Abstract
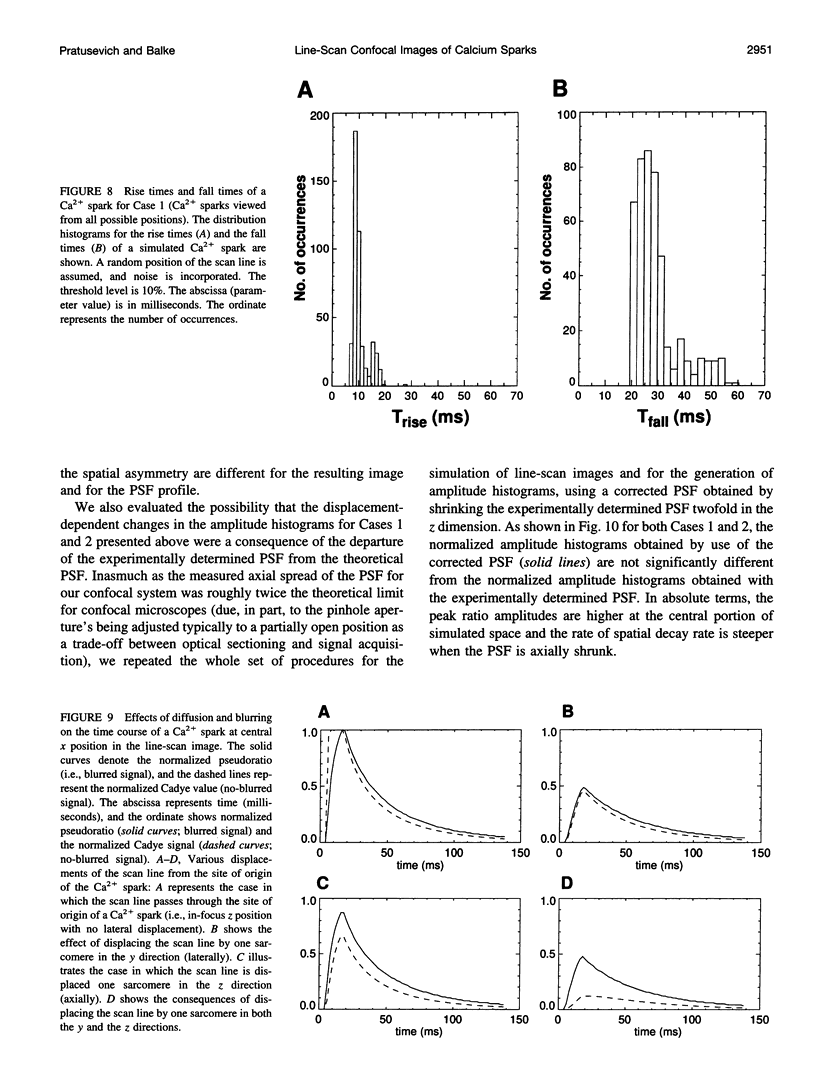
The interpretation of confocal line-scan images of local [Ca2+]i transients (such as Ca2+ sparks in cardiac muscle) is complicated by uncertainties in the position of the origin of the Ca2+ spark (relative to the scan line) and by the dynamics of Ca(2+)-dye interactions. An investigation of the effects of these complications modeled the release, diffusion, binding, and uptake of Ca2+ in cardiac cells (producing a theoretical Ca2+ spark) and image formation in a confocal microscope (after measurement of its point-spread function) and simulated line-scan images of a theoretical Ca2+ spark (when it was viewed from all possible positions relative to the scan line). In line-scan images, Ca2+ sparks that arose in a different optical section or with the site of origin displaced laterally from the scan line appeared attenuated, whereas their rise times slowed down only slightly. These results indicate that even if all Ca2+ sparks are perfectly identical events, except for their site of origin, there will be an apparent variation in the amplitude and other characteristics of Ca2+ sparks as measured from confocal line-scan images. The frequency distributions of the kinetic parameters (i.e., peak amplitude, rise time, fall time) of Ca2+ sparks were calculated for repetitive registration of stereotyped Ca2+ sparks in two experimental situations: 1) random position of the scan line relative to possible SR Ca(2+)-release sites and 2) fixed position of the scan line going through a set of possible SR Ca(2+)-release sites. The effects of noise were incorporated into the model, and a visibility function was proposed to account for the subjective factors that may be involved in the evaluation of Ca(2+)-spark image parameters from noisy experimental recordings. The mean value of the resulting amplitude distributions underestimates the brightness of in-focus Ca2+ sparks because large numbers of out-of-focus Ca2+ sparks are detected (as small Ca2+ sparks). The distribution of peak amplitudes may split into more than one subpopulation even when one is viewing stereotyped Ca2+ sparks because of the discrete locations of possible SR Ca(2+)-release sites in mammalian ventricular heart cells.
Full text
PDF














Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agard D. A., Hiraoka Y., Shaw P., Sedat J. W. Fluorescence microscopy in three dimensions. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;30:353–377. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60986-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backx P. H., de Tombe P. P., Van Deen J. H., Mulder B. J., ter Keurs H. E. A model of propagating calcium-induced calcium release mediated by calcium diffusion. J Gen Physiol. 1989 May;93(5):963–977. doi: 10.1085/jgp.93.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balke C. W., Egan T. M., Wier W. G. Processes that remove calcium from the cytoplasm during excitation-contraction coupling in intact rat heart cells. J Physiol. 1994 Feb 1;474(3):447–462. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin J. R., Bassani J. W., Bers D. M. Intrinsic cytosolic calcium buffering properties of single rat cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Oct;67(4):1775–1787. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80652-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bers D. M., Peskoff A. Diffusion around a cardiac calcium channel and the role of surface bound calcium. Biophys J. 1991 Mar;59(3):703–721. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(91)82284-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatter L. A., Wier W. G. Intracellular diffusion, binding, and compartmentalization of the fluorescent calcium indicators indo-1 and fura-2. Biophys J. 1990 Dec;58(6):1491–1499. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82494-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenfeld H., Zablow L., Sabatini B. Evaluation of cellular mechanisms for modulation of calcium transients using a mathematical model of fura-2 Ca2+ imaging in Aplysia sensory neurons. Biophys J. 1992 Oct;63(4):1146–1164. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81670-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Allen D. G. Model of calcium movements during activation in the sarcomere of frog skeletal muscle. Biophys J. 1984 May;45(5):913–925. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(84)84238-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Cheng H., Lederer W. J. Spatial non-uniformities in [Ca2+]i during excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac myocytes. Biophys J. 1994 Nov;67(5):1942–1956. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80677-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannell M. B., Cheng H., Lederer W. J. The control of calcium release in heart muscle. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1045–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.7754384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carl S. L., Felix K., Caswell A. H., Brandt N. R., Ball W. J., Jr, Vaghy P. L., Meissner G., Ferguson D. G. Immunolocalization of sarcolemmal dihydropyridine receptor and sarcoplasmic reticular triadin and ryanodine receptor in rabbit ventricle and atrium. J Cell Biol. 1995 May;129(3):673–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.3.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Lederer M. R., Lederer W. J., Cannell M. B. Calcium sparks and [Ca2+]i waves in cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1996 Jan;270(1 Pt 1):C148–C159. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1996.270.1.C148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H., Lederer W. J., Cannell M. B. Calcium sparks: elementary events underlying excitation-contraction coupling in heart muscle. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):740–744. doi: 10.1126/science.8235594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forbes M. S., van Neil E. E. Membrane systems of guinea pig myocardium: ultrastructure and morphometric studies. Anat Rec. 1988 Dec;222(4):362–379. doi: 10.1002/ar.1092220409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., KEYNES R. D. Movements of labelled calcium in squid giant axons. J Physiol. 1957 Sep 30;138(2):253–281. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Sedat J. W., Agard D. A. Determination of three-dimensional imaging properties of a light microscope system. Partial confocal behavior in epifluorescence microscopy. Biophys J. 1990 Feb;57(2):325–333. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(90)82534-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keating T. J., Cork R. J. Improved spatial resolution in ratio images using computational confocal techniques. Methods Cell Biol. 1994;40:221–241. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61116-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Cheng H., Santana L. F., Jiang Y. H., Lederer W. J., Schneider M. F. Two mechanisms of quantized calcium release in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1996 Feb 1;379(6564):455–458. doi: 10.1038/379455a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein M. G., Kovacs L., Simon B. J., Schneider M. F. Decline of myoplasmic Ca2+, recovery of calcium release and sarcoplasmic Ca2+ pump properties in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1991 Sep;441:639–671. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipp P., Niggli E. Modulation of Ca2+ release in cultured neonatal rat cardiac myocytes. Insight from subcellular release patterns revealed by confocal microscopy. Circ Res. 1994 May;74(5):979–990. doi: 10.1161/01.res.74.5.979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J. R., Shacklock P. S., Balke C. W., Wier W. G. Local calcium transients triggered by single L-type calcium channel currents in cardiac cells. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1042–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.7754383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- López-López J. R., Shacklock P. S., Balke C. W., Wier W. G. Local, stochastic release of Ca2+ in voltage-clamped rat heart cells: visualization with confocal microscopy. J Physiol. 1994 Oct 1;480(Pt 1):21–29. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattiazzi A., Hove-Madsen L., Bers D. M. Protein kinase inhibitors reduce SR Ca transport in permeabilized cardiac myocytes. Am J Physiol. 1994 Aug;267(2 Pt 2):H812–H820. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1994.267.2.H812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M. T., Cheng H., Rubart M., Santana L. F., Bonev A. D., Knot H. J., Lederer W. J. Relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by calcium sparks. Science. 1995 Oct 27;270(5236):633–637. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5236.633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli E., Lipp P. Subcellular features of calcium signalling in heart muscle: what do we learn? Cardiovasc Res. 1995 Apr;29(4):441–448. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker I., Yao Y. Regenerative release of calcium from functionally discrete subcellular stores by inositol trisphosphate. Proc Biol Sci. 1991 Dec 23;246(1317):269–274. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1991.0154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau E., Meissner G. Single cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-release channel: activation by caffeine. Am J Physiol. 1989 Feb;256(2 Pt 2):H328–H333. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1989.256.2.H328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shacklock P. S., Wier W. G., Balke C. W. Local Ca2+ transients (Ca2+ sparks) originate at transverse tubules in rat heart cells. J Physiol. 1995 Sep 15;487(Pt 3):601–608. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sipido K. R., Wier W. G. Flux of Ca2+ across the sarcoplasmic reticulum of guinea-pig cardiac cells during excitation-contraction coupling. J Physiol. 1991 Apr;435:605–630. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. D. Theory of excitation-contraction coupling in cardiac muscle. Biophys J. 1992 Aug;63(2):497–517. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81615-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinker A., Lindsay A. R., Williams A. J. A model for ionic conduction in the ryanodine receptor channel of sheep cardiac muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum. J Gen Physiol. 1992 Sep;100(3):495–517. doi: 10.1085/jgp.100.3.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugorka A., Ríos E., Blatter L. A. Imaging elementary events of calcium release in skeletal muscle cells. Science. 1995 Sep 22;269(5231):1723–1726. doi: 10.1126/science.7569901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J., Keizer J. Effects of rapid buffers on Ca2+ diffusion and Ca2+ oscillations. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):447–456. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80500-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wier W. G., Yue D. T. Intracellular calcium transients underlying the short-term force-interval relationship in ferret ventricular myocardium. J Physiol. 1986 Jul;376:507–530. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1986.sp016167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimsatt D. K., Hohl C. M., Brierley G. P., Altschuld R. A. Calcium accumulation and release by the sarcoplasmic reticulum of digitonin-lysed adult mammalian ventricular cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):14849–14857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zador A., Koch C., Brown T. H. Biophysical model of a Hebbian synapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6718–6722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]