Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The authors laparoscopic approach for a Nissen fundoplication is presented. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: The technique has been undertaken in 155 patients over 29 months, with 137 patients having been observed for more than 3 months. METHODS: Three hundred sixty degree fundoplication was undertaken using three or four sutures to secure the wrap. Short gastric vessels were not divided, and the anterior wall of the stomach was used to construct the wrap around the esophagus with a large bougie in position. RESULTS: The operation was not completed laparoscopically in 19 patients because a satisfactory wrap could not be achieved. Ten patients undergoing laparoscopic fundoplication underwent a subsequent operation related to the laparoscopic procedure within 6 months, and there was one postoperative death. Seven other patients were readmitted to the hospital several days subsequent to their discharge, four because of pulmonary emboli. Of 137 patients who have been observed for more than 3 months, 133 patients are well and currently are free from reflux symptoms. CONCLUSIONS: In uncomplicated cases, laparoscopic fundoplication has similar advantages to laparoscopic cholecystectomy. In spite of the fact that it has not yet achieved the overall usefulness of open fundoplication, it seems likely that laparoscopic fundoplication will be used increasingly in the treatment of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Full text
PDF
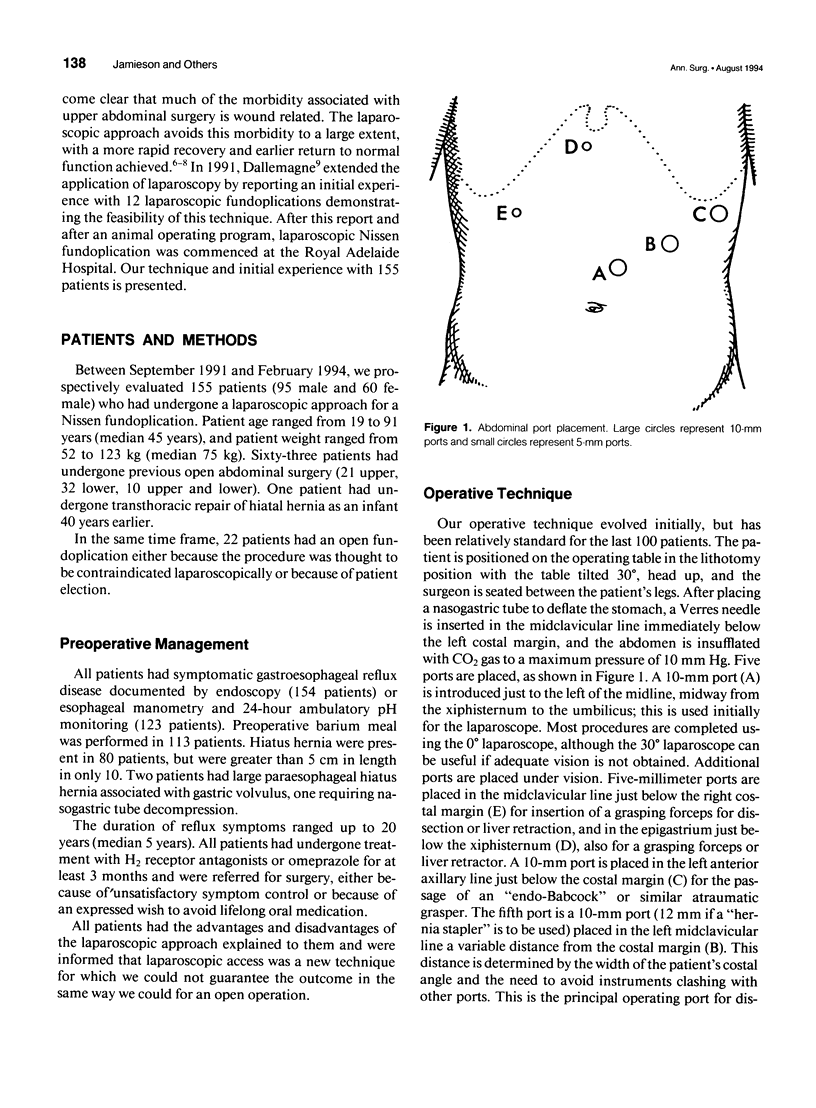

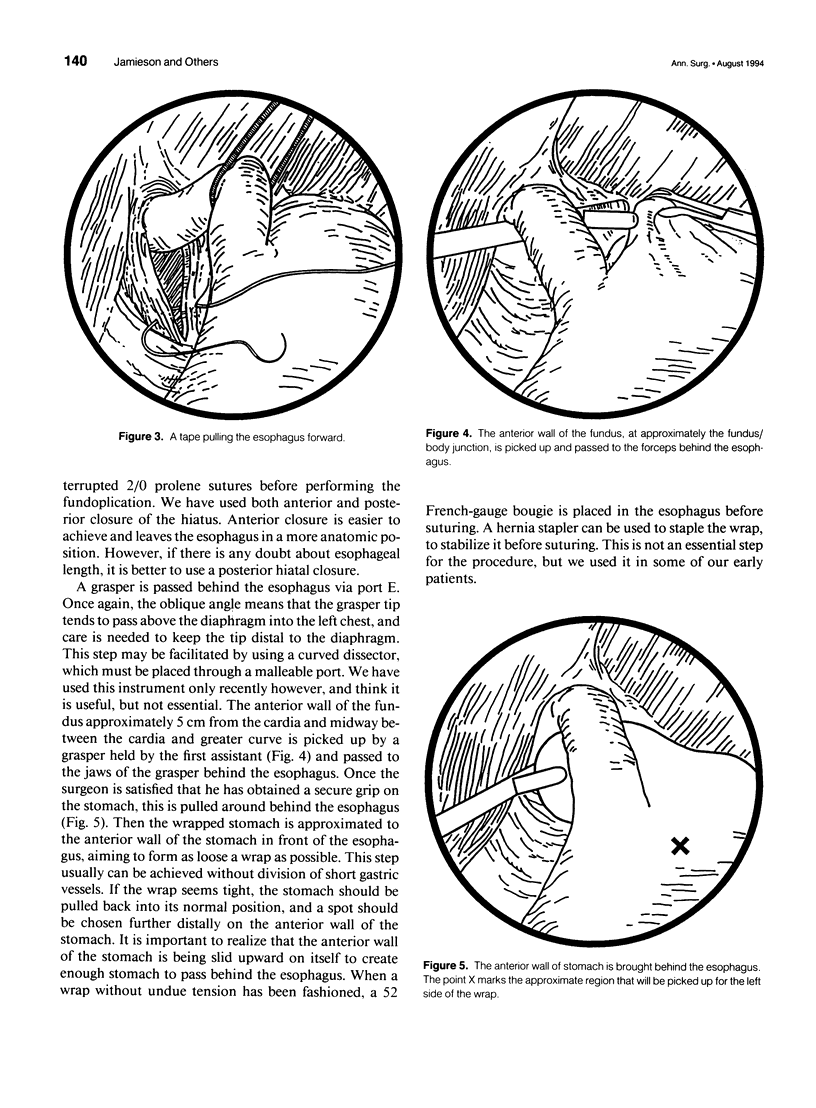





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berguer R., Stiegmann G. V., Yamamoto M., Kim J., Mansour A., Denton J., Norton L. W., Angelchik J. P. Minimal access surgery for gastroesophageal reflux: laparoscopic placement of the Angelchik prosthesis in pigs. Surg Endosc. 1991;5(3):123–126. doi: 10.1007/BF02653217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Congreve D. P. Laparoscopic paraesophageal hernia repair. J Laparoendosc Surg. 1992 Feb;2(1):45–48. doi: 10.1089/lps.1992.2.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuschieri A., Shimi S., Nathanson L. K. Laparoscopic reduction, crural repair, and fundoplication of large hiatal hernia. Am J Surg. 1992 Apr;163(4):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(92)90046-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dallemagne B., Weerts J. M., Jehaes C., Markiewicz S., Lombard R. Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication: preliminary report. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991 Sep;1(3):138–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Bonavina L., Albertucci M. Nissen fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Evaluation of primary repair in 100 consecutive patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Jul;204(1):9–20. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198607000-00002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMeester T. R., Stein H. J. Minimizing the side effects of antireflux surgery. World J Surg. 1992 Mar-Apr;16(2):335–336. doi: 10.1007/BF02071542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois F., Icard P., Berthelot G., Levard H. Coelioscopic cholecystectomy. Preliminary report of 36 cases. Ann Surg. 1990 Jan;211(1):60–62. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199001000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geagea T. Laparoscopic Nissen's fundoplication: preliminary report on ten cases. Surg Endosc. 1991;5(4):170–173. doi: 10.1007/BF02653255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson J., Johnsson F., Joelsson B., Florén C. H., Walther B. Outcome 5 years after 360 degree fundoplication for gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. Br J Surg. 1993 Jan;80(1):46–49. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800800118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddern G. J., Myers J. C., McIntosh N., Bridgewater F. H., Jamieson G. G. The effect of the Angelchik prosthesis on esophageal and gastric function. Arch Surg. 1991 Nov;126(11):1418–1422. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1991.01410350112018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin I. G., Holdsworth P. J., Asker J., Baltas B., Glinatsis M. T., Sue-Ling H., Gibson J., Johnston D., McMahon M. J. Laparoscopic cholecystectomy as a routine procedure for gallstones: results of an 'all-comers' policy. Br J Surg. 1992 Aug;79(8):807–810. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800790833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISSEN R. Eine einfache Operation zur Beeinflussung der Refluxoesophagitis. Schweiz Med Wochenschr. 1956 May 18;86(Suppl 20):590–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NISSEN R. Gastropexy and "fundoplication" in surgical treatment of hiatal hernia. Am J Dig Dis. 1961 Oct;6:954–961. doi: 10.1007/BF02231426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathanson L. K., Shimi S., Cuschieri A. Laparoscopic ligamentum teres (round ligament) cardiopexy. Br J Surg. 1991 Aug;78(8):947–951. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti M., Hell K. Fundoplication for the treatment of gastroesophageal reflux in hiatal hernia. World J Surg. 1977 Jul;1(4):439–443. doi: 10.1007/BF01565907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siewert J. R., Feussner H., Walker S. J. Fundoplication: how to do it? Peri-esophageal wrapping as a therapeutic principal in gastro-esophageal reflux prevention. World J Surg. 1992 Mar-Apr;16(2):326–334. doi: 10.1007/BF02071541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaw A. T., Reddick E. J., Olsen D. O. Laparoscopic laser cholecystectomy: analysis of 500 procedures. Surg Laparosc Endosc. 1991 Mar;1(1):2–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein H. J., Feussner H., Siewert J. R. Minimally invasive antireflux procedures. World J Surg. 1992 Mar-Apr;16(2):347–348. doi: 10.1007/BF02071546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston P. V. A new clinch knot. Obstet Gynecol. 1991 Jul;78(1):144–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]