Abstract
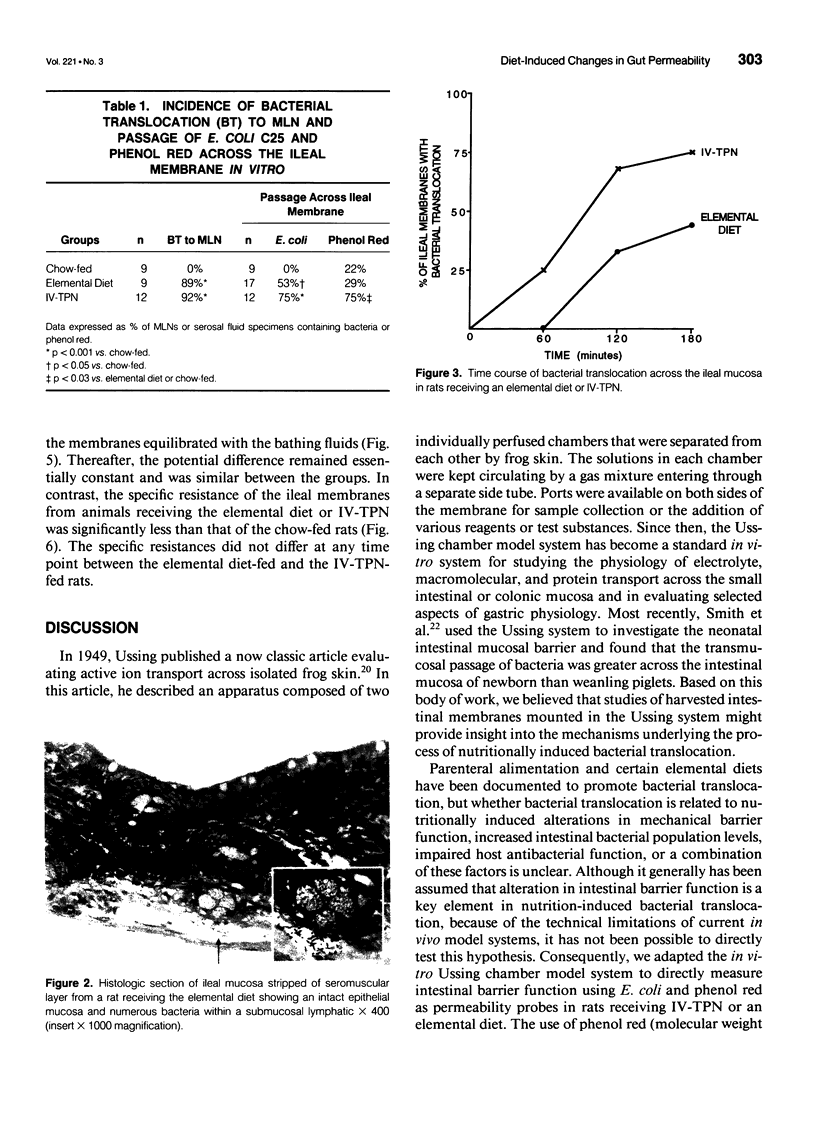
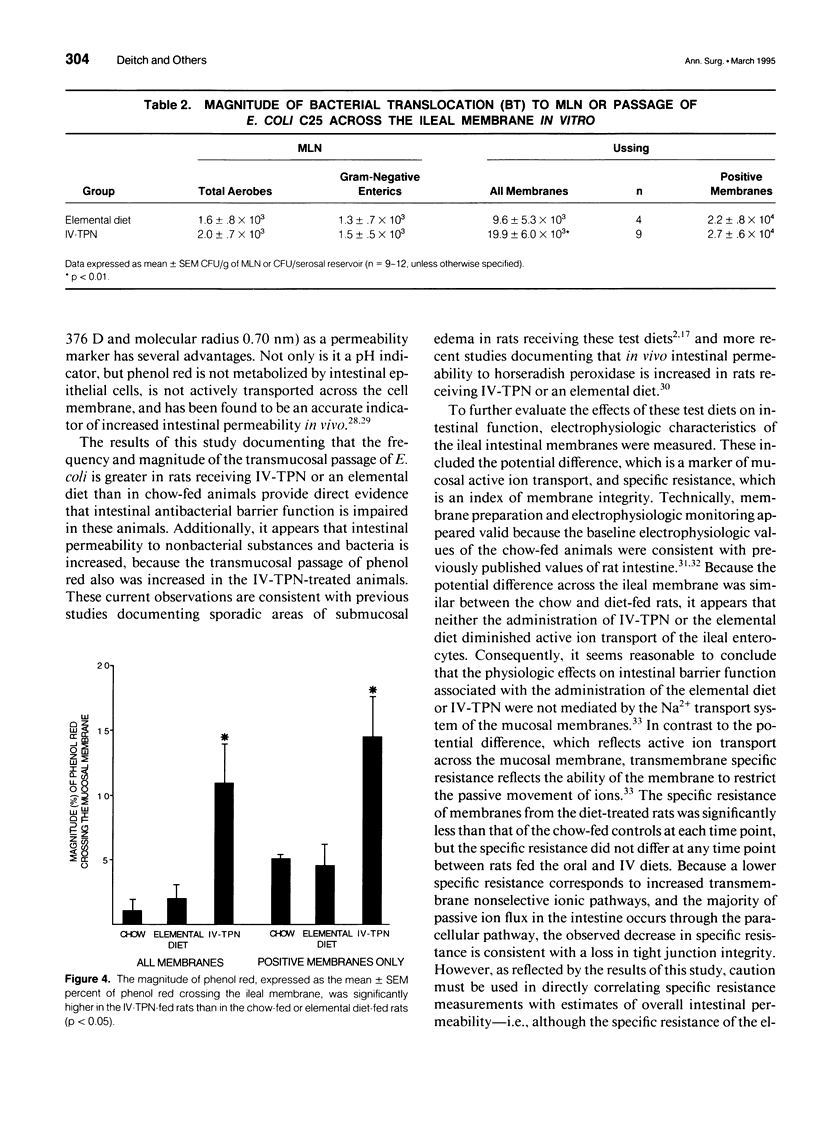
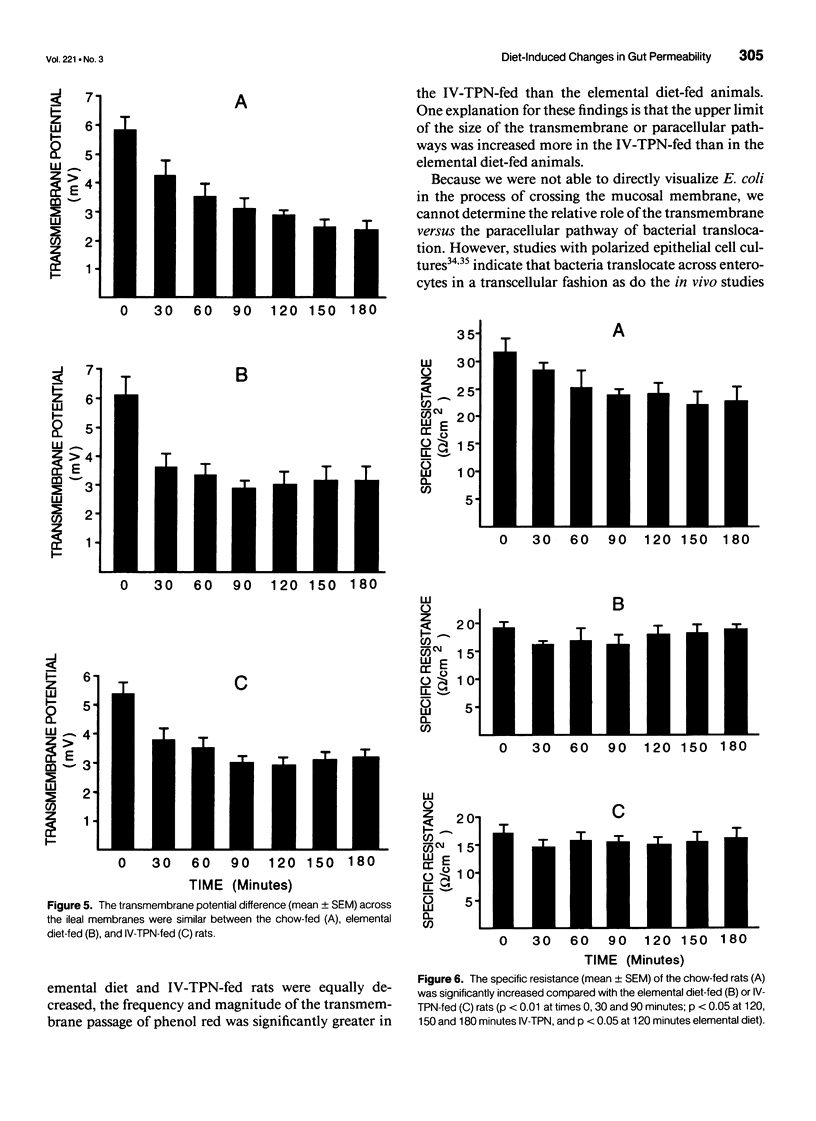
OBJECTIVE: The goal of the current study was to directly assess the role of loss of mucosal barrier function in nutritionally induced bacterial translocation. BACKGROUND: Parenteral and certain elemental enteral diets have been shown to promote bacterial translocation. The mechanisms underlying this observation, especially the question of whether nutritionally induced bacterial translocation is primarily related to loss of intestinal barrier function, versus an impaired immune system, remain to be fully elucidated. METHODS: Bacterial translocation was measured in vivo, ileal mucosal membranes were harvested, and their electrophysiologic properties and barrier function were measured ex vivo in the Ussing chamber system 7 days after receiving total parenteral nutrition solution parenterally (IV-TPN) or enterally (elemental diet). Chow-fed rats served as control subjects. RESULTS: The incidence of bacterial translocation was significantly increased both to the mesenteric lymph nodes in vivo and across the in vitro Ussing chamber-mounted ileal mucosal membranes of the elemental diet-fed and IV-TPN-fed rats. The magnitude of Escherichia coli and phenol red transmucosal passage in the Ussing chamber was significantly higher in the IV-TPN-fed rats than in the elemental diet-fed or chow-fed animals. The potential differences across the ileal membrane were similar between the three groups at all time points. However, the specific resistances of the ileal membranes of the IV-TPN and elemental diet groups were significantly less than the chow-fed animals, indicating increased membrane permeability. CONCLUSIONS: Loss of intestinal barrier function plays a major role in nutritionally induced bacterial translocation, and the loss of mucosal barrier function to both E. coli and phenol red appeared greater in the IV-TPN than the elemental diet-fed rats.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander J. W., Boyce S. T., Babcock G. F., Gianotti L., Peck M. D., Dunn D. L., Pyles T., Childress C. P., Ash S. K. The process of microbial translocation. Ann Surg. 1990 Oct;212(4):496–512. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199010000-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander J. W., MacMillan B. G., Stinnett J. D., Ogle C. K., Bozian R. C., Fischer J. E., Oakes J. B., Morris M. J., Krummel R. Beneficial effects of aggressive protein feeding in severely burned children. Ann Surg. 1980;192(4):505–517. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198010000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alverdy J. C., Aoys E., Moss G. S. Effect of commercially available chemically defined liquid diets on the intestinal microflora and bacterial translocation from the gut. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jan-Feb;14(1):1–6. doi: 10.1177/014860719001400101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alverdy J. C., Aoys E., Moss G. S. Total parenteral nutrition promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Surgery. 1988 Aug;104(2):185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alverdy J. C., Burke D. Total parenteral nutrition: iatrogenic immunosuppression. Nutrition. 1992 Sep-Oct;8(5):359–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. E., Jones W. G., 2nd, Minei J. P., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Lowry S. F., Shires G. T. Bacterial overgrowth and intestinal atrophy in the etiology of gut barrier failure in the rat. Am J Surg. 1991 Feb;161(2):300–304. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(91)91148-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barber A. E., Jones W. G., 2nd, Minei J. P., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Moldawer L. L., Rayburn J. L., Fischer E., Keogh C. V., Shires G. T., Lowry S. F. Harry M. Vars award. Glutamine or fiber supplementation of a defined formula diet: impact on bacterial translocation, tissue composition, and response to endotoxin. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Jul-Aug;14(4):335–343. doi: 10.1177/0148607190014004335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke D. J., Alverdy J. C., Aoys E., Moss G. S. Glutamine-supplemented total parenteral nutrition improves gut immune function. Arch Surg. 1989 Dec;124(12):1396–1399. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1989.01410120042009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz N., Alvarez X., Berg R. D., Deitch E. A. Bacterial translocation across enterocytes: results of a study of bacterial-enterocyte interactions utilizing Caco-2 cells. Shock. 1994 Jan;1(1):67–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Ma W. J., Ma L., Berg R. D., Specian R. D. Protein malnutrition predisposes to inflammatory-induced gut-origin septic states. Ann Surg. 1990 May;211(5):560–568. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199005000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deitch E. A., Winterton J., Li M., Berg R. The gut as a portal of entry for bacteremia. Role of protein malnutrition. Ann Surg. 1987 Jun;205(6):681–692. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198706000-00010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detsky A. S., Baker J. P., O'Rourke K., Goel V. Perioperative parenteral nutrition: a meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med. 1987 Aug;107(2):195–203. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-107-2-195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ducroc R., Heyman M., Beaufrere B., Morgat J. L., Desjeux J. F. Horseradish peroxidase transport across rabbit jejunum and Peyer's patches in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):G54–G58. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1983.245.1.G54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ecknauer R., Buck B., Breitig D. An experimental model for measuring intestinal permeability. Digestion. 1983;26(1):24–32. doi: 10.1159/000198865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evers B. M., Izukura M., Townsend C. M., Jr, Uchida T., Thompson J. C. Differential effects of gut hormones on pancreatic and intestinal growth during administration of an elemental diet. Ann Surg. 1990 May;211(5):630–638. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskel Y., Xu D., Lu Q., Deitch E. Elemental diet-induced bacterial translocation can be hormonally modulated. Ann Surg. 1993 Jun;217(6):634–643. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199306000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovov B., Wills N. K., Lewis S. A. A spectroscopic method for assessing confluence of epithelial cell cultures. Am J Physiol. 1991 Dec;261(6 Pt 1):C1196–C1203. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.261.6.C1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudsk K. A., Croce M. A., Fabian T. C., Minard G., Tolley E. A., Poret H. A., Kuhl M. R., Brown R. O. Enteral versus parenteral feeding. Effects on septic morbidity after blunt and penetrating abdominal trauma. Ann Surg. 1992 May;215(5):503–513. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199205000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. K., Cardona M. A., Kurkchubasche A. G., Smith S. D., Mueller A. R., Lee K. K., Rowe M. I., Schraut W. H. Mucosal glutamine utilization after small-bowel transplantation: an electrophysiologic study. J Surg Res. 1992 Jun;52(6):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(92)90137-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee T. K., Cardona M. A., Kurkchubasche A. G., Smith S. D., Mueller A. R., Lee K. K., Rowe M. I., Schraut W. H. Mucosal glutamine utilization after small-bowel transplantation: an electrophysiologic study. J Surg Res. 1992 Jun;52(6):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(92)90137-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Barenberg D., Carlson S. Effects of cytochalasin D on occluding junctions of intestinal absorptive cells: further evidence that the cytoskeleton may influence paracellular permeability and junctional charge selectivity. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madara J. L., Kirkman R. L. Structural and functional evolution of jejunal allograft rejection in rats and the ameliorating effects of cyclosporine therapy. J Clin Invest. 1985 Feb;75(2):502–512. doi: 10.1172/JCI111726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainous M. R., Deitch E. A. Nutrition and infection. Surg Clin North Am. 1994 Jun;74(3):659–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainous M., Xu D. Z., Lu Q., Berg R. D., Deitch E. A. Oral-TPN-induced bacterial translocation and impaired immune defenses are reversed by refeeding. Surgery. 1991 Aug;110(2):277–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer A. J., Detsky A. S., O'Rourke K. Parenteral nutrition in cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy: a meta-analysis. Nutrition. 1990 May-Jun;6(3):233–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Jones T. N., McCroskey B. L., Peterson V. M. TEN versus TPN following major abdominal trauma--reduced septic morbidity. J Trauma. 1989 Jul;29(7):916–923. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198907000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe P. H., Starlinger M. J., Kasdon E., Marrone G., Silen W. Effect of simulated systemic administration of aspirin, salicylate, and indomethacin on amphibian gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1986 Mar;90(3):559–569. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(86)91109-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Trocki O., Alexander J. W., Kopcha R., Heyd T., Joffe S. N. The effect of route of nutrient administration on the nutritional state, catabolic hormone secretion, and gut mucosal integrity after burn injury. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1987 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–7. doi: 10.1177/014860718701100101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shou J., Redmond H. P., Leon P., Hofmann K. P., Daly J. M. Elemental diet alters macrophage function in mice. J Surg Res. 1991 Sep;51(3):192–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-4804(91)90093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. D., Cardona M. A., Wishnev S. A., Kurkchubasche A. G., Rowe M. I. Unique characteristics of the neonatal intestinal mucosal barrier. J Pediatr Surg. 1992 Mar;27(3):333–338. doi: 10.1016/0022-3468(92)90857-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaeth G., Berg R. D., Specian R. D., Deitch E. A. Food without fiber promotes bacterial translocation from the gut. Surgery. 1990 Aug;108(2):240–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaeth G., Gottwald T., Specian R. D., Mainous M. R., Berg R. D., Deitch E. A. Secretory immunoglobulin A, intestinal mucin, and mucosal permeability in nutritionally induced bacterial translocation in rats. Ann Surg. 1994 Dec;220(6):798–808. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199412000-00014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaeth G., Specian R. D., Berg R. D., Deitch E. A. Bulk prevents bacterial translocation induced by the oral administration of total parenteral nutrition solution. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 Sep-Oct;14(5):442–447. doi: 10.1177/0148607190014005442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Jechorek R. P., Erlandsen S. L. Evidence for the translocation of Enterococcus faecalis across the mouse intestinal tract. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):82–90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Jechorek R. P., Erlandsen S. L., Lavin P. T., Cerra F. B. The effect of dietary glutamine and dietary RNA on ileal flora, ileal histology, and bacterial translocation in mice. Nutrition. 1990 Jan-Feb;6(1):70–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells C. L., Jechorek R. P., Olmsted S. B., Erlandsen S. L. Effect of LPS on epithelial integrity and bacterial uptake in the polarized human enterocyte-like cell line Caco-2. Circ Shock. 1993 Aug;40(4):276–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmore D. W., Smith R. J., O'Dwyer S. T., Jacobs D. O., Ziegler T. R., Wang X. D. The gut: a central organ after surgical stress. Surgery. 1988 Nov;104(5):917–923. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



