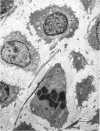
Abstract
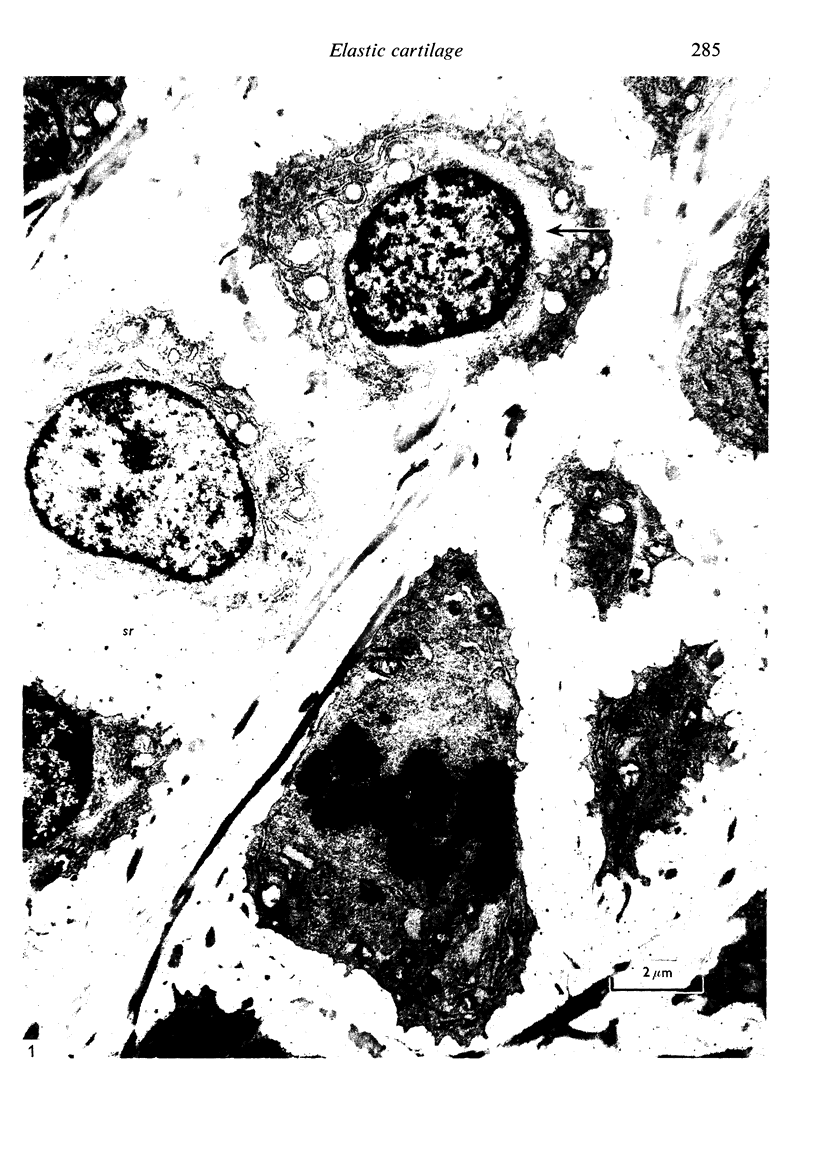
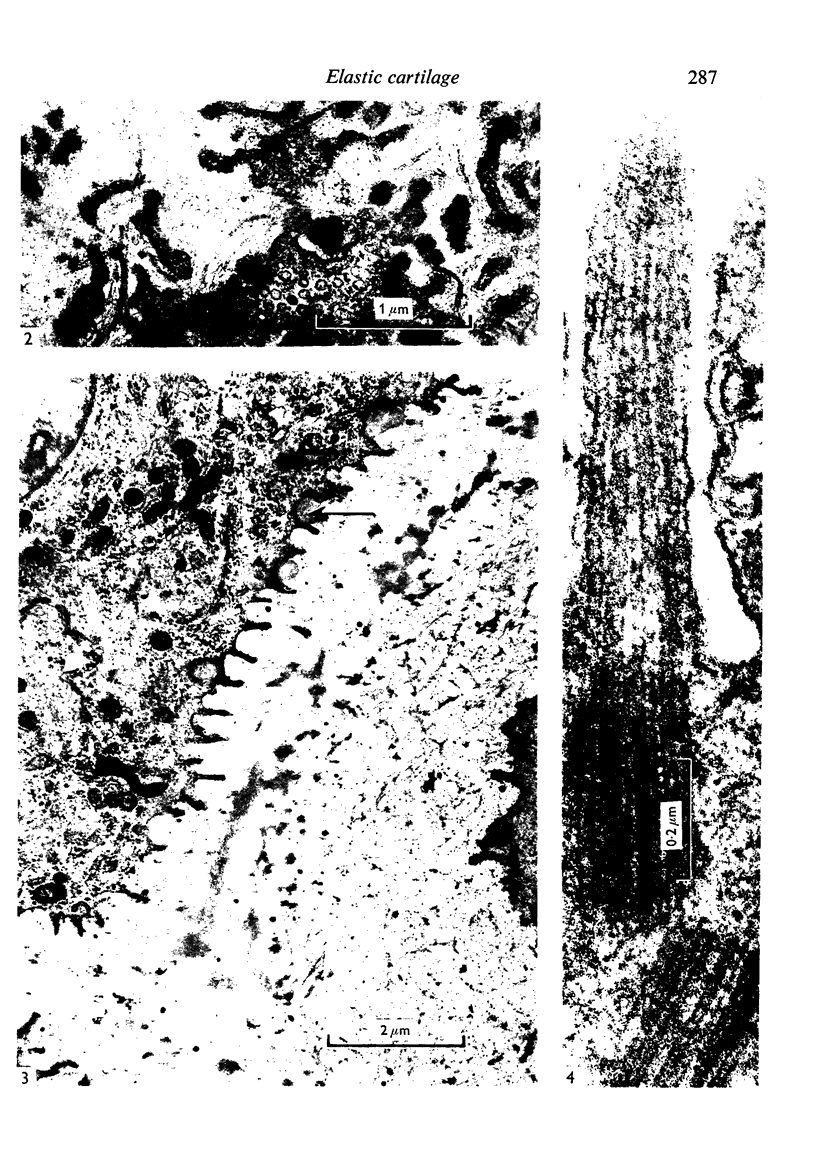
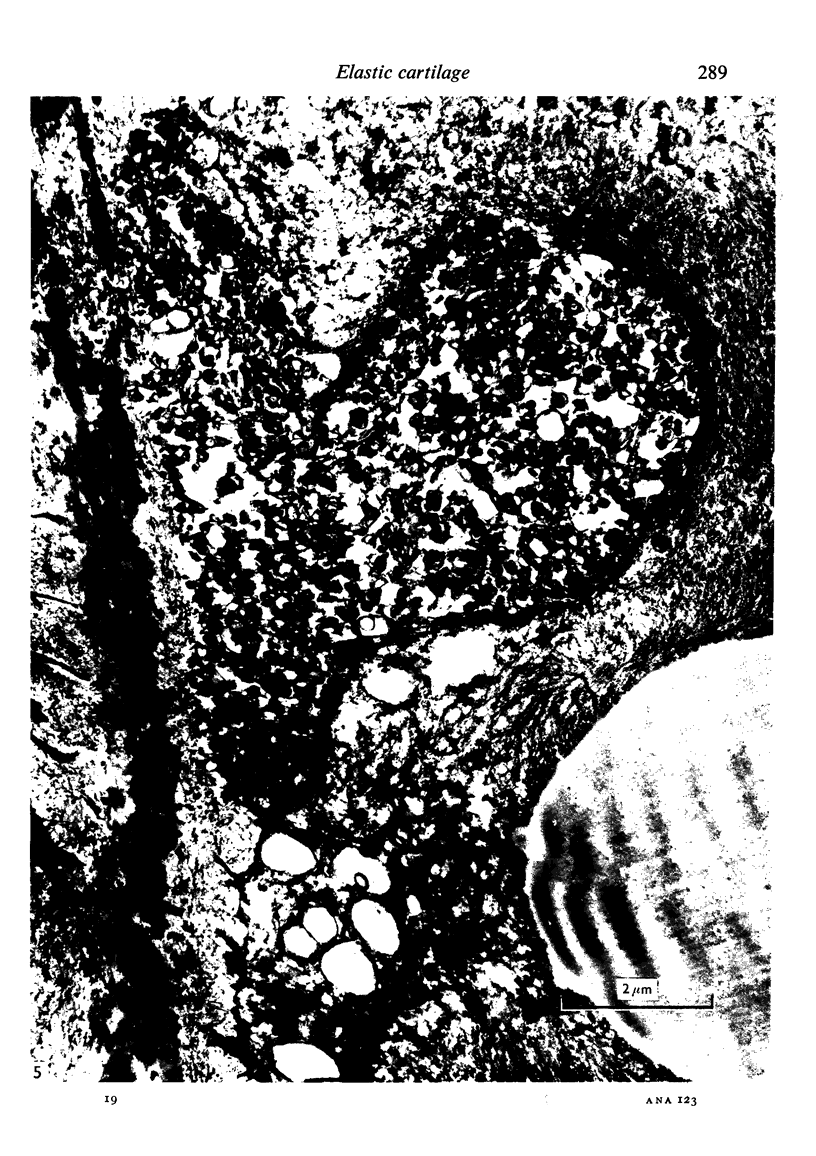
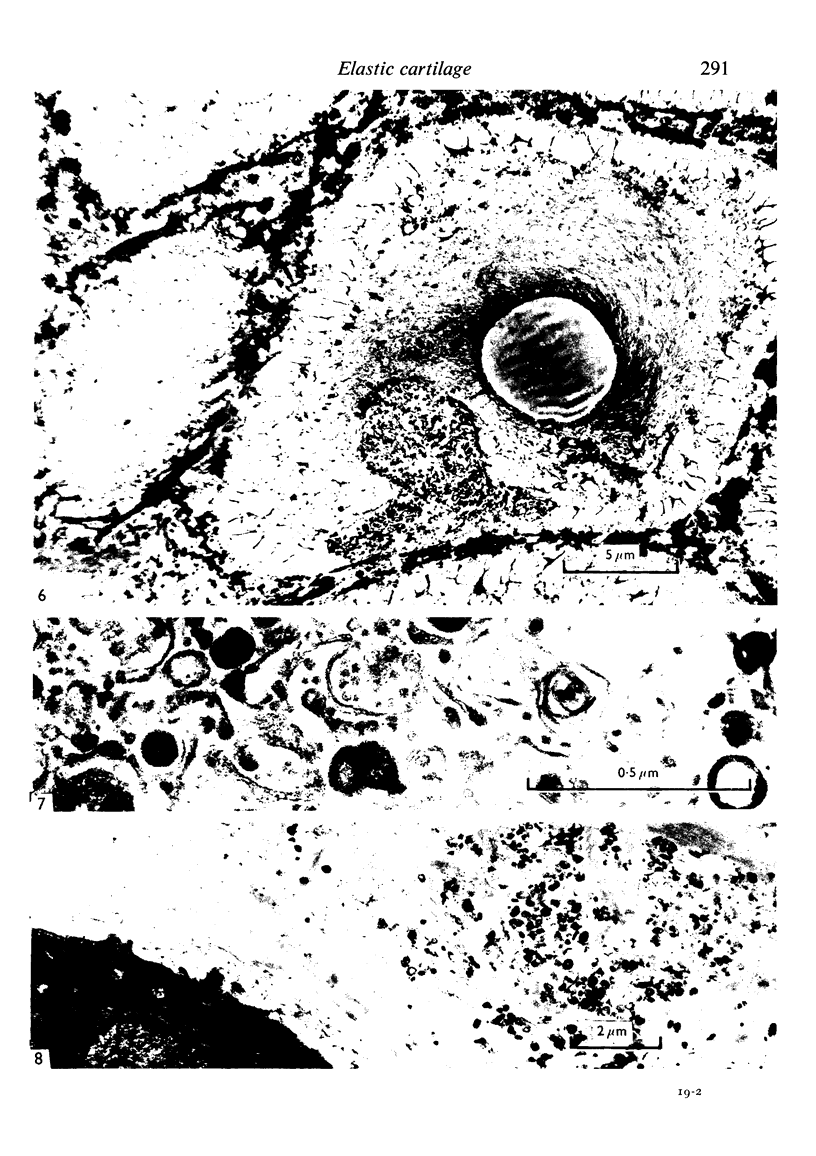
The fine structure of the elastic cartilage of the pinna has been examined in young rabbits aged from 1 day to 1108 days. Changes associated with growth and development are related not only to age but also to the actual situation in the pinna. In the midline, progressive changes are seen from the tip to the base. The changes in the chondroblasts with time are compared with those described in hyaline cartilage. Structures occur that, except for the presence of crystals, are apparently morphologically identical with the matrix vesicles of calcifying cartilage. These matrix vesicles, however, become very prominent with age, and aggregations of them appear to be released into the intercellular tissue from vacuoles at the periphery of the chondroblasts. There is no obvious association with calcification. Occasional single cilia, desmosomes and giant mitochondria are seen. Elastica is present at birth, and eventually every cell is separated from its neighbours by a partial investment of elastica. The quantity of matrix seems to increase with time, and with distance from the tip of the ear. This is accompanied by a marked increase in cell size with time.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON D. R. THE ULTRASTRUCTURE OF ELASTIC AND HYALINE CARTILAGE OF THE RAT. Am J Anat. 1964 May;114:403–434. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001140305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson H. C. Vesicles associated with calcification in the matrix of epiphyseal cartilage. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):59–72. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARNETT C. H., COCHRANE W., PALFREY A. J. AGE CHANGES IN ARTICULAR CARTILAGE OF RABBITS. Ann Rheum Dis. 1963 Nov;22:389–400. doi: 10.1136/ard.22.6.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonucci E. Fine structure and histochemistry of "calcifying globules" in epiphyseal cartilage. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;103(2):192–217. doi: 10.1007/BF00337312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonucci E. Fine structure of early cartilage calcification. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Sep;20(1):33–50. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. I. Ultrastructure of the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):326–341. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cushman S. W. Structure-function relationships in the adipose cell. II. Pinocytosis and factors influencing its activity in the isolated adipose cell. J Cell Biol. 1970 Aug;46(2):342–353. doi: 10.1083/jcb.46.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ECHLIN P. INTRA-CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANOUS INCLUSIONS IN THE BLUE-GREEN ALGA, ANACYSTIS NIDULANS. Arch Mikrobiol. 1964 Oct 2;49:267–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00409749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GHADIALLY F. N., MEACHIM G., COLLINS D. H. EXTRA-CELLULAR LIPID IN THE MATRIX OF HUMAN ARTICULAR CARTILAGE. Ann Rheum Dis. 1965 Mar;24:136–146. doi: 10.1136/ard.24.2.136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee T. K., Jr, Ross R., Hartman J. L. The fine structure of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1966 Jul;30(1):59–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.30.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenlee T. K., Jr, Ross R. The development of the rat flexor digital tendon, a fine structure study. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 May;18(3):354–376. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUFT J. H. Improvements in epoxy resin embedding methods. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1961 Feb;9:409–414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.9.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke M., Krishnan N., McMahon J. T. A routine method for obtaining high contrast without staining sections. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):540–544. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhaud M., Pappas G. D. Cilia formation in the adult cat brain after pargyline treatment. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jun;37(3):599–609. doi: 10.1083/jcb.37.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfrey A. J., Davies D. V. The fine structure of chondrocytes. J Anat. 1966 Apr;100(Pt 2):213–226. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R., Bornstein P. The elastic fiber. I. The separation and partial characterization of its macromolecular components. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):366–381. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutter W. J., Pictet R. L., Morris P. W. Toward molecular mechanisms of developmental processes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:601–646. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABATINI D. D., BENSCH K., BARRNETT R. J. Cytochemistry and electron microscopy. The preservation of cellular ultrastructure and enzymatic activity by aldehyde fixation. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:19–58. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON H., KIMBALL F. B. Studies on cartilage. III. The occurrence of collagen within vacuoles of the golgi apparatus. J Cell Biol. 1962 Mar;12:599–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.12.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON H., ROBINSON R. A. Studies on cartilage: electron microscope observations on normal rabbit ear cartilage. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1958 Jul 25;4(4):401–406. doi: 10.1083/jcb.4.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherft J. P., Daems W. T. Single cilia in chondrocytes. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Aug 30;19(5):546–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80080-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Christie K. N., Frame J. Desmosomes, cilia and acanthosomes associated with keratocytes. J Anat. 1969 Sep;105(Pt 2):383–392. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W. The disposition of proteinpolysaccharide in the epiphysial plate cartilage of the young rabbit. J Cell Sci. 1970 May;6(3):843–864. doi: 10.1242/jcs.6.3.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Friberg U. Electron microscopic enzyme histochemical studies on the cellular genesis of matrix vesicles in the epiphyseal plate. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Oct;41(1):43–59. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(72)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Friberg U. Ultrastructure and acid phosphatase activity of matrix vesicles and cytoplasmic dense bodies in the epiphyseal plate. J Ultrastruct Res. 1970 Dec;33(5):554–573. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(70)90181-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley D. N. Cilia and centrioles of the rat adrenal cortex. J Anat. 1967 Apr;101(Pt 2):223–237. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]