Abstract
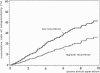
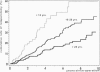
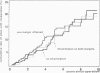
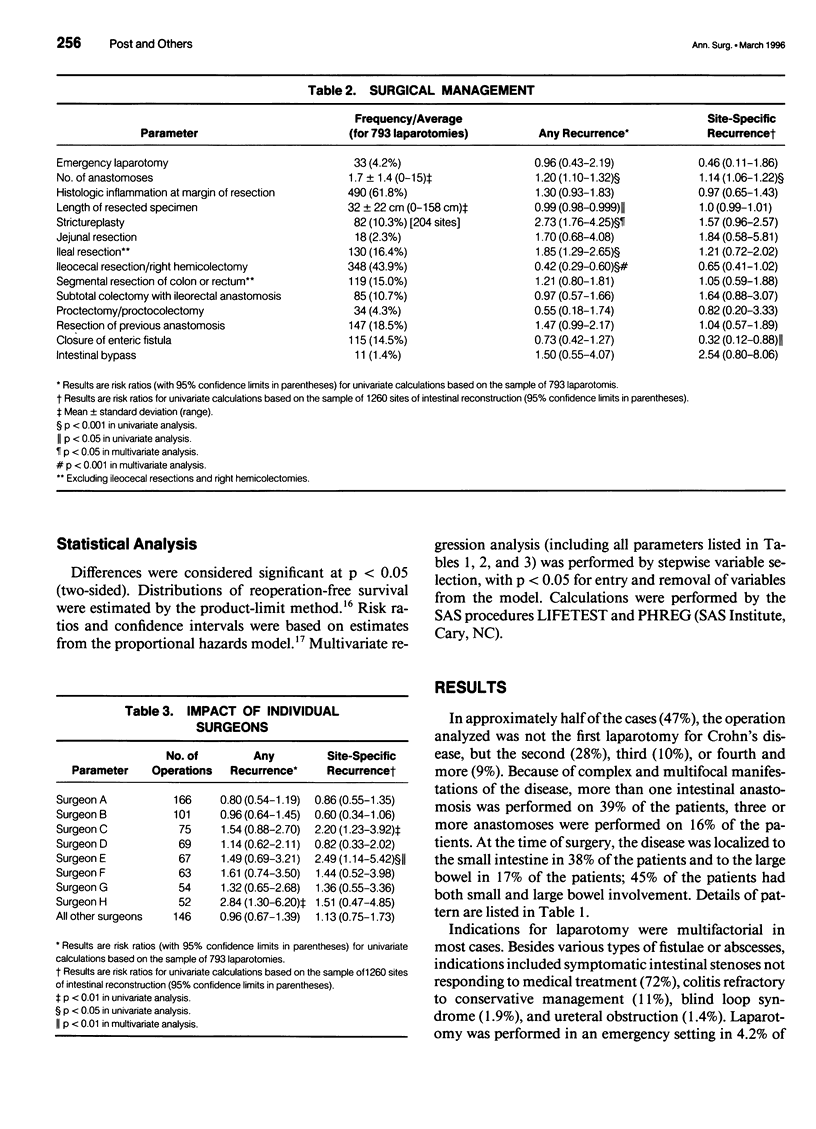
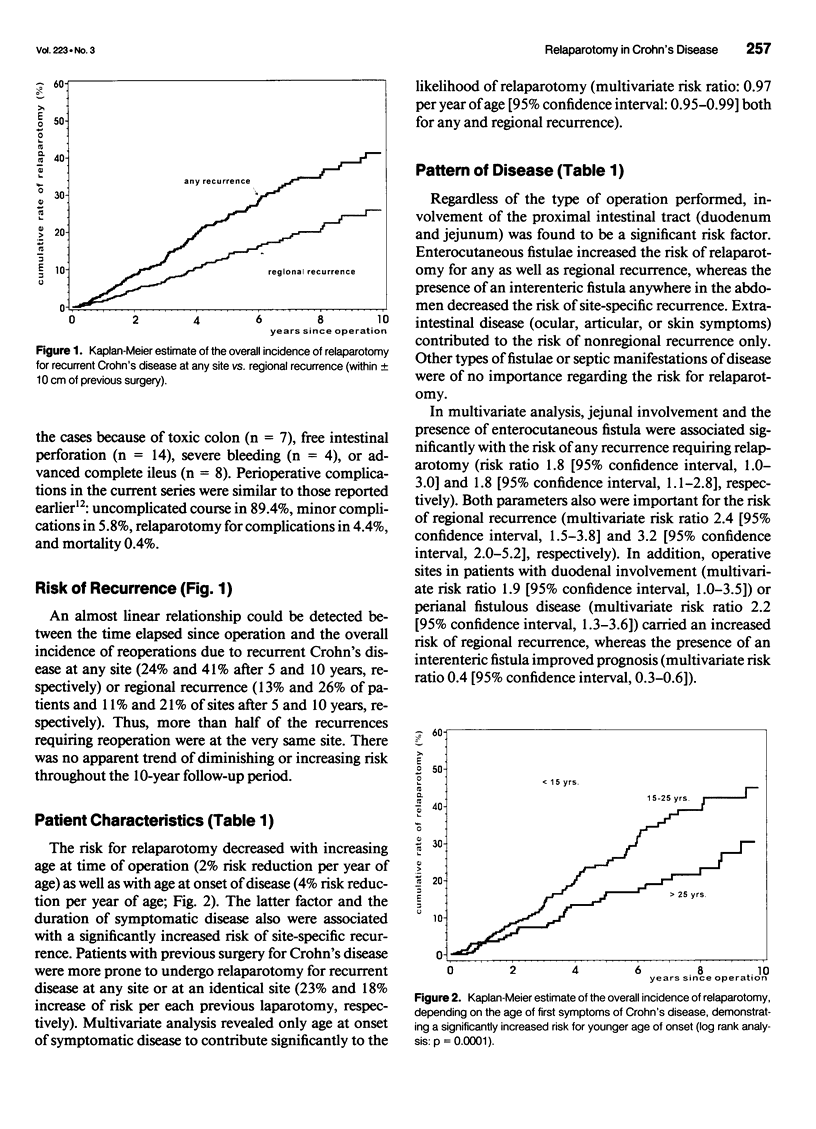
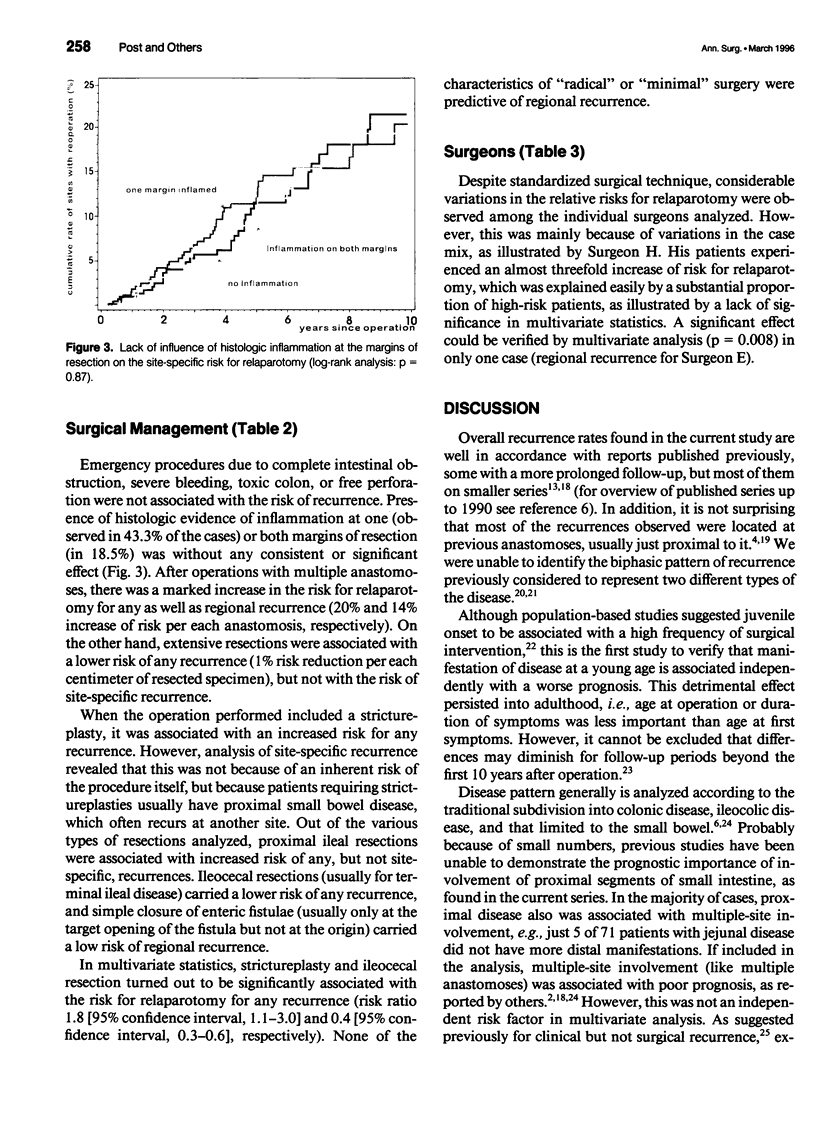
OBJECTIVE: The authors provide a multivariate analysis of a large single-center experience with limited surgery for Crohn's disease. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: During the past decade, the aim of surgery for Crohn's disease has shifted from radical operation, achieving inflammation-free margins of resection, to "minimal surgery," intended to remove just grossly inflamed tissue or performing strictureplasties. METHODS: Seven hundred ninety-three cases of resection and/or strictureplasty in 689 individuals with histologically verified Crohn's disease were followed for a mean period of 50 months (range, 5-166 months). Two different end points were analyzed: 1) any relaparotomy for recurrent (or persistent) Crohn's disease and 2) relaparotomy for site-specific recurrence. More than 30 variables of patient/disease characteristics and surgical management were included in a proportional hazard model. RESULTS: Five parameters were associated independently with the risk for relaparotomy: increased risk coincided with young age at onset of disease, involvement of jejunum, enterocutaneous fistula, or performed strictureplasty, and decreased risk followed ileocecal resection. Site-specific risks of reoperation were calculated on the basis of 1260 intestinal resections or anastomoses performed in these patients. Young age at onset, duodenal and jejunal involvement, presence of enterocutaneous or perianal fistula, and a single surgeon (of 23) were associated significantly with increased risk of regional recurrence but not strictureplasty or inflammation at margins of resection. CONCLUSIONS: Limited surgery for Crohn's disease is not associated with increased risk of regional recurrence requiring reoperation. However, patients with juvenile onset, proximal small bowel disease, and some types of fistulae are at a considerable risk of experiencing early surgical recurrence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cameron J. L., Hamilton S. R., Coleman J., Sitzmann J. V., Bayless T. M. Patterns of ileal recurrence in Crohn's disease. A prospective randomized study. Ann Surg. 1992 May;215(5):546–552. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199205000-00018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chardavoyne R., Flint G. W., Pollack S., Wise L. Factors affecting recurrence following resection for Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1986 Aug;29(8):495–502. doi: 10.1007/BF02562601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cottone M., Rosselli M., Orlando A., Oliva L., Puleo A., Cappello M., Traina M., Tonelli F., Pagliaro L. Smoking habits and recurrence in Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1994 Mar;106(3):643–648. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90697-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Dombal F. T., Burton I., Goligher J. C. Recurrence of Crohn's disease after primary excisional surgery. Gut. 1971 Jul;12(7):519–527. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.7.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehn T. C., Kettlewell M. G., Mortensen N. J., Lee E. C., Jewell D. P. Ten-year experience of strictureplasty for obstructive Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1989 Apr;76(4):339–341. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewe K., Herfarth C., Malchow H., Jesdinsky H. J. Postoperative recurrence of Crohn's disease in relation to radicality of operation and sulfasalazine prophylaxis: a multicenter trial. Digestion. 1989;42(4):224–232. doi: 10.1159/000199850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer R. G., Whelan G., Fazio V. W. Long-term follow-up of patients with Crohn's disease. Relationship between the clinical pattern and prognosis. Gastroenterology. 1985 Jun;88(6):1818–1825. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(85)90006-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazio V. W., Tjandra J. J., Lavery I. C., Church J. M., Milsom J. W., Oakley J. R. Long-term follow-up of strictureplasty in Crohn's disease. Dis Colon Rectum. 1993 Apr;36(4):355–361. doi: 10.1007/BF02053938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein A. J., Lachman P., Sachar D. B., Springhorn J., Heimann T., Janowitz H. D., Aufses A. H., Jr Perforating and non-perforating indications for repeated operations in Crohn's disease: evidence for two clinical forms. Gut. 1988 May;29(5):588–592. doi: 10.1136/gut.29.5.588. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimann T. M., Greenstein A. J., Lewis B., Kaufman D., Heimann D. M., Aufses A. H., Jr Prediction of early symptomatic recurrence after intestinal resection in Crohn's disease. Ann Surg. 1993 Sep;218(3):294–299. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199309000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimann T. M., Greenstein A. J., Mechanic L., Aufses A. H., Jr Early complications following surgical treatment for Crohn's disease. Ann Surg. 1985 Apr;201(4):494–498. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198504000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. C. Aim of surgical treatment of Crohn's disease. Gut. 1984 Mar;25(3):217–222. doi: 10.1136/gut.25.3.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lock M. R., Farmer R. G., Fazio V. W., Jagelman D. G., Lavery I. C., Weakley F. L. Recurrence and reoperation for Crohn's disease: the role of disease location in prognosis. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jun 25;304(26):1586–1588. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198106253042607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald P. J., Fazio V. W., Farmer R. G., Jagelman D. G., Lavery I. C., Ruderman W. B., Easley K. A., Harper P. H. Perforating and nonperforating Crohn's disease. An unpredictable guide to recurrence after surgery. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989 Feb;32(2):117–120. doi: 10.1007/BF02553823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelassi F., Balestracci T., Chappell R., Block G. E. Primary and recurrent Crohn's disease. Experience with 1379 patients. Ann Surg. 1991 Sep;214(3):230–240. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199109000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olaison G., Smedh K., Sjödahl R. Natural course of Crohn's disease after ileocolic resection: endoscopically visualised ileal ulcers preceding symptoms. Gut. 1992 Mar;33(3):331–335. doi: 10.1136/gut.33.3.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennington L., Hamilton S. R., Bayless T. M., Cameron J. L. Surgical management of Crohn's disease. Influence of disease at margin of resection. Ann Surg. 1980 Sep;192(3):311–318. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198009000-00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. K., Hittinger R., Blesovsky L., Fry J. S., Fielding L. P. Local recurrence following 'curative' surgery for large bowel cancer: I. The overall picture. Br J Surg. 1984 Jan;71(1):12–16. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800710104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Podolsky D. K. Inflammatory bowel disease (2) N Engl J Med. 1991 Oct 3;325(14):1008–1016. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199110033251406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post S., Betzler M., von Ditfurth B., Schürmann G., Küppers P., Herfarth C. Risks of intestinal anastomoses in Crohn's disease. Ann Surg. 1991 Jan;213(1):37–42. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199101000-00007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post S., Herfarth C., Schumacher H., Golling M., Schürmann G., Timmermanns G. Experience with ileostomy and colostomy in Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1995 Dec;82(12):1629–1633. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800821213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rutgeerts P., Geboes K., Vantrappen G., Beyls J., Kerremans R., Hiele M. Predictability of the postoperative course of Crohn's disease. Gastroenterology. 1990 Oct;99(4):956–963. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(90)90613-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachar D. B. The problem of postoperative recurrence of Crohn's disease. Med Clin North Am. 1990 Jan;74(1):183–188. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)30594-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon P., Kornbluth A., Aisenberg J., Janowitz H. D. How effective are current drugs for Crohn's disease? A meta-analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992 Apr;14(3):211–215. doi: 10.1097/00004836-199204000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayfan J., Wilson D. A., Allan A., Andrews H., Alexander-Williams J. Recurrence after strictureplasty or resection for Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1989 Apr;76(4):335–338. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800760406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N. A., Hughes L. E. Timing of ileocolonic resection for symptomatic Crohn's disease--the patient's view. Gut. 1994 May;35(5):656–657. doi: 10.1136/gut.35.5.656. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick D. M., Barton J. R., Hamer-Hodges D. W., Nixon S. J., Ferguson A. Population-based study of surgery in juvenile onset Crohn's disease. Br J Surg. 1991 Feb;78(2):171–175. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer M. P., Nelson H., Wolff B. G., Dozois R. R. Strictureplasty for obstructive Crohn's disease: the Mayo experience. Mayo Clin Proc. 1994 Jan;69(1):33–36. doi: 10.1016/s0025-6196(12)61609-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Wong W. D., Rothenberger D. A., Goldberg S. M. Recurrence of Crohn's disease after resection. Br J Surg. 1991 Jan;78(1):10–19. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800780106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]