Abstract
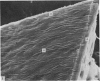
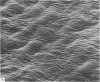
The surface of dog articular cartilage attached to subchondral bone shows many humps on its surface when examined with the scanning electron microscope. The situation here contrasts with that in man and rabbit where large numbers of pits are seen of the surface. Such species variations cast doubts on the idea that pits and humps play a vital role in joint mechanics and lubrication. Ridges and undulations were not found in normal dog cartilage attached to bone, but complex systems of ridges did develop when the cartilage was cut or detached from bone.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clarke I. C. A method for the replication of articular cartilage surfaces suitable for the scanning electron microscope. J Microsc. 1971 Feb;93(1):67–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1971.tb02266.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Human articular surface contours and related surface depression frequency studies. Ann Rheum Dis. 1971 Jan;30(1):15–23. doi: 10.1136/ard.30.1.15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Quantitative measurement of human articular surface topography in vitro by profile recorder and stereomicroscopy techniques. J Microsc. 1973 Apr;97(3):309–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1973.tb03785.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke I. C. Surface characteristics of human articular cartilage--a scanning electron microscope study. J Anat. 1971 Jan;108(Pt 1):23–30. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. V., BARNETT C. H., COCHRANE W., PALFREY A. J. Electron microscopy of articular cartilage in the young adult rabbit. Ann Rheum Dis. 1962 Mar;21:11–22. doi: 10.1136/ard.21.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L. The influence of microscopic technology on knowledge of cartilage surface structure. Ann Rheum Dis. 1972 Jul;31(4):235–258. doi: 10.1136/ard.31.4.235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner D. L., Woodward D. Scanning electron microscopy and replica studies of articular surfaces of guinea-pig synovial joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Jul;28(4):379–391. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.4.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghadially F. N., Ghadially J. A., Oryschak A. F., Yong N. K. Experimental production of ridges on rabbit articular cartilage: a scanning electron microscope study. J Anat. 1976 Feb;121(Pt 1):119–132. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall J. G. Scanning electron microscopy of articular surfaces. Lancet. 1968 Nov 30;2(7579):1194–1194. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91680-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mow V. C., Lai W. M. Some surface characteristics of articular cartilage. I. A scanning electron microscopy study and a theoretical model for the dynamic interaction of synovial fluid and articular cartilage. J Biomech. 1974 Sep;7(5):449–456. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(74)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redler I., Zimny M. L. Scanning electron microscopy of normal and abnormal articular cartilage and synovium. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1970 Oct;52(7):1395–1404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. S., Sikorski J., Dowson D., Longfield M. D., Wright V., Buckley T. Behaviour of synovial fluid on surfaces of articular cartilage. A scanning electron microscope study. Ann Rheum Dis. 1969 Jan;28(1):1–14. doi: 10.1136/ard.28.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]