Abstract
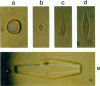
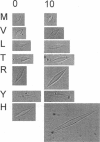
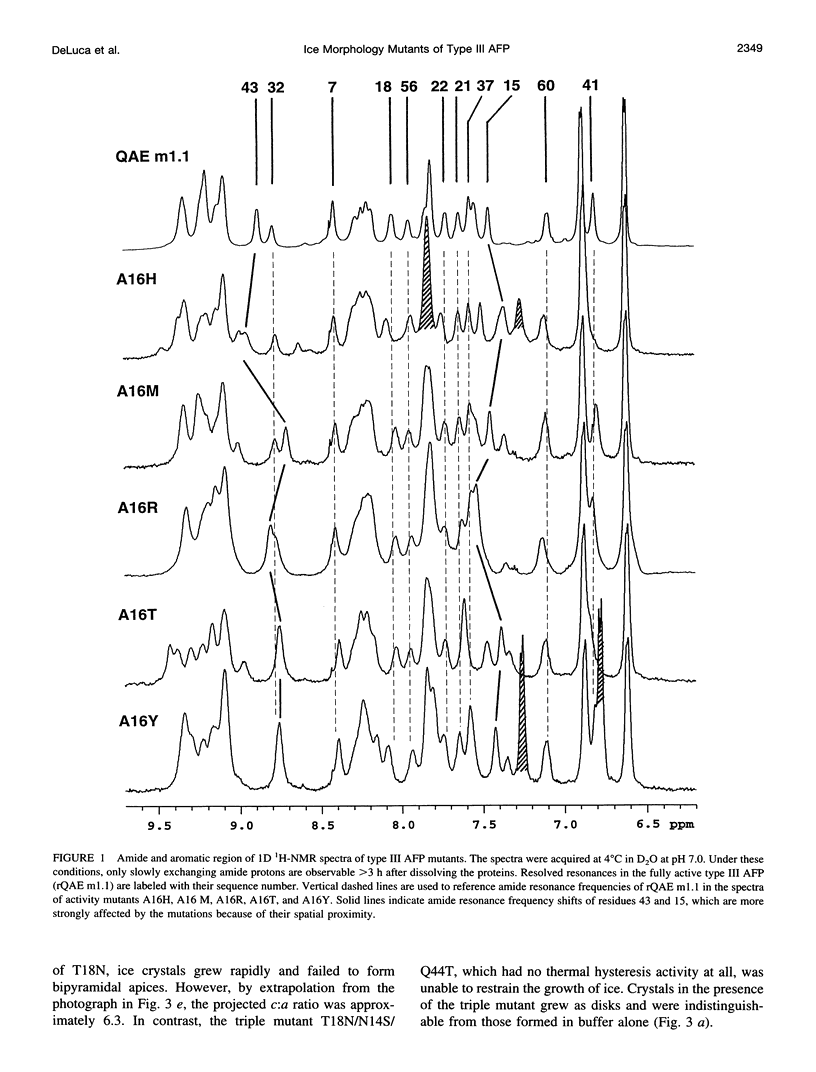
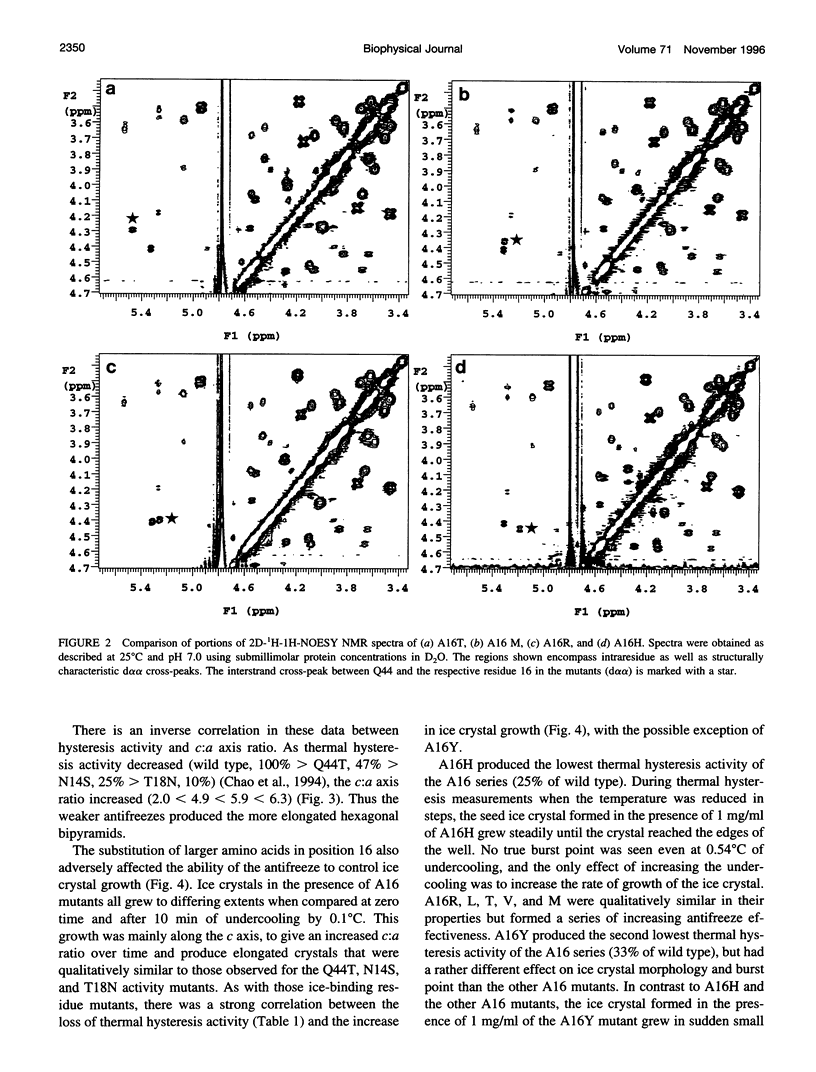
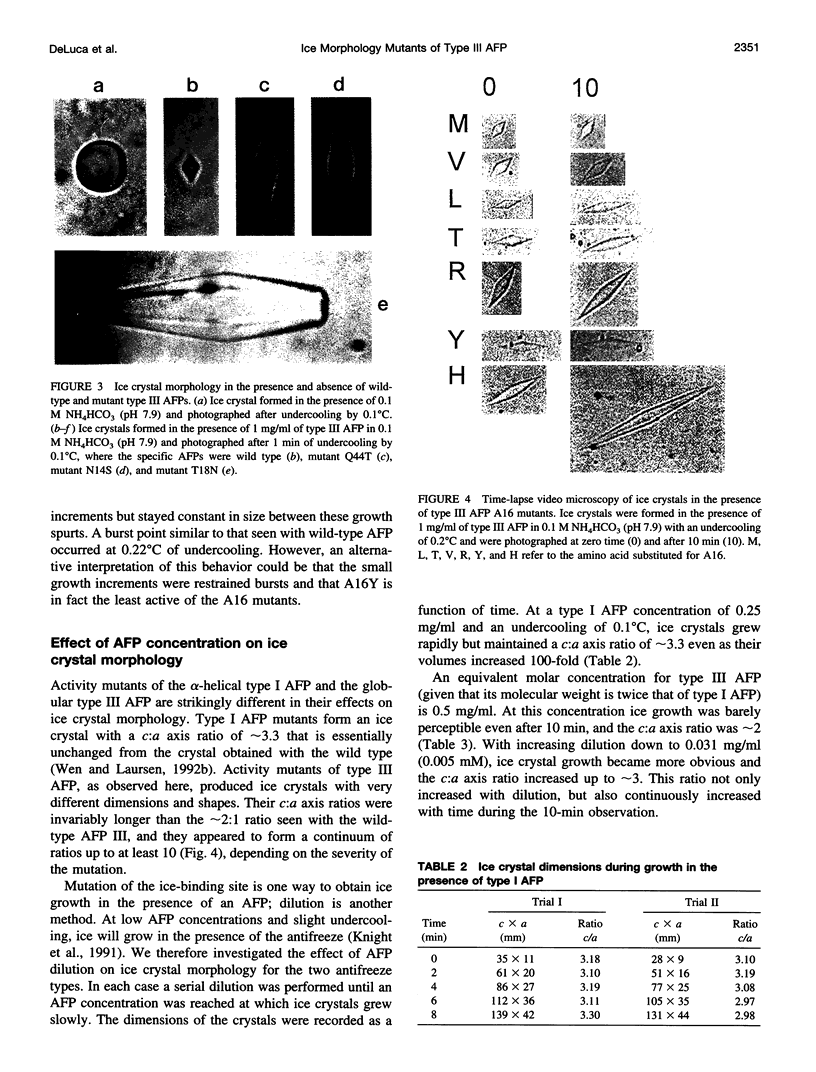
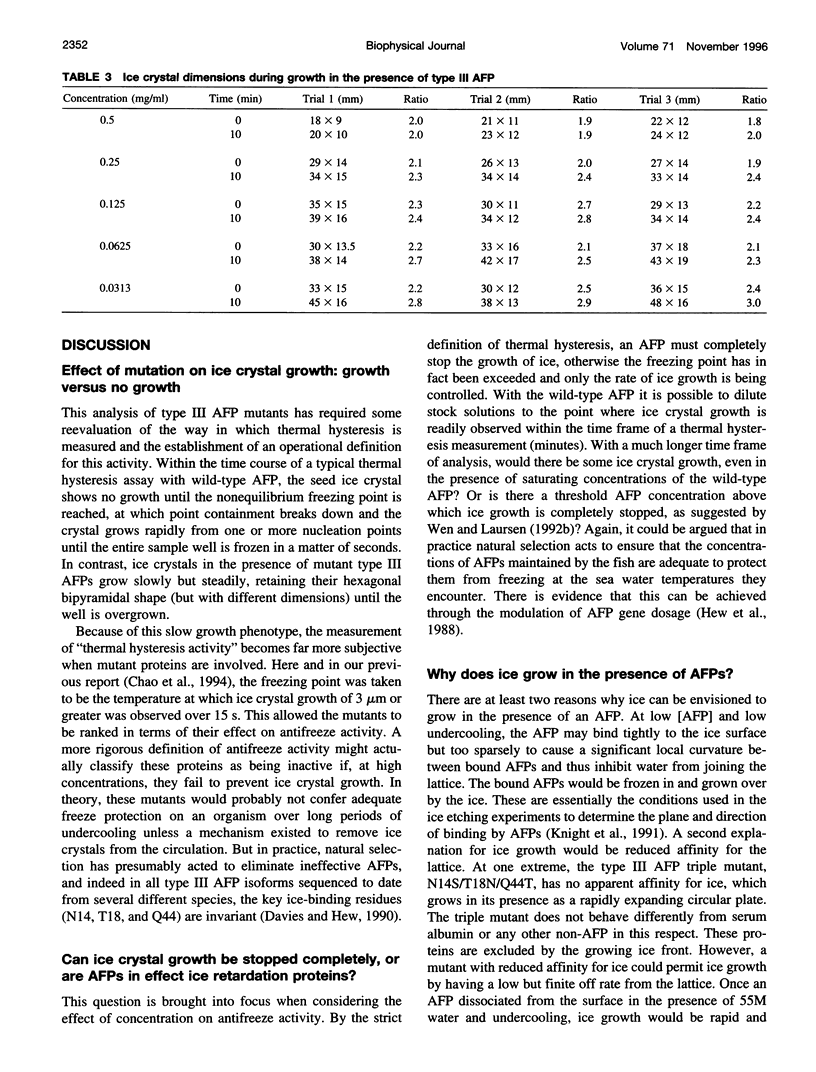
Mutation of residues at the ice-binding site of type III antifreeze protein (AFP) not only reduced antifreeze activity as indicated by the failure to halt ice crystal growth, but also altered ice crystal morphology to produce elongated hexagonal bipyramids. In general, the c axis to a axis ratio of the ice crystal increased from approximately 2 to over 10 with the severity of the mutation. It also increased during ice crystal growth upon serial dilution of the wild-type AFP. This is in marked contrast to the behavior of the alpha-helical type I AFPs, where neither dilution nor mutation of ice-binding residues increases the c:a axial ratio of the ice crystal above the standard 3.3. We suggest that the ice crystal morphology produced by type III AFP and its mutants can be accounted for by the protein binding to the prism faces of ice and operating by step growth inhibition. In this model a decrease in the affinity of the AFP for ice leads to filling in of individual steps at the prism surfaces, causing the ice crystals to grow with a longer c:a axial ratio.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthanarayanan V. S., Hew C. L. Structural studies on the freezing-point-depressing protein of the winter flounder Pseudopleuronectes americanus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 24;74(2):685–689. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)90357-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabartty A., Hew C. L. The effect of enhanced alpha-helicity on the activity of a winter flounder antifreeze polypeptide. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 18;202(3):1057–1063. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao H., Davies P. L., Sykes B. D., Sönnichsen F. D. Use of proline mutants to help solve the NMR solution structure of type III antifreeze protein. Protein Sci. 1993 Sep;2(9):1411–1428. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao H., DeLuca C. I., Davies P. L. Mixing antifreeze protein types changes ice crystal morphology without affecting antifreeze activity. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jan 3;357(2):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)01357-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao H., Sönnichsen F. D., DeLuca C. I., Sykes B. D., Davies P. L. Structure-function relationship in the globular type III antifreeze protein: identification of a cluster of surface residues required for binding to ice. Protein Sci. 1994 Oct;3(10):1760–1769. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560031016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou K. C. Energy-optimized structure of antifreeze protein and its binding mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 20;223(2):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90666-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies P. L., Hew C. L. Biochemistry of fish antifreeze proteins. FASEB J. 1990 May;4(8):2460–2468. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.8.2185972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLuca C. I., Davies P. L., Samis J. A., Elce J. S. Molecular cloning and bacterial expression of cDNA for rat calpain II 80 kDa subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Oct 19;1216(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90040-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeVries A. L., Komatsu S. K., Feeney R. E. Chemical and physical properties of freezing point-depressing glycoproteins from Antarctic fishes. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jun 10;245(11):2901–2908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devries A. L., Lin Y. Structure of a peptide antifreeze and mechanism of adsorption to ice. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Dec 20;495(2):388–392. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hew C. L., Wang N. C., Joshi S., Fletcher G. L., Scott G. K., Hayes P. H., Buettner B., Davies P. L. Multiple genes provide the basis for antifreeze protein diversity and dosage in the ocean pout, Macrozoarces americanus. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 25;263(24):12049–12055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen H., Mori M., Matsui H., Kanaoka M., Yanagi H., Yabusaki Y., Kikuzono Y. Molecular dynamics simulation of winter flounder antifreeze protein variants in solution: correlation between side chain spacing and ice lattice. Protein Eng. 1993 Jan;6(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/protein/6.1.19. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. A., Cheng C. C., DeVries A. L. Adsorption of alpha-helical antifreeze peptides on specific ice crystal surface planes. Biophys J. 1991 Feb;59(2):409–418. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82234-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. A., DeVries A. L., Oolman L. D. Fish antifreeze protein and the freezing and recrystallization of ice. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):295–296. doi: 10.1038/308295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight C. A., Driggers E., DeVries A. L. Adsorption to ice of fish antifreeze glycopeptides 7 and 8. Biophys J. 1993 Jan;64(1):252–259. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81361-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li X. M., Trinh K. Y., Hew C. L., Buettner B., Baenziger J., Davies P. L. Structure of an antifreeze polypeptide and its precursor from the ocean pout, Macrozoarces americanus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 25;260(24):12904–12909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng N. F., Trinh K. Y., Hew C. L. Structure of an antifreeze polypeptide precursor from the sea raven, Hemitripterus americanus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15690–15695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. A., DeVries A. L. Adsorption inhibition as a mechanism of freezing resistance in polar fishes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jun;74(6):2589–2593. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.6.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond J. A., Radding W., DeVries A. L. Circular dichroism of protein and glycoprotein fish antifreezes. Biopolymers. 1977 Nov;16(11):2575–2578. doi: 10.1002/bip.1977.360161119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sicheri F., Yang D. S. Ice-binding structure and mechanism of an antifreeze protein from winter flounder. Nature. 1995 Jun 1;375(6530):427–431. doi: 10.1038/375427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönnichsen F. D., Sykes B. D., Chao H., Davies P. L. The nonhelical structure of antifreeze protein type III. Science. 1993 Feb 19;259(5098):1154–1157. doi: 10.1126/science.8438165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sönnichsen F. D., Sykes B. D., Davies P. L. Comparative modeling of the three-dimensional structure of type II antifreeze protein. Protein Sci. 1995 Mar;4(3):460–471. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560040313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Laursen R. A. A model for binding of an antifreeze polypeptide to ice. Biophys J. 1992 Dec;63(6):1659–1662. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81750-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Laursen R. A. Structure-function relationships in an antifreeze polypeptide. The role of neutral, polar amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 15;267(20):14102–14108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson P. W., Beaglehole D., Devries A. L. Antifreeze glycopeptide adsorption on single crystal ice surfaces using ellipsometry. Biophys J. 1993 Jun;64(6):1878–1884. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81559-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang D. S., Sax M., Chakrabartty A., Hew C. L. Crystal structure of an antifreeze polypeptide and its mechanistic implications. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):232–237. doi: 10.1038/333232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]