Abstract
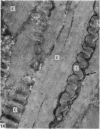
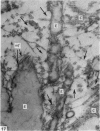
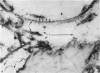
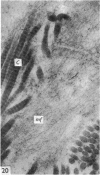
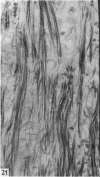
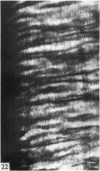
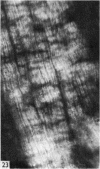
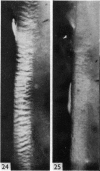
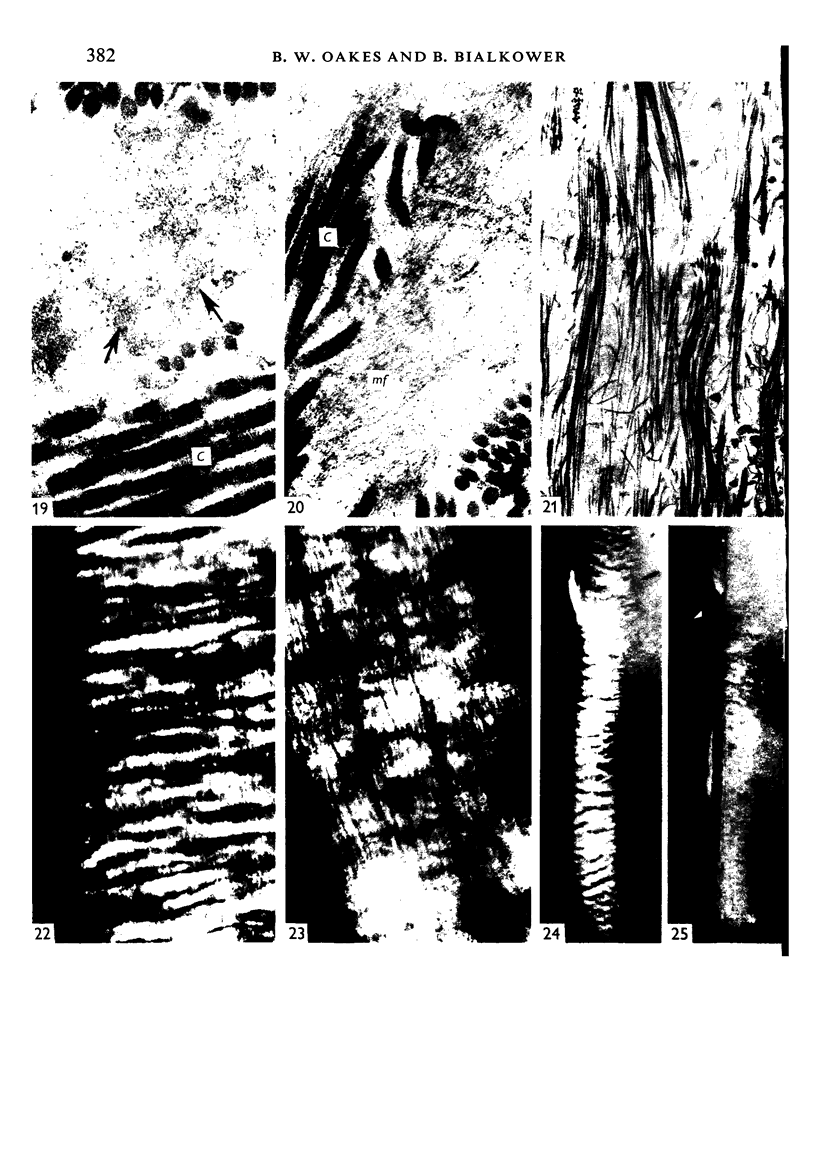
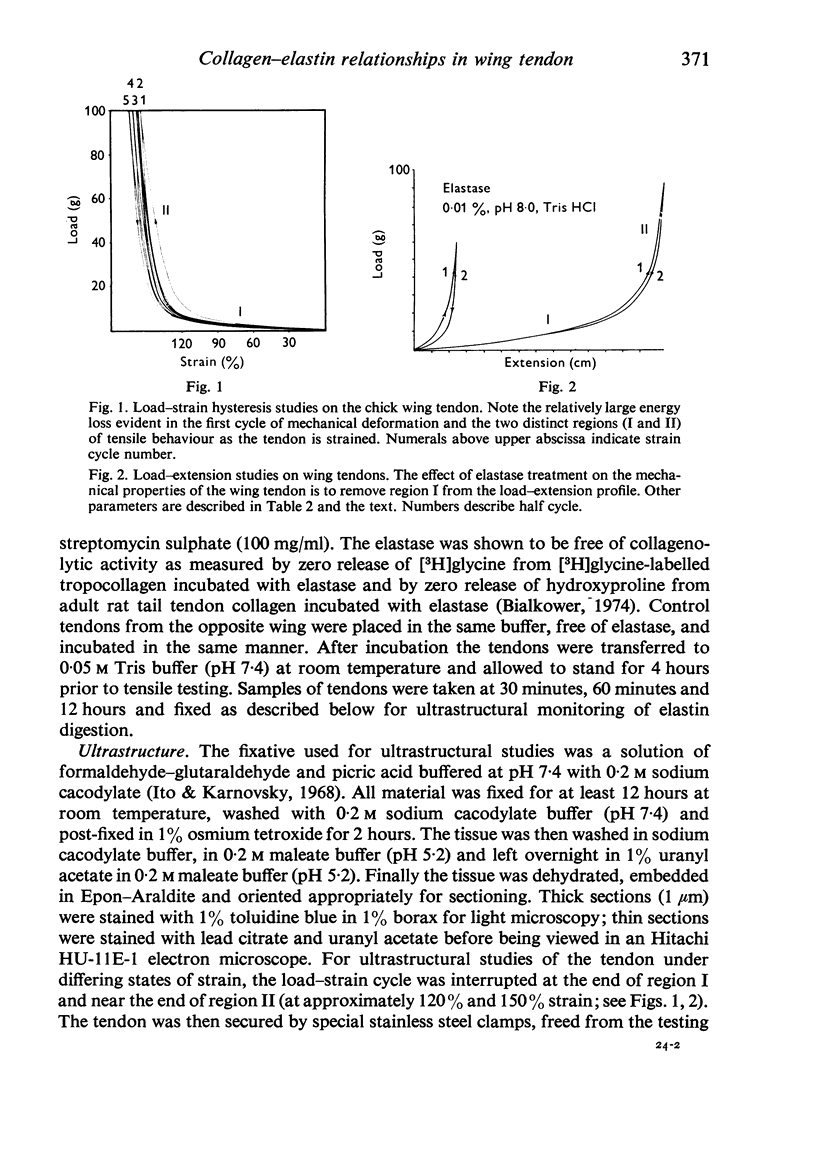
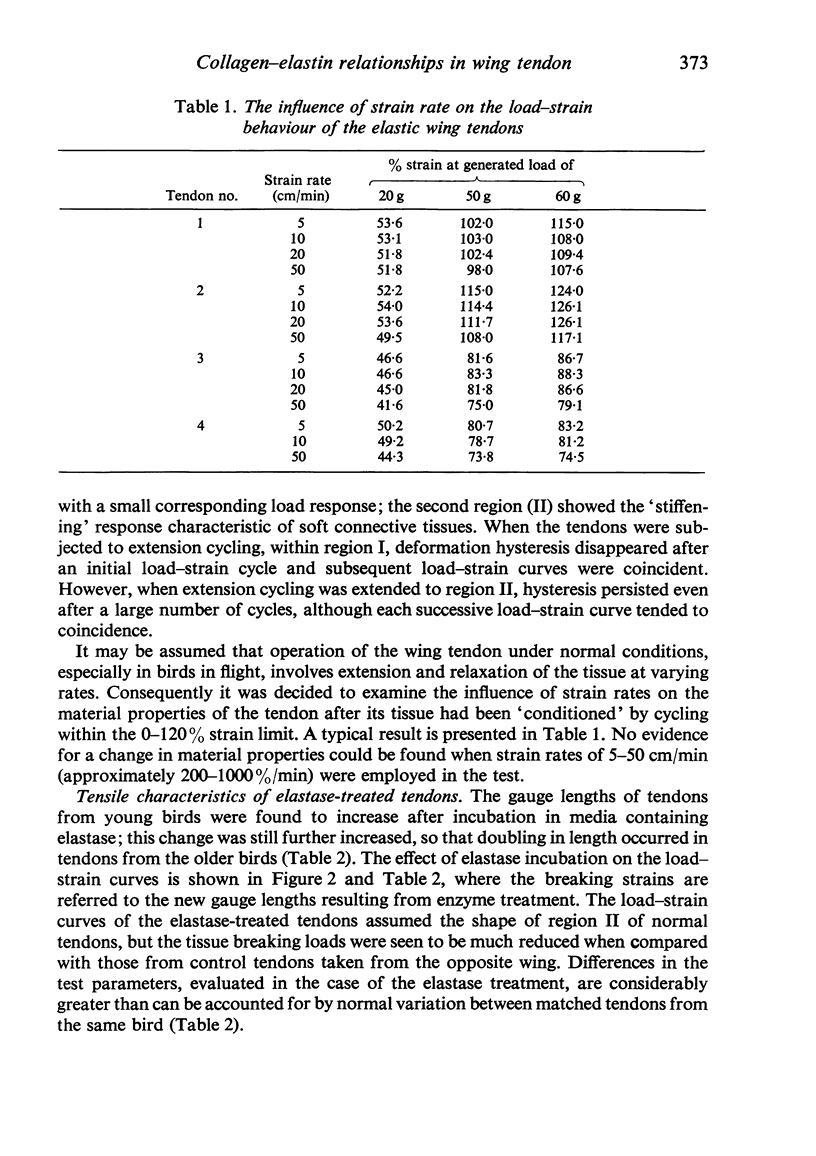
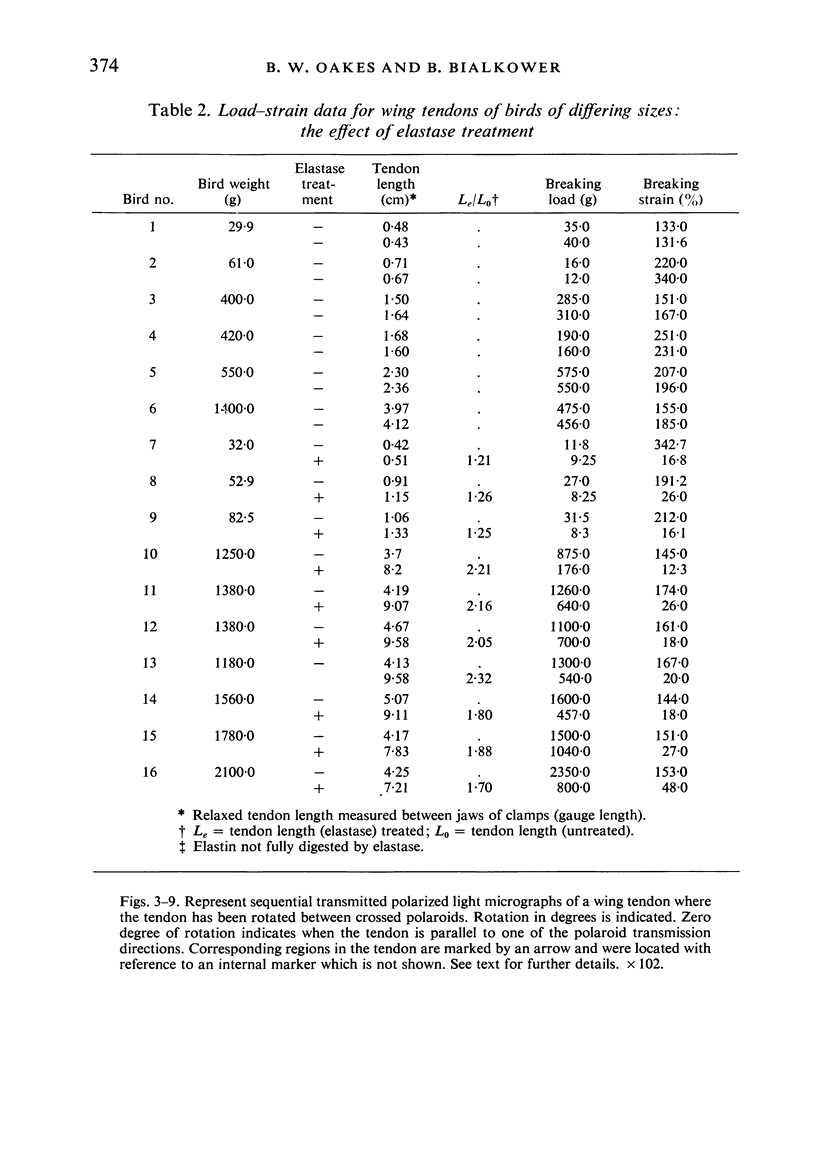
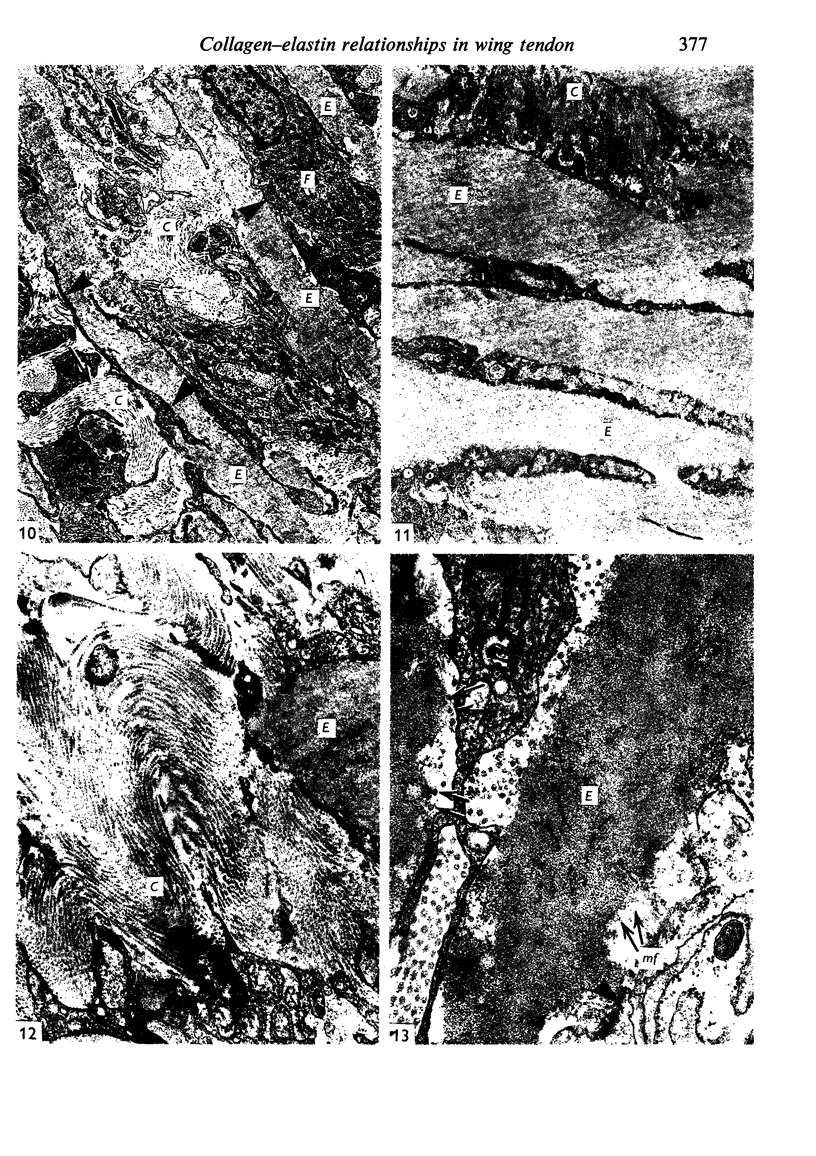
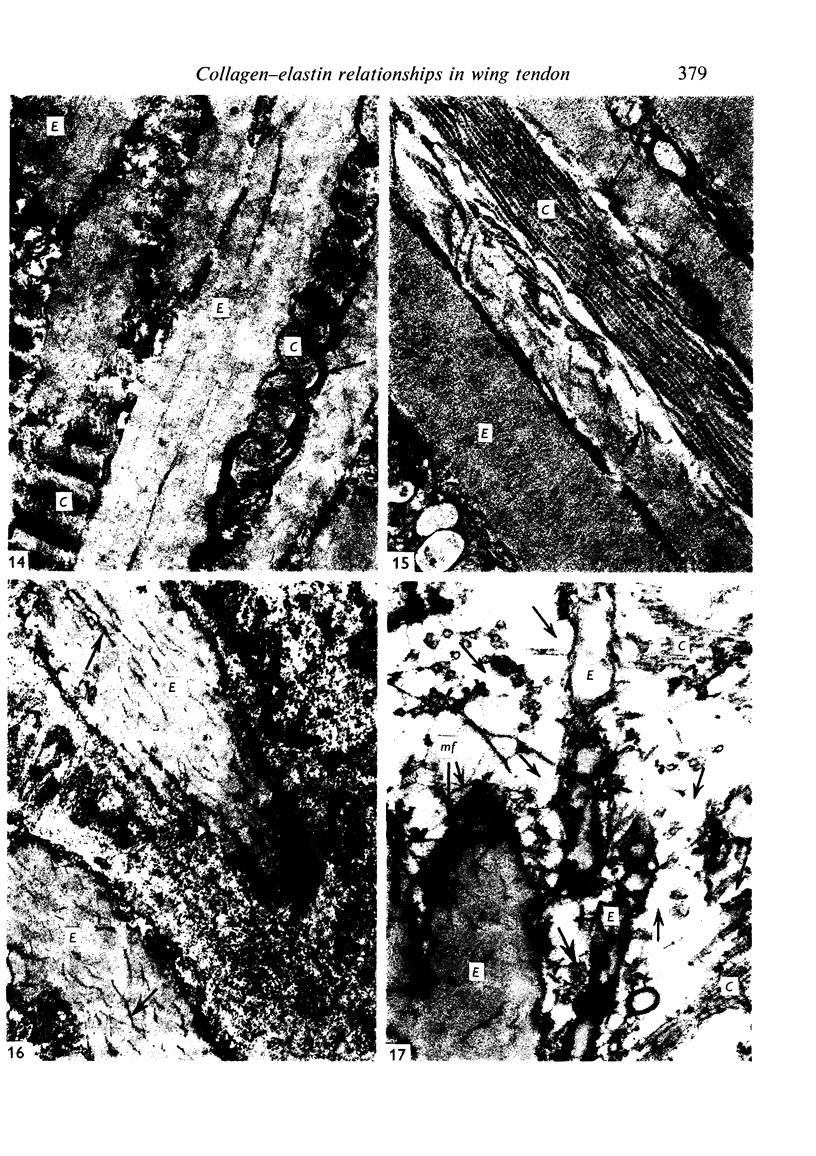
The interaction between collagen and elastin networks under conditions of load-extension has been studied in the elastic wing tendon of the domestic fowl. The load-extention curves obtained could be divided into two regions, the first region representing the ability of the tendon to undergo great extension at low tension, the second representing a limit region where the collagen of the tendon appears to become fully extended. Following removal of the elastin network with pure elastase only the second region of the curve persisted, indicating that elastin is largely responsible for the mechanical event represented by the first region of the curve. The collagen network of tendons apparently is normally held in a folded conformational state by elastin, for elastase treatment results in elongation of tendons even in the absence of loading. Complete removal of elastin, and alignment of collagen bundles were confirmed ultrastructurally in the elongated tendons. The breading load of the elastase-treated tendons was also significangly reduced, indicating that an elastase-sensitive component is a limiting factor in determining the ultimate strength of the tendon.
Full text
PDF













Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURTON A. C. Relation of structure to function of the tissues of the wall of blood vessels. Physiol Rev. 1954 Oct;34(4):619–642. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1954.34.4.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTON R. W., DAINAUSKAS J., CLARK J. W. Elastic properties of single elastic fibers. J Appl Physiol. 1962 May;17:547–551. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1962.17.3.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COULSON W. F., WEISSMAN N., CARNES W. H. CARDIOVASCULAR STUDIES ON COPPER-DEFICIENT SWINE. VII. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF AORTIC AND DERMAL COLLAGEN. Lab Invest. 1965 Mar;14:303–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamant J., Keller A., Baer E., Litt M., Arridge R. G. Collagen; ultrastructure and its relation to mechanical properties as a function of ageing. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1972 Mar 14;180(1060):293–315. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1972.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon J. S., Hunter J. A., Steven F. S. An electron microscopic study of the effect of crude bacterial -amylase and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on human tendon. J Ultrastruct Res. 1972 Mar;38(5):466–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-5320(72)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay J. B., Steven F. S. The fibrous components of bovine ligamentum nuchae observed in the scanning electron microscope. J Microsc. 1973 Sep;99(1):57–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1973.tb03852.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM K. N. The fine structure of normal rat aorta. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1962 Oct;40:341–352. doi: 10.1038/icb.1962.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. S., Cleary E. G. The determination of collagen and elastin. Methods Biochem Anal. 1967;15:25–76. doi: 10.1002/9780470110331.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. S., Sandberg L. B., Cleary E. G. The swelling of bovine ligamentum nuchae as a function of pH. Biochem J. 1965 Sep;96(3):813–817. doi: 10.1042/bj0960813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. W., Taylor J. F. The stress developed by sheets of chick fibroblasts in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1969 Jan;54(1):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(69)90299-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KARRER H. E. An electron microscope study of the aorta in young and in aging mice. J Ultrastruct Res. 1961 Mar;5:1–27. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(61)80002-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajikawa K., Nakanishi I., Hori I., Matsuda Y., Kondo K. [Electron microscopic observations on connective tissues using ruthenium red staining]. J Electron Microsc (Tokyo) 1970;19(4):347–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkaldy-Willis W. H., Murakami H., Emery M. A., Mungai J., Shnitka T. K. Elastogenesis in the cranial patagium of the wing of the chick. Can J Surg. 1967 Jul;10(3):348–358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft J. H. Ruthenium red and violet. I. Chemistry, purification, methods of use for electron microscopy and mechanism of action. Anat Rec. 1971 Nov;171(3):347–368. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091710302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minns R. J., Soden P. D., Jackson D. S. The role of the fibrous components and ground substance in the mechanical properties of biological tissues: a preliminary investigation. J Biomech. 1973 Mar;6(2):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(73)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers D. B., Highton T. C., Rayns D. G. Ruthenium red-positive filaments interconnecting collagen fibrils. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Jan;42(1):87–92. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NUNLEY R. L. The ligamenta flava of the dog. A study of tensile and physical properties. Am J Phys Med. 1958 Oct;37(5):256–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachemson A. L., Evans J. H. Some mechanical properties of the third human lumbar interlaminar ligament (ligamentum flavum). J Biomech. 1968 Aug;1(3):211–220. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(68)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes B. W., Carmichael G. G. Development of the elastic wing ligament in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). J Anat. 1971 Dec;110(Pt 3):502–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes B. W., Carmichael G. G. Proceedings: Ultrastructural studies of the developing rat cruciate ligament using ruthenium red. J Anat. 1973 Dec;116(Pt 3):477–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., MOLINARI S. Electron microscopy of muscular arteries; pial vessels of43 the cat and monkey. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Jun;3:447–468. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEASE D. C., PAULE W. J. Electron microscopy of elastic arteries; the thoracic aorta of the rat. J Ultrastruct Res. 1960 Jun;3:469–483. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(60)90023-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROACH M. R., BURTON A. C. The reason for the shape of the distensibility curves of arteries. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1957 Aug;35(8):681–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. Freeze-etched connective tissue. Int Rev Connect Tissue Res. 1973;6:257–305. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-363706-2.50012-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. C., Dorfman A. The sulfation of chondroitin sulfate in embryonic chick cartilage epiphyses. J Biol Chem. 1969 Jan 25;244(2):348–352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. B., Cliff W. J., Gabbiani G., Irle C., Statkov P. R., Majno G. Myofibroblasts in an avascular fibrous tissue. Lab Invest. 1973 Aug;29(2):197–206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Frame J. Observations on the collagen and proteinpolysaccharide complex of rabbit cornea stroma. J Cell Sci. 1969 Mar;4(2):421–436. doi: 10.1242/jcs.4.2.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steven F. S., Minns R. J., Thomas H. The isolation of chemically pure elastins in a form suitable for mechanical testing. Connect Tissue Res. 1974;2(2):85–90. doi: 10.3109/03008207409152092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thyberg J., Lohmander S., Friberg U. Electron microscopic demonstration of proteoglycans in guinea pig epiphyseal cartilage. J Ultrastruct Res. 1973 Dec;45(5):407–427. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(73)80070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLINSKY H., GLAGOV S. STRUCTURAL BASIS FOR THE STATIC MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE AORTIC MEDIA. Circ Res. 1964 May;14:400–413. doi: 10.1161/01.res.14.5.400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD G. C. Some tensile properties of elastic tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Nov;15(3):311–324. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90032-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtschafter Z. T., Cleary E. G., Jackson D. S., Sandberg L. B. Histological changes during the development of the bovine nuchal ligament. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):481–488. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]