Abstract
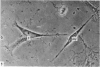
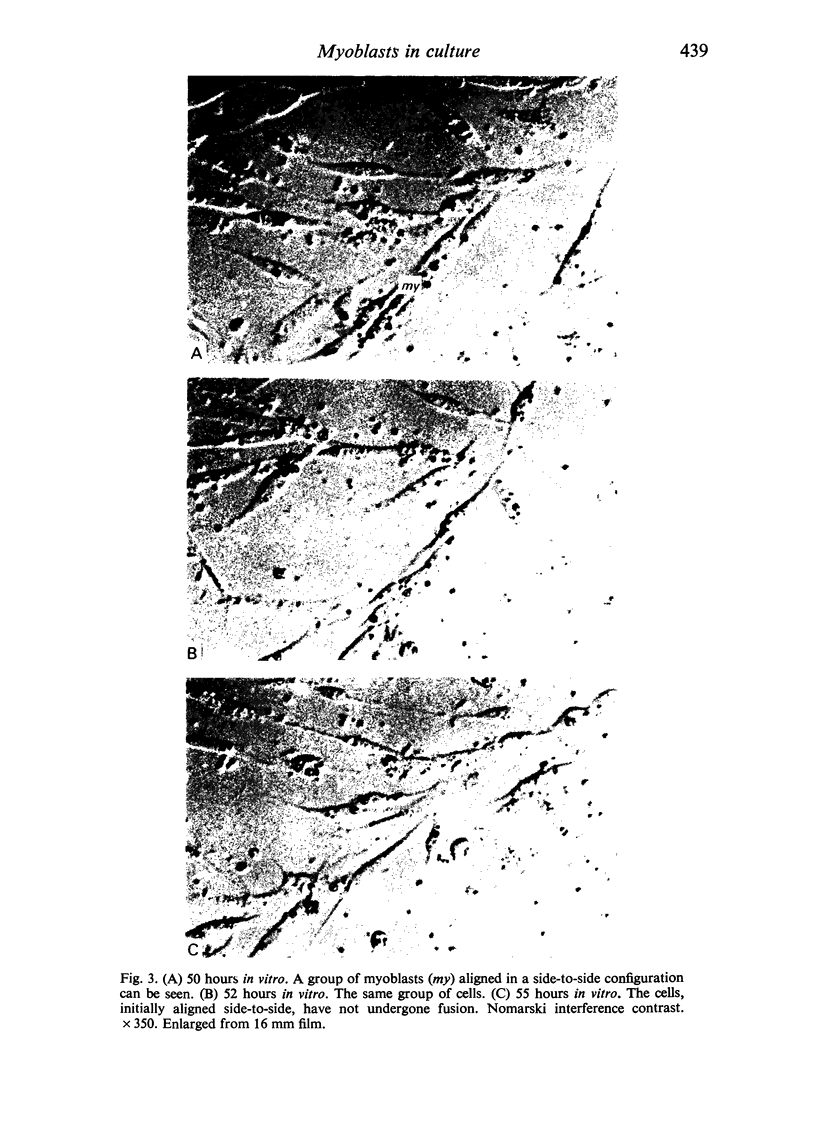
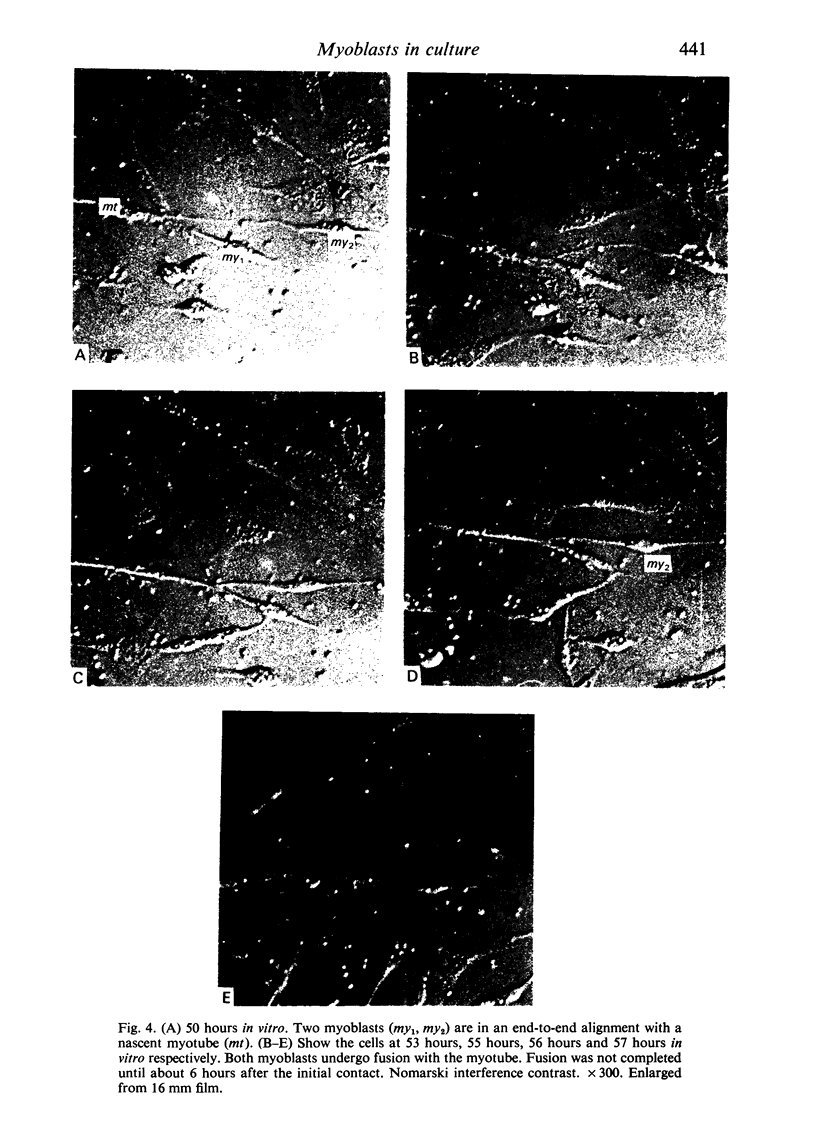
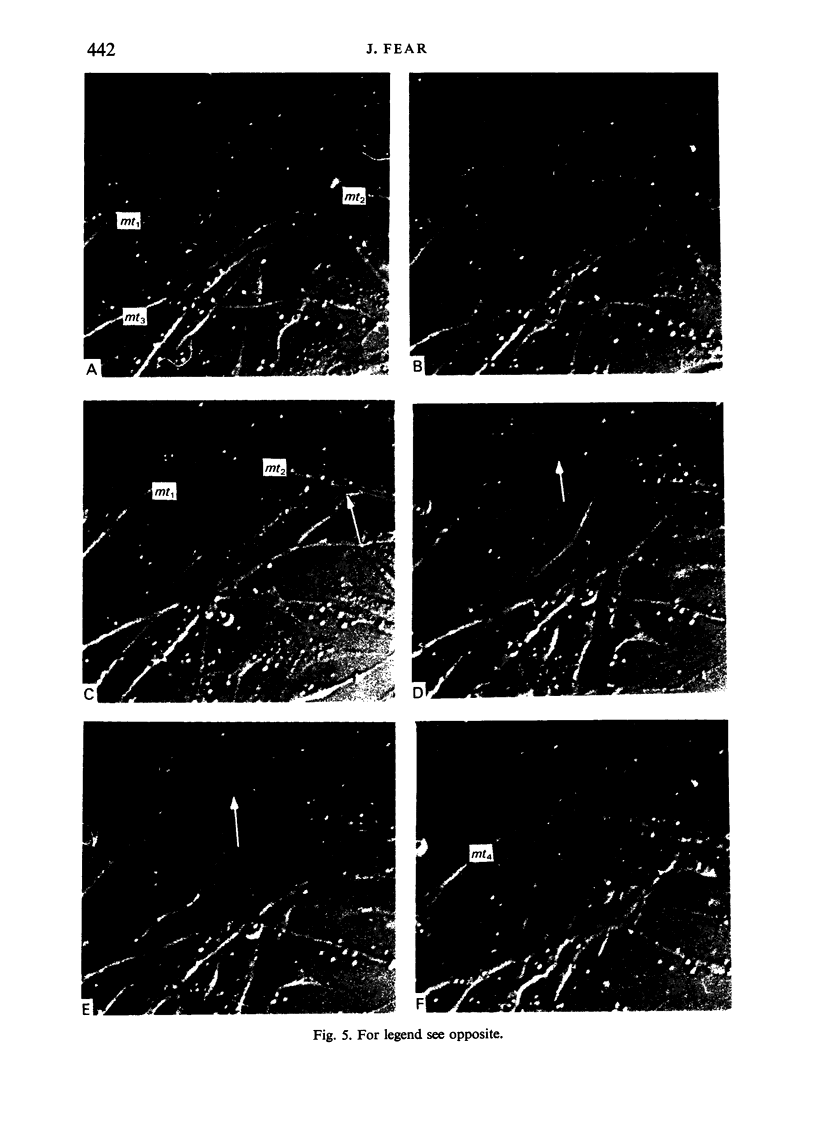
Chick embryo myoblasts were grown as monolayers in culture. The formation of myotubes from myoblasts occurred over a 15 hour period in vitro. Time-lapse cinemicrography was used to study the behaviour of myoblasts during fusion and particular attention was paid to the way in which myoblasts aligned themselves. It was found that fusion tended to follow end-to-end rather than side-to-side alignment of myoblasts. This observation suggests that cell orientation is an important factor in myogenesis. Branched myotubes were frequently observed in culture; an explanation of this is offered.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Mitosis and the processes of differentiation of myogenic cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1969 Apr;41(1):188–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.41.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPERS C. R. Multinucleation of skeletal muscle in vitro. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1960 Jun;7:559–566. doi: 10.1083/jcb.7.3.559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER W. G., KONIGSBERG I. R. Dynamics of myogenesis in vitro. Anat Rec. 1961 Jul;140:195–205. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091400305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauschka S. D., Konigsberg I. R. The influence of collagen on the development of muscle clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Jan;55(1):119–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.55.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KONIGSBERG I. R. Clonal analysis of myogenesis. Science. 1963 Jun 21;140(3573):1273–1284. doi: 10.1126/science.140.3573.1273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipton B. H., Konigsberg I. R. A fine-structural analysis of the fusion of myogenic cells. J Cell Biol. 1972 May;53(2):348–364. doi: 10.1083/jcb.53.2.348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCONA A. Rotation-mediated histogenetic aggregation of dissociated cells. A quantifiable approach to cell interactions in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1961 Jan;22:455–475. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(61)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill M. C., Stockdale F. E. A kinetic analysis of myogenesis in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1972 Jan;52(1):52–65. doi: 10.1083/jcb.52.1.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Przybylski R. J., Blumberg J. M. Ultrastructural aspects of myogenesis in the chick. Lab Invest. 1966 May;15(5):836–863. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHARP J. A. A modification of the Rose perfusion chamber. Exp Cell Res. 1959 Jun;17(3):519–521. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(59)90073-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada Y. Electron microscope observations on the fusion of chick myoblasts in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jan;48(1):128–142. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.1.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada Y., Fischman D. A., Moscona A. A. The fine structure of embryonic chick skeletal muscle cells differentiated in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1967 Nov;35(2):445–453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.35.2.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]