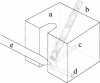
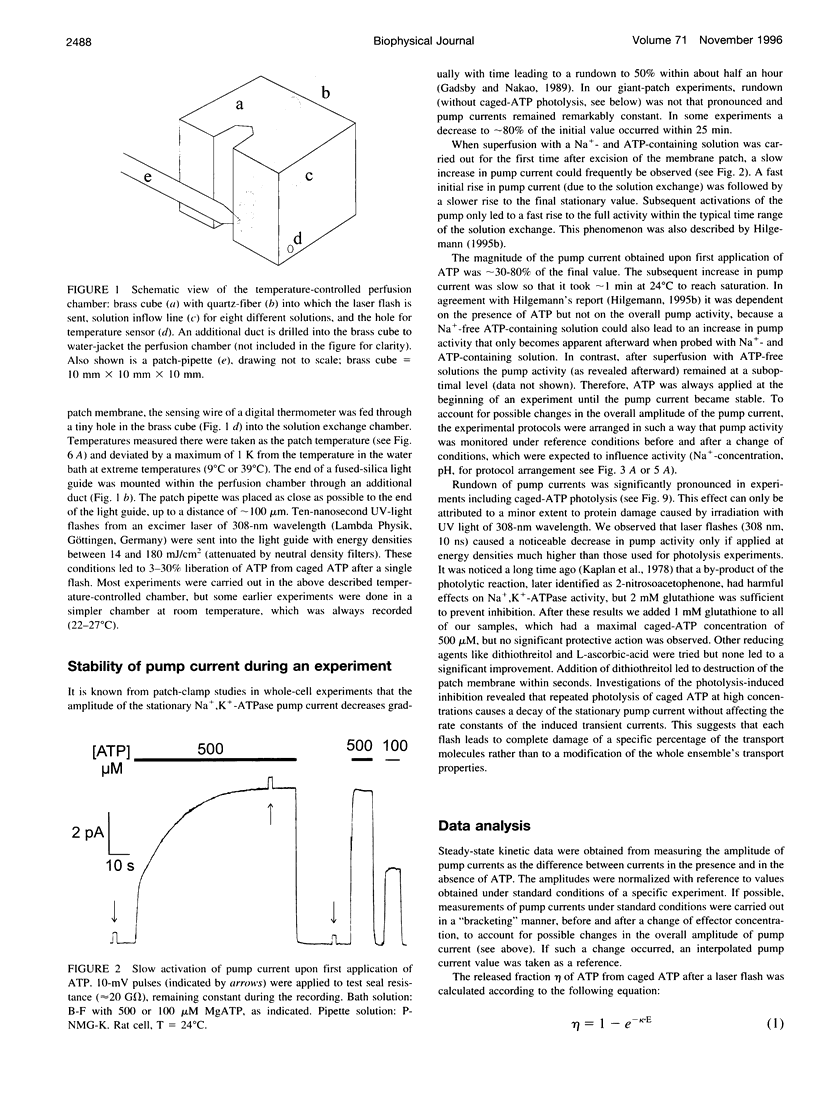
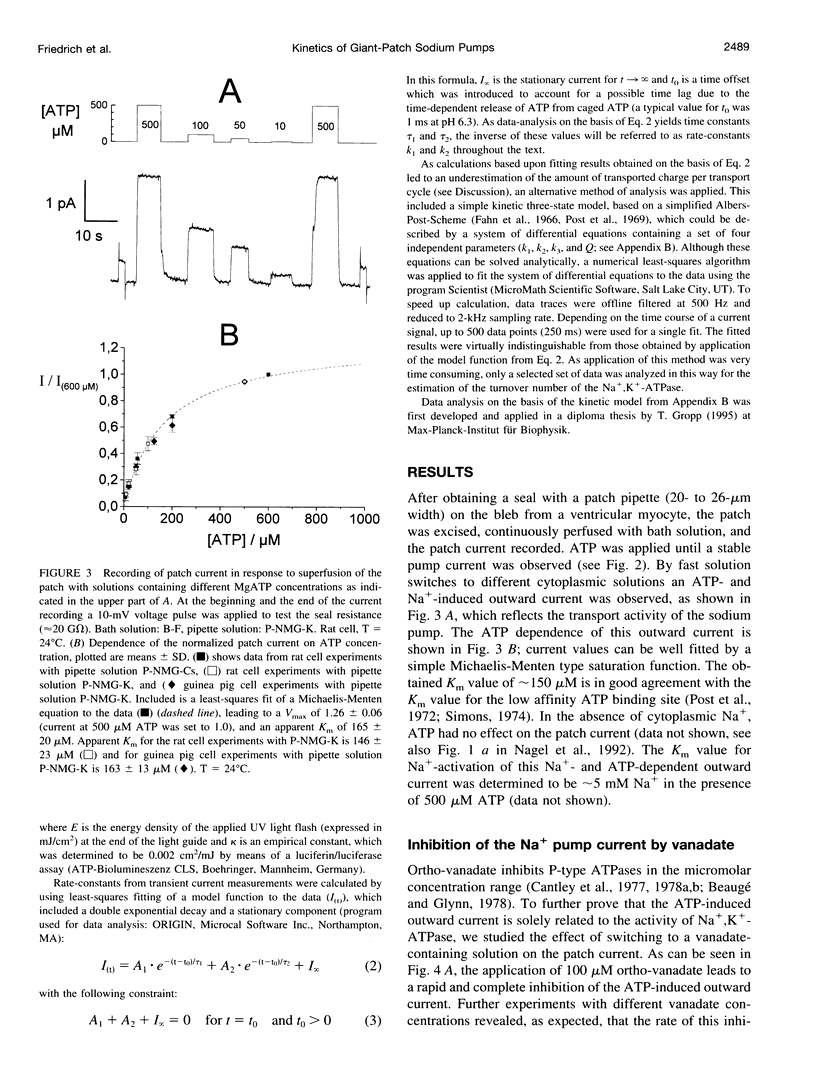
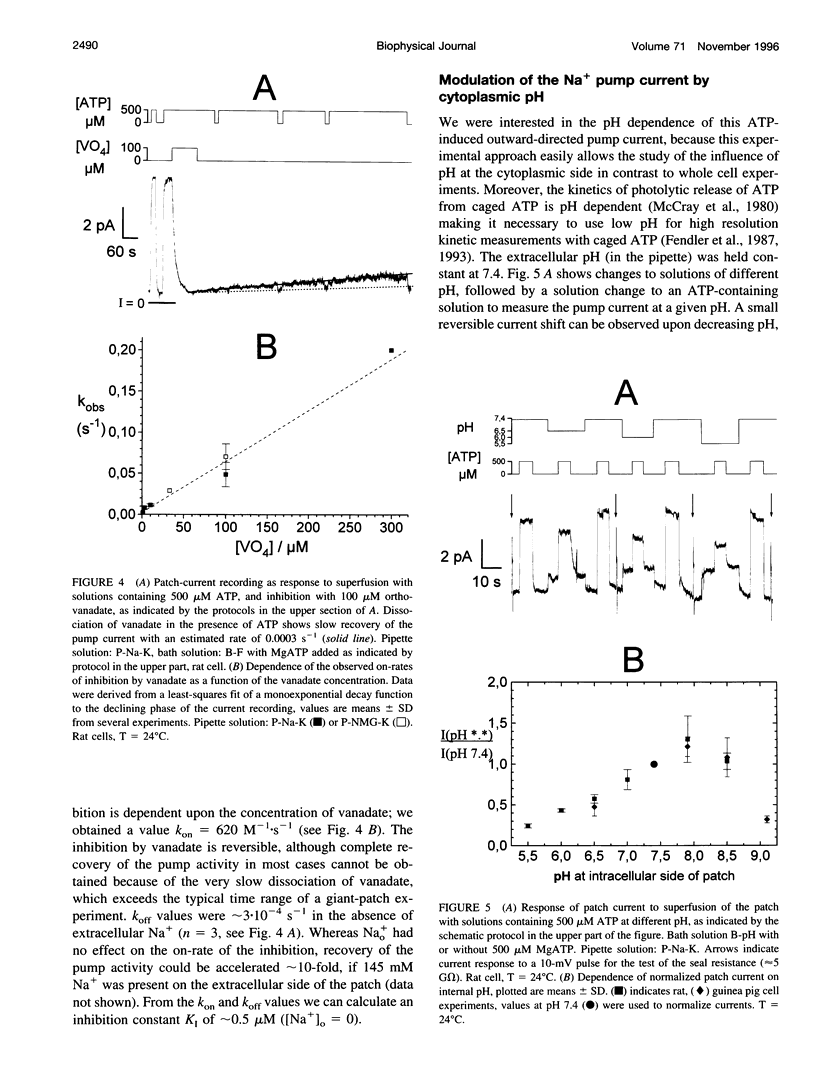
Abstract
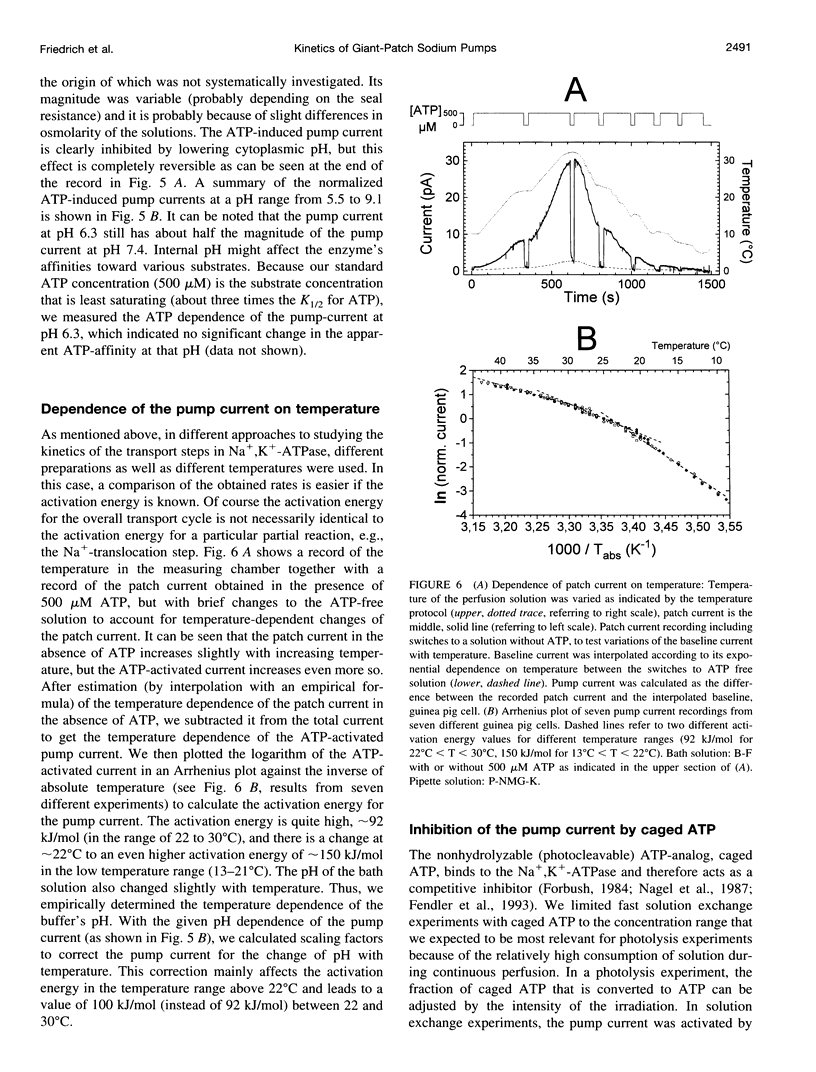
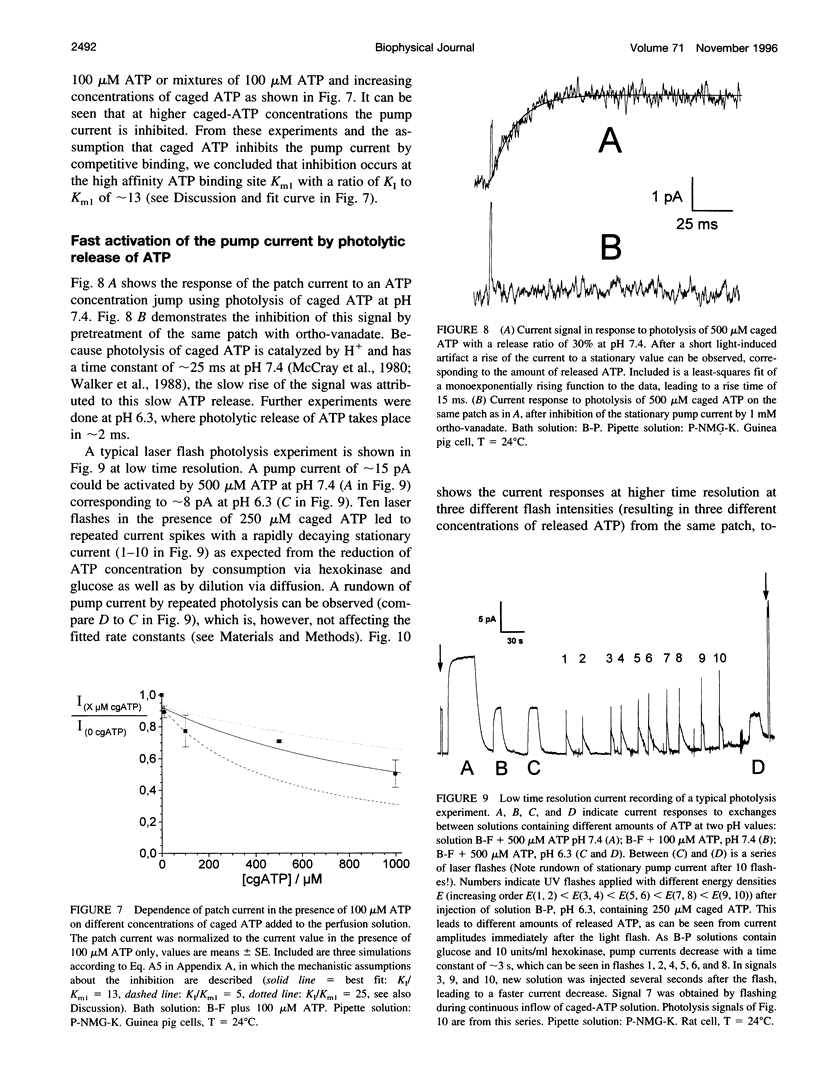
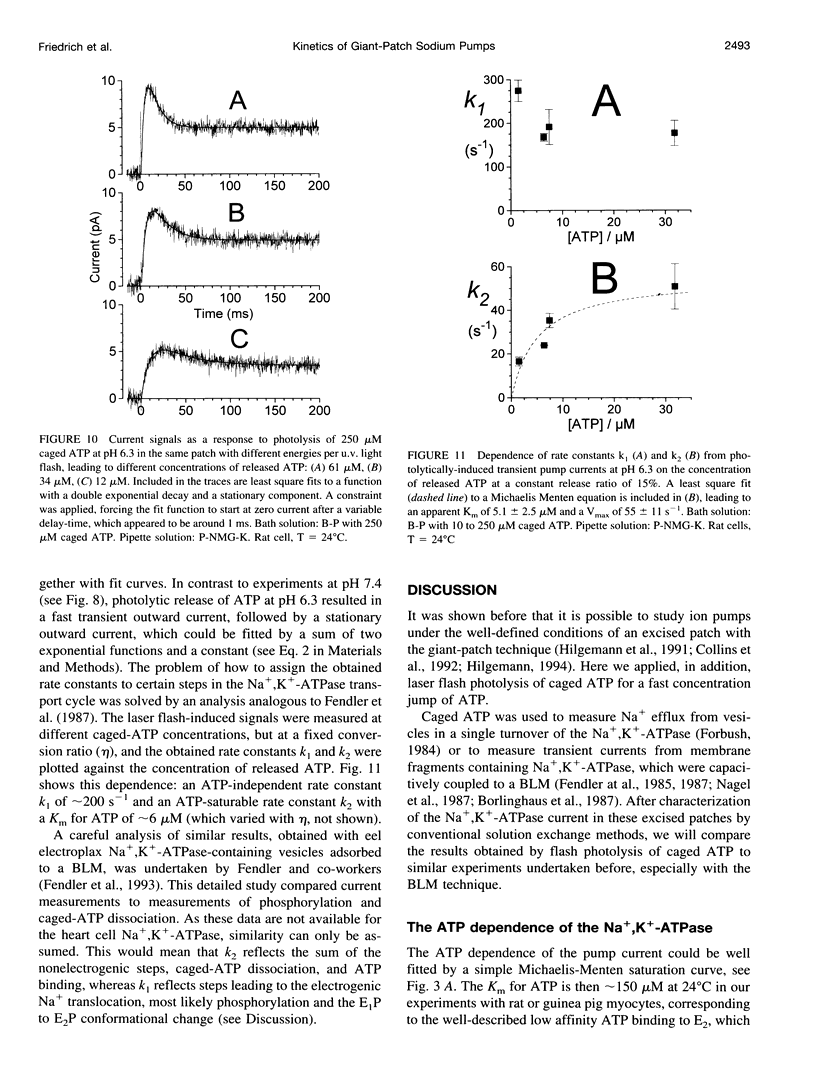
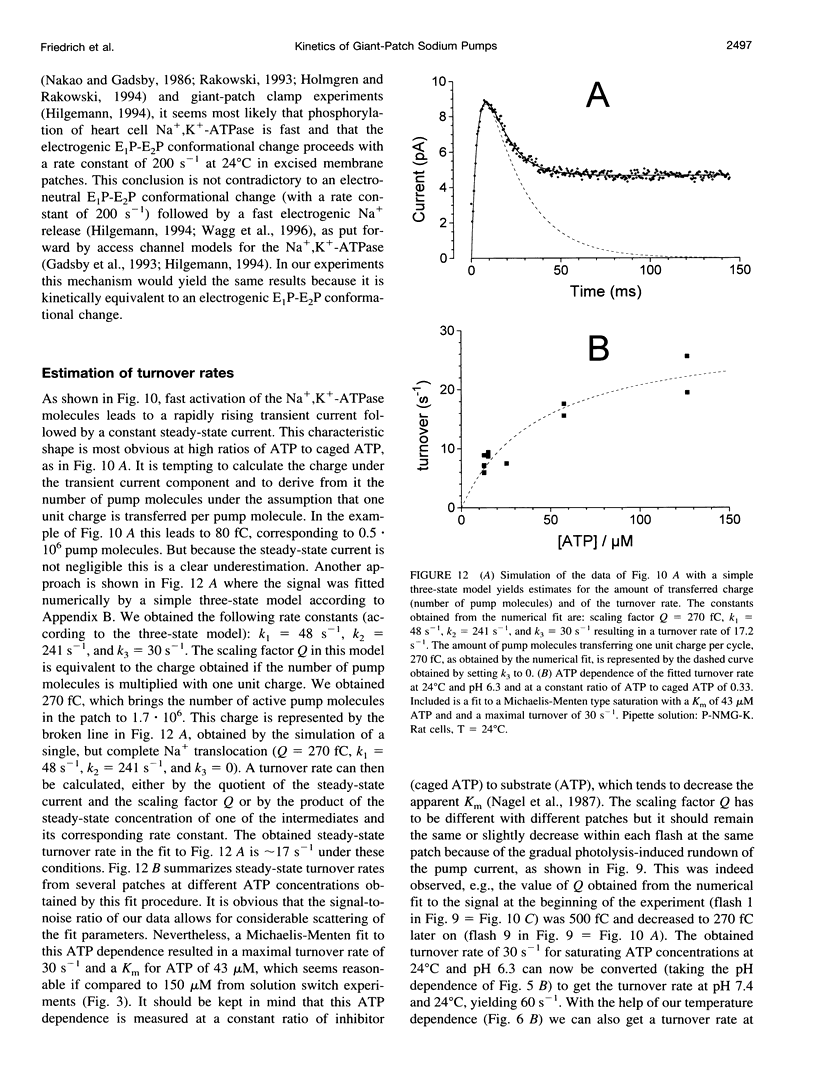
The giant-patch technique was used to study the Na+,K(+)-ATPase in excised patches from rat or guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Na+,K(+)-pump currents showed a saturable ATP dependence with aK(m) of approximately 150 microM at 24 degrees C. The pump current can be completely abolished by ortho-vanadate. Dissociation of vanadate from the enzyme in the absence of extracellular Na+ was slow, with a Koff of 3.10(-4) S-1 (K1 approximately 0.5 microM, at 24 degrees C). Stationary currents were markedly dependent on intracellular pH, with a maximum at pH 7.9. Temperature-dependence measurements of the stationary pump current yielded an activation energy of approximately 100 kJ mol-1. Partial reactions in the transport cycle were investigated by generating ATP concentration jumps through photolytic release of ATP from caged ATP at pH 7.4 and 6.3. Transient outward currents were obtained at pH 6.3 with a fast rising phase followed by a slower decay to a stationary current. It was concluded that the fast rate constant of approximately 200 s-1 at 24 degrees C (pH 6.3) reflects a step rate-limiting the electrogenic Na+ release. Simulating the data with a simple three-state model enabled us to estimate the turnover rate under saturating substrate concentrations, yielding rates (at pH 7.4) of approximately 60 s-1 and 200 s-1 at 24 degrees C and 36 degrees C, respectively.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apell H. J., Borlinghaus R., Läuger P. Fast charge translocations associated with partial reactions of the Na,K-pump: II. Microscopic analysis of transient currents. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(3):179–191. doi: 10.1007/BF01869221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barabás K., Keszthelyi L. Temperature dependence of ATP release from "caged" ATP. Acta Biochim Biophys Acad Sci Hung. 1984;19(3-4):305–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaugé L. A., Glynn I. M. Commercial ATP containing traces of vanadate alters the response of (Na+ + K+) ATPase to external potassium. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):551–552. doi: 10.1038/272551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borlinghaus R., Apell H. J., Läuger P. Fast charge translocations associated with partial reactions of the Na,K-pump: I. Current and voltage transients after photochemical release of ATP. J Membr Biol. 1987;97(3):161–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01869220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Altamirano A. A., Russell J. M. Effects of pH changes on sodium pump fluxes in squid giant axon. Am J Physiol. 1987 Oct;253(4 Pt 1):C547–C554. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.4.C547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Cantley L. G., Josephson L. A characterization of vanadate interactions with the (Na,K)-ATPase. Mechanistic and regulatory implications. J Biol Chem. 1978 Oct 25;253(20):7361–7368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Josephson L., Warner R., Yanagisawa M., Lechene C., Guidotti G. Vanadate is a potent (Na,K)-ATPase inhibitor found in ATP derived from muscle. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7421–7423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Jr, Resh M. D., Guidotti G. Vanadate inhibits the red cell (Na+, K+) ATPase from the cytoplasmic side. Nature. 1978 Apr 6;272(5653):552–554. doi: 10.1038/272552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A., Somlyo A. V., Hilgemann D. W. The giant cardiac membrane patch method: stimulation of outward Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange current by MgATP. J Physiol. 1992 Aug;454:27–57. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmann M., Skou J. C. Temperature-dependencies of various catalytic activities of membrane-bound Na+/K+-ATPase from ox brain, ox kidney and shark rectal gland and of C12E8-solubilized shark Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 20;944(3):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90504-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
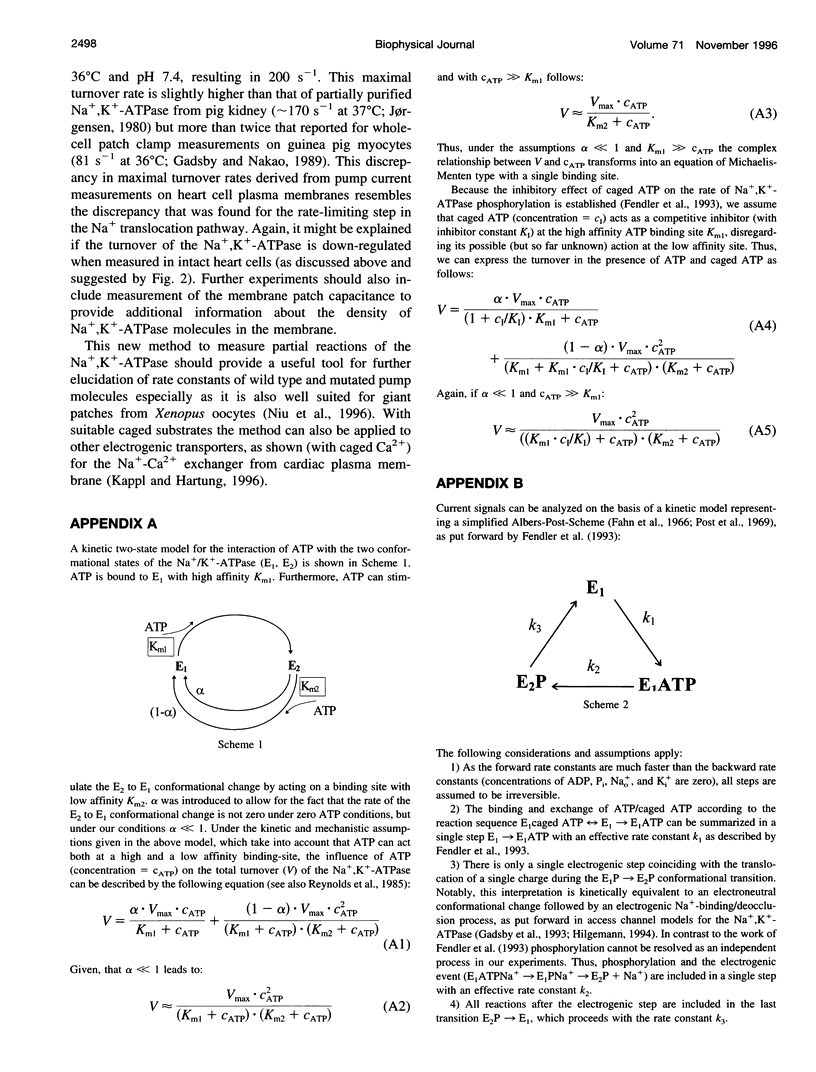
- Fahn S., Koval G. J., Albers R. W. Sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase of Electrophorus electric organ. I. An associated sodium-activated transphosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1882–1889. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Grell E., Bamberg E. Kinetics of pump currents generated by the Na+,K+-ATPase. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):83–88. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80427-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Grell E., Haubs M., Bamberg E. Pump currents generated by the purified Na+K+-ATPase from kidney on black lipid membranes. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3079–3085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fendler K., Jaruschewski S., Hobbs A., Albers W., Froehlich J. P. Pre-steady-state charge translocation in NaK-ATPase from eel electric organ. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Oct;102(4):631–666. doi: 10.1085/jgp.102.4.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbush B., 3rd Na+ movement in a single turnover of the Na pump. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Nakao M., Bahinski A., Nagel G., Suenson M. Charge movements via the cardiac Na,K-ATPase. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1992;607:111–123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Nakao M. Steady-state current-voltage relationship of the Na/K pump in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):511–537. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gadsby D. C., Rakowski R. F., De Weer P. Extracellular access to the Na,K pump: pathway similar to ion channel. Science. 1993 Apr 2;260(5104):100–103. doi: 10.1126/science.7682009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao J., Mathias R. T., Cohen I. S., Baldo G. J. Two functionally different Na/K pumps in cardiac ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1995 Nov;106(5):995–1030. doi: 10.1085/jgp.106.5.995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glynn I. M. Annual review prize lecture. 'All hands to the sodium pump'. J Physiol. 1993 Mar;462:1–30. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W. Channel-like function of the Na,K pump probed at microsecond resolution in giant membrane patches. Science. 1994 Mar 11;263(5152):1429–1432. doi: 10.1126/science.8128223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilgemann D. W. Giant excised cardiac sarcolemmal membrane patches: sodium and sodium-calcium exchange currents. Pflugers Arch. 1989 Nov;415(2):247–249. doi: 10.1007/BF00370601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmgren M., Rakowski R. F. Pre-steady-state transient currents mediated by the Na/K pump in internally perfused Xenopus oocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Mar;66(3 Pt 1):912–922. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(94)80867-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenberg G., Klockner U. Calcium tolerant ventricular myocytes prepared by preincubation in a "KB medium". Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct;395(1):6–18. doi: 10.1007/BF00584963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen P. L. Sodium and potassium ion pump in kidney tubules. Physiol Rev. 1980 Jul;60(3):864–917. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1980.60.3.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Forbush B., 3rd, Hoffman J. F. Rapid photolytic release of adenosine 5'-triphosphate from a protected analogue: utilization by the Na:K pump of human red blood cell ghosts. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1929–1935. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Kenney L. J. Temperature effects on sodium pump phosphoenzyme distribution in human red blood cells. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Jan;85(1):123–136. doi: 10.1085/jgp.85.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimelberg H. K., Papahadjopoulos D. Effects of phospholipid acyl chain fluidity, phase transitions, and cholesterol on (Na+ + K+)-stimulated adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 25;249(4):1071–1080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingrel J. B. Na,K-ATPase: isoform structure, function, and expression. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1992 Jun;24(3):263–270. doi: 10.1007/BF00768847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus M. M., Apell H. J., Roudna M., Schwendener R. A., Weder H. G., Läuger P. (Na+ + K+)-ATPase in artificial lipid vesicles: influence of lipid structure on pumping rate. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 29;854(2):270–278. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(86)90120-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marjanovic M., Willis J. S. ATP dependence of Na(+)-K+ pump of cold-sensitive and cold-tolerant mammalian red blood cells. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:575–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCray J. A., Herbette L., Kihara T., Trentham D. R. A new approach to time-resolved studies of ATP-requiring biological systems; laser flash photolysis of caged ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7237–7241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel G., Fendler K., Grell E., Bamberg E. Na+ currents generated by the purified (Na+ + K+)-ATPase on planar lipid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 23;901(2):239–249. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(87)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagel G., Hwang T. C., Nastiuk K. L., Nairn A. C., Gadsby D. C. The protein kinase A-regulated cardiac Cl- channel resembles the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator. Nature. 1992 Nov 5;360(6399):81–84. doi: 10.1038/360081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. Voltage dependence of Na translocation by the Na/K pump. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):628–630. doi: 10.1038/323628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakao M., Gadsby D. C. [Na] and [K] dependence of the Na/K pump current-voltage relationship in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1989 Sep;94(3):539–565. doi: 10.1085/jgp.94.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POST R. L., SEN A. K., ROSENTHAL A. S. A PHOSPHORYLATED INTERMEDIATE IN ADENOSINE TRIPHOSPHATE-DEPENDENT SODIUM AND POTASSIUM TRANSPORT ACROSS KIDNEY MEMBRANES. J Biol Chem. 1965 Mar;240:1437–1445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post R. L., Hegyvary C., Kume S. Activation by adenosine triphosphate in the phosphorylation kinetics of sodium and potassium ion transport adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Oct 25;247(20):6530–6540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rakowski R. F. Charge movement by the Na/K pump in Xenopus oocytes. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Jan;101(1):117–144. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds J. A., Johnson E. A., Tanford C. Application of the principle of linked functions to ATP-driven ion pumps: kinetics of activation by ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3658–3661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. Potassium: potassium exchange catalysed by the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1974 Feb;237(1):123–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons T. J. The interaction of ATP-analogues possessing a blocked gamma-phosphate group with the sodium pump in human red cells. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(3):731–739. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. L., Zinn K., Cantley L. C. A study of the vanadate-trapped state of the (Na,K)-ATPase. Evidence against interacting nucleotide site models. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9852–9859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweadner K. J. Isozymes of the Na+/K+-ATPase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 9;988(2):185–220. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(89)90019-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B., Blostein R. Comparison of red cell and kidney (Na+ +K+)-ATPase at 0 degrees C. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 28;688(3):685–690. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuddel I., Apell H. J. Electrogenicity of the sodium transport pathway in the Na,K-ATPase probed by charge-pulse experiments. Biophys J. 1995 Sep;69(3):909–921. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)79965-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]