Abstract
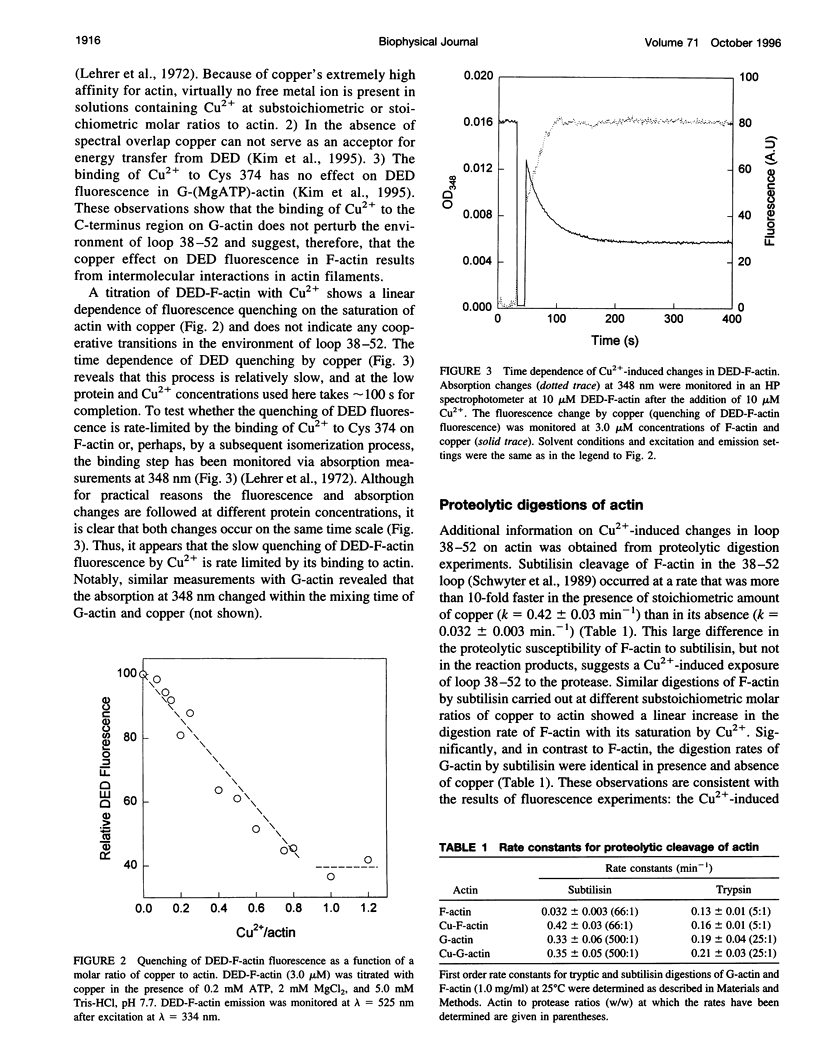
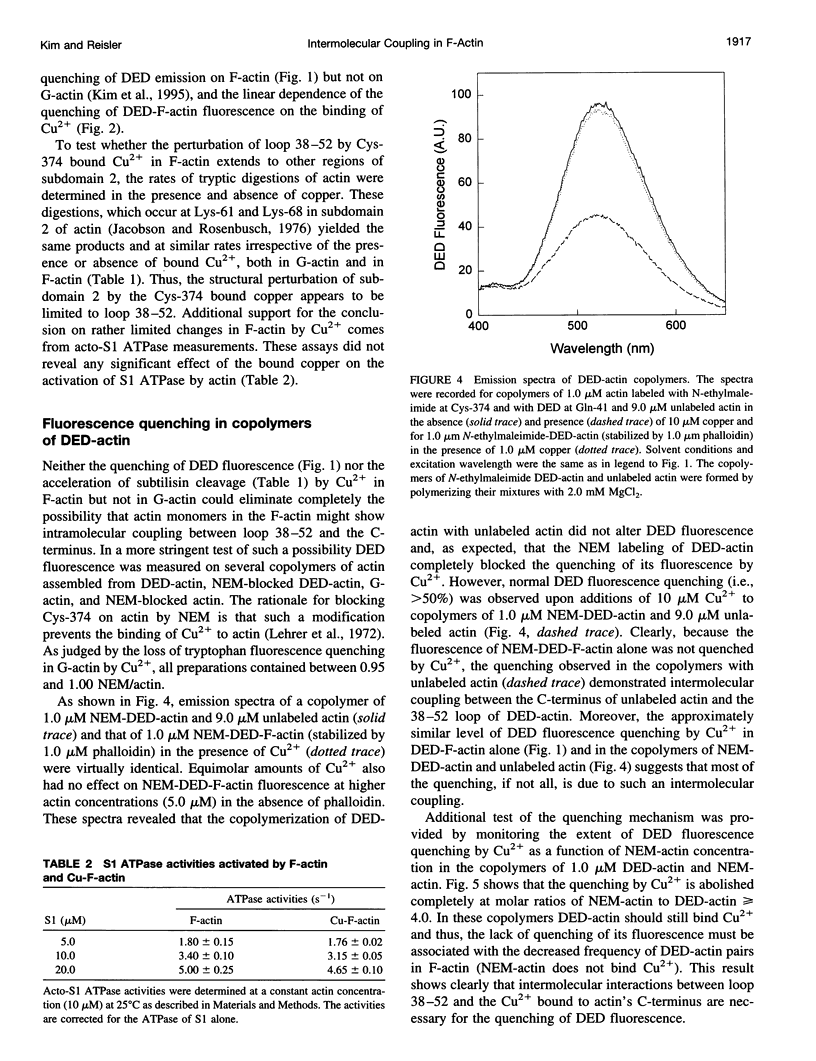
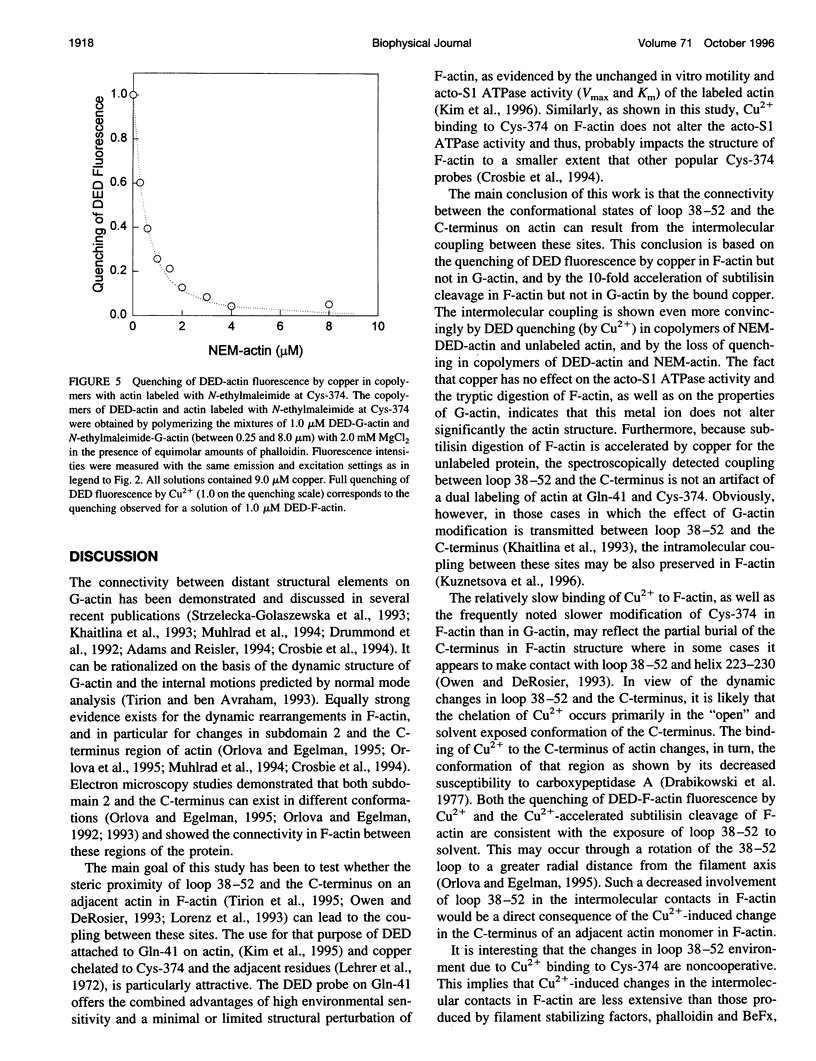
The recently reported structural connectivity in F-actin between the DNase I binding loop on actin (residues 38-52) and the C-terminus region was investigated by fluorescence and proteolytic digestion methods. The binding of copper to Cys-374 on F- but not G-actin quenched the fluorescence of dansyl ethylenediamine (DED) attached to Gin-41 by more than 50%. The blocking of copper binding to DED-actin by N-ethylmaleimide labeling of Cys-374 on actin abolished the fluorescence quenching. The quenching of DED-actin fluorescence was restored in copolymers (1:9) of N-ethylmaleimide-DED-actin with unlabeled actin. The quenching of DED-actin fluorescence by copper was also abolished in copolymers (1:4) of DED-actin and N-ethylmaleimide-actin. These results show intermolecular coupling between loop 38-52 and the C-terminus in F-actin. Consistent with this, the rate of subtilisin cleavage of actin at loop 38-52 was increased by the bound copper by more than 10-fold in F-actin but not in G-actin. Neither acto-myosin subfragment-1 (S1) ATPase activity nor the tryptic digestion of G-actin and F-actin at the Lys-61 and Lys-69 sites were affected by the bound copper. These observations suggest that copper binding to Cys-374 does not induce extensive changes in actin structure and that the perturbation of loop 38-52 environment results from changes in the intermolecular contacts in F-actin.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. B., Reisler E. Sequence 18-29 on actin: antibody and spectroscopic probing of conformational changes. Biochemistry. 1994 Dec 6;33(48):14426–14433. doi: 10.1021/bi00252a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crosbie R. H., Miller C., Cheung P., Goodnight T., Muhlrad A., Reisler E. Structural connectivity in actin: effect of C-terminal modifications on the properties of actin. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1957–1964. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80678-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drabikowski W., Lehrer S., Nagy B., Gergely J. Loss of Cu2+-binding to actin upon removal of the C-terminal phenylalanine by carboxypeptidase A. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1977 May;181(1):359–361. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(77)90515-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewes G., Faulstich H. Cooperative effects on filament stability in actin modified at the C-terminus by substitution or truncation. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 15;212(1):247–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Hennessey E. S., Sparrow J. C. The binding of mutant actins to profilin, ATP and DNase I. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Oct 1;209(1):171–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelman E. H., Orlova A. New insights into actin filament dynamics. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1995 Apr;5(2):172–180. doi: 10.1016/0959-440x(95)80072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fievez S., Carlier M. F. Conformational changes in subdomain-2 of G-actin upon polymerization into F-actin and upon binding myosin subfragment-1. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jan 25;316(2):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81212-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey J. E., Harrington W. F. Self-association in the myosin system at high ionic strength. I. Sensitivity of the interaction to pH and ionic environment. Biochemistry. 1970 Feb 17;9(4):886–893. doi: 10.1021/bi00806a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Rosenbusch J. P. ATP binding to a protease-resistant core of actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2742–2746. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasprzak A. A., Takashi R., Morales M. F. Orientation of actin monomer in the F-actin filament: radial coordinate of glutamine-41 and effect of myosin subfragment 1 binding on the monomer orientation. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 14;27(12):4512–4522. doi: 10.1021/bi00412a044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaitlina S. Y., Moraczewska J., Strzelecka-Gołaszewska H. The actin/actin interactions involving the N-terminus of the DNase-I-binding loop are crucial for stabilization of the actin filament. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Dec 15;218(3):911–920. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E., Miller C. J., Motoki M., Seguro K., Muhlrad A., Reisler E. Myosin-induced changes in F-actin: fluorescence probing of subdomain 2 by dansyl ethylenediamine attached to Gln-41. Biophys J. 1996 Mar;70(3):1439–1446. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79703-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim E., Motoki M., Seguro K., Muhlrad A., Reisler E. Conformational changes in subdomain 2 of G-actin: fluorescence probing by dansyl ethylenediamine attached to Gln-41. Biophys J. 1995 Nov;69(5):2024–2032. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80072-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouyama T., Mihashi K. Fluorimetry study of N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide-labelled F-actin. Local structural change of actin protomer both on polymerization and on binding of heavy meromyosin. Eur J Biochem. 1981;114(1):33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuznetsova I., Antropova O., Turoverov K., Khaitlina S. Conformational changes in subdomain I of actin induced by proteolytic cleavage within the DNase I-binding loop: energy transfer from tryptophan to AEDANS. FEBS Lett. 1996 Mar 25;383(1-2):105–108. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(96)00238-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer S. S., Nagy B., Gergely J. The binding of Cu 2+ to actin without loss of polymerizability: the involvement of the rapidly reacting -SH group. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 May;150(1):164–174. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz M., Popp D., Holmes K. C. Refinement of the F-actin model against X-ray fiber diffraction data by the use of a directed mutation algorithm. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):826–836. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlrad A., Cheung P., Phan B. C., Miller C., Reisler E. Dynamic properties of actin. Structural changes induced by beryllium fluoride. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 22;269(16):11852–11858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlova A., Egelman E. H. A conformational change in the actin subunit can change the flexibility of the actin filament. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):334–341. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlova A., Egelman E. H. Structural basis for the destabilization of F-actin by phosphate release following ATP hydrolysis. J Mol Biol. 1992 Oct 20;227(4):1043–1053. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90520-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlova A., Egelman E. H. Structural dynamics of F-actin: I. Changes in the C terminus. J Mol Biol. 1995 Feb 3;245(5):582–597. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlova A., Prochniewicz E., Egelman E. H. Structural dynamics of F-actin: II. Cooperativity in structural transitions. J Mol Biol. 1995 Feb 3;245(5):598–607. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.0049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen C., DeRosier D. A 13-A map of the actin-scruin filament from the limulus acrosomal process. J Cell Biol. 1993 Oct;123(2):337–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyter D. H., Kron S. J., Toyoshima Y. Y., Spudich J. A., Reisler E. Subtilisin cleavage of actin inhibits in vitro sliding movement of actin filaments over myosin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):465–470. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwyter D., Phillips M., Reisler E. Subtilisin-cleaved actin: polymerization and interaction with myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 11;28(14):5889–5895. doi: 10.1021/bi00440a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strzelecka-Gołaszewska H., Moraczewska J., Khaitlina S. Y., Mossakowska M. Localization of the tightly bound divalent-cation-dependent and nucleotide-dependent conformation changes in G-actin using limited proteolytic digestion. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Feb 1;211(3):731–742. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb17603.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tirion M. M., ben-Avraham D., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C. Normal modes as refinement parameters for the F-actin model. Biophys J. 1995 Jan;68(1):5–12. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80156-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeds A. G., Pope B. Studies on the chymotryptic digestion of myosin. Effects of divalent cations on proteolytic susceptibility. J Mol Biol. 1977 Apr;111(2):129–157. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


