Abstract
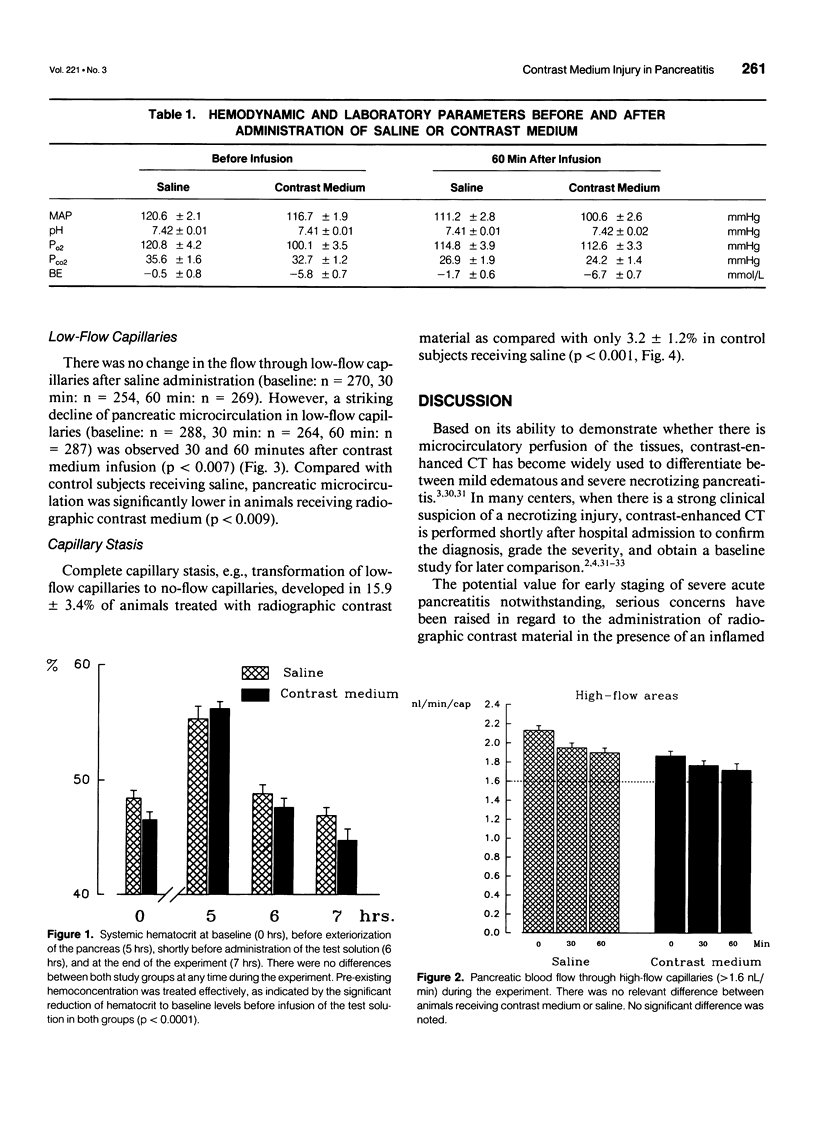
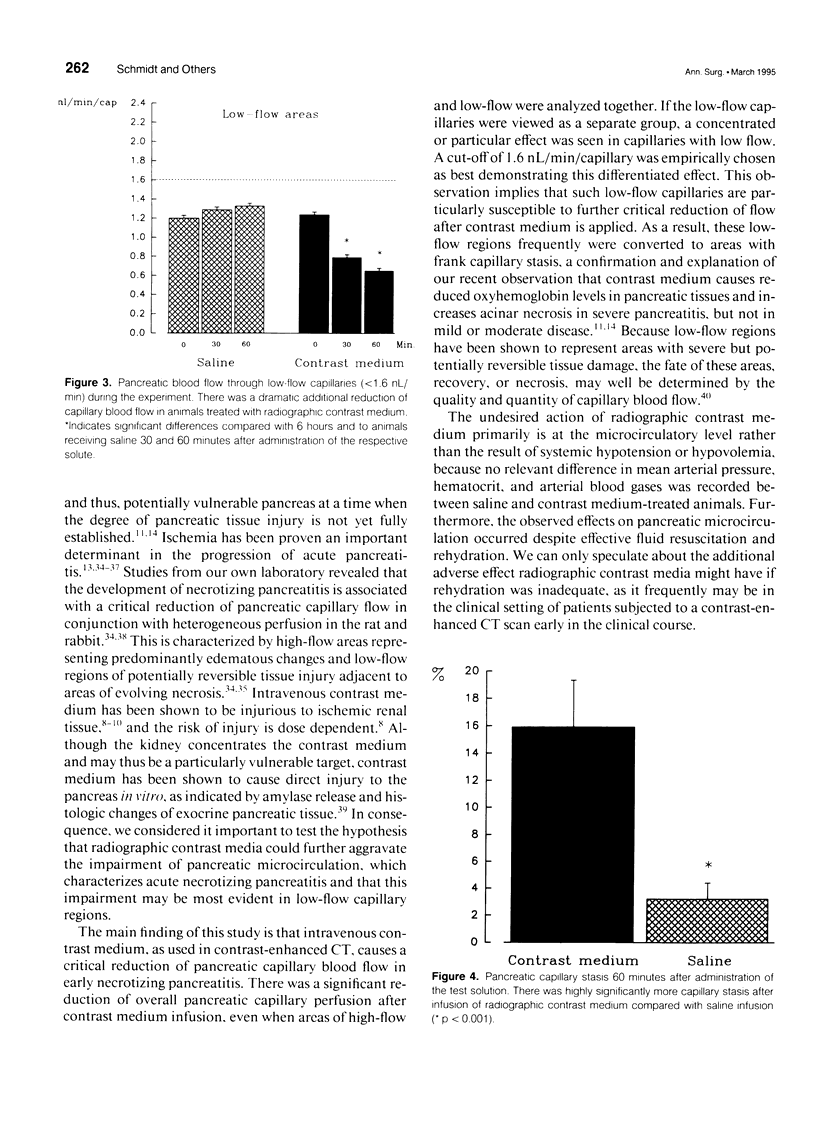
BACKGROUND: Previous reports demonstrated that radiographic contrast medium, as used in contrast-enhanced computed tomography, increases acinar necrosis and mortality in experimental pancreatitis. The authors studied the possibility that these changes may be related to an additional impairment of pancreatic microcirculation. METHODS: Fifty Wistar rats had acute pancreatitis induced by intraductal glycodeoxycholic acid (10 mmol/L for 10 min) and intravenous cerulein (5 micrograms/kg/hr for 6 hrs). After rehydration (16 mL/kg), pancreatic capillary perfusion was quantified by means of intravital microscopy at baseline before intravenous infusion of contrast medium (n = 25) or saline (n = 25), and 30 and 60 minutes thereafter. In addition to total capillary flow, capillaries were categorized as high- or low-flow (> or < 1.6 nL/min). RESULTS: Pancreatic capillary flow did not change in either high- or low-flow capillaries after saline infusion. However, contrast medium infusion induced a significant decrease of total capillary flow (p < 0.001). Analysis according to the relative flow rate revealed that this was primarily because of a significant additional reduction of perfusion in low-flow capillaries (p < 0.0001). Furthermore, complete capillary stasis was observed in 15.9 +/- 3.4% after contrast medium as compared with 3.2 +/- 1.2% after saline infusion (p < 0.006). CONCLUSION: Radiographic contrast medium aggravates the impairment of pancreatic microcirculation in experimental necrotizing pancreatitis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akagi M., Masaki S., Kitazumi K., Mio M., Tasaka K. Comparative study of the adverse effects of various radiographic contrast media, including ioversol, a new low-osmolarity medium. II. The complement system and endothelial cells. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 1991 Sep;13(7):449–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht K. H., Gaehtgens P., Pries A., Heuser M. The Fahraeus effect in narrow capillaries (i.d. 3.3 to 11.0 micron). Microvasc Res. 1979 Jul;18(1):33–47. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(79)90016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aspelin P. Effect of ionic and non-ionic contrast media on red cell deformability in vitro. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1979;20(1):1–12. doi: 10.1177/028418517902001a01. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aspelin P. Effect of ionic and non-ionic contrast media on whole blood viscosity, plasma viscosity and hematocrit in vitro. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1978;19(6):977–989. doi: 10.1177/028418517801900613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balthazar E. J., Ranson J. H., Naidich D. P., Megibow A. J., Caccavale R., Cooper M. M. Acute pancreatitis: prognostic value of CT. Radiology. 1985 Sep;156(3):767–772. doi: 10.1148/radiology.156.3.4023241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbee J. H., Cokelet G. R. The Fahraeus effect. Microvasc Res. 1971 Jan;3(1):6–16. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(71)90002-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry A. R., Millar A. M., Taylor T. V. Pancreatic blood flow in experimental acute pancreatitis. Dig Dis Sci. 1982 May;27(5):444–448. doi: 10.1007/BF01295654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley E. L., 3rd, Murphy F., Ferguson C. Prediction of pancreatic necrosis by dynamic pancreatography. Ann Surg. 1989 Oct;210(4):495–504. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198910000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher E. C., Weissman I. L. Direct fluorescent labeling of cells with fluorescein or rhodamine isothiocyanate. I. Technical aspects. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(2):97–108. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90195-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchler M., Malfertheiner P., Schoetensack C., Uhl W., Beger H. G. Sensitivity of antiproteases, complement factors and C-reactive protein in detecting pancreatic necrosis. Results of a prospective clinical study. Int J Pancreatol. 1986 Oct;1(3-4):227–235. doi: 10.1007/BF02795248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clavien P. A., Hauser H., Meyer P., Rohner A. Value of contrast-enhanced computerized tomography in the early diagnosis and prognosis of acute pancreatitis. A prospective study of 202 patients. Am J Surg. 1988 Mar;155(3):457–466. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(88)80113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deray G., Baumelou B., Martinez F., Brillet G., Jacobs C. Renal vasoconstriction after low and high osmolar contrast agents in ischemic and non ischemic canine kidney. Clin Nephrol. 1991 Aug;36(2):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deray G., Dubois M., Martinez F., Baumelou B., Beaufils H., Bourbouze R., Baumelou A., Jacobs C. Renal effects of radiocontrast agents in rats: a new model of acute renal failure. Am J Nephrol. 1990;10(6):507–513. doi: 10.1159/000168177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desjardins C., Duling B. R. Microvessel hematocrit: measurement and implications for capillary oxygen transport. Am J Physiol. 1987 Mar;252(3 Pt 2):H494–H503. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1987.252.3.H494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton S., Tsay H. M., Yost F., Tweedle M. F. Assays for plasma complement activation by x-ray contrast media. Invest Radiol. 1990 Jul;25(7):789–792. doi: 10.1097/00004424-199007000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández-del Castillo C., Schmidt J., Rattner D. W., Lewandrowski K., Compton C. C., Jehanli A., Patel G., Hermon-Taylor J., Warshaw A. L. Generation and possible significance of trypsinogen activation peptides in experimental acute pancreatitis in the rat. Pancreas. 1992;7(3):263–270. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199205000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foitzik T., Bassi D. G., Fernández-del Castillo C., Warshaw A. L., Rattner D. W. Intravenous contrast medium impairs oxygenation of the pancreas in acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the rat. Arch Surg. 1994 Jul;129(7):706–711. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1994.01420310038006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foitzik T., Bassi D. G., Schmidt J., Lewandrowski K. B., Fernandez-del Castillo C., Rattner D. W., Warshaw A. L. Intravenous contrast medium accentuates the severity of acute necrotizing pancreatitis in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1994 Jan;106(1):207–214. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(94)95457-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudgeon A. M., Heath D. I., Hurley P., Jehanli A., Patel G., Wilson C., Shenkin A., Austen B. M., Imrie C. W., Hermon-Taylor J. Trypsinogen activation peptides assay in the early prediction of severity of acute pancreatitis. Lancet. 1990 Jan 6;335(8680):4–8. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90135-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelmqvist B., Wattsgård C., Borgström A., Lasson A., Nyman U., Aspelin P., Ohlsson K. Early diagnosis and classification in acute pancreatitis. A comparison of clinical outcome with findings at computed tomography and Ranson's prognostic signs. Digestion. 1989;44(4):177–183. doi: 10.1159/000199909. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley P. R., Cook A., Jehanli A., Austen B. M., Hermon-Taylor J. Development of radioimmunoassays for free tetra-L-aspartyl-L-lysine trypsinogen activation peptides (TAP). J Immunol Methods. 1988 Jul 22;111(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(88)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isenmann R., Büchler M., Uhl W., Malfertheiner P., Martini M., Beger H. G. Pancreatic necrosis: an early finding in severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 1993 May;8(3):358–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kivisaari L., Somer K., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Schröder T., Kivilaakso E., Lempinen M. Early detection of acute fulminant pancreatitis by contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1983 Jan;18(1):39–41. doi: 10.3109/00365528309181556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar E., Endrich B., Messmer K. Microcirculation of the pancreas. A quantitative study of physiology and changes in pancreatitis. Int J Microcirc Clin Exp. 1990 Feb;9(1):85–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar E., Mall G., Messmer K., Herfarth C., Rattner D. W., Warshaw A. L. Improvement of impaired pancreatic microcirculation by isovolemic hemodilution protects pancreatic morphology in acute biliary pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1993 Feb;176(2):144–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar E., Messmer K., Warshaw A. L., Herfarth C. Pancreatic ischaemia in experimental acute pancreatitis: mechanism, significance and therapy. Br J Surg. 1990 Nov;77(11):1205–1210. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800771104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larvin M., Chalmers A. G., McMahon M. J. Dynamic contrast enhanced computed tomography: a precise technique for identifying and localising pancreatic necrosis. BMJ. 1990 Jun 2;300(6737):1425–1428. doi: 10.1136/bmj.300.6737.1425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G., Einzig S., Rysavy J., Borgwardt B., Salomonowitz E., Cragg A., Amplatz K. Role of ischemia in contrast-induced renal damage: an experimental study. Circulation. 1984 Apr;69(4):783–789. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.69.4.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordestgaard A. G., Wilson S. E., Williams R. A. Early computerized tomography as a predictor of outcome in acute pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 1986 Jul;152(1):127–132. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(86)90162-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuutinen P., Kivisaari L., Standertskjöld-Nordenstam C. G., Lempinen M., Schröder T. Microangiography of the pancreas in experimental oedemic and haemorrhagic pancreatitis. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1986;126:12–17. doi: 10.3109/00365528609091885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEFFER R. B., LAZZARINI-ROBERTSON A., Jr, SAFADI D., MIXTER G., Jr, SECOY C. F., HINTON J. W. Gradations of pancreatitis, edematous, through hemorrhagic, experimentally produced by controlled injection of microspheres into blood vessels in dogs. Surgery. 1962 Jun;51:764–769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puolakkainen P. A. Early assessment of acute pancreatitis. A comparative study of computed tomography and laboratory tests. Acta Chir Scand. 1989;155(1):25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranson J. H., Balthazar E., Caccavale R., Cooper M. Computed tomography and the prediction of pancreatic abscess in acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 1985 May;201(5):656–665. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198505000-00016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Litwin S. B., Laver M. B. Effect of contrast media used in angiocardiography on hemoglobin-oxygen equilibrium. Invest Radiol. 1973 Jul-Aug;8(4):191–198. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197307000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiantarelli P., Peroni F., Tirone P., Rosati G. Effects of iodinated contrast media on erythrocytes. I. Effects of canine erythrocytes on morphology. Invest Radiol. 1973 Jul-Aug;8(4):199–204. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197307000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Fernández-del Castillo C., Rattner D. W., Lewandrowski K., Compton C. C., Warshaw A. L. Trypsinogen-activation peptides in experimental rat pancreatitis: prognostic implications and histopathologic correlates. Gastroenterology. 1992 Sep;103(3):1009–1016. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(92)90036-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Lewandrowsi K., Warshaw A. L., Compton C. C., Rattner D. W. Morphometric characteristics and homogeneity of a new model of acute pancreatitis in the rat. Int J Pancreatol. 1992 Aug;12(1):41–51. doi: 10.1007/BF02927069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Rattner D. W., Lewandrowski K., Compton C. C., Mandavilli U., Knoefel W. T., Warshaw A. L. A better model of acute pancreatitis for evaluating therapy. Ann Surg. 1992 Jan;215(1):44–56. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199201000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. J. ABSCESS OF LIVER IN YOUNG INFANT. Cal State J Med. 1918 Jul;16(7):337–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock K. P., Riemann J. F. In-vitro-Untersuchungen zur Rolle des Kontrastmittels bei Pankreatitiden nach ERCP. Z Gastroenterol. 1981 Mar;19(3):128–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vetterlein F., Pethö A., Schmidt G. Morphometric investigation of the microvascular system of pancreatic exocrine and endocrine tissue in the rat. Microvasc Res. 1987 Sep;34(2):231–238. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(87)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerhackl B., Dussel R., Steinhausen M. Erythrocyte flow and dynamic hematocrit in the renal papilla of the rat. Am J Physiol. 1985 Dec;249(6 Pt 2):F898–F902. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.249.6.F898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


