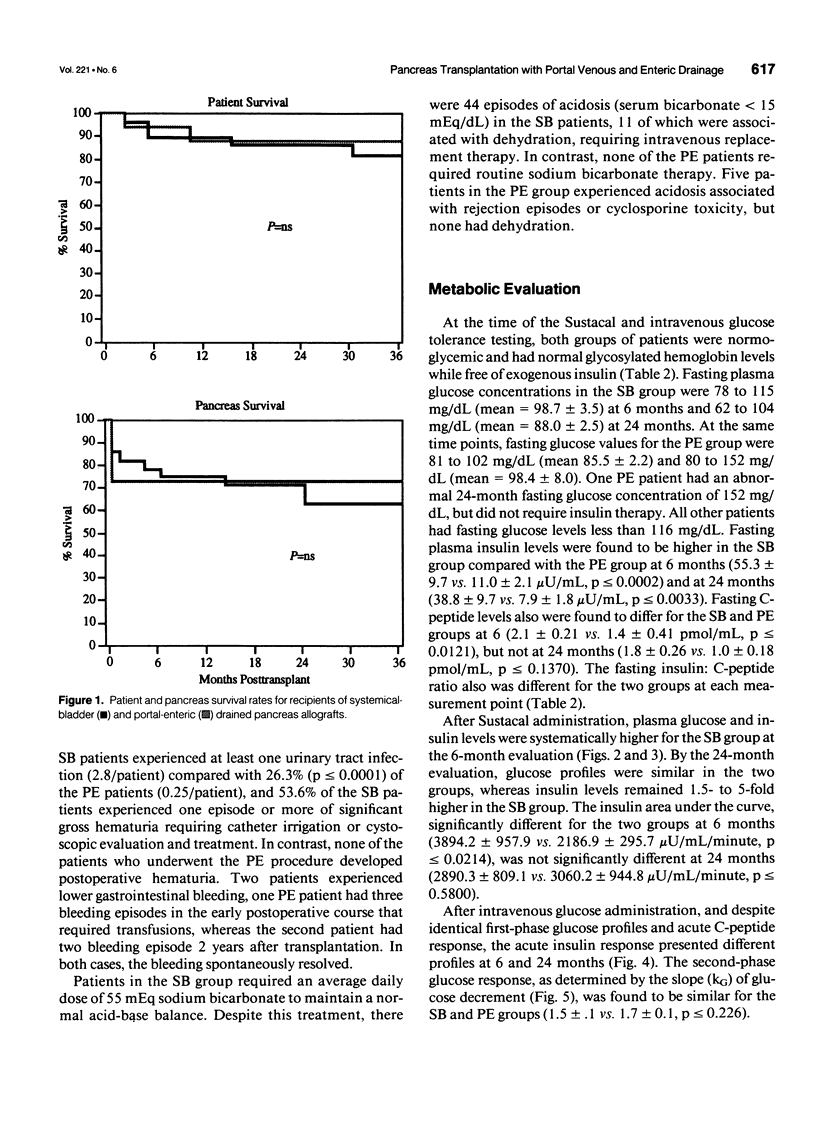
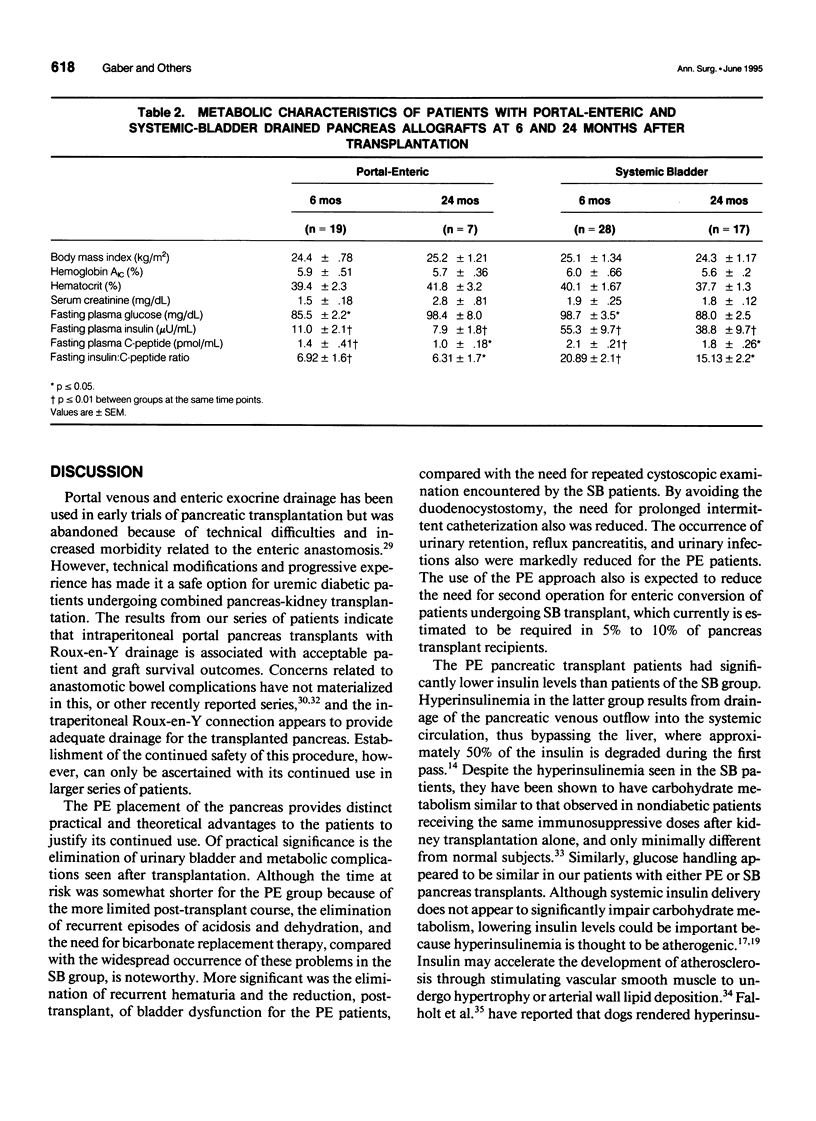
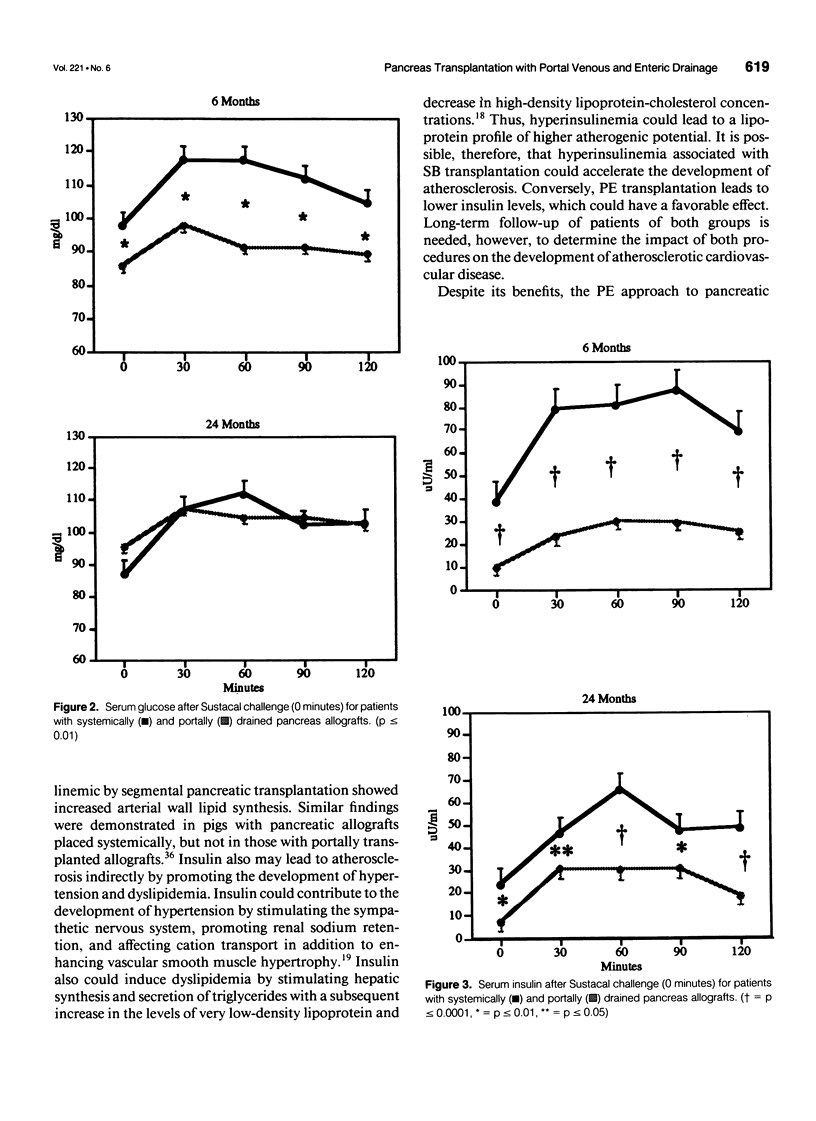
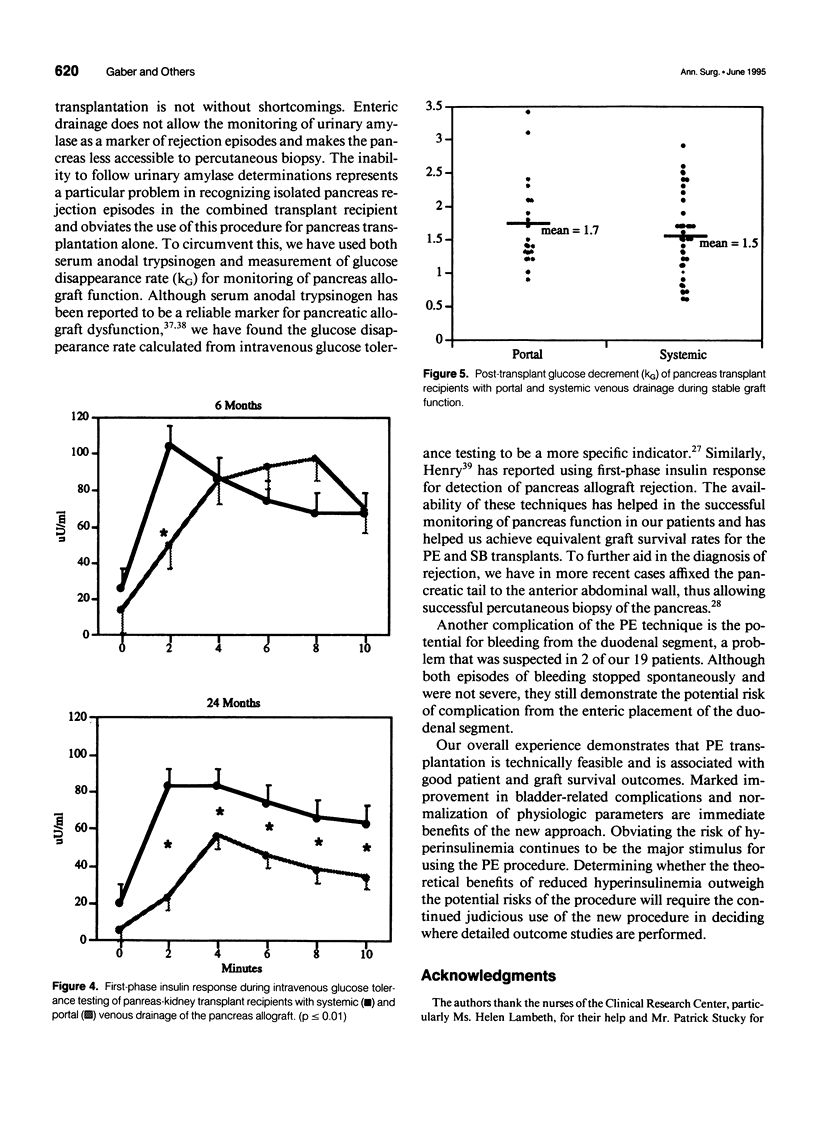
Abstract
PURPOSE: The standard method for pancreatic transplantation involves drainage of exocrine secretions into the urinary bladder with venous outflow into the systemic circulation. Despite the high success rate associated with this approach, it often leads to complications, including chemical cystitis, reflux pancreatitis, metabolic acidosis, and hyperinsulinemia. The authors developed a new technique of pancreatic transplantation with portal drainage of endocrine secretions and enteric drainage of exocrine secretions (PE), which theoretically should be more physiologic. PROCEDURES: All patients were insulin-dependent diabetics with end-stage renal disease who underwent combined kidney-pancreas transplantation. Between 1990 and 1994, 19 patients have been transplanted using intraperitoneal placement of the pancreas allograft with exocrine drainage into a Roux-en Y loop and venous drainage into the portal circulations (PE). A comparison group of all patients undergoing standard systemic-bladder (SB) transplantation between April 1989 and March 1993 (n = 28) also was studied. Patient follow-up ranges from 6 months to 5 years for the SB patients (mean = 2.5 years) and 6 months to 4 years for the PE patients (mean = 1.6 years). Routine follow-up includes documentation of the clinical course and detailed endocrine studies. FINDINGS: Patient and graft actuarial survival at 1 and 3 years is no different for SB and PE patients. Urinary tract infections occurred in 89.3% of the SB patients (2.8/patient) versus 26.3% of the PE patients (0.25/patient, p < or = 0.0001). None of the PE patients experienced hematuria compared with 53.6% of the SB patients (p < or = 0.0001); however, two PE patients had melanotic episodes. The incidence of urinary retention and reflux pancreatitis was 32.1% versus 5.3% (p < or = 0.028) for SB and PE groups, respectively. Patients in the SB group required sodium bicarbonate therapy (mean = 55 mEq/day) although no PE patient required routine therapy; despite this, SB patients experienced more episodes of acidosis (44 vs. 5). Endocrine studies indicate no difference in glycosylated hemoglobin or fasting and stimulated glucose values throughout the follow-up period. In contrast, hyperinsulinemia was evident in both fasting and stimulated tests for the SB patients, with values consistently two- to fivefold higher than those of the PE group. CONCLUSIONS: These results indicate that PE and SB pancreas transplantation are equivalent in terms of patient and graft survival and suggest that the PE approach is associated with a decreased incidence of metabolic and bladder-related complications. In addition, the PE approach eliminates the state of peripheral hyperinsulinemia that characterizes the SB procedure. Continued follow-up will be necessary to determine if long-term outcomes will differ for patients with PE and SB grafts.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bilous R. W., Mauer S. M., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S., Goetz F. C., Steffes M. W. The effects of pancreas transplantation on the glomerular structure of renal allografts in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes. N Engl J Med. 1989 Jul 13;321(2):80–85. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198907133210204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman J. D., Polonsky K. S., Jaspan J. B., Sturis J., Van Cauter E., Thistlethwaite J. R. Insulin secretory profiles and C-peptide clearance kinetics at 6 months and 2 years after kidney-pancreas transplantation. Diabetes. 1992 Oct;41(10):1346–1354. doi: 10.2337/diab.41.10.1346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne R. Y. Paratopic segmental pancreas grafting: a technique with portal venous drainage. Lancet. 1984 Mar 17;1(8377):595–597. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90998-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottrell D. A., Henry M. L., O'Dorisio T. M., Tesi R. J., Ferguson R. M., Osei K. Sequential metabolic studies of pancreas allograft function in type 1 diabetic recipients. Diabet Med. 1992 Jun;9(5):438–443. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-5491.1992.tb01814.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E. Insulin resistance. A multifaceted syndrome responsible for NIDDM, obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Care. 1991 Mar;14(3):173–194. doi: 10.2337/diacare.14.3.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diem P., Abid M., Redmon J. B., Sutherland D. E., Robertson R. P. Systemic venous drainage of pancreas allografts as independent cause of hyperinsulinemia in type I diabetic recipients. Diabetes. 1990 May;39(5):534–540. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.5.534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmer D. S., Hathaway D. K., Shokouh-Amiri H., Hughes T., Gaber A. O. The relationship of glucose disappearance rate (kG) to acute pancreas allograft rejection. Transplantation. 1994 May 15;57(9):1400–1405. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199405150-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falholt K., Cutfield R., Alejandro R., Heding L., Mintz D. The effects of hyperinsulinemia on arterial wall and peripheral muscle metabolism in dogs. Metabolism. 1985 Dec;34(12):1146–1149. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(85)90161-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber A. O., Cardoso S., Pearson S., Abell T., Gaber L., Hathaway D., Alakkad M., Cromer R., Britt L. G. Improvement in autonomic function following combined pancreas-kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1991 Feb;23(1 Pt 2):1660–1662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber A. O., Gaber L. W., Shokouh-Amiri M. H., Hathaway D. Percutaneous biopsy of pancreas transplants. Transplantation. 1992 Sep;54(3):548–550. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199209000-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaber A. O., Shokouh-Amiri H., Grewal H. P., Britt L. G. A technique for portal pancreatic transplantation with enteric drainage. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1993 Oct;177(4):417–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groth C. G., Tydén G., Lundgren G., Wilczek H., Klintmalm G., Ost L., Gunnarsson R., Ostman J. Segmental pancreatic transplantation with enteric exocrine diversion. World J Surg. 1984 Apr;8(2):257–261. doi: 10.1007/BF01655144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. K., Abell T., Cardoso S., Hartwig M. S., el Gebely S., Gaber A. O. Improvement in autonomic and gastric function following pancreas-kidney versus kidney-alone transplantation and the correlation with quality of life. Transplantation. 1994 Mar 27;57(6):816–822. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199403270-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D. K., Hartwig M. S., Milstead J., Elmer D., Evans S., Gaber A. O. Improvement in quality of life reported by diabetic recipients of kidney-only and pancreas-kidney allografts. Transplant Proc. 1994 Apr;26(2):512–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H., Homan M., Velosa J., Robertson P., Rizza R. Effects of pancreas transplantation on postprandial glucose metabolism. N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 31;325(18):1278–1283. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110313251804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly W. D., Lillehei R. C., Merkel F. K., Idezuki Y., Goetz F. C. Allotransplantation of the pancreas and duodenum along with the kidney in diabetic nephropathy. Surgery. 1967 Jun;61(6):827–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy W. R., Navarro X., Goetz F. C., Sutherland D. E., Najarian J. S. Effects of pancreatic transplantation on diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med. 1990 Apr 12;322(15):1031–1037. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199004123221503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefèbvre P. J. Pancreatic transplantation: why, when and who? Diabetologia. 1992 May;35(5):494–497. doi: 10.1007/BF02342451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsbad S., Christiansen E., Tibell A., Tydén G., Rasmussen K., Burcharth F. Beta-cell dysfunction following successful segmental pancreas transplantation. Danish-Swedish Study Group of Metabolic Effect of Pancreas Transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1994 Apr;26(2):469–470. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks W. H., Borgström A., Sollinger H., Marks C. Serum immunoreactive anodal trypsinogen and urinary amylase as biochemical markers for rejection of clinical whole-organ pancreas allografts having exocrine drainage into the urinary bladder. Transplantation. 1990 Jan;49(1):112–115. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199001000-00025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mühlbacher F., Gnant M. F., Auinger M., Steininger R., Klauser R., Prager R., Karnel F. Pancreatic venous drainage to the portal vein: a new method in human pancreas transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1990 Apr;22(2):636–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathan D. M., Fogel H., Norman D., Russell P. S., Tolkoff-Rubin N., Delmonico F. L., Auchincloss H., Jr, Camuso J., Cosimi A. B. Long-term metabolic and quality of life results with pancreatic/renal transplantation in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Transplantation. 1991 Jul;52(1):85–91. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199107000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nghiem D. D., Gonwa T. A., Corry R. J. Metabolic effects of urinary diversion of exocrine secretions in pancreatic transplantation. Transplantation. 1987 Jan;43(1):70–73. doi: 10.1097/00007890-198701000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkal M., Marks C., Lorber M. I., Marks W. H. A three-year experience with serum anodal trypsinogen as a biochemical marker for rejection in pancreatic allografts. False positives, tissue biopsy, comparison with other markers, and diagnostic strategies. Transplantation. 1992 Feb;53(2):415–419. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199202010-00028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson R. P. Seminars in medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston: Pancreatic and islet transplantation for diabetes--cures or curiosities? N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 24;327(26):1861–1868. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212243272607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenlof L. K., Earnhardt R. C., Pruett T. L., Stevenson W. C., Douglas M. T., Cornett G. C., Hanks J. B. Pancreas transplantation. An initial experience with systemic and portal drainage of pancreatic allografts. Ann Surg. 1992 Jun;215(6):586–597. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199206000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki T., Pirsch J. D., D'Alessandro A. M., Knechtle S. J., Kalayoglu M., Belzer F. O., Sollinger H. W. Simultaneous pancreas-kidney transplantation at University of Wisconsin-Madison Hospital. Clin Transpl. 1991:135–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokouh-Amiri M. H., Falholt K., Holst J. J., Rahimi-Saber S., Orbaek Andersen H., Jensen S. L. Pancreas endocrine function in pigs after segmental pancreas autotransplantation with either systemic or portal venous drainage. Transplant Proc. 1992 Jun;24(3):799–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shokouh-Amiri M. H., Gaber A. O., Gaber L. W., Jensen S. L., Hughes T. A., Elmer D., Britt L. G. Pancreas transplantation with portal venous drainage and enteric exocrine diversion: a new technique. Transplant Proc. 1992 Jun;24(3):776–777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. W., Bierman E. L., Ross R. Effect of insulin on the proliferation of cultured primate arterial smooth muscle cells. Circ Res. 1975 Feb;36(2):319–327. doi: 10.1161/01.res.36.2.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. W. Insulin and atheroma. 20-yr perspective. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):631–654. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland D., Gruessner A., Moudry-Munns K. International Pancreas Transplant Registry report. Transplant Proc. 1994 Apr;26(2):407–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toledo-Pereyra L. H., Mittal V. K. Complications of pancreas transplantation-effect of technique. Transplant Proc. 1987 Feb;19(1 Pt 3):2319–2322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


