Abstract
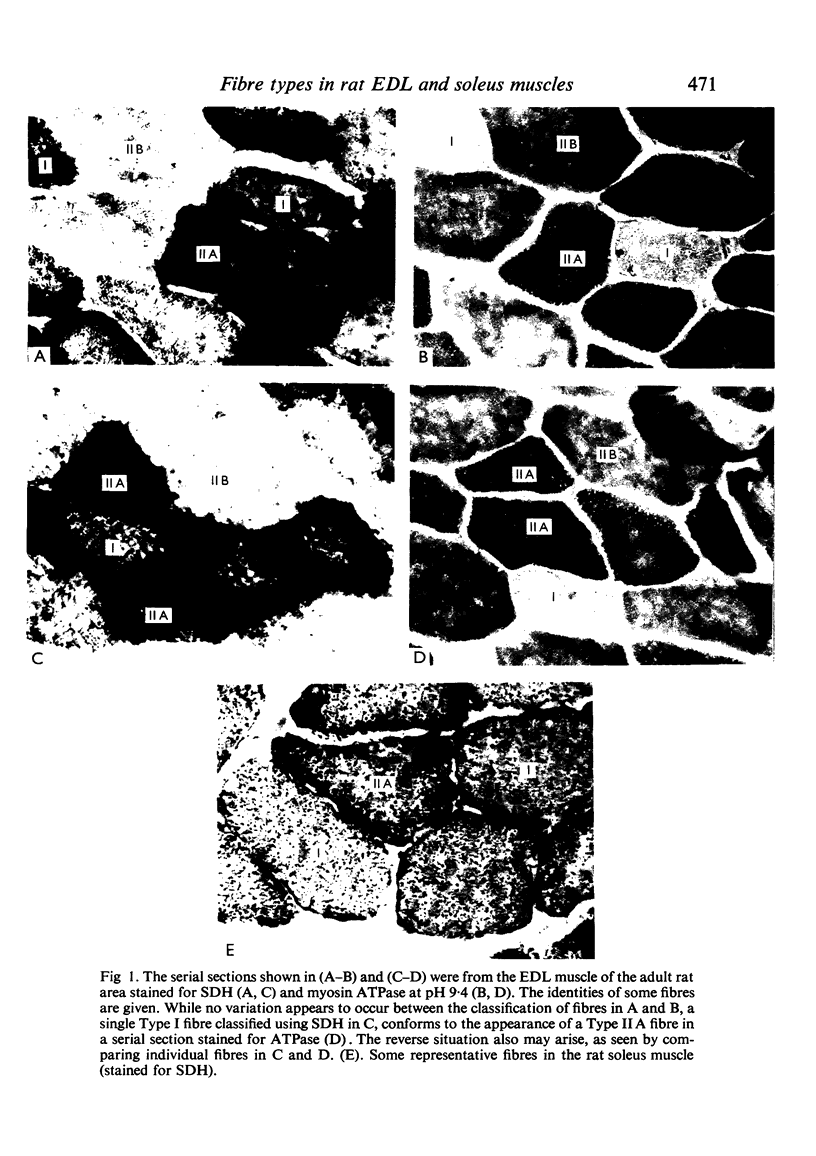
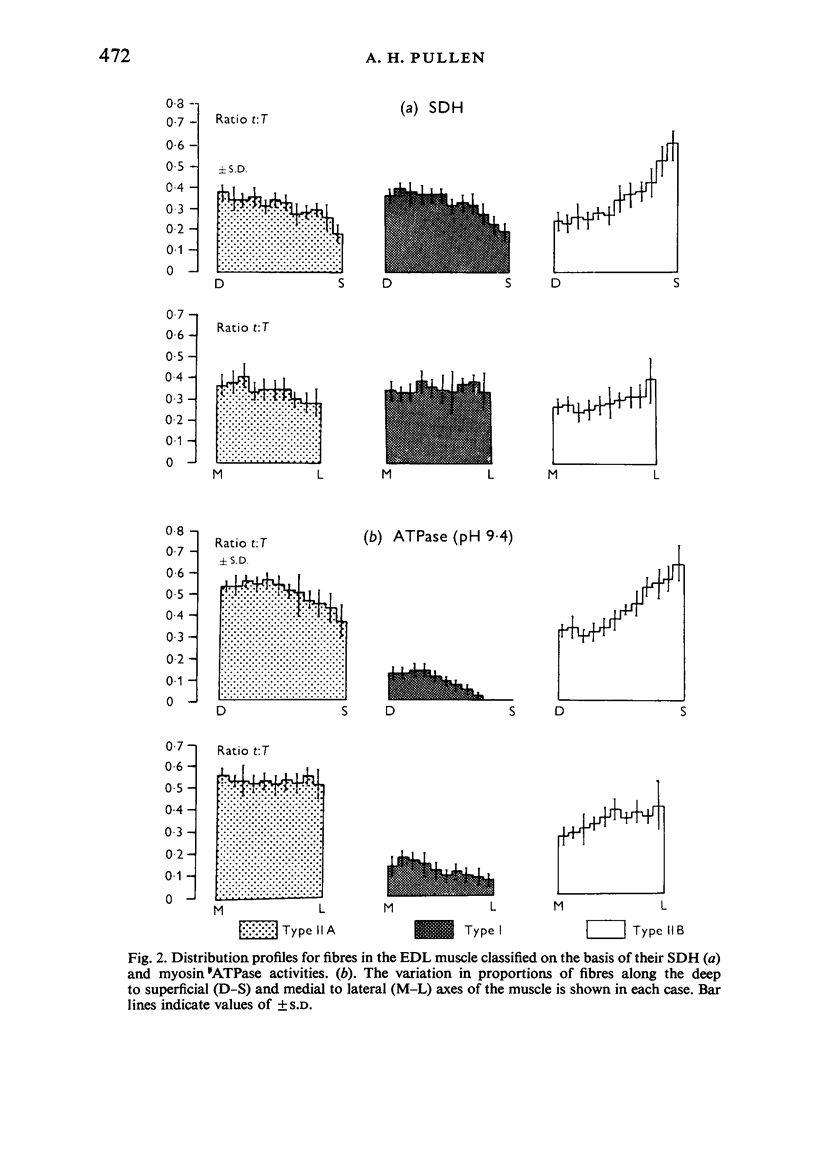
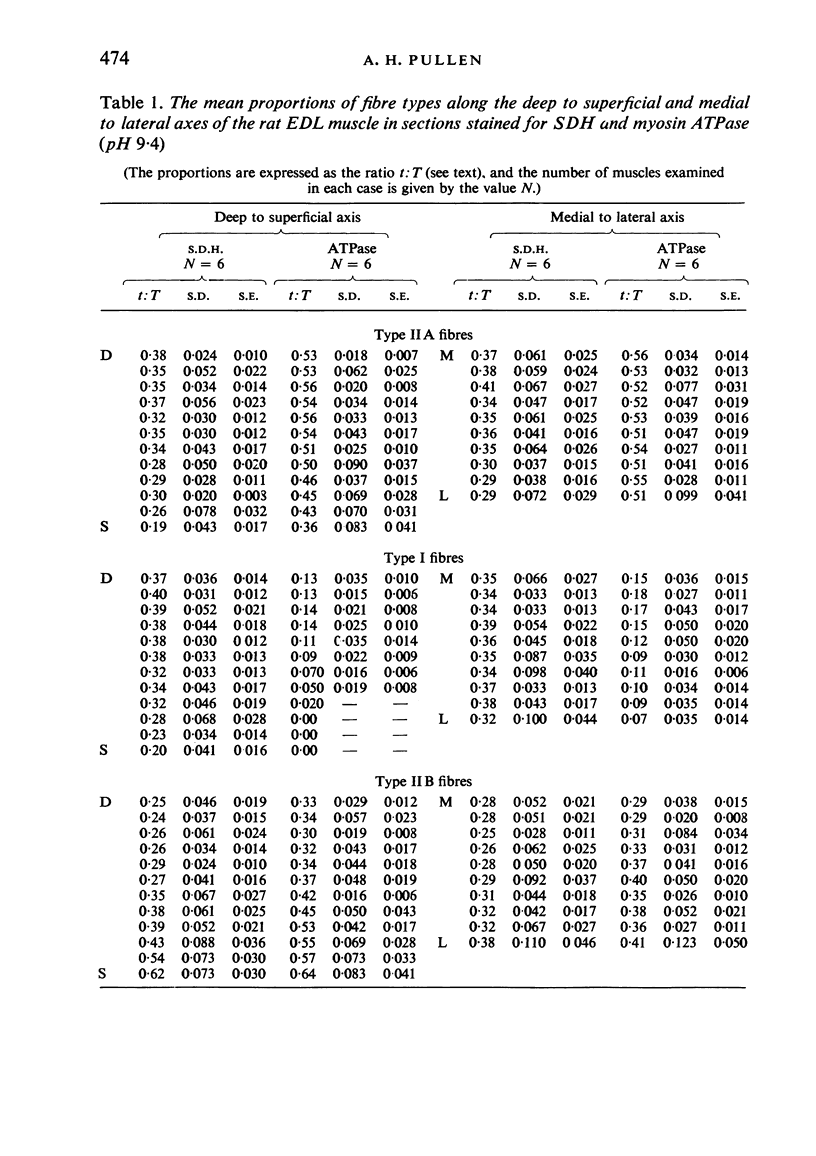
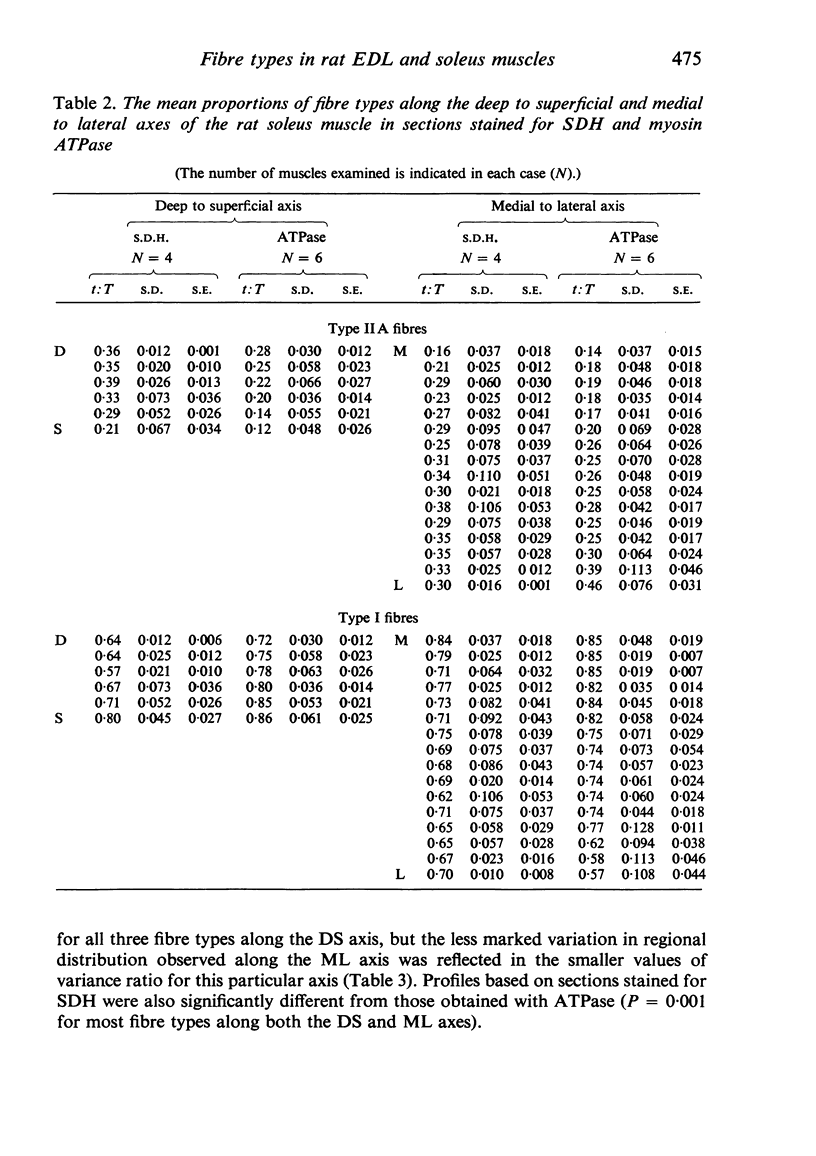
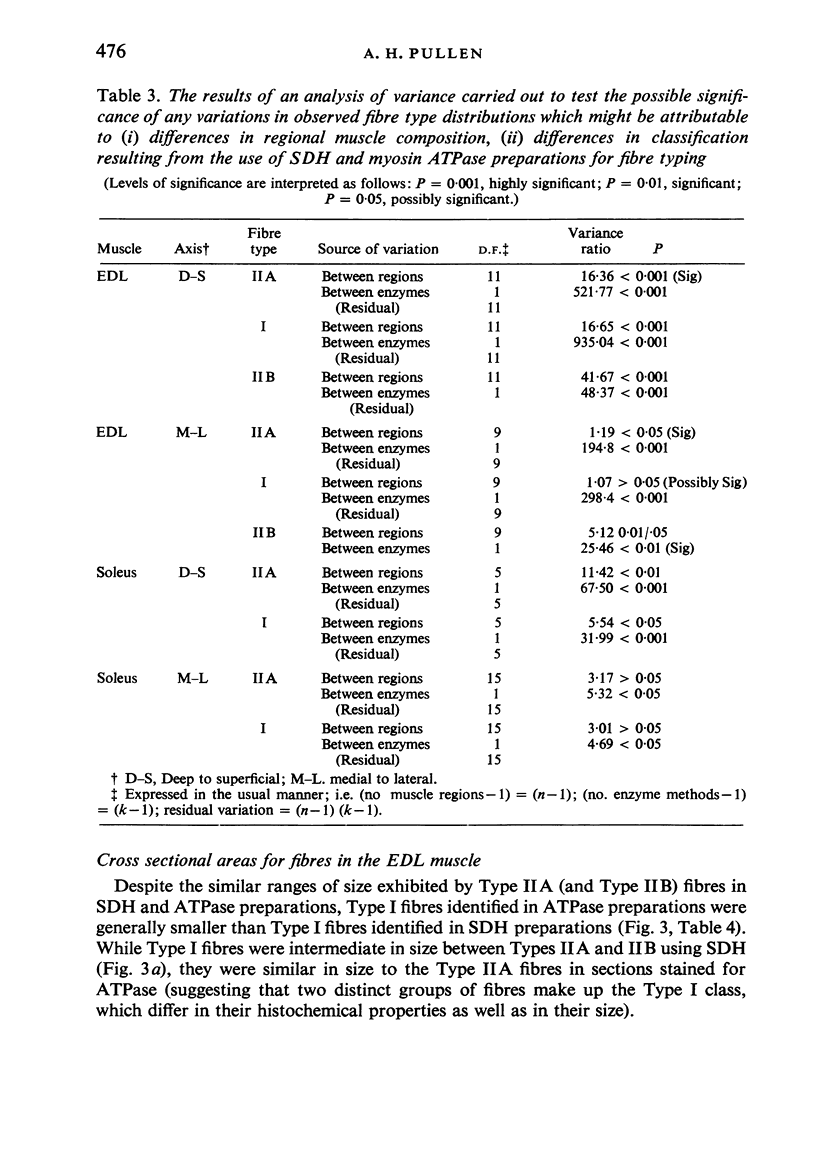
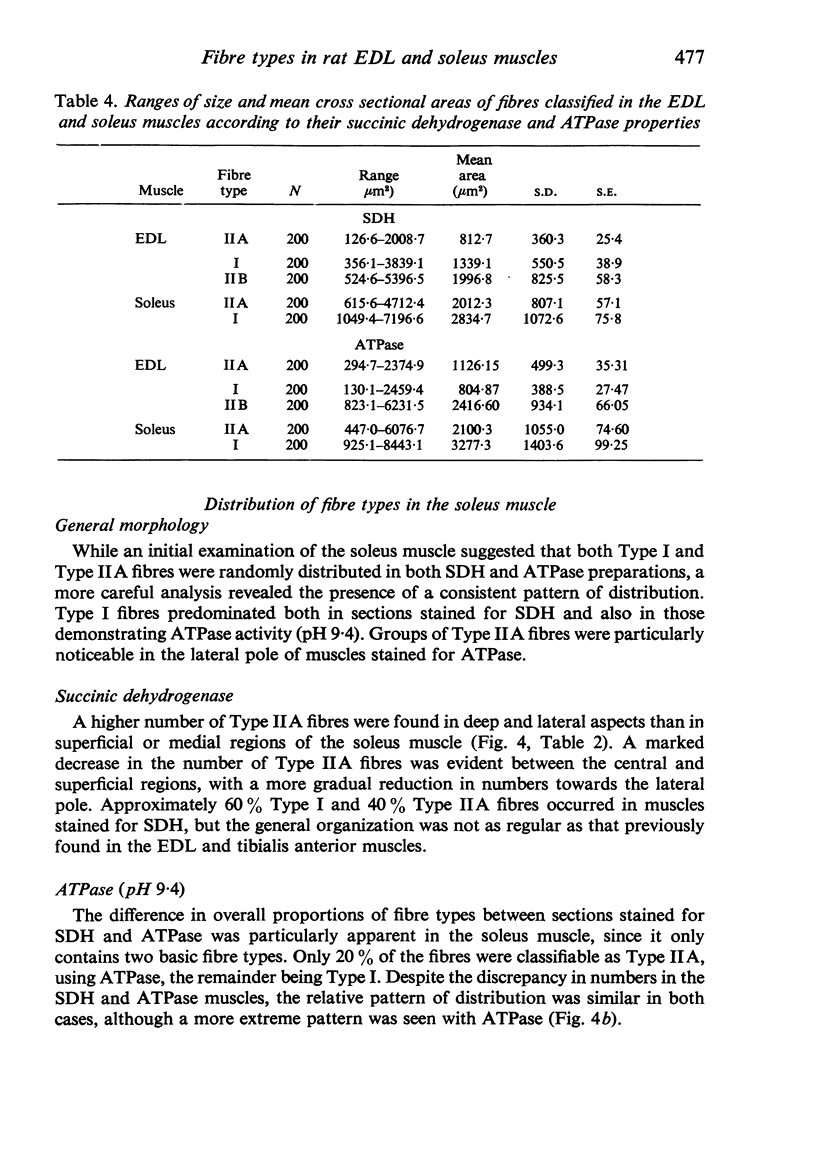
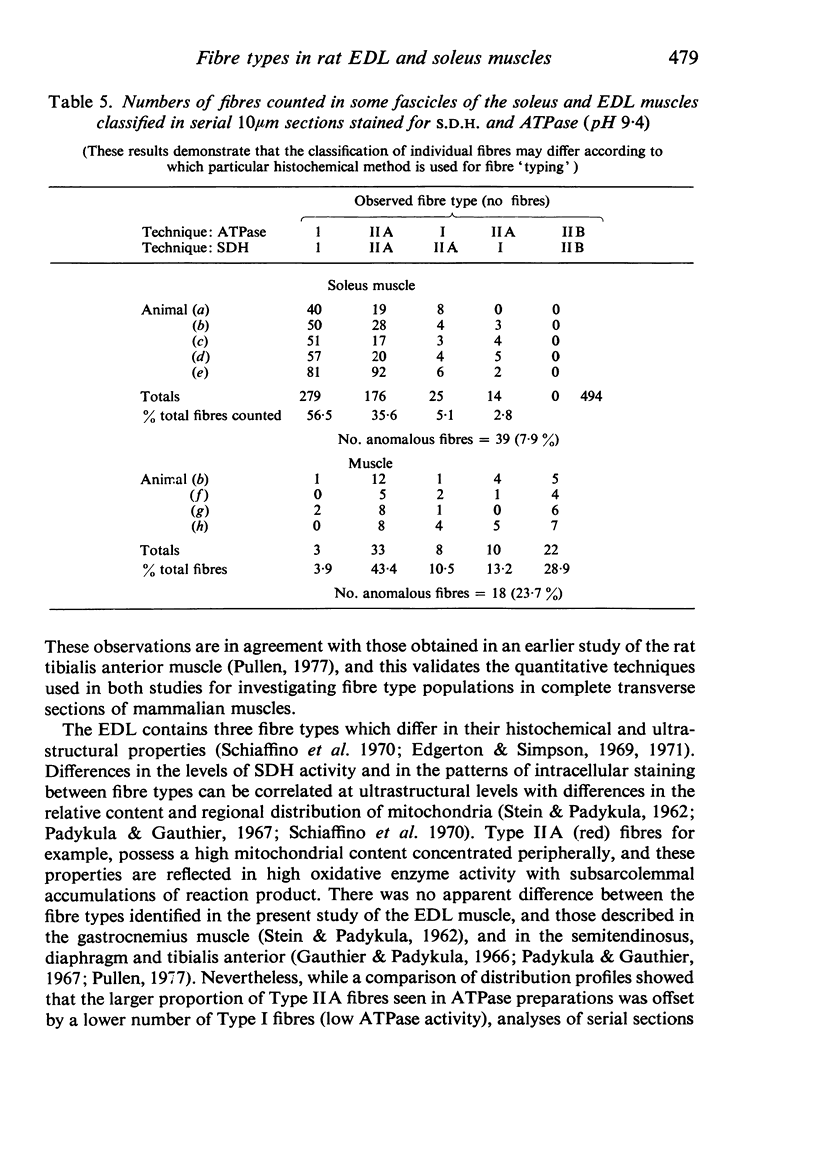
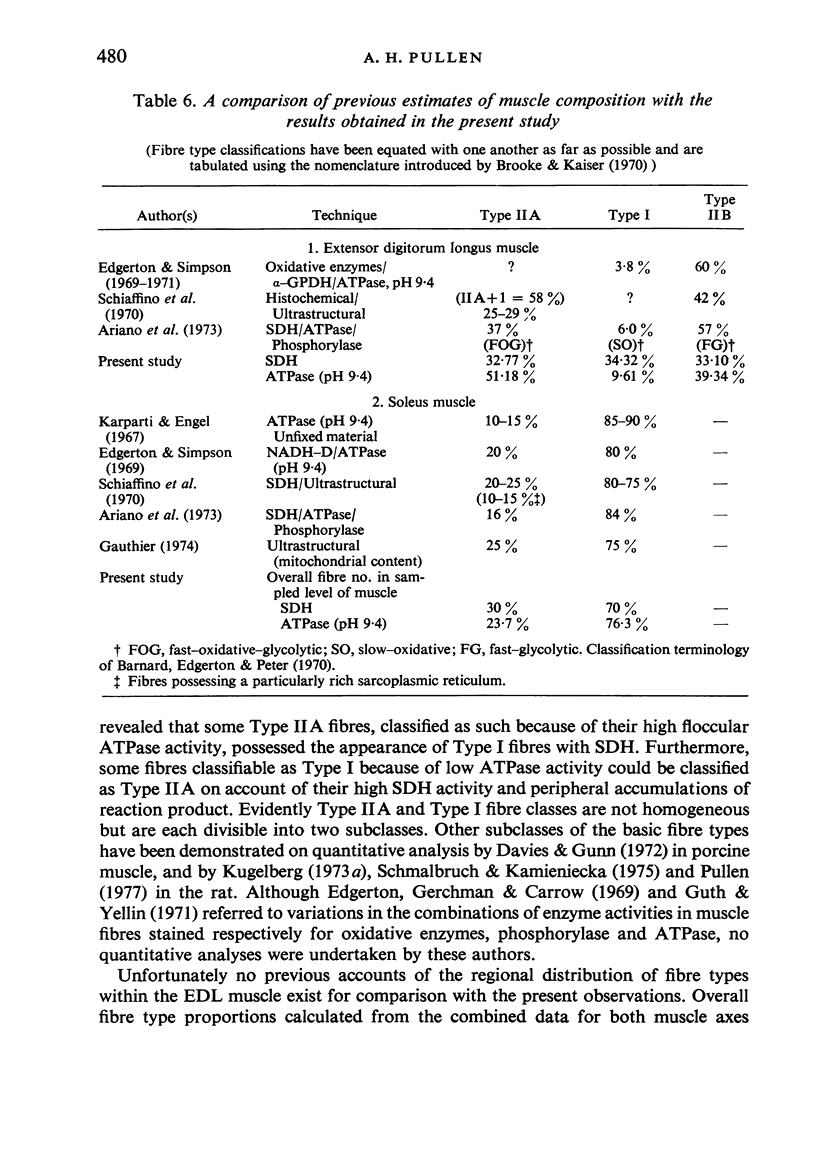
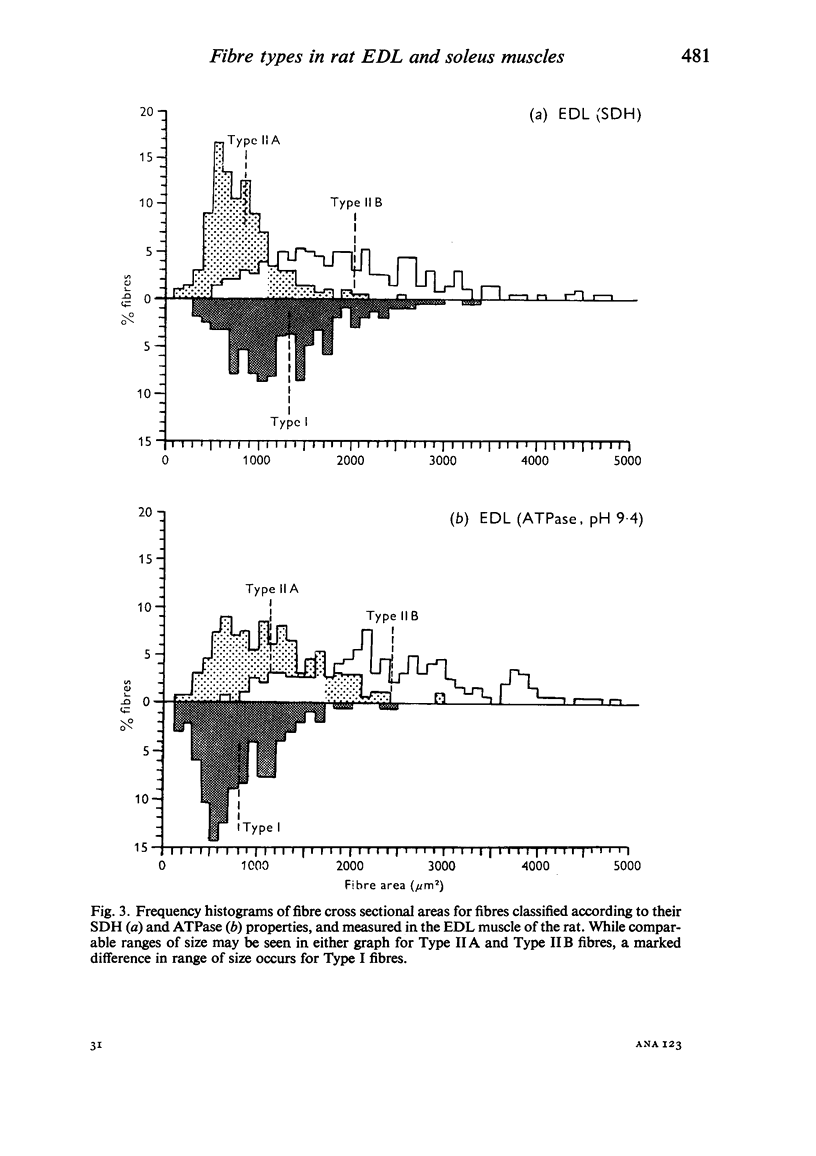
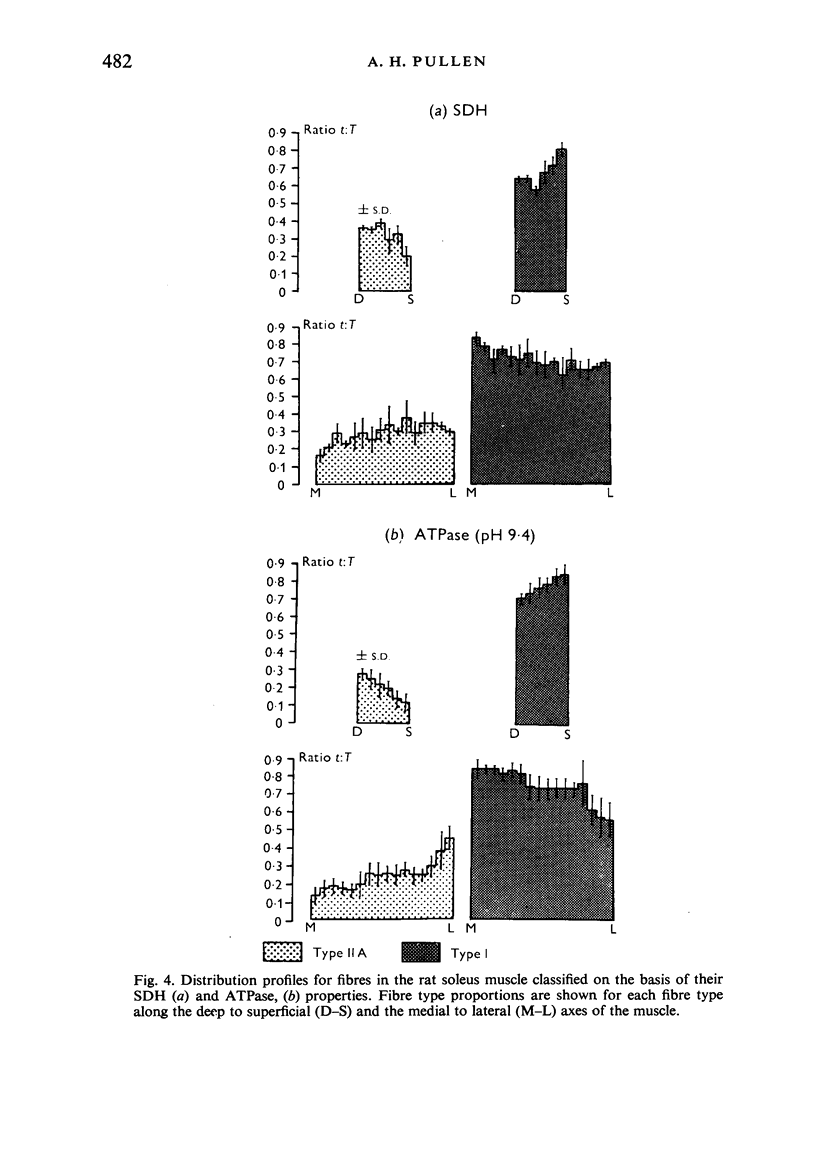
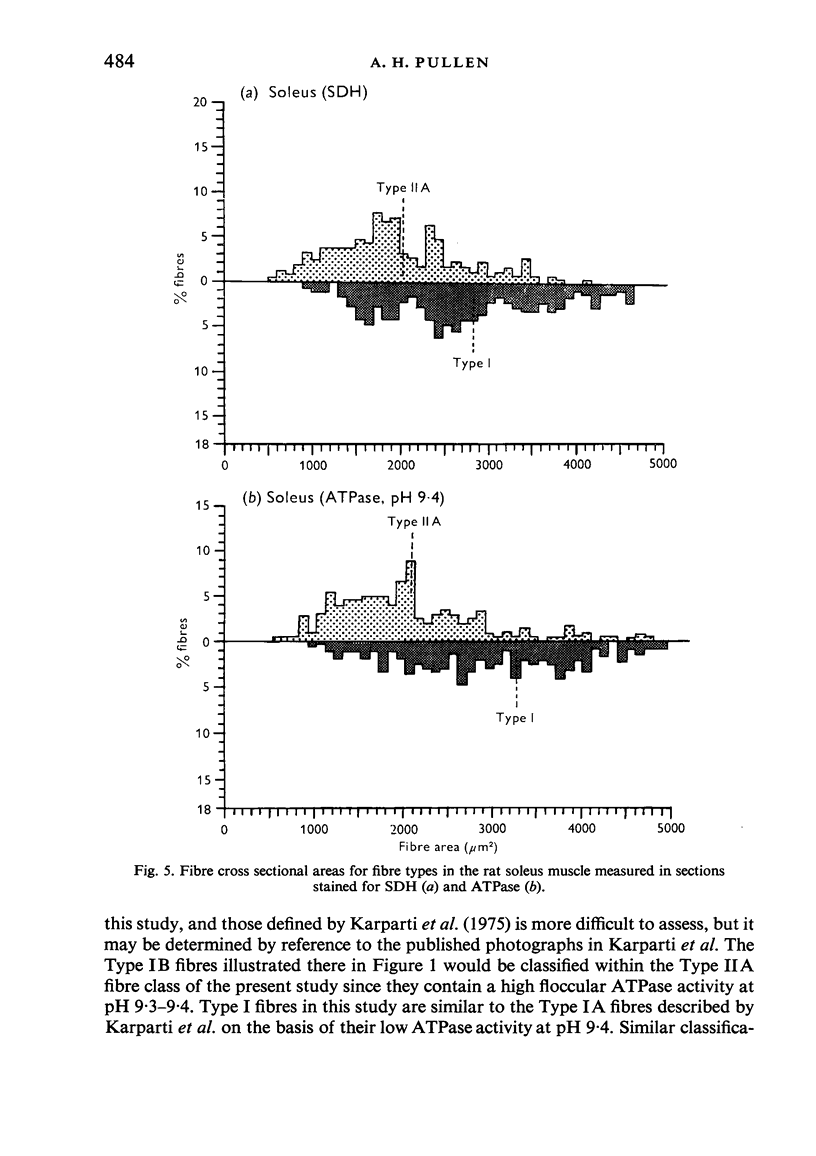
Histochemical fibre types classified in sections stained for succinic dehydrogenase (sdh) and myosin ATPase at pH 9.4, were found to be distributed in a consistent manner within the extensor digitorum longus (EDL) and 4 soleus muscles of the adult rat. Simple morphometric techniques applied to complete transverse sections of both muscles showed that the relative distributions and proportions of fibre types along their deep to superficial, and medial to lateral, axes varied accoording to the histochemical method used for fibre typing. Similar differences occurred when the relative ranges of size exhibited by each fibre type were compared in sections stained for SDH and ATPase, and the discrepancies in fibre classification were confirmed by an analysis of individual fibres in serial sections. The findings are discussed in relation to those previosly reported for the EDL and soleus muscles of the rat.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aherne W. A method of determining the cross sectional area of muscle fibres. J Neurol Sci. 1968 Nov-Dec;7(3):519–528. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(68)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariano M. A., Armstrong R. B., Edgerton V. R. Hindlimb muscle fiber populations of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):51–55. doi: 10.1177/21.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R. J., Edgerton V. R., Peter J. B. Effect of exercise on skeletal muscle. I. Biochemical and histochemical properties. J Appl Physiol. 1970 Jun;28(6):762–766. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1970.28.6.762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooke M. H., Kaiser K. K. Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol. 1970 Oct;23(4):369–379. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1970.00480280083010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. I. Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscles. Physiol Rev. 1972 Jan;52(1):129–197. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1972.52.1.129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A. S., Gunn H. M. Histochemical fibre types in the mammalian diaphragm. J Anat. 1972 May;112(Pt 1):41–60. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton V. R., Gerchman L., Carrow R. Histochemical changes in rat skeletal muscle after exercise. Exp Neurol. 1969 May;24(1):110–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton V. R., Simpson D. R. Dynamic and metabolic relationships in the rat extensor digitorum longus muscle. Exp Neurol. 1971 Feb;30(2):374–376. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4886(71)80016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgerton V. R., Simpson D. R. The intermediate muscle fiber of rats and guinea pigs. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 Dec;17(12):828–838. doi: 10.1177/17.12.828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F., Padykula H. A. Cytological studies of fiber types in skeletal muscle. A comparative study of the mammalian diaphragm. J Cell Biol. 1966 Feb;28(2):333–354. doi: 10.1083/jcb.28.2.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier G. F. Some ultrastructural and cytochemical features of fiber populations in the soleus muscle. Anat Rec. 1974 Dec;180(4):551–563. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091800402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Samaha F. J. Qualitative differences between actomyosin ATPase of slow and fast mammalian muscle. Exp Neurol. 1969 Sep;25(1):138–152. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(69)90077-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth L., Yellin H. The dynamic nature of the so-called "fiber types" of nammalian skeletal muscle. Exp Neurol. 1971 May;31(2):227–300. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(71)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Eisen A. A., Carpenter S. Letter to the editor: Subtypes of the histochemical type I muscle fibers. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Jan;23(1):89–91. doi: 10.1177/23.1.46875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpati G., Engel W. K. Neuronal trophic function. A new aspect demonstrated histochemically in developing soleus muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Nov;17(5):542–545. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470290096012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugelberg E. Histochemical composition, contraction speed and fatiguability of rat soleus motor units. J Neurol Sci. 1973 Oct;20(2):177–198. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(73)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLINE S. W., GLENNER G. G. ULTRARAPID TISSUE FREEZING IN LIQUID NITROGEN. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 Oct;12:777–783. doi: 10.1177/12.10.777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullen A. H. The distribution and relative sizes of three histochemical fibre types in the rat tibialis anterior muscle. J Anat. 1977 Feb;123(Pt 1):1–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEIN J. M., PADYKULA H. A. Histochemical classification of individual skeletal muscle fibers of the rat. Am J Anat. 1962 Mar;110:103–123. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001100203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiaffino S., Hanzlíková V., Pierobon S. Relations between structure and function in rat skeletal muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1970 Oct;47(1):107–119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.47.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmalbruch H., Kamieniecka Z. Histochemical fiber typing and staining intensity in cat and rat muscles. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Jun;23(6):395–401. doi: 10.1177/23.6.125297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]