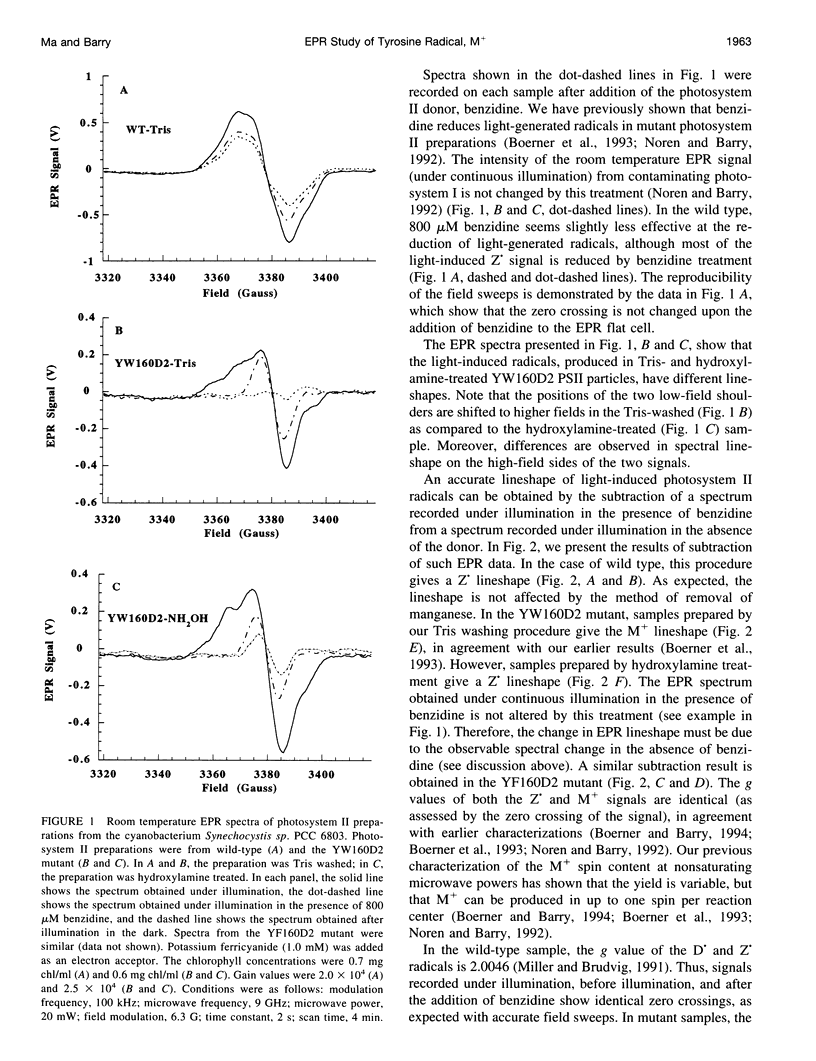
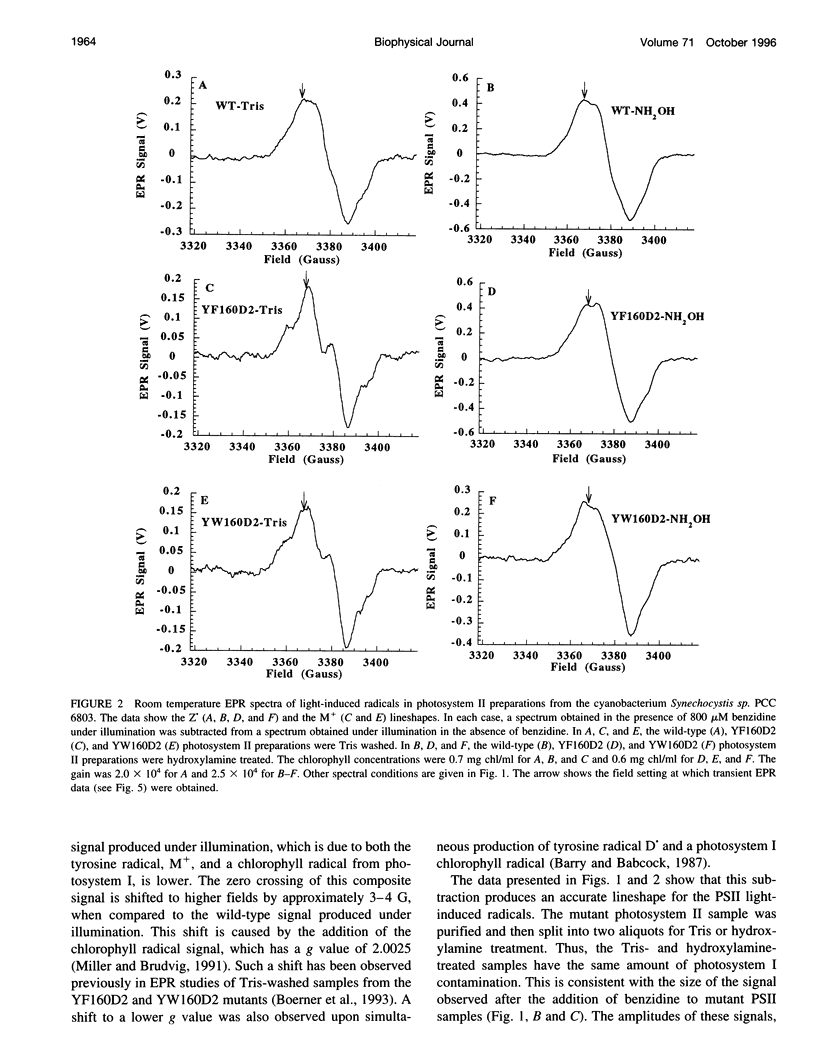
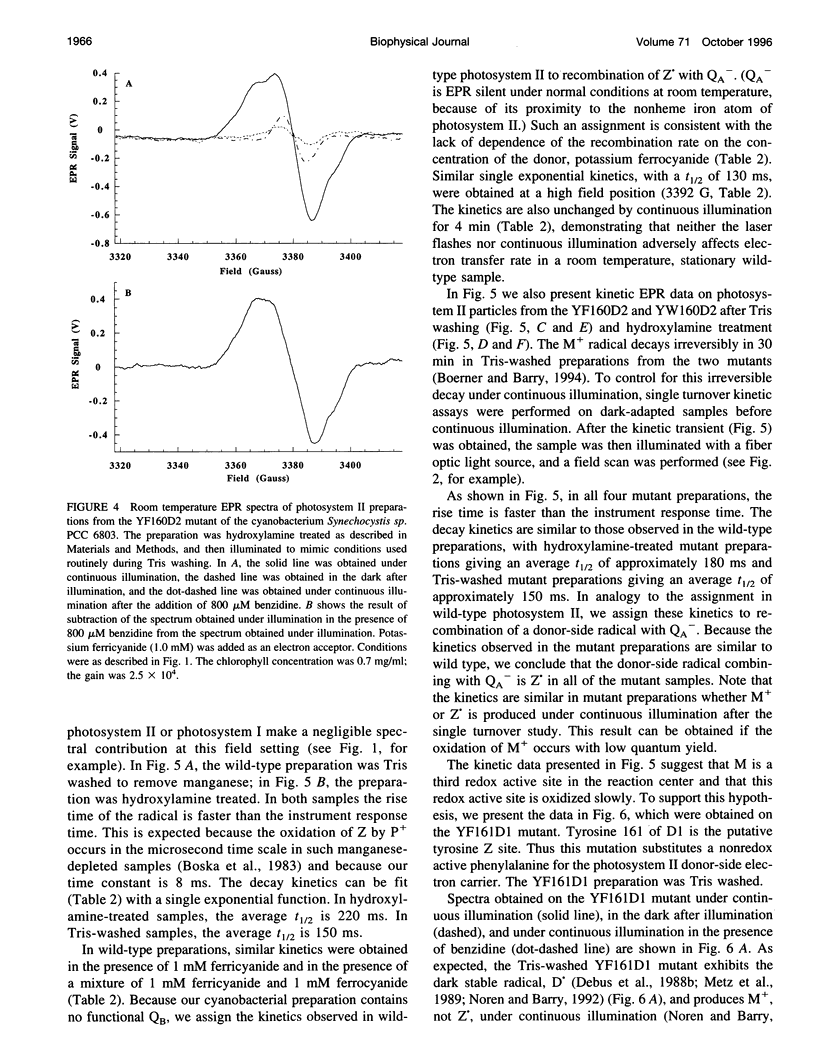
Abstract
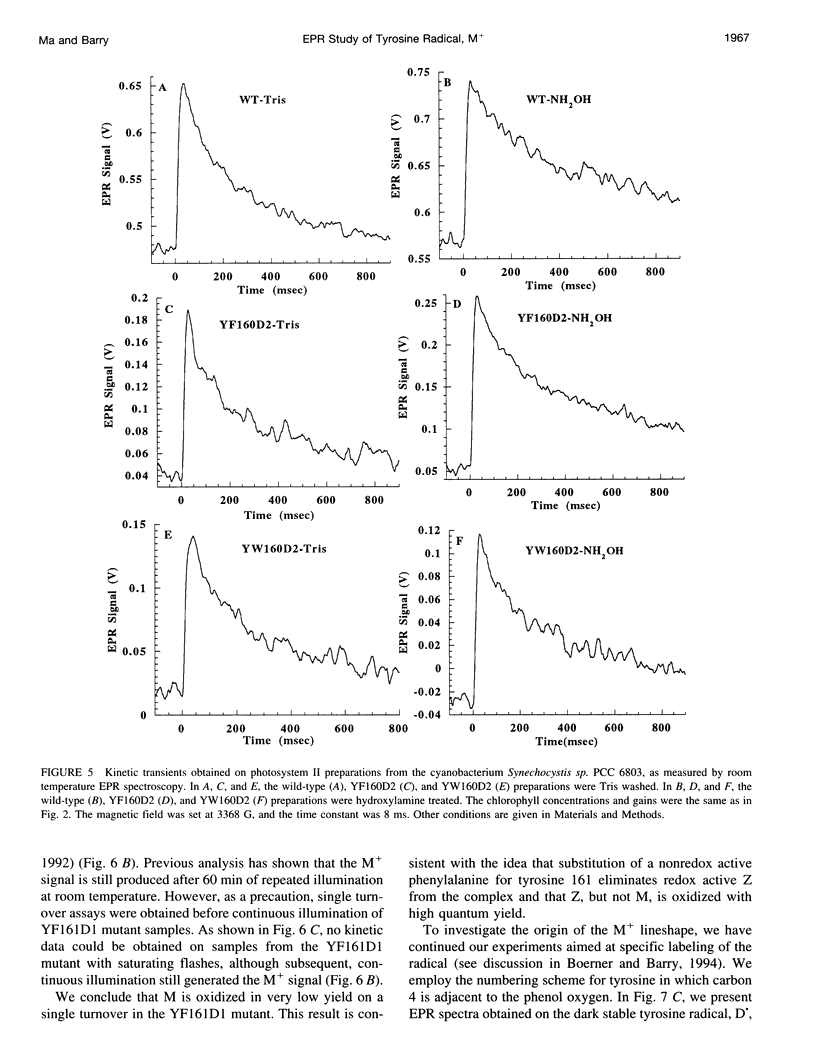
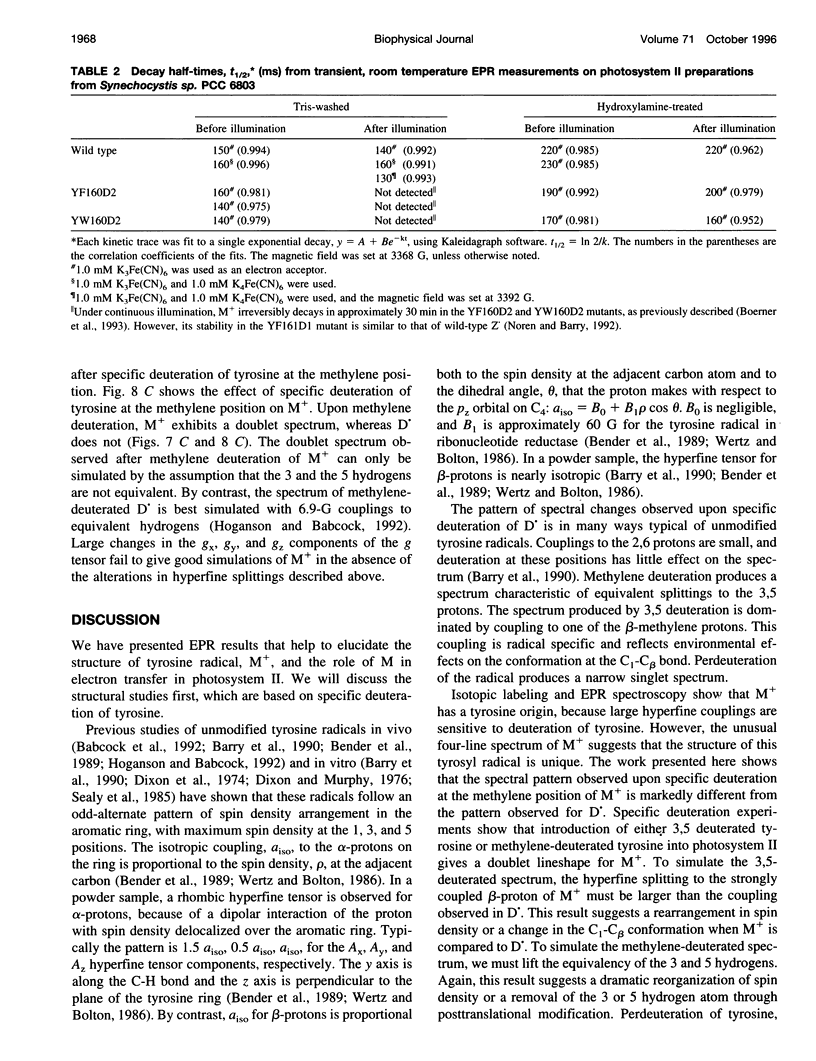
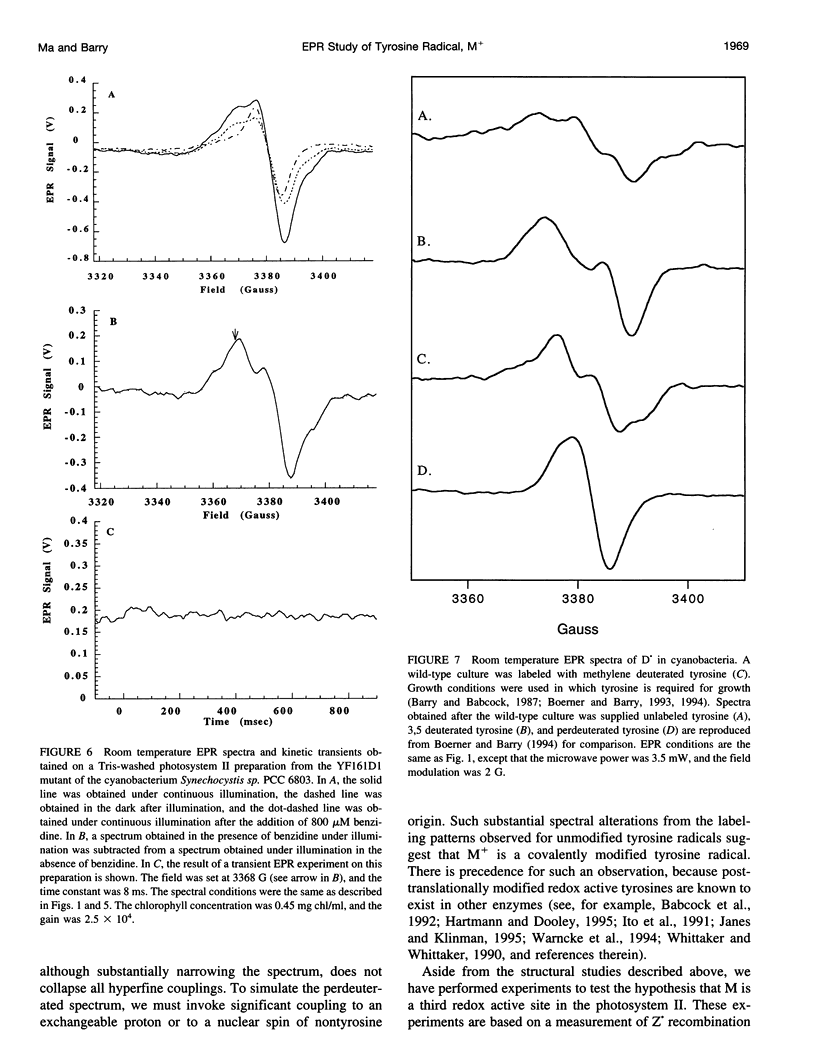
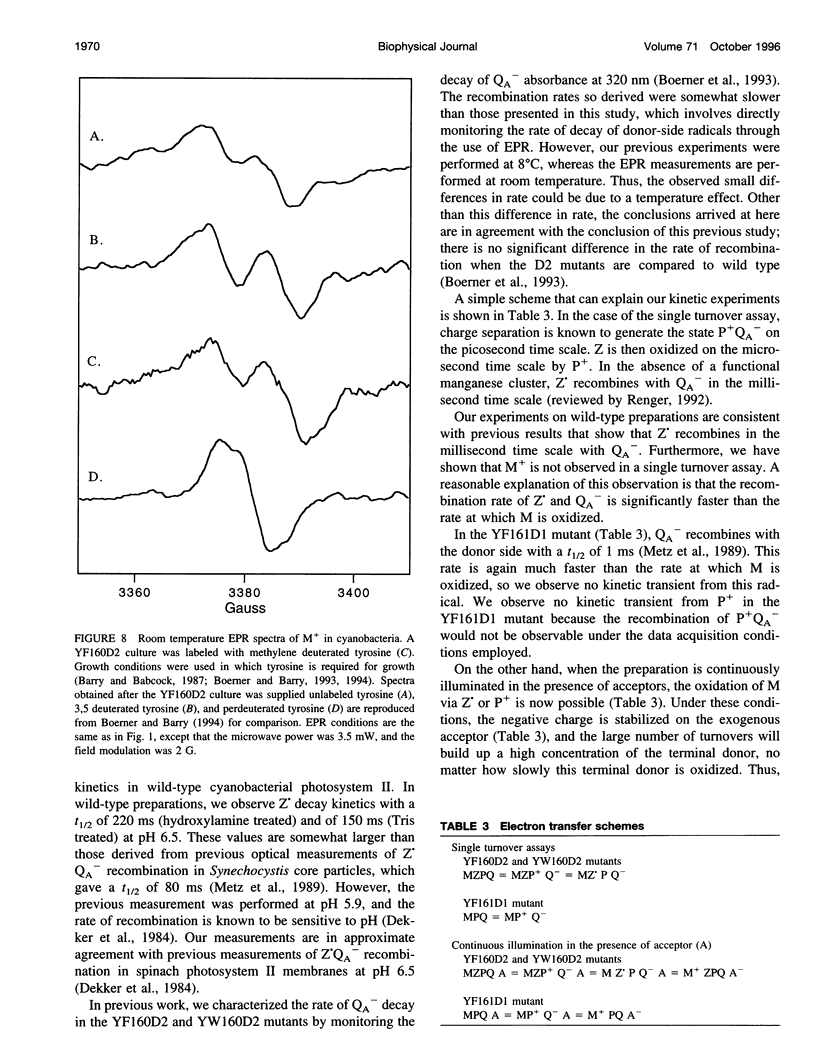
Photosystem II contains two well-characterized tyrosine radicals, D(.) and Z(.). Z is an electron carrier between the primary chlorophyll donor and the manganese catalytic site and is essential for enzymatic function. On the other hand, D forms a stable radical with no known role in oxygen evolution. D(.) and Z(.) give rise to similar, but not identical, room temperature electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) signals, which can be distinguished by their decay kinetics. A third room temperature EPR signal has also been observed in site-directed mutants in which a nonredox active amino acid is substituted at the D or Z site. This four-line EPR signal has been shown to have a tyrosine origin by isotopic labeling (Boerner and Barry, 1994, J. Biol. Chem. 269:134-137), but such an EPR signal has never before been observed from a tyrosyl radical. The radical giving rise to this third unique signal has been named M+. Here we provide kinetic evidence that this signal arises from a third redox active tyrosine, distinct from tyrosine D and Z, in the photosystem II reaction center. Isotopic labeling and EPR spectroscopy provide evidence that M is a covalently modified tyrosine.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babcock G. T., Sauer K. Two electron donation sites for exogenous reductants in chloroplast photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 8;396(1):48–62. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(75)90188-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry B. A., Babcock G. T. Tyrosine radicals are involved in the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7099–7103. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry B. A. The role of redox-active amino acids in the photosynthetic water-oxidizing complex. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 Jan;57(1):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb02275.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry B. A. Tyrosyl radicals in photosystem II. Methods Enzymol. 1995;258:303–319. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)58053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry B. A., el-Deeb M. K., Sandusky P. O., Babcock G. T. Tyrosine radicals in photosystem II and related model compounds. Characterization by isotopic labeling and EPR spectroscopy. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20139–20143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. T., MacDonald G. M., Nguyen A. P., Debus R. J., Barry B. A. A difference infrared study of hydrogen bonding to the Z. tyrosyl radical of photosystem II. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jan 27;270(4):1589–1594. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.4.1589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerner R. J., Barry B. A. EPR evidence that the M+ radical, which is observed in three site-directed mutants of photosystem II, is a tyrosine radical. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 7;269(1):134–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerner R. J., Barry B. A. Isotopic labeling and EPR spectroscopy show that a tyrosine residue is the terminal electron donor, Z, in manganese-depleted photosystem II preparations. J Biol Chem. 1993 Aug 15;268(23):17151–17154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerner R. J., Bixby K. A., Nguyen A. P., Noren G. H., Debus R. J., Barry B. A. Removal of stable tyrosine radical D+ affects the structure or redox properties of tyrosine Z in manganese-depleted photosystem II particles from Synechocystis 6803. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1817–1823. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerner R. J., Nguyen A. P., Barry B. A., Debus R. J. Evidence from directed mutagenesis that aspartate 170 of the D1 polypeptide influences the assembly and/or stability of the manganese cluster in the photosynthetic water-splitting complex. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6660–6672. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus R. J., Barry B. A., Babcock G. T., McIntosh L. Site-directed mutagenesis identifies a tyrosine radical involved in the photosynthetic oxygen-evolving system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):427–430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus R. J., Barry B. A., Sithole I., Babcock G. T., McIntosh L. Directed mutagenesis indicates that the donor to P+680 in photosystem II is tyrosine-161 of the D1 polypeptide. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9071–9074. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus R. J. The manganese and calcium ions of photosynthetic oxygen evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 16;1102(3):269–352. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(92)90133-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frasch W. D., Cheniae G. M. Flash Inactivation of Oxygen Evolution: IDENTIFICATION OF S(2) AS THE TARGET OF INACTIVATION BY TRIS. Plant Physiol. 1980 Apr;65(4):735–745. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.4.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann C., Dooley D. M. Detection of reaction intermediates in topa quinone enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1995;258:69–90. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)58038-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoganson C. W., Babcock G. T. Protein-tyrosyl radical interactions in photosystem II studied by electron spin resonance and electron nuclear double resonance spectroscopy: comparison with ribonucleotide reductase and in vitro tyrosine. Biochemistry. 1992 Dec 1;31(47):11874–11880. doi: 10.1021/bi00162a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito N., Phillips S. E., Stevens C., Ogel Z. B., McPherson M. J., Keen J. N., Yadav K. D., Knowles P. F. Novel thioether bond revealed by a 1.7 A crystal structure of galactose oxidase. Nature. 1991 Mar 7;350(6313):87–90. doi: 10.1038/350087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janes S. M., Klinman J. P. Isolation of 2,4,5-trihydroxyphenylalanine quinone (topa quinone) from copper amine oxidases. Methods Enzymol. 1995;258:20–34. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(95)58034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald G. M., Barry B. A. Difference FT-IR study of a novel biochemical preparation of photosystem II. Biochemistry. 1992 Oct 13;31(40):9848–9856. doi: 10.1021/bi00155a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz J. G., Nixon P. J., Rögner M., Brudvig G. W., Diner B. A. Directed alteration of the D1 polypeptide of photosystem II: evidence that tyrosine-161 is the redox component, Z, connecting the oxygen-evolving complex to the primary electron donor, P680. Biochemistry. 1989 Aug 22;28(17):6960–6969. doi: 10.1021/bi00443a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. F., Brudvig G. W. A guide to electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of Photosystem II membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jan 3;1056(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(05)80067-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nanba O., Satoh K. Isolation of a photosystem II reaction center consisting of D-1 and D-2 polypeptides and cytochrome b-559. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):109–112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noren G. H., Barry B. A. The YF161D1 mutant of Synechocystis 6803 exhibits an EPR signal from a light-induced photosystem II radical. Biochemistry. 1992 Apr 7;31(13):3335–3342. doi: 10.1021/bi00128a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noren G. H., Boerner R. J., Barry B. A. EPR characterization of an oxygen-evolving photosystem II preparation from the transformable cyanobacterium Synechocystis 6803. Biochemistry. 1991 Apr 23;30(16):3943–3950. doi: 10.1021/bi00230a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp R. R., Yocum C. F. Factors influencing hydroxylamine inactivation of photosynthetic water oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Mar 12;635(1):90–104. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(81)90010-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermass W. F., Rutherford A. W., Hansson O. Site-directed mutagenesis in photosystem II of the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803: Donor D is a tyrosine residue in the D2 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8477–8481. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker M. M., Whittaker J. W. A tyrosine-derived free radical in apogalactose oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9610–9613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yocum C. F., Yerkes C. T., Blankenship R. E., Sharp R. R., Babcock G. T. Stoichiometry, inhibitor sensitivity, and organization of manganese associated with photosynthetic oxygen evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7507–7511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]