a wide temperature range. The lattice dimensions show that the intrinsic radius of lipid monolayer curvature increases as the double bond is moved toward the tail ends. A measure of the bending moduli of these lipid monolayers shows a higher value for the 9 position, and lower values for the other two. Consideration of the bilayer-to-hexagonal transition in terms of bending and interstitial energies provides a rationale for the relative values of T(H).
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barton P. G., Gunstone F. D. Hydrocarbon chain packing and molecular motion in phospholipid bilayers formed from unsaturated lecithins. Synthesis and properties of sixteen positional isomers of 1,2-dioctadecenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphorylcholine. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4470–4476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berde C. B., Andersen H. C., Hudson B. S. A theory of the effects of head-group structure and chain unsaturation on the chain melting transition of phospholipid dispersions. Biochemistry. 1980 Sep 2;19(18):4279–4293. doi: 10.1021/bi00559a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernomordik L., Kozlov M. M., Zimmerberg J. Lipids in biological membrane fusion. J Membr Biol. 1995 Jul;146(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF00232676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell R. B. Regulation of CTP:phosphocholine cytidylyltransferase by lipids. 2. Surface curvature, acyl chain length, and lipid-phase dependence for activation. Biochemistry. 1991 Jun 18;30(24):5881–5888. doi: 10.1021/bi00238a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullis P. R., de Kruijff B. Lipid polymorphism and the functional roles of lipids in biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):399–420. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M., Bryszewska M. Modulation of the bilayer to hexagonal phase transition and solvation of phosphatidylethanolamines in aqueous salt solutions. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 29;27(24):8776–8779. doi: 10.1021/bi00424a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller S. L., Bezrukov S. M., Gruner S. M., Tate M. W., Vodyanoy I., Parsegian V. A. Probability of alamethicin conductance states varies with nonlamellar tendency of bilayer phospholipids. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81040-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlov M. M., Leikin S., Rand R. P. Bending, hydration and interstitial energies quantitatively account for the hexagonal-lamellar-hexagonal reentrant phase transition in dioleoylphosphatidylethanolamine. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1603–1611. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80633-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUZZATI V., HUSSON F. The structure of the liquid-crystalline phasis of lipid-water systems. J Cell Biol. 1962 Feb;12:207–219. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.2.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindblom G., Hauksson J. B., Rilfors L., Bergenståhl B., Wieslander A., Eriksson P. O. Membrane lipid regulation in Acholeplasma laidlawii grown with saturated fatty acids. Biosynthesis of a triacylglucolipid forming reversed micelles. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 5;268(22):16198–16207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCallum C. D., Epand R. M. Insulin receptor autophosphorylation and signaling is altered by modulation of membrane physical properties. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 14;34(6):1815–1824. doi: 10.1021/bi00006a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Fuller N. L., Gruner S. M., Parsegian V. A. Membrane curvature, lipid segregation, and structural transitions for phospholipids under dual-solvent stress. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):76–87. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Fuller N. L. Structural dimensions and their changes in a reentrant hexagonal-lamellar transition of phospholipids. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):2127–2138. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)81008-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rietveld A. G., Chupin V. V., Koorengevel M. C., Wienk H. L., Dowhan W., de Kruijff B. Regulation of lipid polymorphism is essential for the viability of phosphatidylethanolamine-deficient Escherichia coli cells. J Biol Chem. 1994 Nov 18;269(46):28670–28675. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rilfors L., Hauksson J. B., Lindblom G. Regulation and phase equilibria of membrane lipids from Bacillus megaterium and Acholeplasma laidlawii strain A containing methyl-branched acyl chains. Biochemistry. 1994 May 24;33(20):6110–6120. doi: 10.1021/bi00186a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seddon J. M. Structure of the inverted hexagonal (HII) phase, and non-lamellar phase transitions of lipids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Feb 28;1031(1):1–69. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(90)90002-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senisterra G., Epand R. M. Role of membrane defects in the regulation of the activity of protein kinase C. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993 Jan;300(1):378–383. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1993.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel D. P. Energetics of intermediates in membrane fusion: comparison of stalk and inverted micellar intermediate mechanisms. Biophys J. 1993 Nov;65(5):2124–2140. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81256-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternin E., Fine B., Bloom M., Tilcock C. P., Wong K. F., Cullis P. R. Acyl chain orientational order in the hexagonal HII phase of phospholipid-water dispersions. Biophys J. 1988 Oct;54(4):689–694. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83004-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


