Abstract
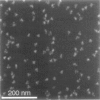
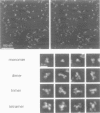
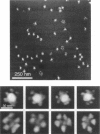
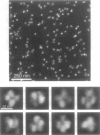
It has long been recognized that one of the major limitations in biological atomic force microscopy (AFM) is the softness of most biological samples, which are easily deformed or damaged by the AFM tip, because of the high pressure in the contact area, especially from the very sharp tips required for high resolution. Another is the molecular motion present at room temperature due to thermal fluctuation. Using an AFM operated in liquid nitrogen vapor (cryo-AFM), we demonstrate that cryo-AFM can be applied to a large variety of biological samples, from immunoglobulins to DNA to cell surfaces. The resolution achieved with cryo-AFM is much improved when compared with AFM at room temperature with similar specimens, and is comparable to that of cryo-electron microscopy on randomly oriented macromolecules. We will also discuss the technical problems that remain to be solved for achieving even higher resolution with cryo-AFM and other possible applications of this novel technique.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersen G. R., Koch T. J., Dolmer K., Sottrup-Jensen L., Nyborg J. Low resolution X-ray structure of human methylamine-treated alpha 2-macroglobulin. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 20;270(42):25133–25141. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.42.25133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Starkey P. M. The interaction of alpha 2-macroglobulin with proteinases. Characteristics and specificity of the reaction, and a hypothesis concerning its molecular mechanism. Biochem J. 1973 Aug;133(4):709–724. doi: 10.1042/bj1330709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binnig G, Quate CF, Gerber C. Atomic force microscope. Phys Rev Lett. 1986 Mar 3;56(9):930–933. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.56.930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer J. W., Randall T. D., Parkhouse R. M., Corley R. B. IgM hexamers? Immunol Today. 1994 Apr;15(4):165–168. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(94)90313-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bustamante C., Vesenka J., Tang C. L., Rees W., Guthold M., Keller R. Circular DNA molecules imaged in air by scanning force microscopy. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 14;31(1):22–26. doi: 10.1021/bi00116a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DODGE J. T., MITCHELL C., HANAHAN D. J. The preparation and chemical characteristics of hemoglobin-free ghosts of human erythrocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Jan;100:119–130. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90042-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delain E., Pochon F., Barray M., Van Leuven F. Ultrastructure of alpha 2-macroglobulins. Electron Microsc Rev. 1992;5(2):231–281. doi: 10.1016/0892-0354(92)90012-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edidin M. Patches and fences: probing for plasma membrane domains. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1993;17:165–169. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1993.supplement_17.24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A. Biological applications of scanning probe microscopes. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1991;20:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.20.060191.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flicker P. F., Wallimann T., Vibert P. Electron microscopy of scallop myosin. Location of regulatory light chains. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):723–741. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallett P., Offer G., Miles M. J. Atomic force microscopy of the myosin molecule. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4):1604–1606. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80333-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han W., Mou J., Sheng J., Yang J., Shao Z. Cryo atomic force microscopy: a new approach for biological imaging at high resolution. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 4;34(26):8215–8220. doi: 10.1021/bi00026a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Hoh J. H. Biomolecular imaging with the atomic force microscope. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1994;23:115–139. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.23.060194.000555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansma H. G., Laney D. E., Bezanilla M., Sinsheimer R. L., Hansma P. K. Applications for atomic force microscopy of DNA. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80343-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson E., Haydon P. G., Sakaguchi D. S. Actin filament dynamics in living glial cells imaged by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1992 Sep 25;257(5078):1944–1946. doi: 10.1126/science.1411511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. The potential and limitations of neutrons, electrons and X-rays for atomic resolution microscopy of unstained biological molecules. Q Rev Biophys. 1995 May;28(2):171–193. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000305x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., Schoenenberger C. A. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of MDCK monolayers by atomic force microscopy. J Cell Sci. 1994 May;107(Pt 5):1105–1114. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.5.1105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikai A., Kikuchi M., Nishigai M. Internal structure of ovomacroglobulin studied by electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8280–8284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ill C. R., Keivens V. M., Hale J. E., Nakamura K. K., Jue R. A., Cheng S., Melcher E. D., Drake B., Smith M. C. A COOH-terminal peptide confers regiospecific orientation and facilitates atomic force microscopy of an IgG1. Biophys J. 1993 Mar;64(3):919–924. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81452-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larquet E., Boisset N., Pochon F., Lamy J. Architecture of native human alpha 2-macroglobulin studied by cryoelectron microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction. J Struct Biol. 1994 Jul-Aug;113(1):87–98. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1994.1034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. B., Figler N. L., Gonias S. L. Identification of alpha 2-macroglobulin conformational intermediates by electron microscopy and image analysis. Comparison of alpha 2-macroglobulin-thrombin and alpha 2-macroglobulin reacted with cis-dichlorodiammineplatinum(II) and trypsin. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):6347–6352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Transmembrane signaling: the joy of aggregation. J Immunol. 1992 Sep 1;149(5):1477–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mou J., Czajkowsky D. M., Zhang Y., Shao Z. High-resolution atomic-force microscopy of DNA: the pitch of the double helix. FEBS Lett. 1995 Sep 11;371(3):279–282. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00906-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mou J., Yang J., Shao Z. Atomic force microscopy of cholera toxin B-oligomers bound to bilayers of biologically relevant lipids. J Mol Biol. 1995 May 5;248(3):507–512. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1995.0238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller D. J., Schabert F. A., Büldt G., Engel A. Imaging purple membranes in aqueous solutions at sub-nanometer resolution by atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1995 May;68(5):1681–1686. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80345-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkhouse R. M., Askonas B. A., Dourmashkin R. R. Electron microscopic studies of mouse immunoglobulin M; structure and reconstitution following reduction. Immunology. 1970 Apr;18(4):575–584. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins S. J., Nealis A. S., Sutton B. J., Feinstein A. Solution structure of human and mouse immunoglobulin M by synchrotron X-ray scattering and molecular graphics modelling. A possible mechanism for complement activation. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1345–1366. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90937-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poljak R. J. X-ray diffraction studies of immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1975;21:1–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putman C. A., van der Werf K. O., de Grooth B. G., van Hulst N. F., Greve J. Viscoelasticity of living cells allows high resolution imaging by tapping mode atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1749–1753. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80649-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodgers W., Glaser M. Distributions of proteins and lipids in the erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12591–12598. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schabert F. A., Henn C., Engel A. Native Escherichia coli OmpF porin surfaces probed by atomic force microscopy. Science. 1995 Apr 7;268(5207):92–94. doi: 10.1126/science.7701347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao Z., Yang J. Progress in high resolution atomic force microscopy in biology. Q Rev Biophys. 1995 May;28(2):195–251. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500003061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shao Z., Yang J., Somlyo A. P. Biological atomic force microscopy: from microns to nanometers and beyond. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 1995;11:241–265. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.11.110195.001325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheets E. D., Simson R., Jacobson K. New insights into membrane dynamics from the analysis of cell surface interactions by physical methods. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;7(5):707–714. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80113-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smythe E., Warren G. The mechanism of receptor-mediated endocytosis. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):689–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16424.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. H., Fritz M., Radmacher M., Cleveland J. P., Schmidt C. F., Hansma P. K. Protein tracking and detection of protein motion using atomic force microscopy. Biophys J. 1996 May;70(5):2421–2431. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79812-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urry D. W. Entropic elastic processes in protein mechanisms. I. Elastic structure due to an inverse temperature transition and elasticity due to internal chain dynamics. J Protein Chem. 1988 Feb;7(1):1–34. doi: 10.1007/BF01025411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Langendries A., Vander Maelen C. Homogenous IgA monomers, dimers, trimers and tetramers from the same IgA myeloma serum. Immunol Invest. 1995 May;24(4):631–641. doi: 10.3109/08820139509066863. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. F., Cech T. R. Tertiary structure around the guanosine-binding site of the Tetrahymena ribozyme. Science. 1992 Apr 24;256(5056):526–529. doi: 10.1126/science.1315076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Mou J., Shao Z. Molecular resolution atomic force microscopy of soluble proteins in solution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Mar 2;1199(2):105–114. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(94)90104-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Mou J., Shao Z. Structure and stability of pertussis toxin studied by in situ atomic force microscopy. FEBS Lett. 1994 Jan 24;338(1):89–92. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)80122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Takeyasu K., Shao Z. Atomic force microscopy of DNA molecules. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 20;301(2):173–176. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81241-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Tamm L. K., Somlyo A. P., Shao Z. Promises and problems of biological atomic force microscopy. J Microsc. 1993 Sep;171(Pt 3):183–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1993.tb03375.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Tamm L. K., Tillack T. W., Shao Z. New approach for atomic force microscopy of membrane proteins. The imaging of cholera toxin. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jan 20;229(2):286–290. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]