Abstract
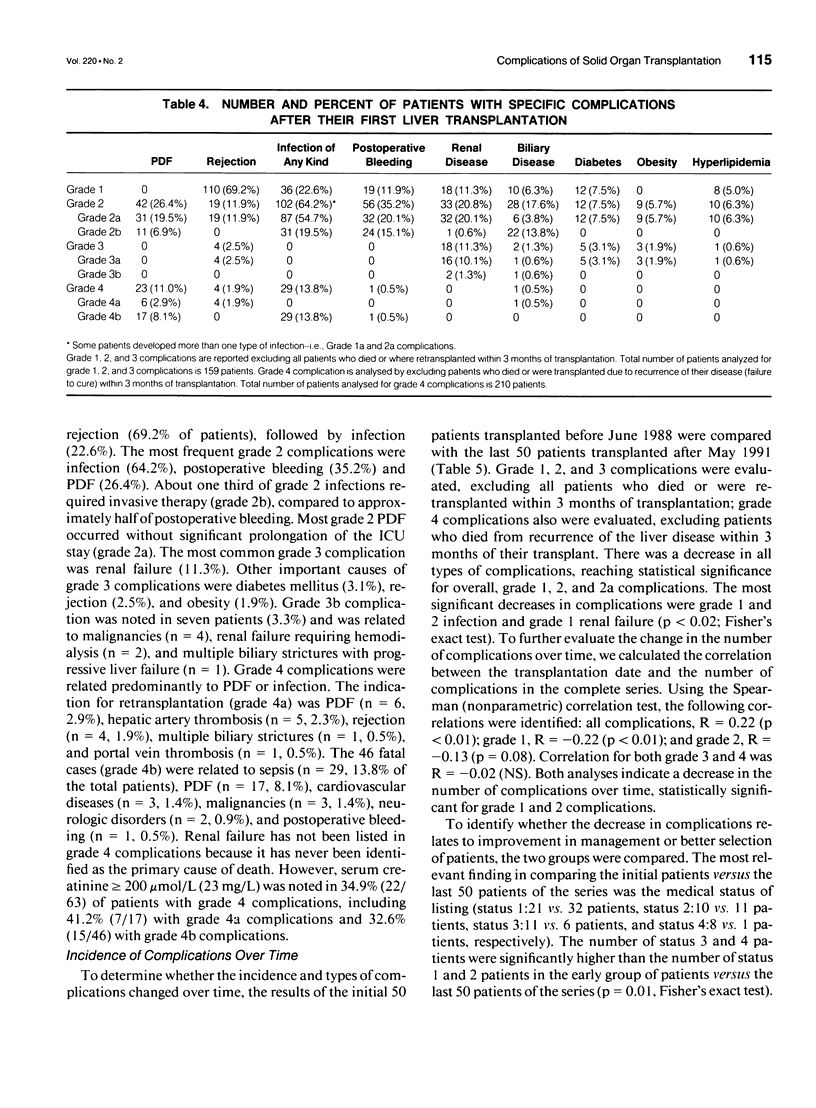
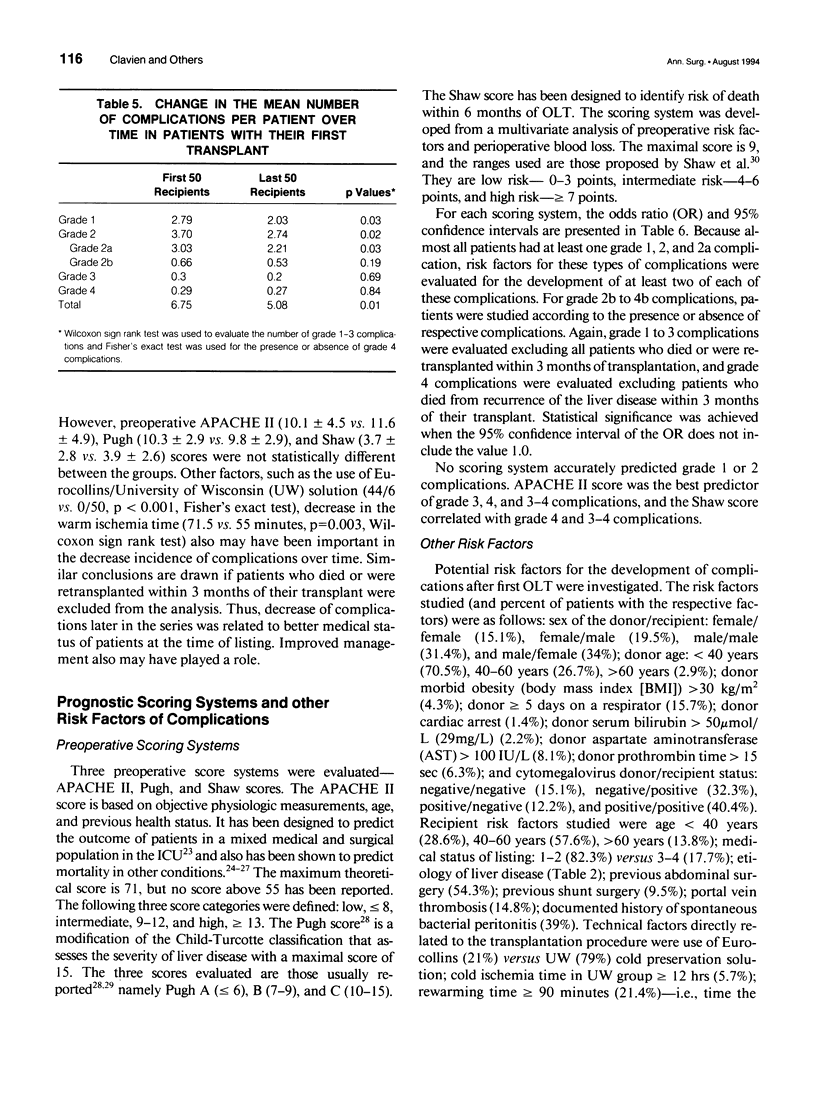
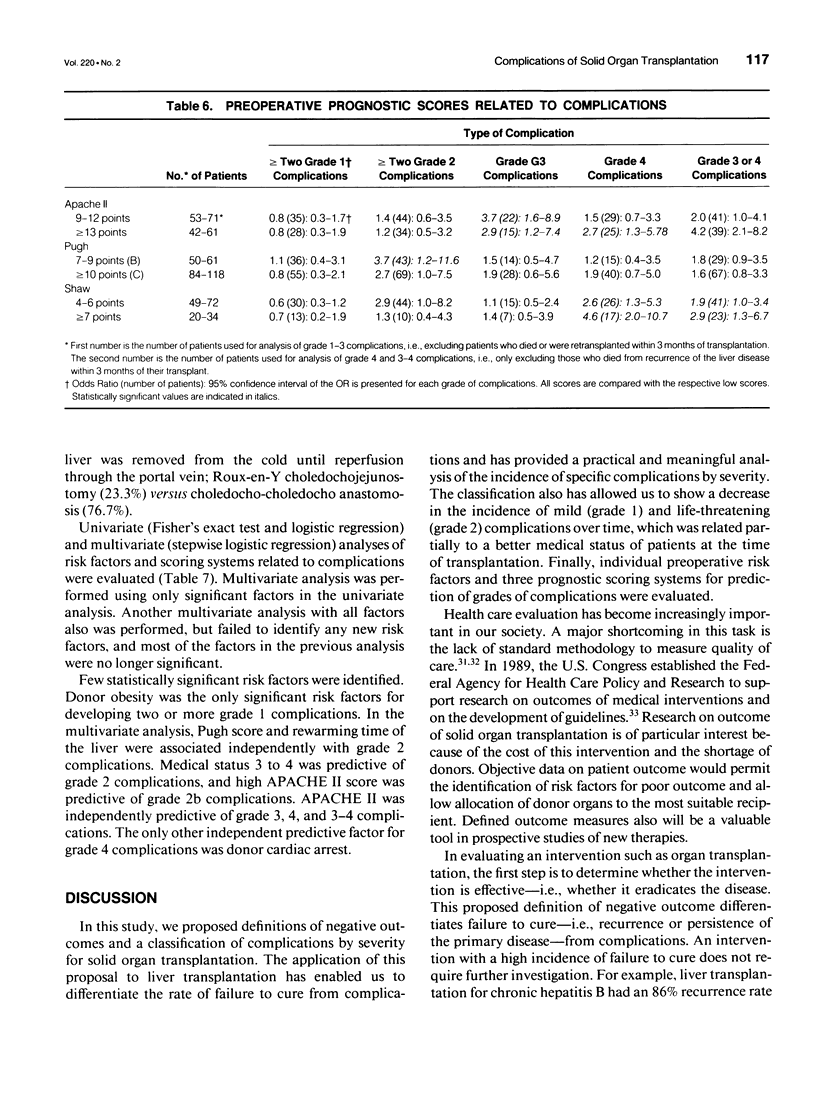
OBJECTIVE: This study defined negative outcomes of solid organ transplantation, proposed a new classification of complications by severity, and applied the classification to evaluate the results of orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). SUMMARY AND BACKGROUND DATA: The lack of uniform reporting of negative outcomes has made reports of transplantation procedures difficult to interpret and compare. In fact, only mortality is well reported; morbidity rates and severity of complications have been poorly described. METHODS: Based on previous definition and classification of complications for general surgery, a new classification for transplantation in four grades is proposed. Results including risk factors of the first 215 OLTs performed at the University of Toronto have been evaluated using the classification. RESULTS: All but two patients (99%) had at least one complication of any kind, 92% of patients surviving more than 3 months had grade 1 (minor) complications, 74% had grade 2 (life-threatening) complications, and 30% had grade 3 (residual disability or cancer) complications. Twenty-nine per cent of patients had grade 4 complications (retransplantation or death). The most common grade 1 complications were steroid responsive rejection (69% of patients) and infection that did not require antibiotics or invasive procedures (23%). Grade 2 complications primarily were infection requiring antibiotics or invasive procedures (64%), postoperative bleeding requiring > 3 units of packed red cells (35%), primary dysfunction (26%), and biliary disease treated with antibiotics or requiring invasive procedures (18%). The most frequent grade 3 complication was renal failure, which is defined as a permanent rise in serum creatinine levels > or = twice the pretransplantation values (11%). Grade 4 complications (retransplantation or death) mainly were infection (14%) and primary dysfunction (11%). Comparison between the first and last 50 OLTs of the series indicates a significant decrease in the mean number of grade 1 and 2 complications. This was partially a result of better medical status of patients at the time of transplantation. Using univariate and multivariate analyses of risk factors, the best predictor of grade 1 complications was donor obesity; for grade 2 complications, the best predictor was a donor liver rewarming time of > 90 minutes, and for grade 3 and 4 complications, the best predictor was the APACHE II scoring system and donor cardiac arrest. CONCLUSIONS: Standardized definitions and classifications of complications of transplantation will allow us to better evaluate and compare results of transplantation among centers and over time, and better compare effectiveness of new therapies. Orthotopic liver transplantation still is a procedure with high morbidity that requires careful analysis of risk factors to optimize selection of patients and organ sharing.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baliga P., Merion R. M., Turcotte J. G., Ham J. M., Henley K. S., Lucey M. R., Schork A., Shyr Y., Campbell D. A., Jr Preoperative risk factor assessment in liver transplantation. Surgery. 1992 Oct;112(4):704–711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bein T., Forst H., Pratschke E. Apache-II-scoring in the liver transplant recipient. Intensive Care Med. 1992;18(1):60–61. doi: 10.1007/BF01706434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bismuth H., Castaing D., Ericzon B. G., Otte J. B., Rolles K., Ringe B., Sloof M. Hepatic transplantation in Europe. First Report of the European Liver Transplant Registry. Lancet. 1987 Sep 19;2(8560):674–676. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(87)92453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisneros C., Guillén F., Gomez R., Gutierrez J., Vorwald P., Montero A., Moreno E. Analysis of warm ischemia time for prediction of primary nonfunction of the hepatic graft. Transplant Proc. 1991 Jun;23(3):1976–1976. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavien P. A., Harvey P. R., Strasberg S. M. Preservation and reperfusion injuries in liver allografts. An overview and synthesis of current studies. Transplantation. 1992 May;53(5):957–978. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavien P. A., Sanabria J. R., Mentha G., Borst F., Buhler L., Roche B., Cywes R., Tibshirani R., Rohner A., Strasberg S. M. Recent results of elective open cholecystectomy in a North American and a European center. Comparison of complications and risk factors. Ann Surg. 1992 Dec;216(6):618–626. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199212000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavien P. A., Sanabria J. R., Strasberg S. M. Proposed classification of complications of surgery with examples of utility in cholecystectomy. Surgery. 1992 May;111(5):518–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein A. M. The outcomes movement--will it get us where we want to go? N Engl J Med. 1990 Jul 26;323(4):266–270. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199007263230410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- First M. R. Transplantation in the nineties. Transplantation. 1992 Jan;53(1):1–11. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199201000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gagner M., Franco D., Vons C., Smadja C., Rossi R. L., Braasch J. W. Analysis of morbidity and mortality rates in right hepatectomy with the preoperative APACHE II score. Surgery. 1991 Sep;110(3):487–492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray B. H. The legislative battle over health services research. Health Aff (Millwood) 1992 Winter;11(4):38–66. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.11.4.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray D. S. Diagnosis and prevalence of obesity. Med Clin North Am. 1989 Jan;73(1):1–13. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30688-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greig P. D., Woolf G. M., Sinclair S. B., Abecassis M., Strasberg S. M., Taylor B. R., Blendis L. M., Superina R. A., Glynn M. F., Langer B. Treatment of primary liver graft nonfunction with prostaglandin E1. Transplantation. 1989 Sep;48(3):447–453. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198909000-00020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubernatis G., Tusch G., Ringe B., Bunzendahl H., Pichlmayr R. Score-aided decision making in patients with severe liver damage after hepatic transplantation. World J Surg. 1989 May-Jun;13(3):259–265. doi: 10.1007/BF01659031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante-Rivard C., Esnaola S., Villeneuve J. P. Clinical and statistical validity of conventional prognostic factors in predicting short-term survival among cirrhotics. Hepatology. 1987 Jul-Aug;7(4):660–664. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840070408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassirer J. P. The quality of care and the quality of measuring it. N Engl J Med. 1993 Oct 21;329(17):1263–1265. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199310213291710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knaus W. A., Draper E. A., Wagner D. P., Zimmerman J. E. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985 Oct;13(10):818–829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. R., Wright T. L. Liver transplantation for patients with hepatitis B: what have we learned from our results? Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):796–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larvin M., McMahon M. J. APACHE-II score for assessment and monitoring of acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1989 Jul 22;2(8656):201–205. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeau G., Yanaga K., Marsh J. W., Tzakis A. G., Makowka L., Gordon R. D., Todo S., Stieber A. C., Iwatsuki S., Starzl T. E. Analysis of surgical complications after 397 hepatic transplantations. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990 Apr;170(4):317–322. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyström P. O., Bax R., Dellinger E. P., Dominioni L., Knaus W. A., Meakins J. L., Ohmann C., Solomkin J. S., Wacha H., Wittmann D. H. Proposed definitions for diagnosis, severity scoring, stratification, and outcome for trials on intraabdominal infection. Joint Working Party of SIS North America and Europe. World J Surg. 1990 Mar-Apr;14(2):148–158. doi: 10.1007/BF01664867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte J. B. Recent developments in liver transplantation. Lessons from a 5-year experience. J Hepatol. 1991 May;12(3):386–393. doi: 10.1016/0168-8278(91)90845-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer M., Schaffner F., Thung S. N. Excessive weight gain after liver transplantation. Transplantation. 1991 Apr;51(4):797–800. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199104000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrillo R. P., Mason A. L. Hepatitis B and liver transplantation. Problems and promises. N Engl J Med. 1993 Dec 16;329(25):1885–1887. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199312163292512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploeg R. J., D'Alessandro A. M., Knechtle S. J., Stegall M. D., Pirsch J. D., Hoffmann R. M., Sasaki T., Sollinger H. W., Belzer F. O., Kalayoglu M. Risk factors for primary dysfunction after liver transplantation--a multivariate analysis. Transplantation. 1993 Apr;55(4):807–813. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199304000-00024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh R. N., Murray-Lyon I. M., Dawson J. L., Pietroni M. C., Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973 Aug;60(8):646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Report of the National Cholesterol Education Program Expert Panel on Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Cholesterol in Adults. The Expert Panel. Arch Intern Med. 1988 Jan;148(1):36–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schein M., Gecelter G. APACHE II score in massive upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage from peptic ulcer: prognostic value and potential clinical applications. Br J Surg. 1989 Jul;76(7):733–736. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw B. W., Jr, Wood R. P., Gordon R. D., Iwatsuki S., Gillquist W. P., Starzl T. E. Influence of selected patient variables and operative blood loss on six-month survival following liver transplantation. Semin Liver Dis. 1985 Nov;5(4):385–393. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1040637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starzl T. E., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D. Liver transplantation (1). N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 12;321(15):1014–1022. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910123211505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasberg S. M., Clavien P. A. Cholecystolithiasis: lithotherapy for the 1990s. Hepatology. 1992 Sep;16(3):820–839. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840160332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasberg S. M., Sanabria J. R., Clavien P. A. Complications of laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Can J Surg. 1992 Jun;35(3):275–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todo S., Demetris A. J., Van Thiel D., Teperman L., Fung J. J., Starzl T. E. Orthotopic liver transplantation for patients with hepatitis B virus-related liver disease. Hepatology. 1991 Apr;13(4):619–626. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright T. L., Donegan E., Hsu H. H., Ferrell L., Lake J. R., Kim M., Combs C., Fennessy S., Roberts J. P., Ascher N. L. Recurrent and acquired hepatitis C viral infection in liver transplant recipients. Gastroenterology. 1992 Jul;103(1):317–322. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)91129-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


