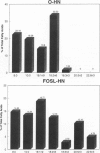
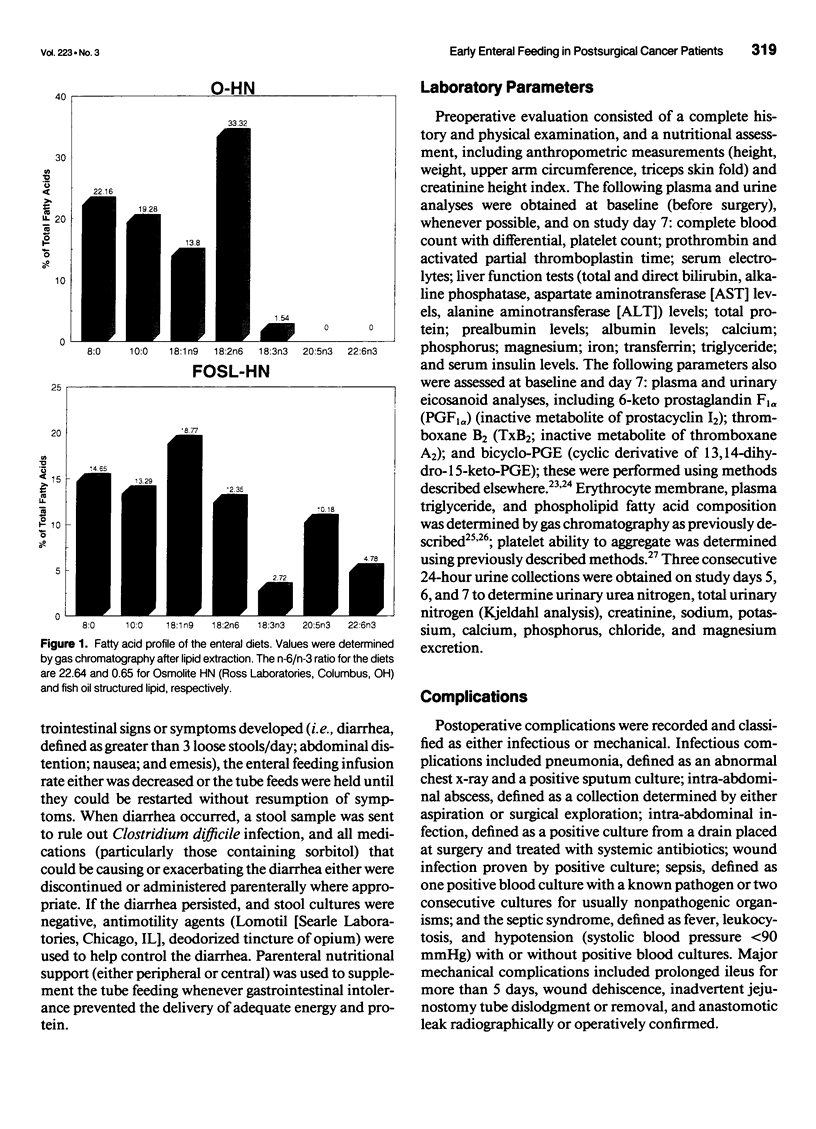
Abstract
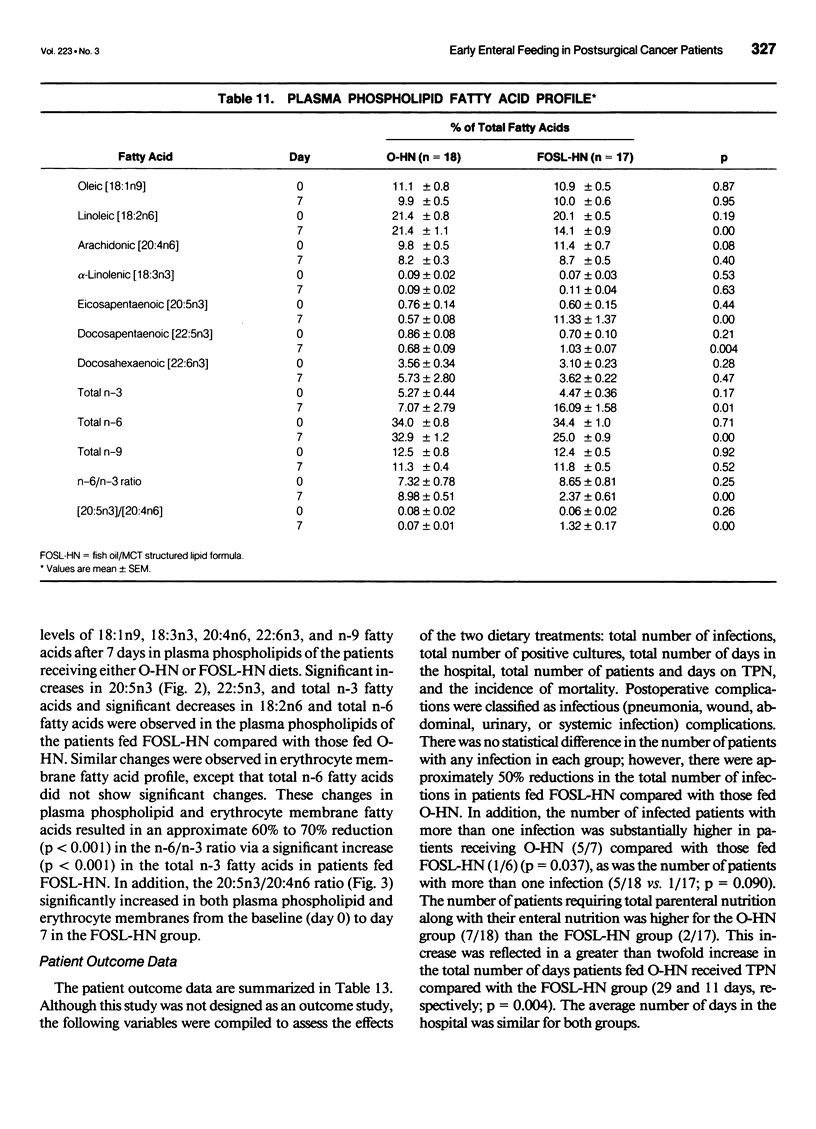
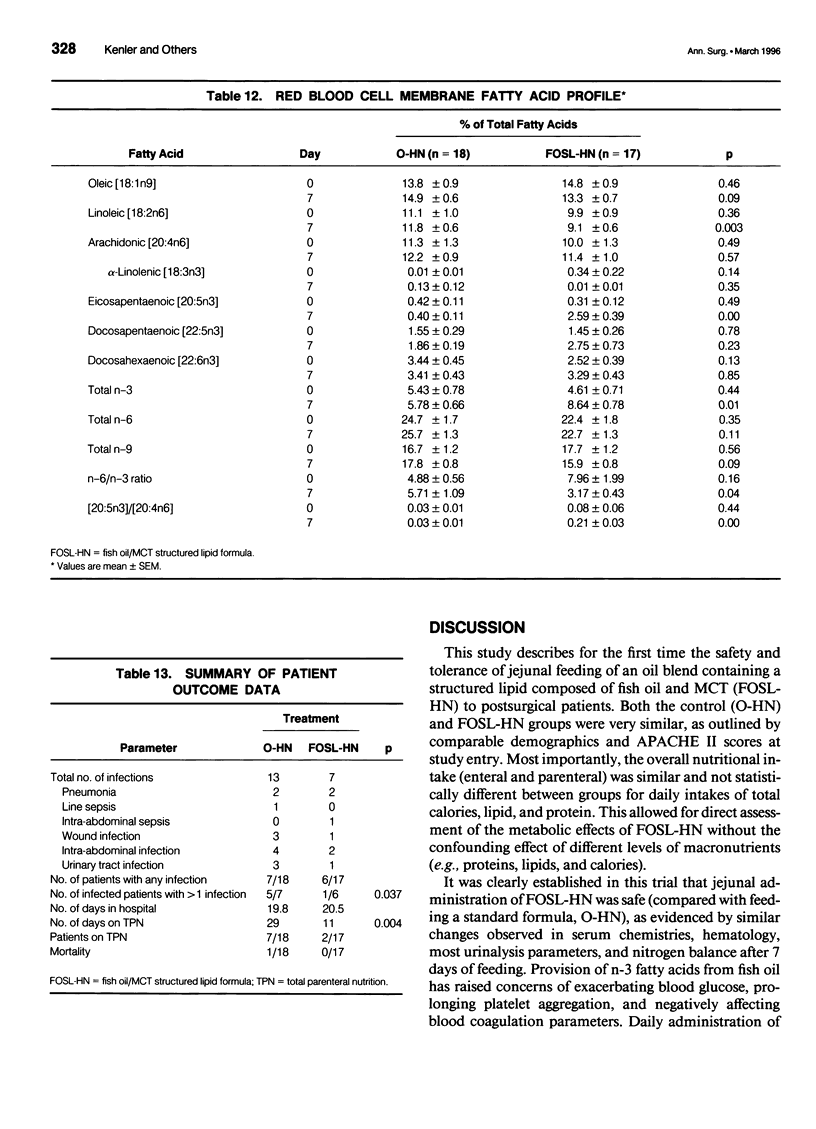
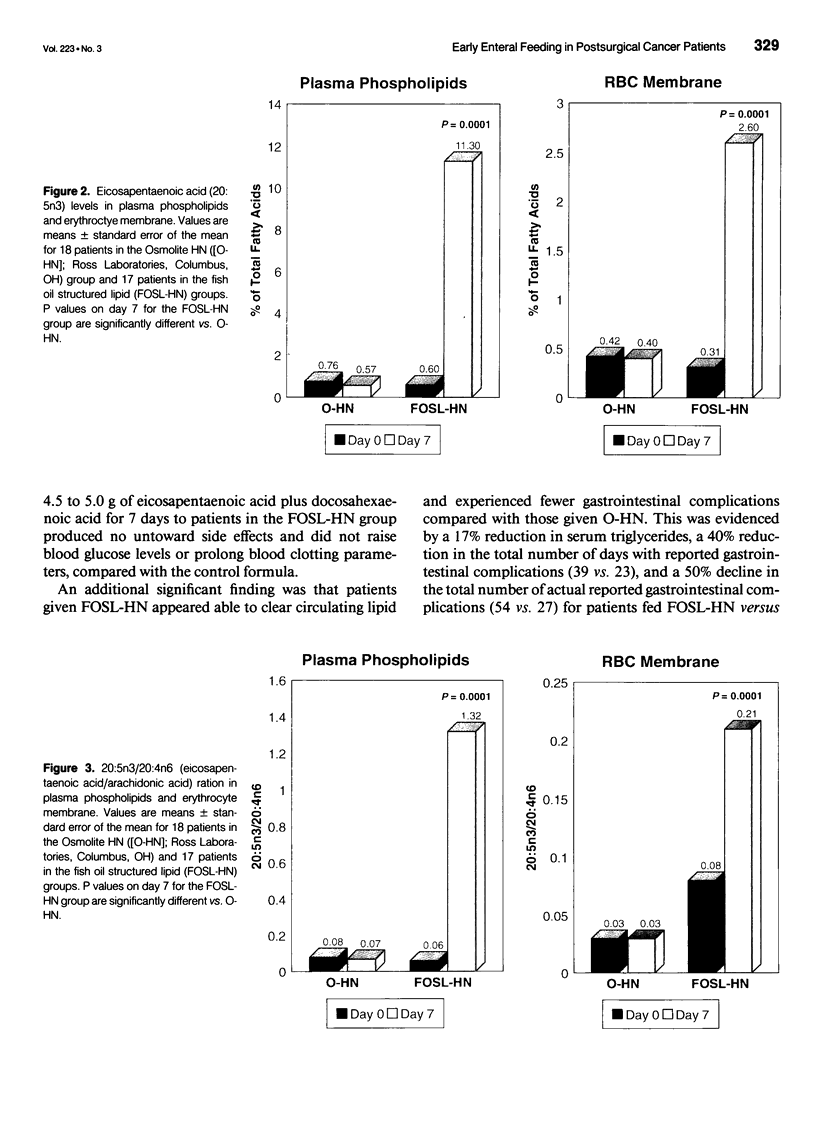
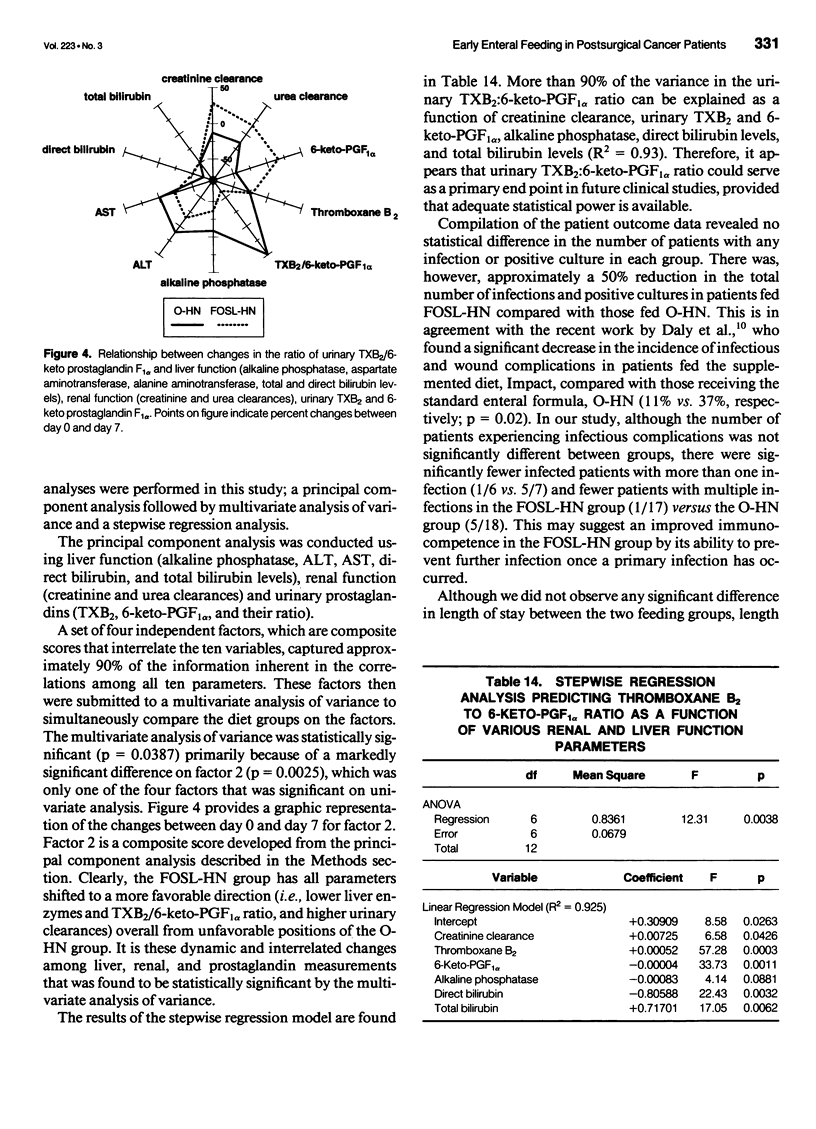
OBJECTIVES: The authors compared the safety, gastrointestinal tolerance, and clinical efficacy of feeding an enteral diet containing a fish oil/medium-chain triglyceride structured lipid (FOSL-HN) versus an isonitrogenous, isocaloric formula (O-HN) in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery for upper gastrointestinal malignancies. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Previous studies suggest that feeding with n-3 fatty acids from fish oil can alter eicosanoid and cytokine production, yielding an improved immunocompetence and a reduced inflammatory response to injury. The use of n-3 fatty acids as a structured lipid can improve long-chain fatty acid absorption. METHODS: This prospective, blinded, randomized trial was conducted in 50 adult patients who were jejunally fed either FOSL-HN or O-HN for 7 days. Serum chemistries, hematology, urinalysis, gastrointestinal complications, liver and renal function, plasma and erythrocyte fatty acid analysis, urinary prostaglandins, and outcome parameters were measured at baseline and on day 7. Comparisons were made in 18 and 17 evaluable patients based a priori on the ability to reach a tube feeding rate of 40 mL/hour. RESULTS: Patients receiving FOSL-HN experienced no untoward side effects, significant incorporation of eicosapentaenoic acid into plasma and erythrocyte phospholipids, and a 50% decline in the total number of gastrointestinal complications and infections compared with patients given O-HN. The data strongly suggest improved liver and renal function during the postoperative period in the FOSL-HN group. CONCLUSION: Early enteral feeding with FOSL-HN was safe and well tolerated. Results suggest that the use of such a formula during the postoperative period may reduce the number of infections and gastrointestinal complications per patient, as well as improve renal and liver function through modulation of urinary prostaglandin levels. Additional clinical trials to fully quantify clinical benefits and optimize nutritional support with FOSL-HN should be undertaken.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S., Yeh Y. Y., Jensen G. L. Changes in plasma and erythrocyte fatty acids in patients fed enteral formulas containing different fats. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1993 Jan-Feb;17(1):30–34. doi: 10.1177/014860719301700130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alverdy J., Chi H. S., Sheldon G. F. The effect of parenteral nutrition on gastrointestinal immunity. The importance of enteral stimulation. Ann Surg. 1985 Dec;202(6):681–684. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198512000-00003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett R. H., Dechert R. E., Mault J. R., Ferguson S. K., Kaiser A. M., Erlandson E. E. Measurement of metabolism in multiple organ failure. Surgery. 1982 Oct;92(4):771–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L., Hallowell E., Heddle R. Protein status of general surgical patients. JAMA. 1974 Nov 11;230(6):858–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bower R. H., Cerra F. B., Bershadsky B., Licari J. J., Hoyt D. B., Jensen G. L., Van Buren C. T., Rothkopf M. M., Daly J. M., Adelsberg B. R. Early enteral administration of a formula (Impact) supplemented with arginine, nucleotides, and fish oil in intensive care unit patients: results of a multicenter, prospective, randomized, clinical trial. Crit Care Med. 1995 Mar;23(3):436–449. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199503000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen M. S., Høy C. E., Becker C. C., Redgrave T. G. Intestinal absorption and lymphatic transport of eicosapentaenoic (EPA), docosahexaenoic (DHA), and decanoic acids: dependence on intramolecular triacylglycerol structure. Am J Clin Nutr. 1995 Jan;61(1):56–61. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/61.1.56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. M., Lieberman M. D., Goldfine J., Shou J., Weintraub F., Rosato E. F., Lavin P. Enteral nutrition with supplemental arginine, RNA, and omega-3 fatty acids in patients after operation: immunologic, metabolic, and clinical outcome. Surgery. 1992 Jul;112(1):56–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMichele S. J., Karlstad M. D., Bistrian B. R., Istfan N., Babayan V. K., Blackburn G. L. Enteral nutrition with structured lipid: effect on protein metabolism in thermal injury. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Dec;50(6):1295–1302. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/50.6.1295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endres S., Ghorbani R., Kelley V. E., Georgilis K., Lonnemann G., van der Meer J. W., Cannon J. G., Rogers T. S., Klempner M. S., Weber P. C. The effect of dietary supplementation with n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on the synthesis of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor by mononuclear cells. N Engl J Med. 1989 Feb 2;320(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198902023200501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feingold K. R., Serio M. K., Adi S., Moser A. H., Grunfeld C. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates hepatic lipid synthesis and secretion. Endocrinology. 1989 May;124(5):2336–2342. doi: 10.1210/endo-124-5-2336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y. M., Marano M. A., Moldawer L. L., Wei H., Calvano S. E., Kenney J. S., Allison A. C., Cerami A., Shires G. T., Lowry S. F. The acute splanchnic and peripheral tissue metabolic response to endotoxin in humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1896–1904. doi: 10.1172/JCI114651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollaher C. J., Fechner K., Karlstad M., Babayan V. K., Bistrian B. R. The effect of increasing levels of fish oil-containing structured triglycerides on protein metabolism in parenterally fed rats stressed by burn plus endotoxin. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1993 May-Jun;17(3):247–253. doi: 10.1177/0148607193017003247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottschlich M. M., Jenkins M., Warden G. D., Baumer T., Havens P., Snook J. T., Alexander J. W. Differential effects of three enteral dietary regimens on selected outcome variables in burn patients. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1990 May-Jun;14(3):225–236. doi: 10.1177/0148607190014003225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunfeld C., Soued M., Adi S., Moser A. H., Dinarello C. A., Feingold K. R. Evidence for two classes of cytokines that stimulate hepatic lipogenesis: relationships among tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1 and interferon-alpha. Endocrinology. 1990 Jul;127(1):46–54. doi: 10.1210/endo-127-1-46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hales C. A., Sonne L., Peterson M., Kong D., Miller M., Watkins W. D. Role of thromboxane and prostacyclin in pulmonary vasomotor changes after endotoxin in dogs. J Clin Invest. 1981 Aug;68(2):497–505. doi: 10.1172/JCI110281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard V. S., McKenna M. C. Absorption of safflower oil and structured lipid preparations in patients with cystic fibrosis. Lipids. 1987 Jun;22(6):424–428. doi: 10.1007/BF02537273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jandacek R. J., Whiteside J. A., Holcombe B. N., Volpenhein R. A., Taulbee J. D. The rapid hydrolysis and efficient absorption of triglycerides with octanoic acid in the 1 and 3 positions and long-chain fatty acid in the 2 position. Am J Clin Nutr. 1987 May;45(5):940–945. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/45.5.940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen G. L., McGarvey N., Taraszewski R., Wixson S. K., Seidner D. L., Pai T., Yeh Y. Y., Lee T. W., DeMichele S. J. Lymphatic absorption of enterally fed structured triacylglycerol vs physical mix in a canine model. Am J Clin Nutr. 1994 Oct;60(4):518–524. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/60.4.518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston D. E., Peterson M. B., Mion F., Berninger R. W., Jefferson D. M. Synthesis and degradation of eicosanoids in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1991 Jun;43(2):119–132. doi: 10.1016/0952-3278(91)90182-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley V. E., Mackie J., Strom T. B. Cyclosporin A plus fish oil: accentuate the positive, eliminate the negative. Transplant Proc. 1989 Feb;21(1 Pt 1):848–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudsk K. A., Croce M. A., Fabian T. C., Minard G., Tolley E. A., Poret H. A., Kuhl M. R., Brown R. O. Enteral versus parenteral feeding. Effects on septic morbidity after blunt and penetrating abdominal trauma. Ann Surg. 1992 May;215(5):503–513. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199205000-00013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopes S. M., Trimbo S. L., Mascioli E. A., Blackburn G. L. Human plasma fatty acid variations and how they are related to dietary intake. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Mar;53(3):628–637. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.3.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall L. A., Johnston P. V. alpha-Linolenic and linoleic acids and the immune response. Prog Lipid Res. 1981;20:731–734. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(81)90133-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascioli E. A., Iwasa Y., Trimbo S., Leader L., Bistrian B. R., Blackburn G. L. Endotoxin challenge after menhaden oil diet: effects on survival of guinea pigs. Am J Clin Nutr. 1989 Feb;49(2):277–282. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/49.2.277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mascioli E., Leader L., Flores E., Trimbo S., Bistrian B., Blackburn G. Enhanced survival to endotoxin in guinea pigs fed IV fish oil emulsion. Lipids. 1988 Jun;23(6):623–625. doi: 10.1007/BF02535609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna M. C., Hubbard V. S., Bieri J. G. Linoleic acid absorption from lipid supplements in patients with cystic fibrosis with pancreatic insufficiency and in control subjects. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 1985 Feb;4(1):45–51. doi: 10.1097/00005176-198502000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Memon R. A., Grunfeld C., Moser A. H., Feingold K. R. Tumor necrosis factor mediates the effects of endotoxin on cholesterol and triglyceride metabolism in mice. Endocrinology. 1993 May;132(5):2246–2253. doi: 10.1210/endo.132.5.8477669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meydani S. N., Endres S., Woods M. M., Goldin B. R., Soo C., Morrill-Labrode A., Dinarello C. A., Gorbach S. L. Oral (n-3) fatty acid supplementation suppresses cytokine production and lymphocyte proliferation: comparison between young and older women. J Nutr. 1991 Apr;121(4):547–555. doi: 10.1093/jn/121.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Feliciano D. V., Andrassy R. J., McArdle A. H., Booth F. V., Morgenstein-Wagner T. B., Kellum J. M., Jr, Welling R. E., Moore E. E. Early enteral feeding, compared with parenteral, reduces postoperative septic complications. The results of a meta-analysis. Ann Surg. 1992 Aug;216(2):172–183. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199208000-00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore F. A., Moore E. E., Kudsk K. A., Brown R. O., Bower R. H., Koruda M. J., Baker C. C., Barbul A. Clinical benefits of an immune-enhancing diet for early postinjury enteral feeding. J Trauma. 1994 Oct;37(4):607–615. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199410000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nixon D. W., Heymsfield S. B., Cohen A. E., Kutner M. H., Ansley J., Lawson D. H., Rudman D. Protein-calorie undernutrition in hospitalized cancer patients. Am J Med. 1980 May;68(5):683–690. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90254-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombo J. D., Bistrian B. R., Fechner K. D., Blackburn G. L., Forse R. A. Rapid incorporation of fish or olive oil fatty acids into rat hepatic sinusoidal cell phospholipids after continuous enteral feeding during endotoxemia. Am J Clin Nutr. 1993 May;57(5):643–649. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/57.5.643. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palombo J. D., Lopes S. M., Zeisel S. H., Jenkins R. L., Albers J. J., Blackburn G. L., Bistrian B. R. Effectiveness of orthotopic liver transplantation on the restoration of cholesterol metabolism in patients with end-stage liver disease. Gastroenterology. 1987 Dec;93(6):1170–1177. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90241-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillipson B. E., Rothrock D. W., Connor W. E., Harris W. S., Illingworth D. R. Reduction of plasma lipids, lipoproteins, and apoproteins by dietary fish oils in patients with hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 1985 May 9;312(19):1210–1216. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198505093121902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Trocki O., Alexander J. W., Kopcha R., Heyd T., Joffe S. N. The effect of route of nutrient administration on the nutritional state, catabolic hormone secretion, and gut mucosal integrity after burn injury. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr. 1987 Jan-Feb;11(1):1–7. doi: 10.1177/014860718701100101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swails W. S., Bell S. J., Bistrian B. R., Lewis E. J., Pfister D., Forse R. A., Kelly S., Blackburn G. L. Fish-oil-containing diet and platelet aggregation. Nutrition. 1993 May-Jun;9(3):211–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teo T. C., DeMichele S. J., Selleck K. M., Babayan V. K., Blackburn G. L., Bistrian B. R. Administration of structured lipid composed of MCT and fish oil reduces net protein catabolism in enterally fed burned rats. Ann Surg. 1989 Jul;210(1):100–107. doi: 10.1097/00000658-198907000-00015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshino S., Ellis E. F. Effect of a fish-oil-supplemented diet on inflammation and immunological processes in rats. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1987;84(3):233–240. doi: 10.1159/000234429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Heide J. J., Bilo H. J., Donker J. M., Wilmink J. M., Tegzess A. M. Effect of dietary fish oil on renal function and rejection in cyclosporine-treated recipients of renal transplants. N Engl J Med. 1993 Sep 9;329(11):769–773. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309093291105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]