Abstract
To examine if the Ca2(+)-binding kinetics of troponin C (TnC) can influence the rate of cross-bridge force production, we studied the effects of calmidazolium (CDZ) on steady-state force and the rate of force redevelopment (ktr) in skinned rabbit psoas muscle fibers. CDZ increased the Ca2(+)-sensitivity of steady-state force and ktr at submaximal levels of activation, but increased ktr to a greater extent than can be explained by increased force alone. This occurred in the absence of any significant effects of CDZ on solution ATPase or in vitro motility of fluorescently labeled F-actin, suggesting that CDZ did not directly influence cross-bridge cycling. CDZ was strongly bound to TnC in aqueous solutions, and its effects on force production could be reversed by extraction of CDZ-exposed native TnC and replacement with purified (unexposed) rabbit skeletal TnC. These experiments suggest that the method of CDZ action in fibers is to bind to TnC and increase its Ca2(+)-binding affinity, which results in an increased rate of force production at submaximal [Ca2+]. The results also demonstrate that the Ca2(+)-binding kinetics of TnC influence the kinetics of ktr.
Full text
PDF

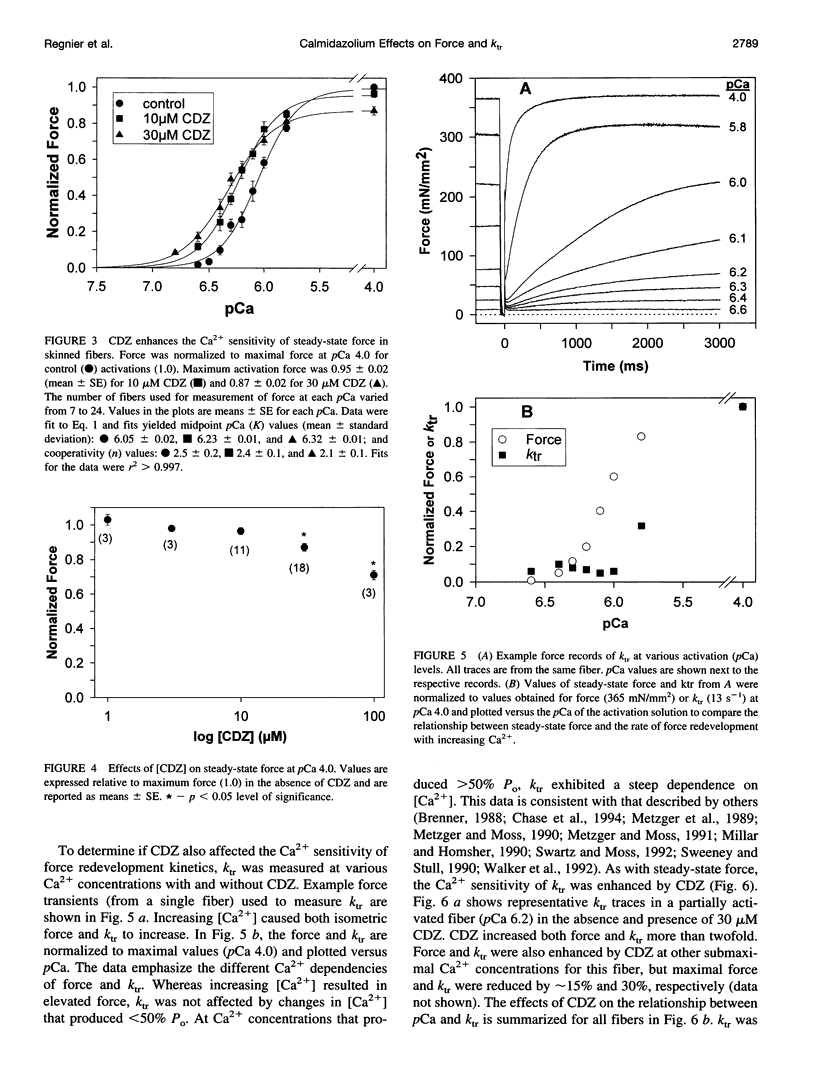
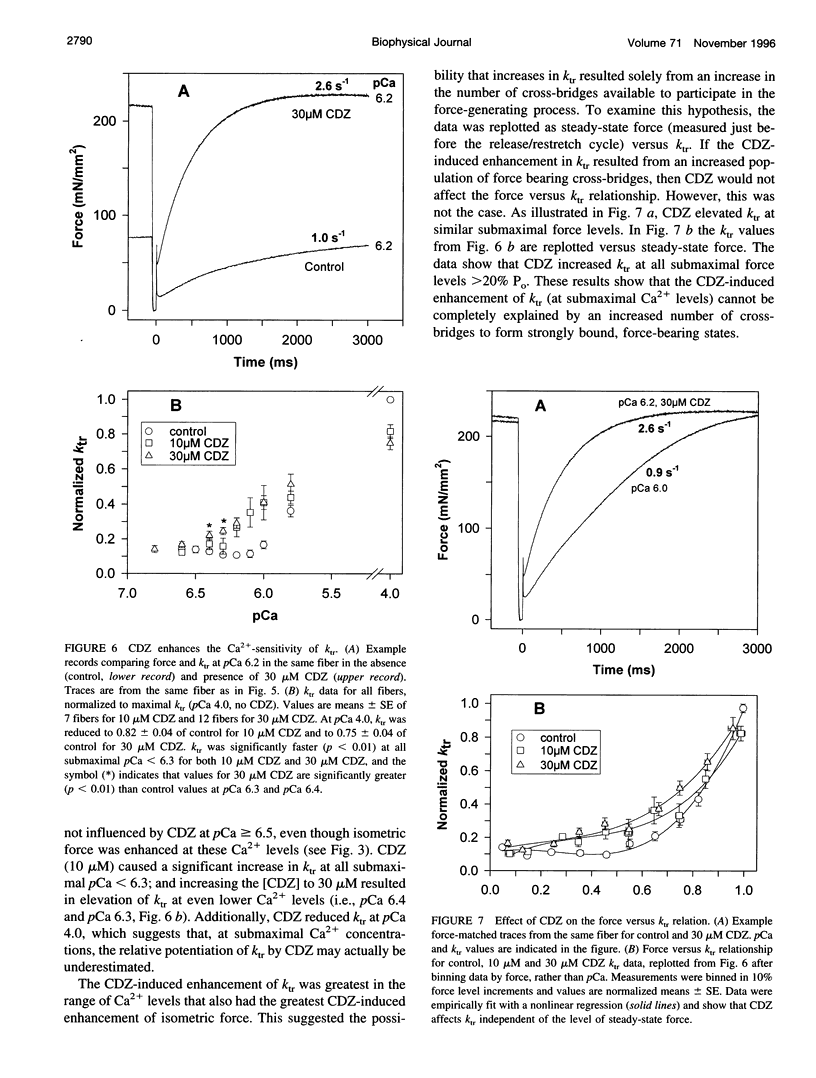
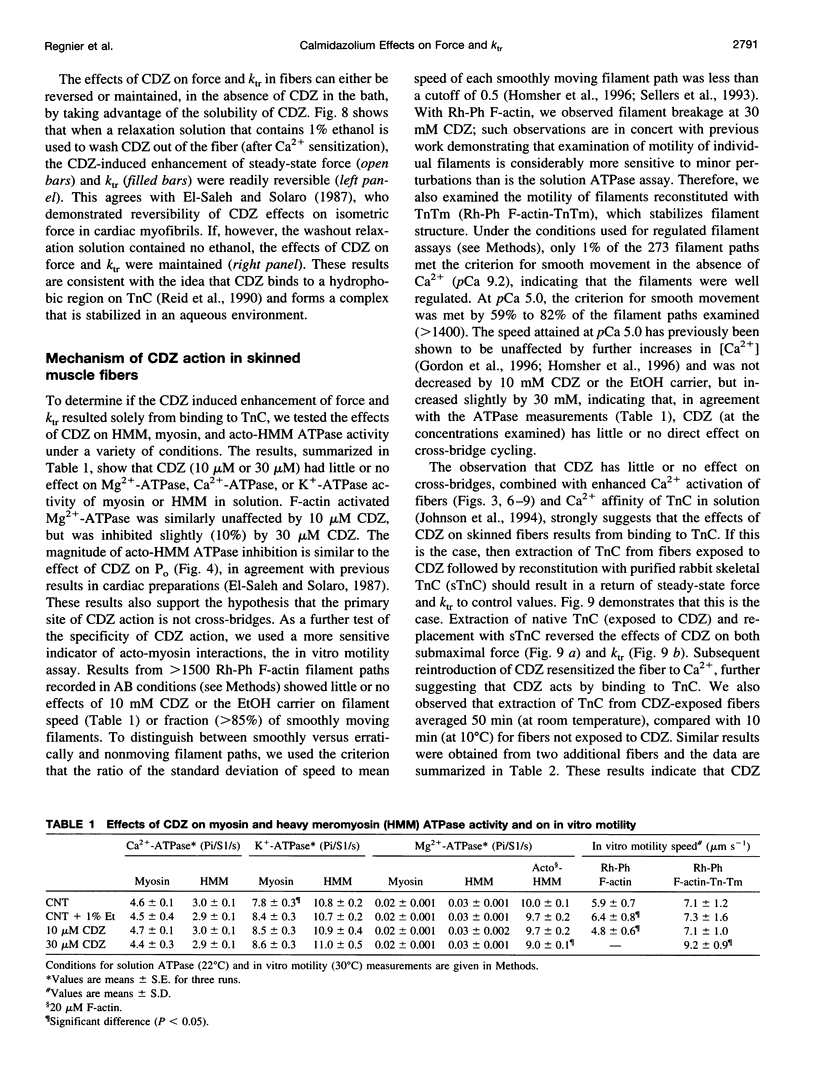


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B. Effect of Ca2+ on cross-bridge turnover kinetics in skinned single rabbit psoas fibers: implications for regulation of muscle contraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B., Eisenberg E. Rate of force generation in muscle: correlation with actomyosin ATPase activity in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3542–3546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. Technique for stabilizing the striation pattern in maximally calcium-activated skinned rabbit psoas fibers. Biophys J. 1983 Jan;41(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84411-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chalovich J. M. Actin mediated regulation of muscle contraction. Pharmacol Ther. 1992;55(2):95–148. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(92)90013-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Kushmerick M. J. Effects of pH on contraction of rabbit fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1988 Jun;53(6):935–946. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83174-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Martyn D. A., Hannon J. D. Isometric force redevelopment of skinned muscle fibers from rabbit activated with and without Ca2+. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1994–2001. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80682-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase P. B., Martyn D. A., Kushmerick M. J., Gordon A. M. Effects of inorganic phosphate analogues on stiffness and unloaded shortening of skinned muscle fibres from rabbit. J Physiol. 1993 Jan;460:231–246. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1993.sp019469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farah C. S., Reinach F. C. The troponin complex and regulation of muscle contraction. FASEB J. 1995 Jun;9(9):755–767. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.9.9.7601340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geeves M. A., Conibear P. B. The role of three-state docking of myosin S1 with actin in force generation. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):194S–201S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon J. D., Chase P. B., Martyn D. A., Huntsman L. L., Kushmerick M. J., Gordon A. M. Calcium-independent activation of skeletal muscle fibers by a modified form of cardiac troponin C. Biophys J. 1993 May;64(5):1632–1637. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81517-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsher E., Kim B., Bobkova A., Tobacman L. S. Calcium regulation of thin filament movement in an in vitro motility assay. Biophys J. 1996 Apr;70(4):1881–1892. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79753-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard J., Hunt A. J., Baek S. Assay of microtubule movement driven by single kinesin molecules. Methods Cell Biol. 1993;39:137–147. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60167-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Collins J. H., Robertson S. P., Potter J. D. A fluorescent probe study of Ca2+ binding to the Ca2+-specific sites of cardiac troponin and troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9635–9640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Nakkula R. J., Vasulka C., Smillie L. B. Modulation of Ca2+ exchange with the Ca(2+)-specific regulatory sites of troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 25;269(12):8919–8923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kron S. J., Toyoshima Y. Y., Uyeda T. Q., Spudich J. A. Assays for actin sliding movement over myosin-coated surfaces. Methods Enzymol. 1991;196:399–416. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)96035-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landesberg A., Sideman S. Coupling calcium binding to troponin C and cross-bridge cycling in skinned cardiac cells. Am J Physiol. 1994 Mar;266(3 Pt 2):H1260–H1271. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.266.3.H1260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lowey S. Preparation of myosin and its subfragments from rabbit skeletal muscle. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):55–71. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn D. A., Chase P. B., Hannon J. D., Huntsman L. L., Kushmerick M. J., Gordon A. M. Unloaded shortening of skinned muscle fibers from rabbit activated with and without Ca2+. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1984–1993. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80681-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martyn D. A., Gordon A. M. Length and myofilament spacing-dependent changes in calcium sensitivity of skeletal fibres: effects of pH and ionic strength. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1988 Oct;9(5):428–445. doi: 10.1007/BF01774069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara I., Umazume Y., Yagi N. Lateral filamentary spacing in chemically skinned murine muscles during contraction. J Physiol. 1985 Mar;360:135–148. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1985.sp015608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKillop D. F., Geeves M. A. Regulation of the interaction between actin and myosin subfragment 1: evidence for three states of the thin filament. Biophys J. 1993 Aug;65(2):693–701. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81110-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Greaser M. L., Moss R. L. Variations in cross-bridge attachment rate and tension with phosphorylation of myosin in mammalian skinned skeletal muscle fibers. Implications for twitch potentiation in intact muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):855–883. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Calcium-sensitive cross-bridge transitions in mammalian fast and slow skeletal muscle fibers. Science. 1990 Mar 2;247(4946):1088–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.2309121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger J. M., Moss R. L. Kinetics of a Ca(2+)-sensitive cross-bridge state transition in skeletal muscle fibers. Effects due to variations in thin filament activation by extraction of troponin C. J Gen Physiol. 1991 Aug;98(2):233–248. doi: 10.1085/jgp.98.2.233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millar N. C., Homsher E. The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibers. A steady-state and transient kinetic study. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20234–20240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovaska M., Taskinen J. A model for human cardiac troponin C and for modulation of its Ca2+ affinity by drugs. Proteins. 1991;11(2):79–94. doi: 10.1002/prot.340110202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Spudich J. A. Purification of muscle actin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):164–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85020-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. N., Hunter W. C., Berman M. R. Estimated time course of Ca2+ bound to troponin C during relaxation in isolated cardiac muscle. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 2):H1013–H1024. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.260.3.H1013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter J. D. Preparation of troponin and its subunits. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):241–263. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85024-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regnier M., Morris C., Homsher E. Regulation of the cross-bridge transition from a weakly to strongly bound state in skinned rabbit muscle fibers. Am J Physiol. 1995 Dec;269(6 Pt 1):C1532–C1539. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1995.269.6.C1532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid D. G., MacLachlan L. K., Gajjar K., Voyle M., King R. J., England P. J. A proton nuclear magnetic resonance and molecular modeling study of calmidazolium (R24571) binding to calmodulin and skeletal muscle troponin C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9744–9753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers J. R., Cuda G., Wang F., Homsher E. Myosin-specific adaptations of the motility assay. Methods Cell Biol. 1993;39:23–49. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60159-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie L. B. Preparation and identification of alpha- and beta-tropomyosins. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):234–241. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swartz D. R., Moss R. L. Influence of a strong-binding myosin analogue on calcium-sensitive mechanical properties of skinned skeletal muscle fibers. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 5;267(28):20497–20506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweeney H. L., Stull J. T. Alteration of cross-bridge kinetics by myosin light chain phosphorylation in rabbit skeletal muscle: implications for regulation of actin-myosin interaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):414–418. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobacman L. S. Thin filament-mediated regulation of cardiac contraction. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:447–481. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.58.030196.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uyeda T. Q., Kron S. J., Spudich J. A. Myosin step size. Estimation from slow sliding movement of actin over low densities of heavy meromyosin. J Mol Biol. 1990 Aug 5;214(3):699–710. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90287-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Lu Z., Moss R. L. Effects of Ca2+ on the kinetics of phosphate release in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 5;267(4):2459–2466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White H. D. Special instrumentation and techniques for kinetic studies of contractile systems. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):698–708. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahalak G. I., Ma S. P. Muscle activation and contraction: constitutive relations based directly on cross-bridge kinetics. J Biomech Eng. 1990 Feb;112(1):52–62. doi: 10.1115/1.2891126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Saleh S. C., Solaro R. J. Calmidazolium, a calmodulin antagonist, stimulates calcium-troponin C and calcium-calmodulin-dependent activation of striated muscle myofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17240–17246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



