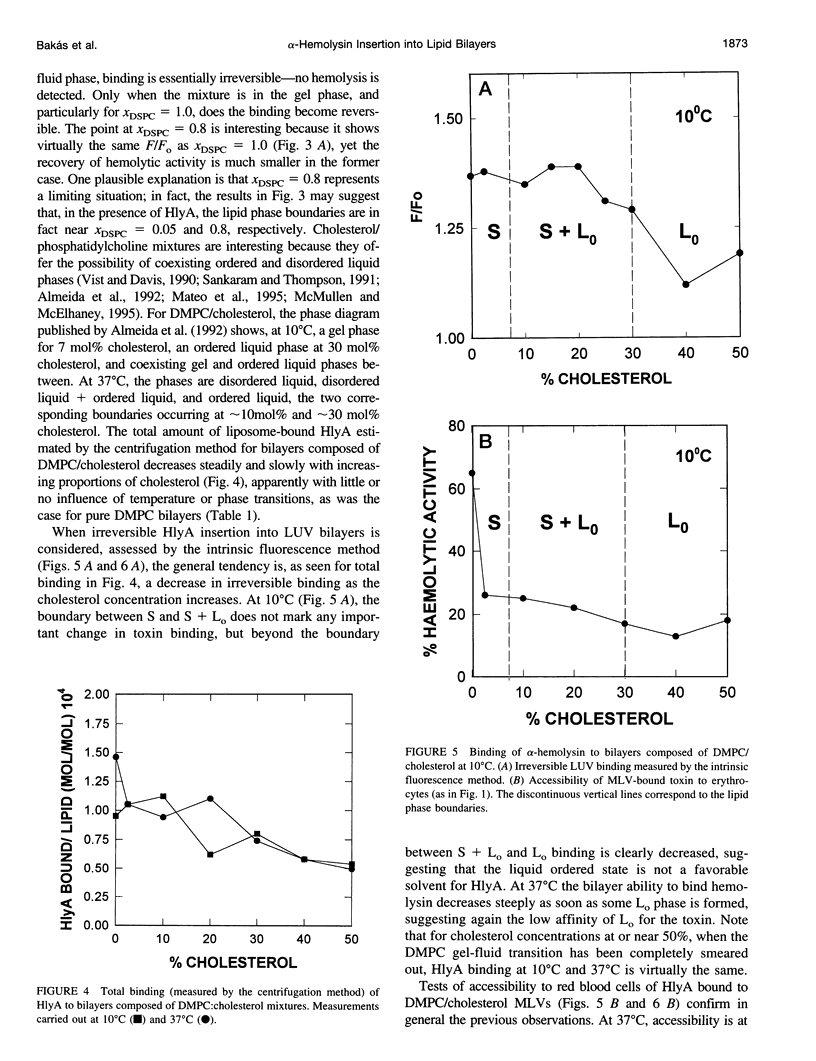
Abstract
Alpha-Hemolysin is an extracellular protein toxin (107 kDa) produced by some pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli. Although stable in aqueous medium, it can bind to lipid bilayers and produce membrane disruption in model and cell membranes. Previous studies had shown that toxin binding to the bilayer did not always lead to membrane lysis. In this paper, we find that alpha-hemolysin may bind the membranes in at least two ways, a reversible adsorption and an irreversible insertion. Reversibility is detected by the ability of liposome-bound toxin to induce hemolysis of added horse erythrocytes; insertion is accompanied by an increase in the protein intrinsic fluorescence. Toxin insertion does not necessarily lead to membrane lysis. Studies of alpha-hemolysin insertion into bilayers formed from a variety of single phospholipids, or binary mixtures of phospholipids, or of phospholipid and cholesterol, reveal that irreversible insertion is favored by fluid over gel states, by low over high cholesterol concentrations, by disordered liquid phases over gel or ordered liquid phases, and by gel over ordered liquid phases. These results are relevant to the mechanism of action of alpha-hemolysin and provide new insights into the membrane insertion of large proteins.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almeida P. F., Vaz W. L., Thompson T. E. Lateral diffusion in the liquid phases of dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine/cholesterol lipid bilayers: a free volume analysis. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6739–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhakdi S., Tranum-Jensen J. C5b-9 assembly: average binding of one C9 molecule to C5b-8 without poly-C9 formation generates a stable transmembrane pore. J Immunol. 1986 Apr 15;136(8):2999–3005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher M. S., Munro S. Cholesterol and the Golgi apparatus. Science. 1993 Sep 3;261(5126):1280–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.8362242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brumm T., Jørgensen K., Mouritsen O. G., Bayerl T. M. The effect of increasing membrane curvature on the phase transition and mixing behavior of a dimyristoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine/ distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphatidylcholine lipid mixture as studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1373–1379. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79695-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman D. Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 May;8(2):185–235. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chervaux C., Holland I. B. Random and directed mutagenesis to elucidate the functional importance of helix II and F-989 in the C-terminal secretion signal of Escherichia coli hemolysin. J Bacteriol. 1996 Feb;178(4):1232–1236. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.4.1232-1236.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coote J. G. Structural and functional relationships among the RTX toxin determinants of gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1992 Feb;8(2):137–161. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1992.tb04961.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibble A. R., Yeager M. D., Feigenson G. W. Partitioning of gramicidin A' between coexisting fluid and gel phospholipid phases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Dec 12;1153(2):155–162. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90400-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannavy K., Rospert S., Schatz G. Protein import into mitochondria: a paradigm for the translocation of polypeptides across membranes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Aug;5(4):694–700. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90142-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenman L., Liebow C., Rothman S. Transport of proteins across membranes--a paradigm in transition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Dec 20;1241(3):341–370. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(95)00009-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Zakim D. The spontaneous incorporation of proteins into preformed bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Apr 27;906(1):33–68. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(87)90004-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen K., Sperotto M. M., Mouritsen O. G., Ipsen J. H., Zuckermann M. J. Phase equilibria and local structure in binary lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 10;1152(1):135–145. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90240-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knoll W., Ibel K., Sackmann E. Small-angle neutron scattering study of lipid phase diagrams by the contrast variation method. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 27;20(22):6379–6383. doi: 10.1021/bi00525a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemmon M. A., Engelman D. M. Specificity and promiscuity in membrane helix interactions. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):17–20. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine Y. K., Wilkins M. H. Structure of oriented lipid bilayers. Nat New Biol. 1971 Mar 17;230(11):69–72. doi: 10.1038/newbio230069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig A., Benz R., Goebel W. Oligomerization of Escherichia coli haemolysin (HlyA) is involved in pore formation. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Oct;241(1-2):89–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00280205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer L. D., Hope M. J., Cullis P. R. Vesicles of variable sizes produced by a rapid extrusion procedure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 13;858(1):161–168. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90302-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMullen T. P., McElhaney R. N. New aspects of the interaction of cholesterol with dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers as revealed by high-sensitivity differential scanning calorimetry. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Mar 8;1234(1):90–98. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(94)00266-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G., Moser C., Pellet S., Welch R. Pore-formation by Escherichia coli hemolysin (HlyA) and other members of the RTX toxins family. Toxicology. 1994 Feb 28;87(1-3):249–267. doi: 10.1016/0300-483x(94)90254-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menestrina G., Ropele M., Dalla Serra M., Pederzolli C., Hugo F., Pellet S., Welch R. A. Binding of antibodies to functional epitopes on the pore formed by Escherichia coli hemolysin in cells and model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1995 Aug 23;1238(1):72–80. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(95)00113-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monette M., Van Calsteren M. R., Lafleur M. Effect of cholesterol on the polymorphism of dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine/melittin complexes: an NMR study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Jul 4;1149(2):319–328. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90217-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nezil F. A., Bloom M. Combined influence of cholesterol and synthetic amphiphillic peptides upon bilayer thickness in model membranes. Biophys J. 1992 May;61(5):1176–1183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81926-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostolaza H., Bartolomé B., Ortiz de Zárate I., de la Cruz F., Goñi F. M. Release of lipid vesicle contents by the bacterial protein toxin alpha-haemolysin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Apr 8;1147(1):81–88. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(93)90318-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostolaza H., Bartolomé B., Serra J. L., de la Cruz F., Goñi F. M. Alpha-haemolysin from E. coli. Purification and self-aggregation properties. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):195–198. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80291-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostolaza H., Goñi F. M. Interaction of the bacterial protein toxin alpha-haemolysin with model membranes: protein binding does not always lead to lytic activity. FEBS Lett. 1995 Sep 11;371(3):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00927-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostolaza H., Soloaga A., Goñi F. M. The binding of divalent cations to Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Feb 15;228(1):39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pott T., Dufourc E. J. Action of melittin on the DPPC-cholesterol liquid-ordered phase: a solid state 2H-and 31P-NMR study. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80272-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes Mateo C., Ulises Acuña A., Brochon J. C. Liquid-crystalline phases of cholesterol/lipid bilayers as revealed by the fluorescence of trans-parinaric acid. Biophys J. 1995 Mar;68(3):978–987. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80273-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rytömaa M., Kinnunen P. K. Reversibility of the binding of cytochrome c to liposomes. Implications for lipid-protein interactions. J Biol Chem. 1995 Feb 17;270(7):3197–3202. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.7.3197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Marsh D., Gierasch L. M., Thompson T. E. Reorganization of lipid domain structure in membranes by a transmembrane peptide: an ESR spin label study on the effect of the Escherichia coli outer membrane protein A signal peptide on the fluid lipid domain connectivity in binary mixtures of dimyristoyl phosphatidylcholine and distearoyl phosphatidylcholine. Biophys J. 1994 Jun;66(6):1959–1968. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80989-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Marsh D., Thompson T. E. Determination of fluid and gel domain sizes in two-component, two-phase lipid bilayers. An electron spin resonance spin label study. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):340–349. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81619-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sankaram M. B., Thompson T. E. Cholesterol-induced fluid-phase immiscibility in membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8686–8690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Packman L. C., Koronakis V., Hughes C. Fatty acylation of two internal lysine residues required for the toxic activity of Escherichia coli hemolysin. Science. 1994 Dec 23;266(5193):1992–1996. doi: 10.1126/science.7801126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surewicz W. K., Epand R. M. Role of peptide structure in lipid-peptide interactions: a fluorescence study of the binding of pentagastrin-related pentapeptides to phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):6072–6077. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita T., Watanabe M., Yasuda T. Influence of membrane fluidity on the assembly of Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin, a channel-forming protein, in liposome membrane. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 5;267(19):13391–13397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaz W. L., Melo E. C., Thompson T. E. Translational diffusion and fluid domain connectivity in a two-component, two-phase phospholipid bilayer. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):869–876. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82733-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen J. A., Ruonala M., Vauhkonen M., Somerharju P. Lateral organization of liquid-crystalline cholesterol-dimyristoylphosphatidylcholine bilayers. Evidence for domains with hexagonal and centered rectangular cholesterol superlattices. Biochemistry. 1995 Sep 12;34(36):11568–11581. doi: 10.1021/bi00036a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vist M. R., Davis J. H. Phase equilibria of cholesterol/dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine mixtures: 2H nuclear magnetic resonance and differential scanning calorimetry. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):451–464. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. P., Lewis R. N., Hodges R. S., McElhaney R. N. Peptide models of helical hydrophobic transmembrane segments of membrane proteins. 2. Differential scanning calorimetric and FTIR spectroscopic studies of the interaction of Ac-K2-(LA)12-K2-amide with phosphatidylcholine bilayers. Biochemistry. 1995 Feb 21;34(7):2362–2371. doi: 10.1021/bi00007a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kruijff B. Anionic phospholipids and protein translocation. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jun 6;346(1):78–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


