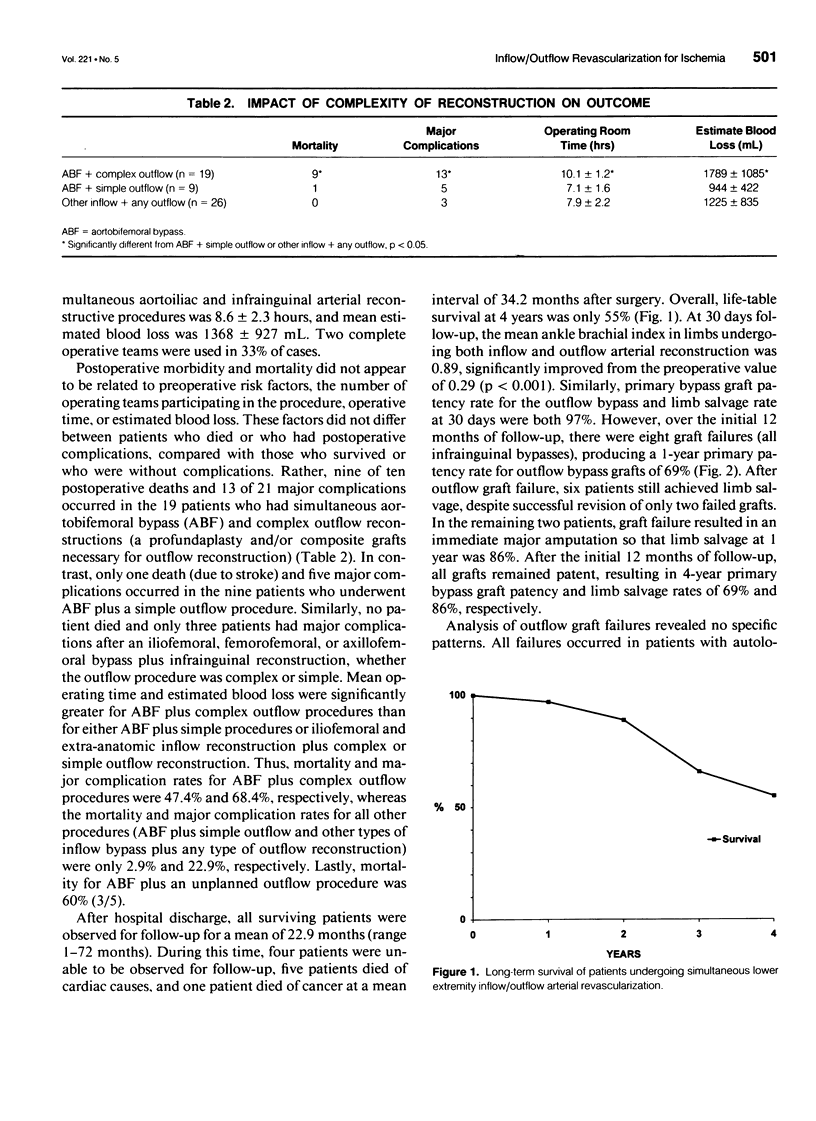
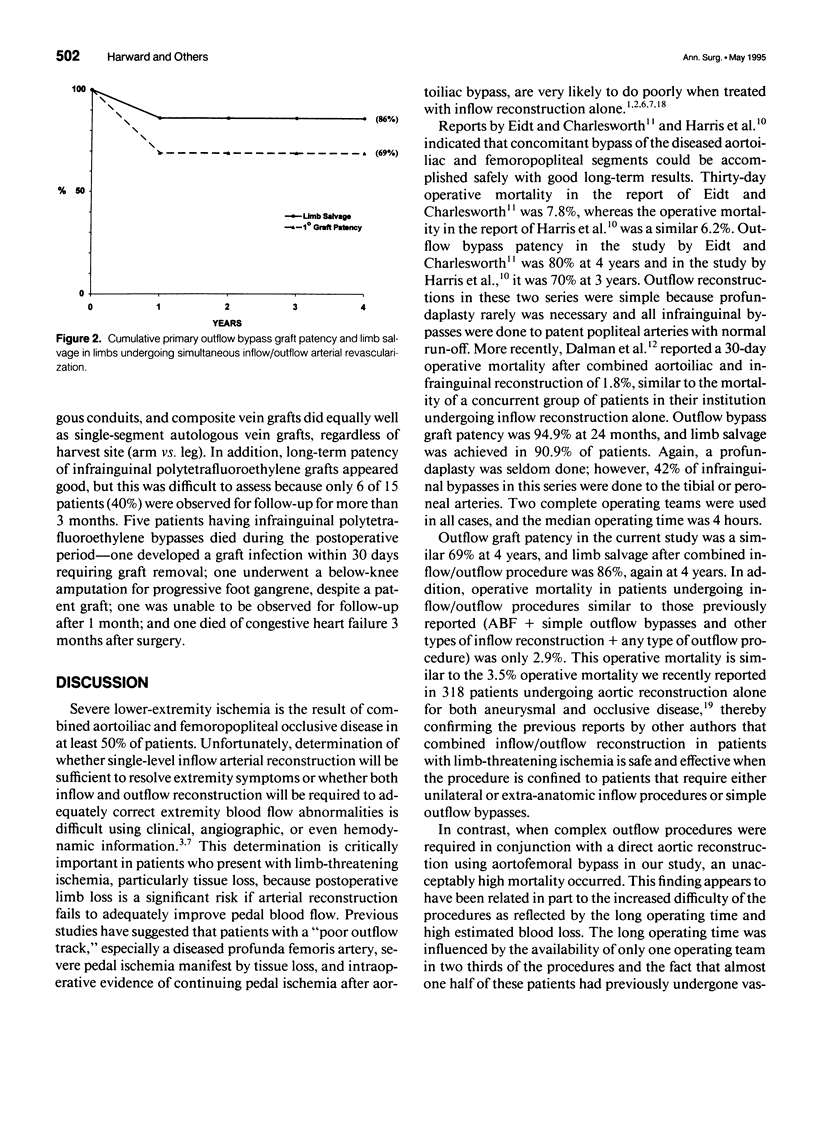
Abstract
SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Limb-threatening ischemia due to severe multilevel arterial occlusive disease may require both inflow and outflow bypass to achieve limb salvage. Simultaneous inflow/outflow bypass has been advocated because the cumulative risks of separate staged inflow/outflow procedures can be avoided. However, the magnitude of complete revascularization is substantial; thus, the morbidity and mortality of simultaneous inflow/outflow bypass may be excessive. METHODS: The medical records of 450 patients undergoing lower extremity arterial reconstruction between 1988 and 1994 were retrospectively reviewed, allowing identification of 54 patients who had undergone simultaneous aortoiliac and infrainguinal bypasses. This group consisted of 38 men and 26 women (mean age: 64.7 years), with significant cardiac disease in 24, smoking history in 53, and diabetes mellitus in 15. Indications for surgery were limb-threatening ischemia in 48 (89%) and severe short-distance claudication in 6 (11%). Inflow disease was corrected by direct aortoiliac reconstruction in 28, whereas other extra-anatomic bypasses were constructed in 26. Outflow revascularization required infrainguinal bypass to the infragenicular arteries in 46 (below-knee popliteal: 21; tibial: 25), a concomitant profundaplasty in 26, and a composite bypass conduit in 14. RESULTS: Limb salvage was 97% at 30 days whereas morbidity/mortality were 61% and 19%, respectively. However, the majority of complications and deaths occurred in patients undergoing aortic inflow plus complex outflow procedures (profundaplasty and/or composite bypass conduits), in which the morbidity/mortality rates were 84.2% and 47.4%, respectively, compared with rates of 45.7% and 2.9% (p < 0.01) after all other inflow/outflow procedures. The increased difficulty of these complex procedures is reflected in the significantly greater blood loss and operative times (1853 mL and 10.0 hours) compared with similar values (1125 mL and 7.7 hours)(p < 0.01) for all other inflow/outflow procedures. CONCLUSION: Simultaneous inflow/outflow bypasses are effective and safe in patients with severe, multilevel arterial occlusive disease, except when a complex outflow procedure is needed in conjunction with direct aortoiliac reconstruction. In the latter setting, a staged procedure is recommended because it may be associated with less morbidity and mortality.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird R. J., Feldman P., Miles J. T., Madras P. M., Gurry J. F. Subsequent downstream repair after aorta-iliac and aorta-femoral bypass operations. Surgery. 1977 Dec;82(6):785–793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bandyk D. F., Cato R. F., Towne J. B. A low flow velocity predicts failure of femoropopliteal and femorotibial bypass grafts. Surgery. 1985 Oct;98(4):799–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. R., Whelen T. J., Cohen A., Spencer F. C. Combined aorto-iliac and femoropopliteal occlusive disease: limitations of total aortofemoropopliteal bypass. Ann Surg. 1966 Jan;163(1):121–130. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196601000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone G. E., Hayes A. C., Slaymaker E. E., Barnes R. W. Value of segmental limb blood pressures in predicting results of aortofemoral bypass. Am J Surg. 1976 Dec;132(6):733–738. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(76)90446-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewster D. C., Perler B. A., Robison J. G., Darling R. C. Aortofemoral graft for multilevel occlusive disease. Predictors of success and need for distal bypass. Arch Surg. 1982 Dec;117(12):1593–1600. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1982.01380360065010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalman R. L., Taylor L. M., Jr, Moneta G. L., Yeager R. A., Porter J. M. Simultaneous operative repair of multilevel lower extremity occlusive disease. J Vasc Surg. 1991 Feb;13(2):211–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dardik H., Ibrahim I. M., Jarrah M., Sussman B., Dardik I. Synchronous aortofemoral or iliofemoral bypass with revascularization of the lower extremity. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1979 Nov;149(5):676–680. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eidt J., Charlesworth D. Combined aortobifemoral and femoropopliteal bypass in the management of patients with extensive atherosclerosis. Ann Vasc Surg. 1987 May;1(4):453–460. doi: 10.1016/S0890-5096(06)60730-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanigan D. P., Williams L. R., Schwartz J. A., Schuler J. J., Gray B. Hemodynamic evaluation of the aortoiliac system based on pharmacologic vasodilatation. Surgery. 1983 May;93(5):709–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris P. L., Bigley D. J., McSweeney L. Aortofemoral bypass and the role of concomitant femorodistal reconstruction. Br J Surg. 1985 Apr;72(4):317–320. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800720426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyden B., Vollmar J., Voss E. U. Principles of operation for combined aortoiliac and femoropopliteal occlusive lesions. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1980 Oct;151(4):519–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londrey G. L., Hodgson K. J., Spadone D. P., Ramsey D. E., Barkmeier L. D., Sumner D. S. Initial experience with color-flow duplex scanning of infrainguinal bypass grafts. J Vasc Surg. 1990 Sep;12(3):284–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue G. D., Long W. D., Smith R. B., 3rd Perspective concerning aorto-femoral arterial reconstruction. Ann Surg. 1971 Jun;173(6):940–944. doi: 10.1097/00000658-197106010-00012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royster T. S., Lynn R., Mulcare R. J. Combined aortoiliac and femoropopliteal occlusive disease. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Dec;143(6):949–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson R. H., Scher L. A., Veith F. J. Combined segment arterial disease. Surgery. 1985 Apr;97(4):385–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seeger J. M., Rosenthal G. R., Self S. B., Flynn T. C., Limacher M. C., Harward T. R. Does routine stress-thallium cardiac scanning reduce postoperative cardiac complications? Ann Surg. 1994 Jun;219(6):654–663. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199406000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumner D. S., Strandness D. E. Aortoiliac reconstruction in patients with combined iliac and superficial femoral arterial occlusion. Surgery. 1978 Sep;84(3):348–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. S., Edwards W. H. Combined aorto-femoral-popliteal arterial reconstruction. J Cardiovasc Surg (Torino) 1973 Mar-Apr;14(2):200–207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


