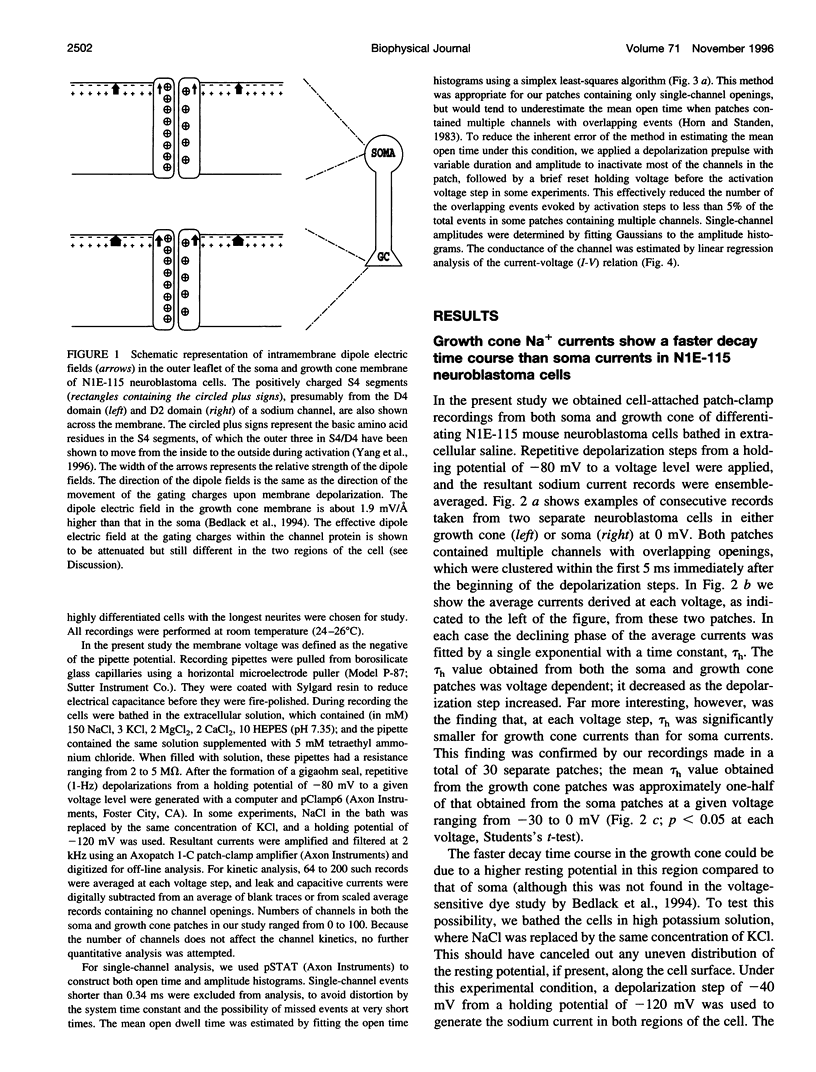
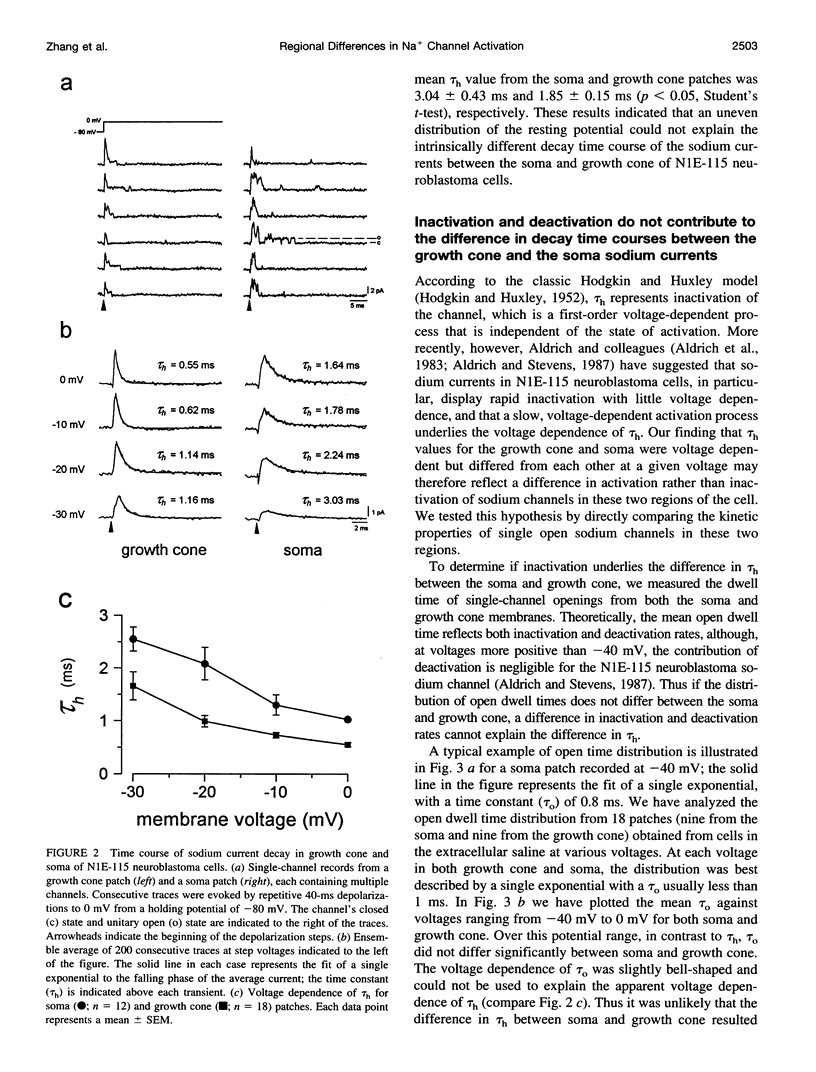
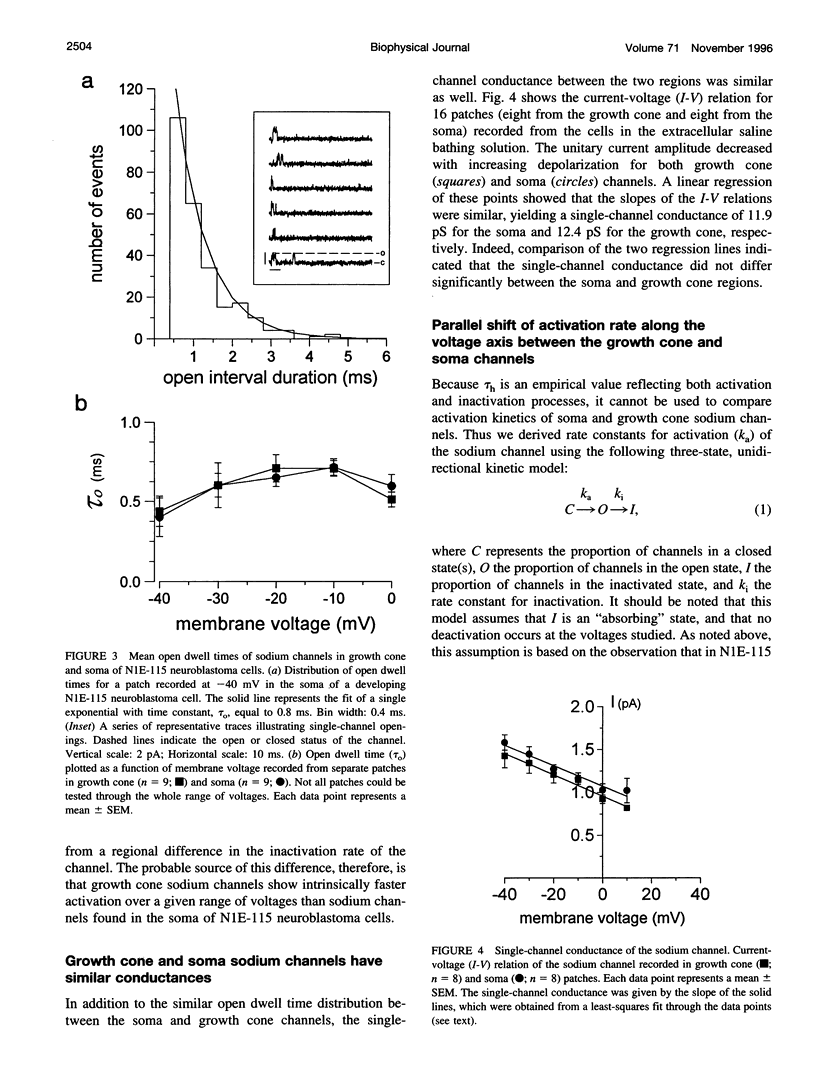
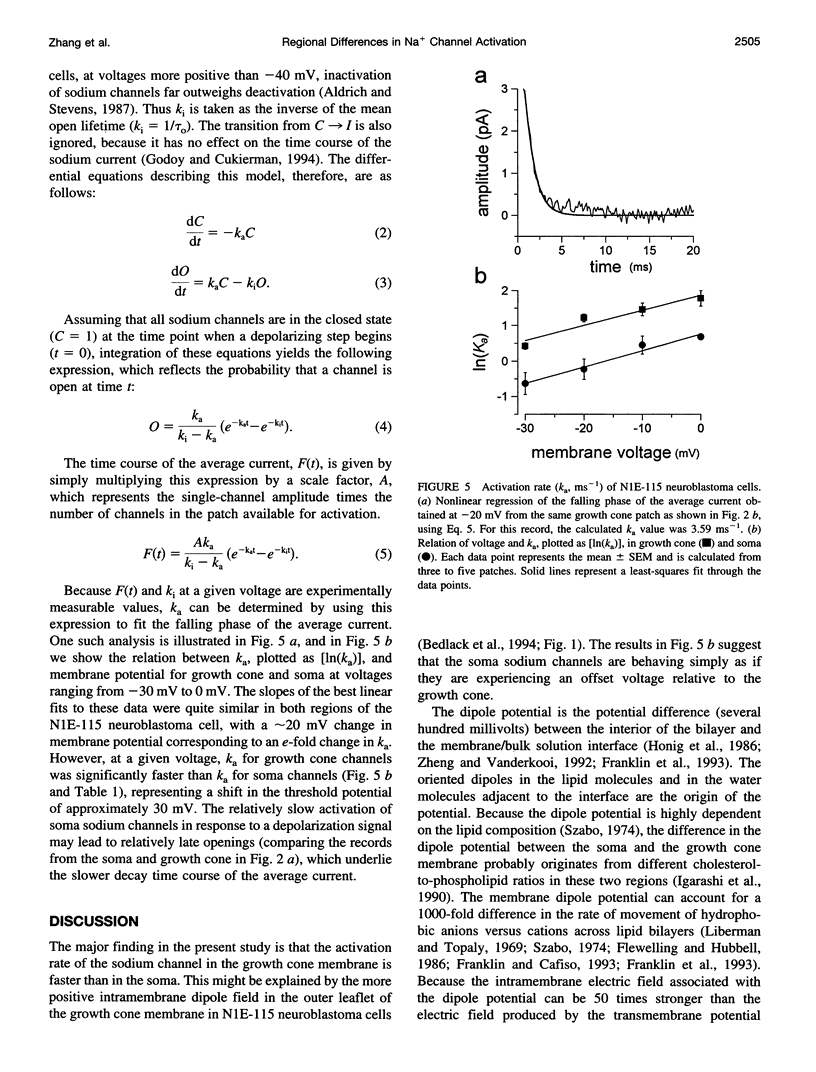
Abstract
Kinetics of voltage-gated ionic channels fundamentally reflect the response of the channels to local electric fields. In this report cell-attached patch-clamp studies reveal that the voltage-dependent activation rate of sodium channels residing in the growth cone membrane differs from that of soma sodium channels in differentiating N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells. Because other electrophysiological properties of these channels do not differ, this finding may be a reflection of the difference in intramembrane electric field in these two regions of the cell. This represents a new mechanism for channels to attain a range of activities both within and between cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldrich R. W., Corey D. P., Stevens C. F. A reinterpretation of mammalian sodium channel gating based on single channel recording. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):436–441. doi: 10.1038/306436a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich R. W., Stevens C. F. Voltage-dependent gating of single sodium channels from mammalian neuroblastoma cells. J Neurosci. 1987 Feb;7(2):418–431. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-02-00418.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M., Bezanilla F., Rojas E. Destruction of sodium conductance inactivation in squid axons perfused with pronase. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Oct;62(4):375–391. doi: 10.1085/jgp.62.4.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong C. M. Sodium channels and gating currents. Physiol Rev. 1981 Jul;61(3):644–683. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.3.644. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedlack R. S., Jr, Wei M. D., Fox S. H., Gross E., Loew L. M. Distinct electric potentials in soma and neurite membranes. Neuron. 1994 Nov;13(5):1187–1193. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90056-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedlack R. S., Jr, Wei M., Loew L. M. Localized membrane depolarizations and localized calcium influx during electric field-guided neurite growth. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90178-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belardetti F., Schacher S., Siegelbaum S. A. Action potentials, macroscopic and single channel currents recorded from growth cones of Aplysia neurones in culture. J Physiol. 1986 May;374:289–313. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connor J. A. Digital imaging of free calcium changes and of spatial gradients in growing processes in single, mammalian central nervous system cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6179–6183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cukierman S. Asymmetric electrostatic effects on the gating of rat brain sodium channels in planar lipid membranes. Biophys J. 1991 Oct;60(4):845–855. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82118-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davenport R. W., Kater S. B. Local increases in intracellular calcium elicit local filopodial responses in Helisoma neuronal growth cones. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90179-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. The membrane dipole potential in a total membrane potential model. Applications to hydrophobic ion interactions with membranes. Biophys J. 1986 Feb;49(2):541–552. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(86)83664-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin J. C., Cafiso D. S., Flewelling R. F., Hubbell W. L. Probes of membrane electrostatics: synthesis and voltage-dependent partitioning of negative hydrophobic ion spin labels in lipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1993 Mar;64(3):642–653. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81423-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin J. C., Cafiso D. S. Internal electrostatic potentials in bilayers: measuring and controlling dipole potentials in lipid vesicles. Biophys J. 1993 Jul;65(1):289–299. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81051-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godoy C. M., Cukierman S. Diacylglycerol-induced activation of protein kinase C attenuates Na+ currents by enhancing inactivation from the closed state. Pflugers Arch. 1994 Dec;429(2):245–252. doi: 10.1007/BF00374319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross E., Bedlack R. S., Jr, Loew L. M. Dual-wavelength ratiometric fluorescence measurement of the membrane dipole potential. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):208–216. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80471-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honig B. H., Hubbell W. L., Flewelling R. F. Electrostatic interactions in membranes and proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:163–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi M., Waki H., Hirota M., Hirabayashi Y., Obata K., Ando S. Differences in lipid composition between isolated growth cones from the forebrain and those from the brainstem in the fetal rat. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Jan 1;51(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90252-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji S., Weiss J. N., Langer G. A. Modulation of voltage-dependent sodium and potassium currents by charged amphiphiles in cardiac ventricular myocytes. Effects via modification of surface potential. J Gen Physiol. 1993 Mar;101(3):355–375. doi: 10.1085/jgp.101.3.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan P. C. How pore mouth charge distributions alter the permeability of transmembrane ionic channels. Biophys J. 1987 Feb;51(2):297–311. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(87)83336-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., West J. W., Lai Y., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1151–1159. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90135-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyers D. E. Distribution of ionic currents in the soma and growing region of an identified peptidergic neuron in defined culture. J Neurophysiol. 1993 Feb;69(2):406–415. doi: 10.1152/jn.1993.69.2.406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):115–118. doi: 10.1126/science.1656525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Wu C. H., Narahashi T. Removal of sodium channel inactivation in squid giant axons by n-bromoacetamide. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Mar;71(3):227–247. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.3.227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patlak J. Molecular kinetics of voltage-dependent Na+ channels. Physiol Rev. 1991 Oct;71(4):1047–1080. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.4.1047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streit J., Lux H. D. Distribution of calcium currents in sprouting PC12 cells. J Neurosci. 1989 Dec;9(12):4190–4199. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-12-04190.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stühmer W., Conti F., Suzuki H., Wang X. D., Noda M., Yahagi N., Kubo H., Numa S. Structural parts involved in activation and inactivation of the sodium channel. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):597–603. doi: 10.1038/339597a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo G. Dual mechanism for the action of cholesterol on membrane permeability. Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):47–49. doi: 10.1038/252047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson S., Coombs J. Spatial distribution of Ca currents in molluscan neuron cell bodies and regional differences in the strength of inactivation. J Neurosci. 1988 Jun;8(6):1929–1939. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-06-01929.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Usowicz M. M., Sugimori M., Cherksey B., Llinás R. P-type calcium channels in the somata and dendrites of adult cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1185–1199. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90076-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P. M., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Identification of an intracellular peptide segment involved in sodium channel inactivation. Science. 1988 Sep 23;241(4873):1658–1661. doi: 10.1126/science.241.4873.1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev P., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Inhibition of inactivation of single sodium channels by a site-directed antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8147–8151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., George A. L., Jr, Horn R. Molecular basis of charge movement in voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 1996 Jan;16(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang N., Horn R. Evidence for voltage-dependent S4 movement in sodium channels. Neuron. 1995 Jul;15(1):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng C., Vanderkooi G. Molecular origin of the internal dipole potential in lipid bilayers: calculation of the electrostatic potential. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):935–941. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81673-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zona C., Eusebi F., Miledi R. Glycosylation is required for maintenance of functional voltage-activated channels in growing neocortical neurons of the rat. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Mar 22;239(1295):119–127. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


