Abstract
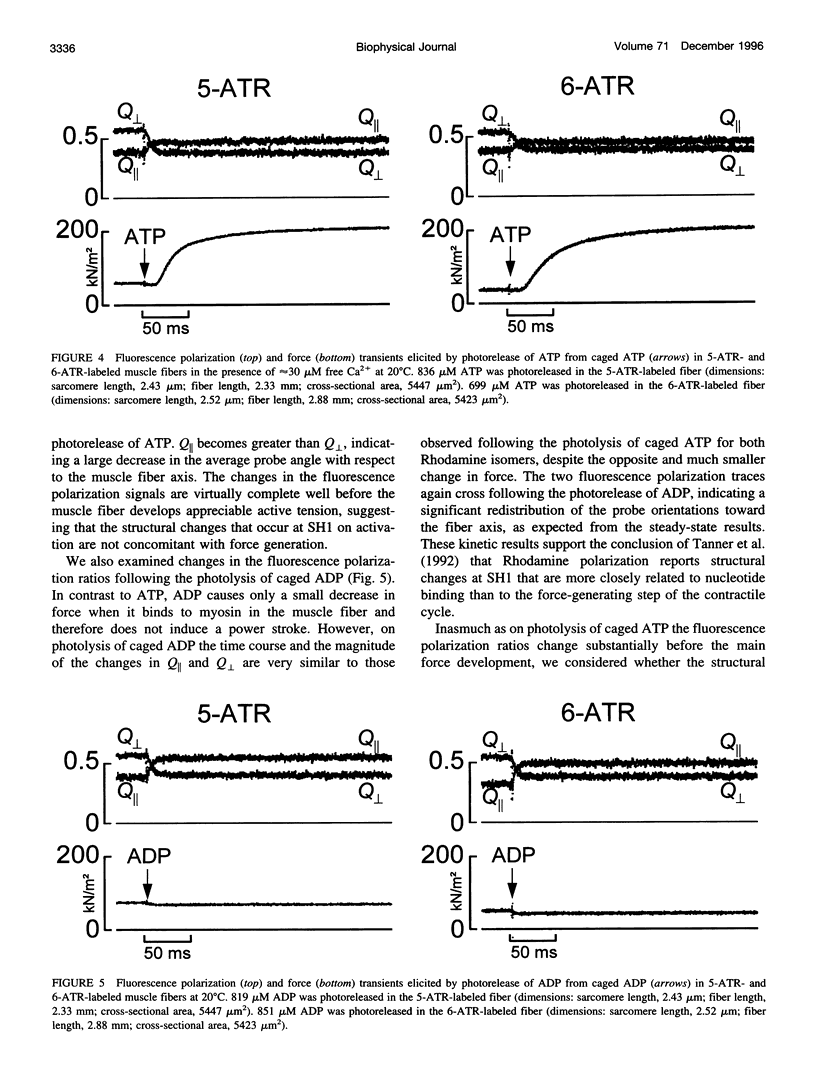
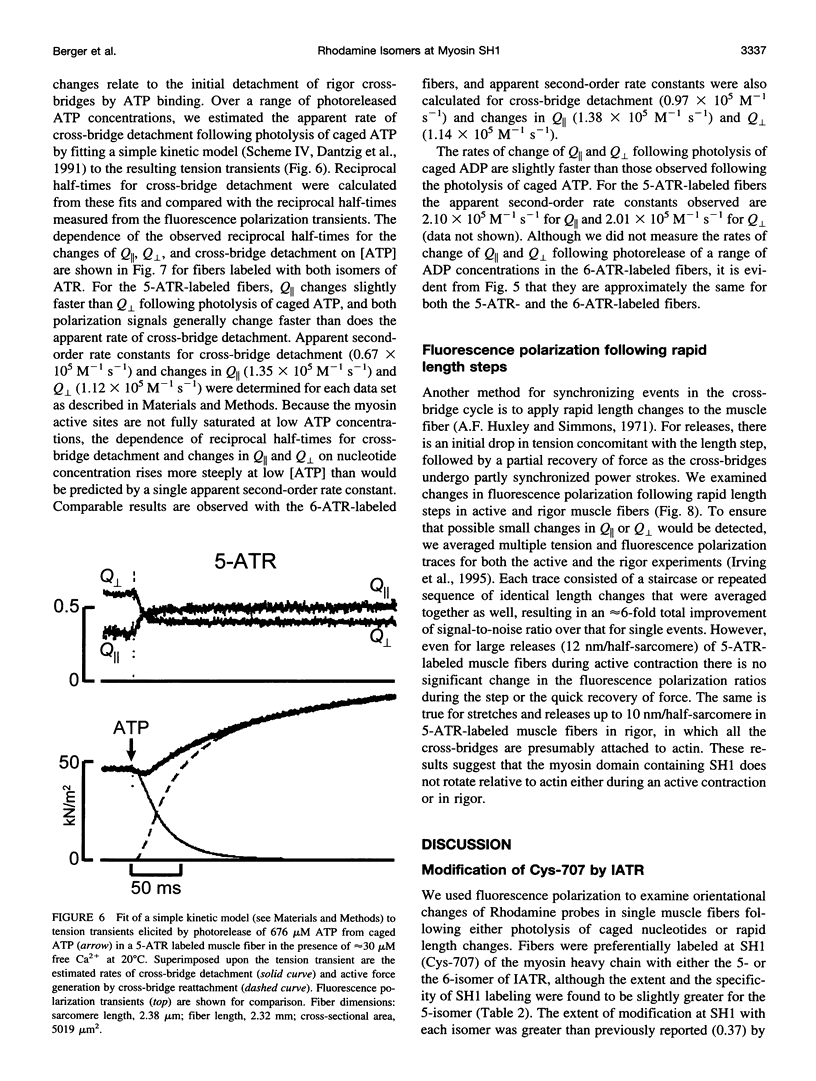
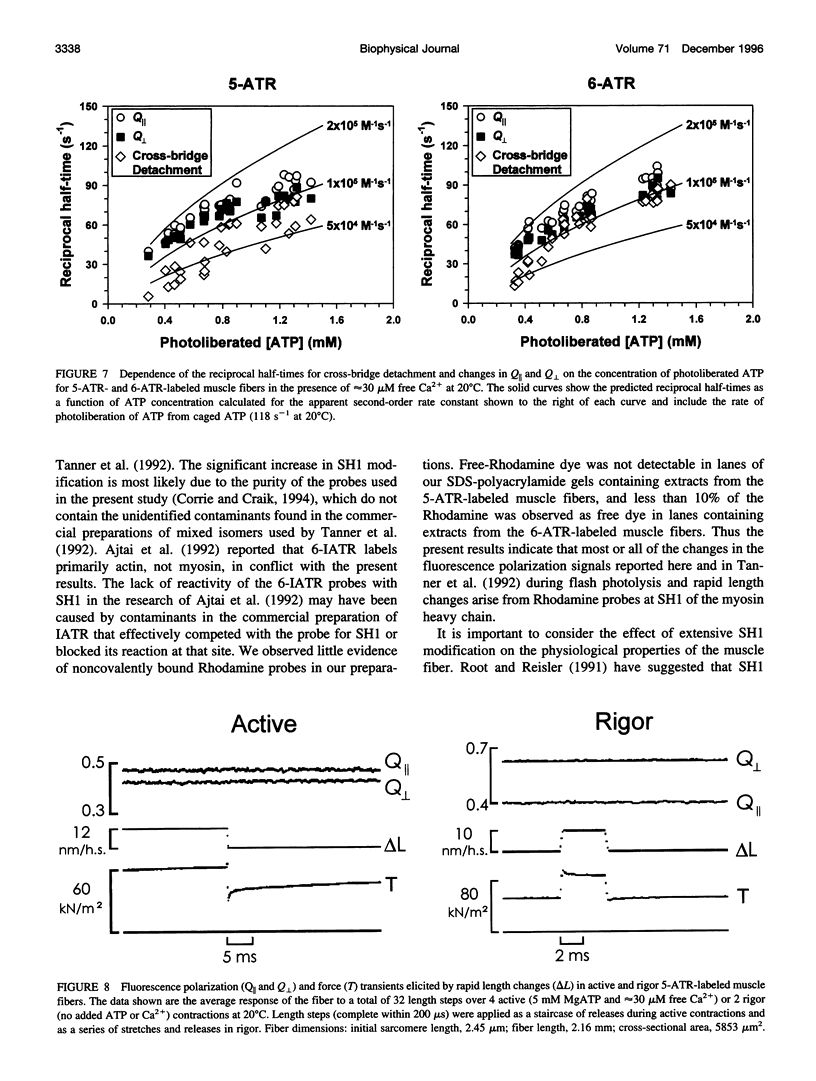
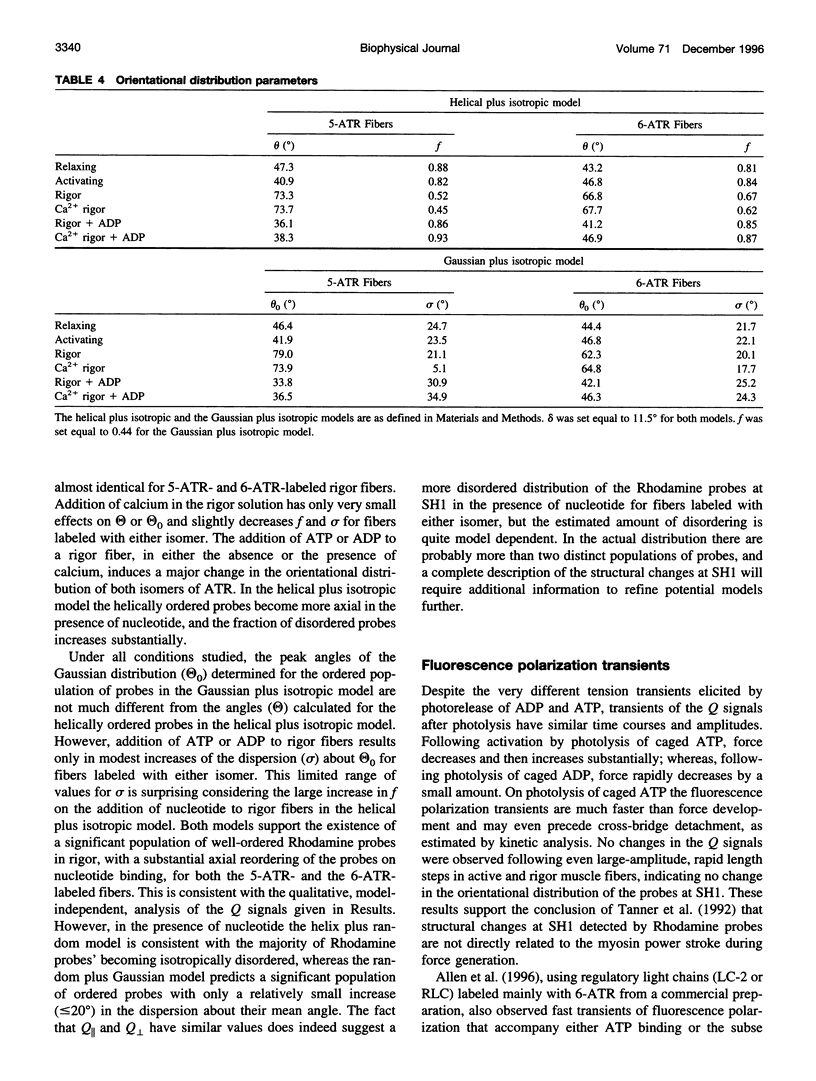
Fluorescence polarization was used to examine orientational changes of Rhodamine probes in single, skinned muscle fibers from rabbit psoas muscle following either photolysis of caged nucleotides or rapid length changes. Fibers were extensively and predominantly labeled at SH1 (Cys-707) of the myosin heavy chain with either the 5- or the 6-isomer of iodoacetamidotetramethylrhodamine. Results from spectroscopic experiments utilizing the two Rhodamine isomers were quite similar. Following photolysis of either caged ATP or caged ADP, probes promptly reoriented toward the muscle fiber axis. Changes in the fluorescence polarization signals with transients elicited by the photolysis of caged ATP in the presence of saturating Ca2+ greatly preceded active force generation. Photolysis of caged ADP caused only a small, rapid decrease in force but elicited changes in the fluorescence polarization signals with time course and amplitude similar to those following photolysis of caged ATP. Fluorescence polarization signals were virtually unchanged by rapid length steps in both rigor and active muscle fibers. These results indicate that structural changes monitored by Rhodamine probes at SH1 are not associated directly with the force-generating event of muscle contraction. However, the fluorescence polarization transients were slightly faster than the estimated rate of cross-bridge detachment following photolysis of caged ATP, suggesting that the observed structural changes at SH1 may be involved in the communication pathway between the nucleotide- and actin-binding sites of myosin.
Full text
PDF
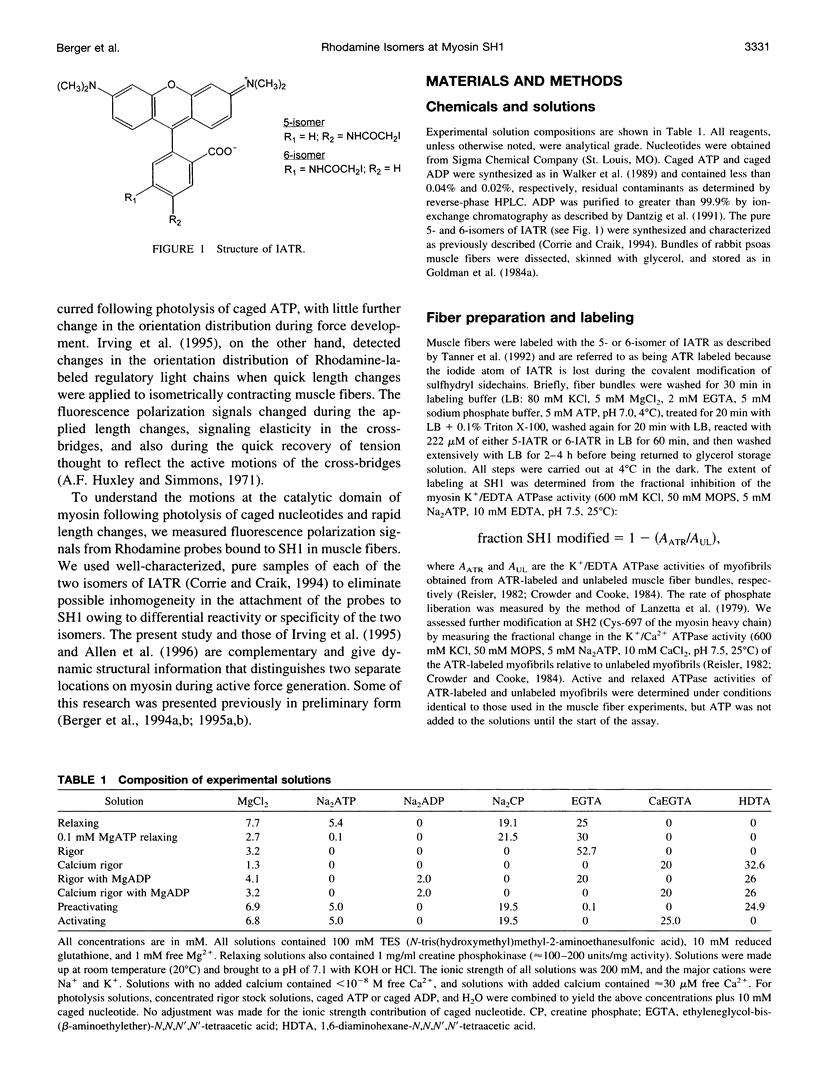


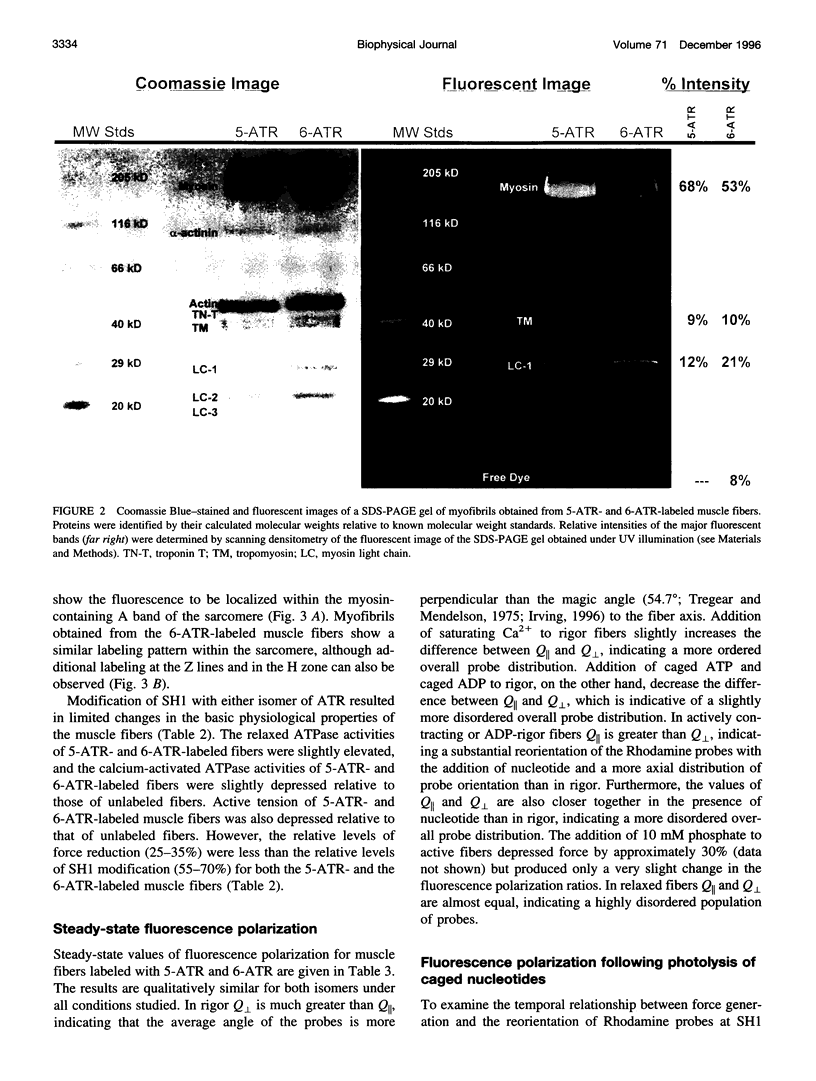
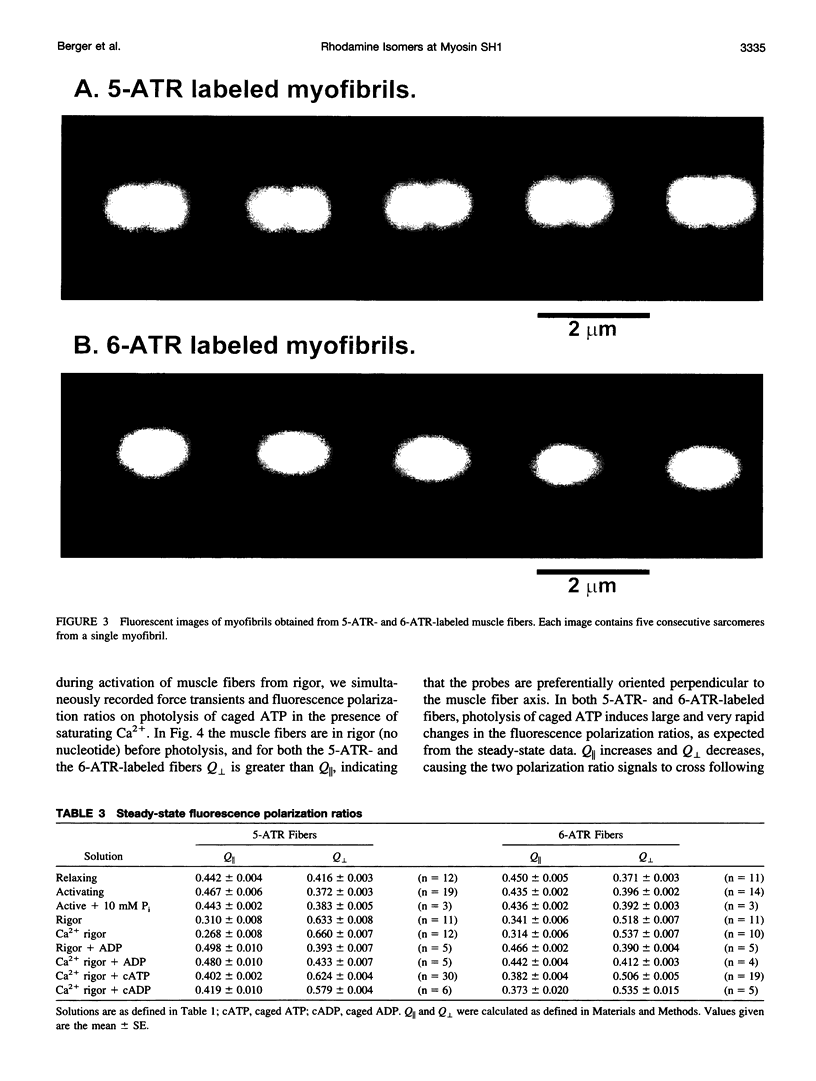




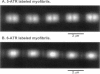
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. S., Ling N., Irving M., Goldman Y. E. Orientation changes in myosin regulatory light chains following photorelease of ATP in skinned muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1996 Apr;70(4):1847–1862. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79750-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnett V. A., Thomas D. D. Microsecond rotational motion of spin-labeled myosin heads during isometric muscle contraction. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance. Biophys J. 1989 Sep;56(3):517–523. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82698-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Craik J. S., Trentham D. R., Corrie J. E., Goldman Y. E. Fluorescence polarization from isomers of tetramethylrhodamine at SH-1 in rabbit psoas muscle fibers. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):78S–80S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Svensson E. C., Thomas D. D. Photolysis of a photolabile precursor of ATP (caged ATP) induces microsecond rotational motions of myosin heads bound to actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8753–8757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound intermediates of the myosin adenosine triphosphatase cycle in myofibrils. Biophys J. 1994 Jul;67(1):250–261. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(94)80476-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger C. L., Thomas D. D. Rotational dynamics of actin-bound myosin heads in active myofibrils. Biochemistry. 1993 Apr 13;32(14):3812–3821. doi: 10.1021/bi00065a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borejdo J., Assulin O., Ando T., Putnam S. Cross-bridge orientation in skeletal muscle measured by linear dichroism of an extrinsic chromophore. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):391–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90205-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burghardt T. P., Ando T., Borejdo J. Evidence for cross-bridge order in contraction of glycerinated skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7515–7519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cecchi G., Colomo F., Lombardi V. A loudspeaker servo system for determination of mechanical characteristics of isolated muscle fibres. Boll Soc Ital Biol Sper. 1976 May 30;52(10):733–736. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke R., Crowder M. S., Thomas D. D. Orientation of spin labels attached to cross-bridges in contracting muscle fibres. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):776–778. doi: 10.1038/300776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder M. S., Cooke R. The effect of myosin sulphydryl modification on the mechanics of fibre contraction. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1984 Apr;5(2):131–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00712152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dantzig J. A., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Cross-bridge kinetics in the presence of MgADP investigated by photolysis of caged ATP in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1991 Jan;432:639–680. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1991.sp018405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Matta J. J., Thomas D. D. Effect of ADP on the orientation of spin-labeled myosin heads in muscle fibers: a high-resolution study with deuterated spin labels. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 19;29(24):5865–5871. doi: 10.1021/bi00476a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fajer P. G., Fajer E. A., Thomas D. D. Myosin heads have a broad orientational distribution during isometric muscle contraction: time-resolved EPR studies using caged ATP. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5538–5542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenczi M. A., Homsher E., Trentham D. R. The kinetics of magnesium adenosine triphosphate cleavage in skinned muscle fibres of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1984 Jul;352:575–599. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. J., Smith C. A., Thoden J. B., Smith R., Sutoh K., Holden H. M., Rayment I. X-ray structures of the myosin motor domain of Dictyostelium discoideum complexed with MgADP.BeFx and MgADP.AlF4-. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 18;34(28):8960–8972. doi: 10.1021/bi00028a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Initiation of active contraction by photogeneration of adenosine-5'-triphosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:605–624. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Hibberd M. G., Trentham D. R. Relaxation of rabbit psoas muscle fibres from rigor by photochemical generation of adenosine-5'-triphosphate. J Physiol. 1984 Sep;354:577–604. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman Y. E., Simmons R. M. Control of sarcomere length in skinned muscle fibres of Rana temporaria during mechanical transients. J Physiol. 1984 May;350:497–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huston E. E., Grammer J. C., Yount R. G. Flexibility of the myosin heavy chain: direct evidence that the region containing SH1 and SH2 can move 10 A under the influence of nucleotide binding. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 13;27(25):8945–8952. doi: 10.1021/bi00425a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley A. F., Simmons R. M. Proposed mechanism of force generation in striated muscle. Nature. 1971 Oct 22;233(5321):533–538. doi: 10.1038/233533a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huxley H. E. The mechanism of muscular contraction. Science. 1969 Jun 20;164(3886):1356–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3886.1356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M., St Claire Allen T., Sabido-David C., Craik J. S., Brandmeier B., Kendrick-Jones J., Corrie J. E., Trentham D. R., Goldman Y. E. Tilting of the light-chain region of myosin during step length changes and active force generation in skeletal muscle. Nature. 1995 Jun 22;375(6533):688–691. doi: 10.1038/375688a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irving M. Steady-state polarization from cylindrically symmetric fluorophores undergoing rapid restricted motion. Biophys J. 1996 Apr;70(4):1830–1835. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79748-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jontes J. D., Wilson-Kubalek E. M., Milligan R. A. A 32 degree tail swing in brush border myosin I on ADP release. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):751–753. doi: 10.1038/378751a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRADLEY L. B. The relationship between sulfhydryl groups and the activation of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Forbush B., 3rd, Hoffman J. F. Rapid photolytic release of adenosine 5'-triphosphate from a protected analogue: utilization by the Na:K pump of human red blood cell ghosts. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1929–1935. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Shrimpton C., Sleep J., Kendrick-Jones J., Irving M. Fluorescent probes of the orientation of myosin regulatory light chains in relaxed, rigor, and contracting muscle. Biophys J. 1996 Apr;70(4):1836–1846. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79749-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raucher D., Fajer E. A., Sár C., Hideg K., Zhao Y., Kawai M., Fajer P. G. A novel electron paramagnetic resonance spin label and its application to study the cross-bridge cycle. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):128S–134S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Holden H. M., Whittaker M., Yohn C. B., Lorenz M., Holmes K. C., Milligan R. A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):58–65. doi: 10.1126/science.8316858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Rypniewski W. R., Schmidt-Bäse K., Smith R., Tomchick D. R., Benning M. M., Winkelmann D. A., Wesenberg G., Holden H. M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science. 1993 Jul 2;261(5117):50–58. doi: 10.1126/science.8316857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisler E. Sulfhydryl modification and labeling of myosin. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):84–93. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger C. D., Tregear R. T. Letter: Crossbridge angle when ADP is bound to myosin. J Mol Biol. 1974 Jun 25;86(2):495–497. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90033-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root D. D., Cheung P., Reisler E. Catalytic cooperativity induced by SH1 labeling of myosin filaments. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):286–294. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Rayment I. X-ray structure of the magnesium(II)-pyrophosphate complex of the truncated head of Dictyostelium discoideum myosin to 2.7 A resolution. Biochemistry. 1995 Jul 18;34(28):8973–8981. doi: 10.1021/bi00028a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Rayment I. X-ray structure of the magnesium(II).ADP.vanadate complex of the Dictyostelium discoideum myosin motor domain to 1.9 A resolution. Biochemistry. 1996 Apr 30;35(17):5404–5417. doi: 10.1021/bi952633+. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemori S., Yamaguchi M., Yagi N. Effects of adenosine diphosphate on the structure of myosin cross-bridges: an X-ray diffraction study on a single skinned frog muscle fibre. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1995 Dec;16(6):571–577. doi: 10.1007/BF00130238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J. W., Thomas D. D., Goldman Y. E. Transients in orientation of a fluorescent cross-bridge probe following photolysis of caged nucleotides in skeletal muscle fibres. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):185–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90725-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thirlwell H., Sleep J. A., Ferenczi M. A. Inhibition of unloaded shortening velocity in permeabilized muscle fibres by caged ATP compounds. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1995 Apr;16(2):131–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00122531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Ramachandran S., Roopnarine O., Hayden D. W., Ostap E. M. The mechanism of force generation in myosin: a disorder-to-order transition, coupled to internal structural changes. Biophys J. 1995 Apr;68(4 Suppl):135S–141S. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tregear R. T., Mendelson R. A. Polarization from a helix of fluorophores and its relation to that obtained from muscle. Biophys J. 2009 Jan 1;15(5):455–467. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85830-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. W., Reid G. P., Trentham D. R. Synthesis and properties of caged nucleotides. Methods Enzymol. 1989;172:288–301. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(89)72019-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker M., Wilson-Kubalek E. M., Smith J. E., Faust L., Milligan R. A., Sweeney H. L. A 35-A movement of smooth muscle myosin on ADP release. Nature. 1995 Dec 14;378(6558):748–751. doi: 10.1038/378748a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhukarev V., Ashton F., Sanger J. M., Sanger J. W., Shuman H. Organization and structure of actin filament bundles in Listeria-infected cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1995;30(3):229–246. doi: 10.1002/cm.970300307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]