Abstract
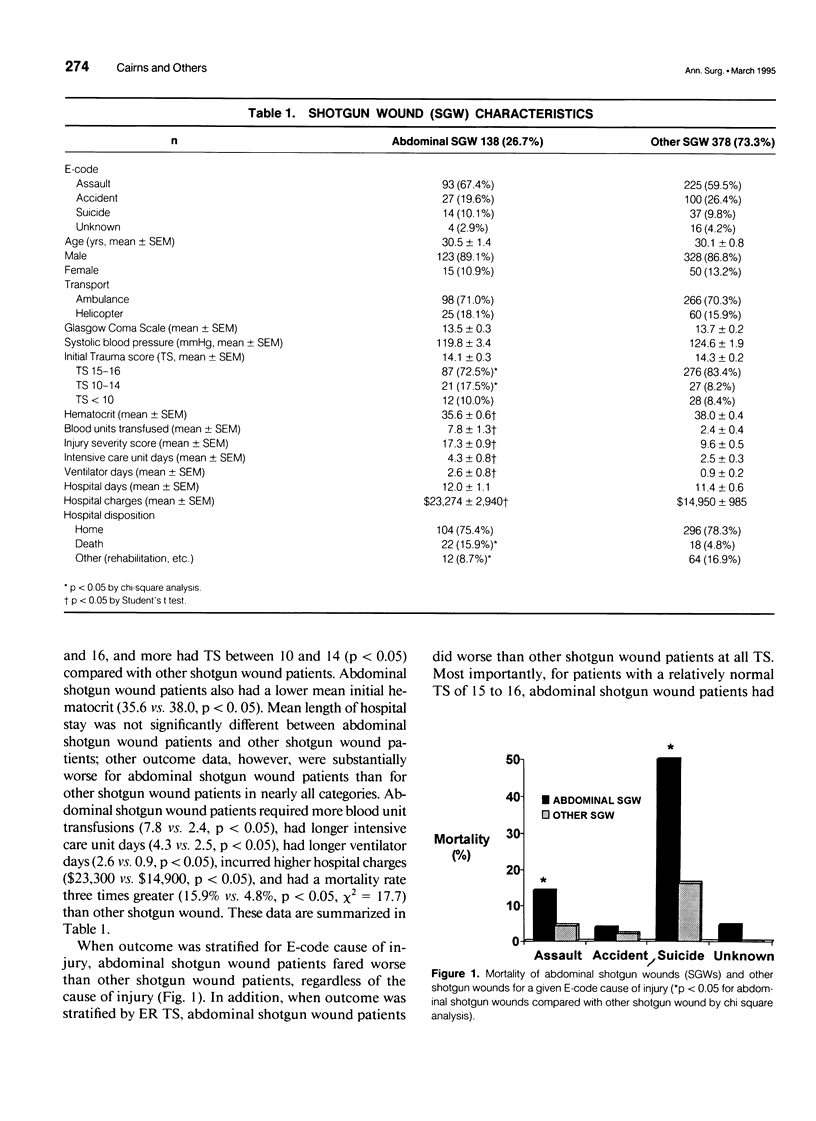
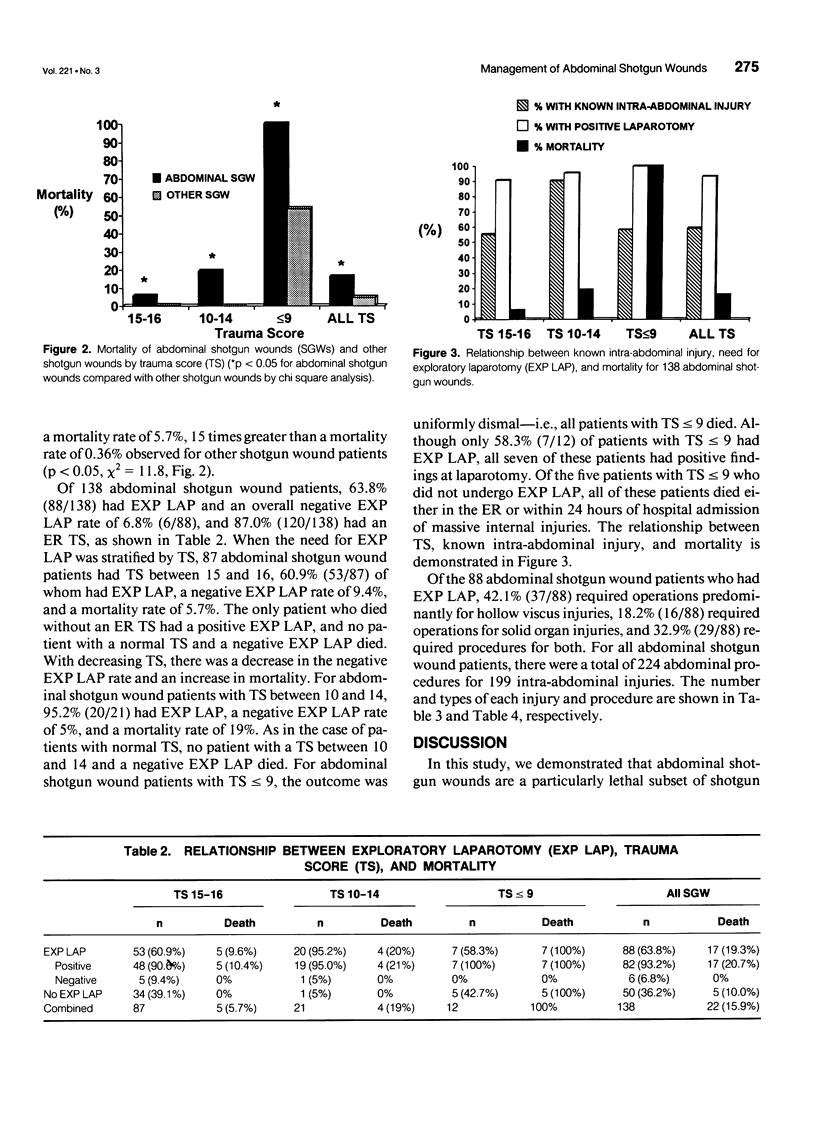
OBJECTIVE: The management and outcome of 138 abdominal shotgun wounds were examined over a 5-year period. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: It has been proposed that exploratory laparotomy may be unnecessary and even overused in a subset of patients with abdominal shotgun wounds. METHODS: Data on shotgun wound patients from October 1987 through March 1992 from a statewide trauma registry were examined. Patients with abdominal shotgun wounds were identified and compared with patients with nonabdominal shotgun wounds. RESULTS: Of 516 shotgun wound patients, 138 (26.7%) had abdominal wounds and 88 (63.8%) had exploratory laparotomies. Abdominal shotgun wounds resulted in significantly longer number of intensive care unit days (4.3 vs. 2.5, p < 0.05), a greater number of blood units transfused (7.8 vs. 2.4, p < 0.05), and a higher mortality (15.9% vs. 4.8%, p < 0.05) when compared with nonabdominal shotgun wounds. When stratified for trauma score, the mortality for abdominal shotgun wounds always was significantly greater than for nonabdominal shotgun wounds. All abdominal shotgun wound patients with trauma scores less than ten died. The negative laparotomy rate for abdominal shotgun wound patients with normal trauma scores was 9.4%. No patient with a negative laparotomy died. CONCLUSION: Abdominal shotgun wounds are a particularly lethal subset of shotgun wounds. Although some abdominal shotgun wound patients can be managed without laparotomy, the morbidity and mortality for these injuries are substantial, even in patients with normal trauma score. Clinical judgment is an excellent predictor of the need for laparotomy.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell M. J. The management of shotgun wounds. J Trauma. 1971 Jun;11(6):522–527. doi: 10.1097/00005373-197106000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitenecker R. Shotgun wound patterns. Am J Clin Pathol. 1969 Sep;52(3):258–269. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/52.3.258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DRYE J. C., SHUSTER G. Shotgun wounds. Am J Surg. 1953 Mar;85(3):438–443. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(53)90635-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint L. M., Cryer H. M., Howard D. A., Richardson J. D. Approaches to the management of shotgun injuries. J Trauma. 1984 May;24(5):415–419. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198405000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glezer J. A., Minard G., Croce M. A., Fabian T. C., Kudsk K. A. Shotgun wounds to the abdomen. Am Surg. 1993 Feb;59(2):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimes W. R., Deitch E. A., McDonald J. C. A clinical review of shotgun wounds to the chest and abdomen. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1985 Feb;160(2):148–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledgerwood A. M. The management of shotgun wounds. Surg Clin North Am. 1977 Feb;57(1):111–120. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)41137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandal A. K., Boitano M. A., Lundy L. J., Alexander J. L. Shotgun wounds of the abodomen: revisited. Am Surg. 1979 Jan;45(1):5–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oller D. W., Rutledge R., Clancy T., Cunningham P., Thomason M., Meredith W., Moylan J., Baker C. C. Vascular injuries in a rural state: a review of 978 patients from a state trauma registry. J Trauma. 1992 Jun;32(6):740–746. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199206000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordog G. J., Wasserberger J., Balasubramaniam S. Shotgun wound ballistics. J Trauma. 1988 May;28(5):624–631. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198805000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERMAN R. T., PARRISH R. A. Management of shotgun injuries: a review of 152 cases. J Trauma. 1963 Jan;3:76–86. doi: 10.1097/00005373-196301000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. L., Poindexter J. M., Jr, Stovall I. Principles of management of shotgun wounds. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990 Feb;170(2):97–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


