Abstract
OBJECTIVE: The authors determined whether the decrease in lymphocytes after surgery is related to apoptosis. SUMMARY BACKGROUND DATA: Surgery induces a profound but transient depletion of circulating lymphocytes, However, the mechanism underlying this phenomenon is unclear. METHODS: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were obtained from 18 patients before and after elective surgery and studied for morphologic and biochemical markers of apoptosis, DNA fragmentation, and Fas expression. RESULTS: The DNA staining of peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained after surgery, which had been cultured for 24 hours in vitro, showed chromatin condensation and fragmentation of cells into collapsed spheres. Moreover, DNA isolated from these peripheral blood mononuclear cells formed a ladder of oligonucleosomal fragments. However, peripheral blood mononuclear cells obtained before surgery showed neither of these changes. The observation that none of these apoptotic cells ingested latex suggested that they were of lymphocytic origin. Fas-positive lymphocytes increased significantly 2 hours after the start of surgery and returned to preoperative levels by postoperative day 7. Anti-Fas antibody augmented apoptosis, whereas ZB4, a Fas antagonist, inhibited apoptosis in lymphocytes after surgery. CONCLUSIONS: These results indicate that circulating lymphocytes in the early perioperative period are susceptible to Fas-mediated apoptosis, which may cause depletion of circulating lymphocytes after surgery.
Full text
PDF


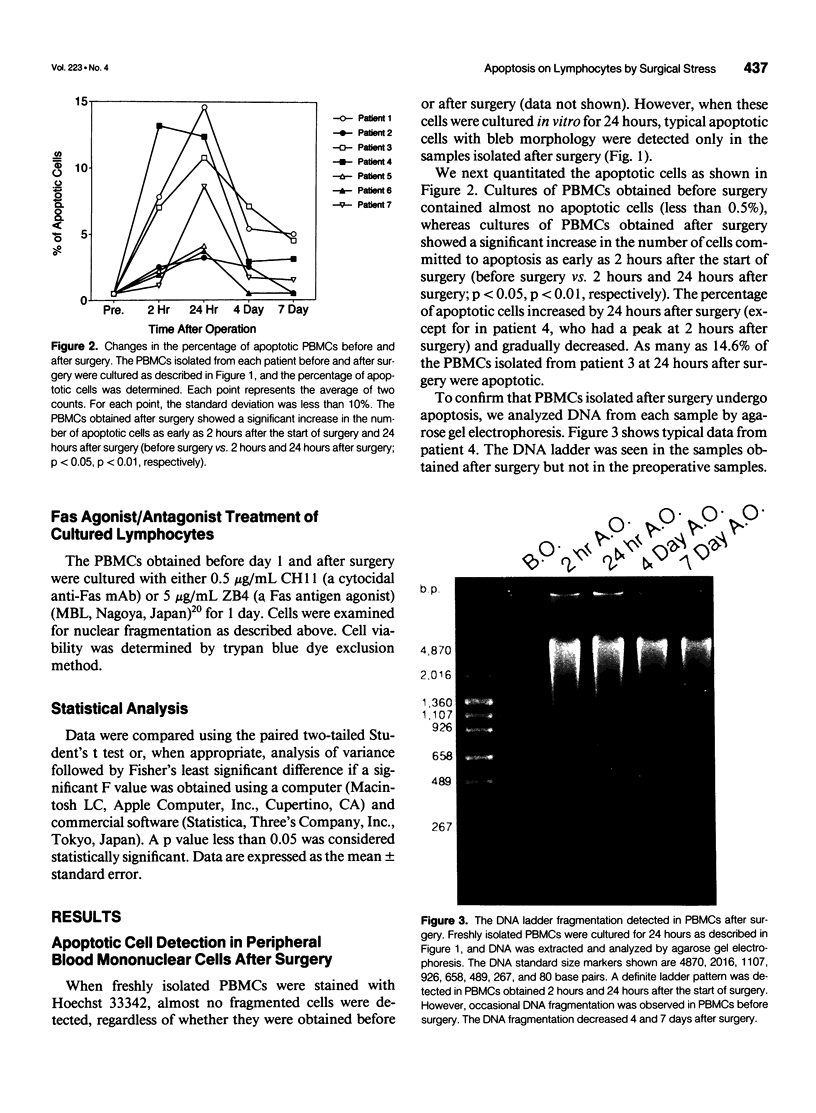
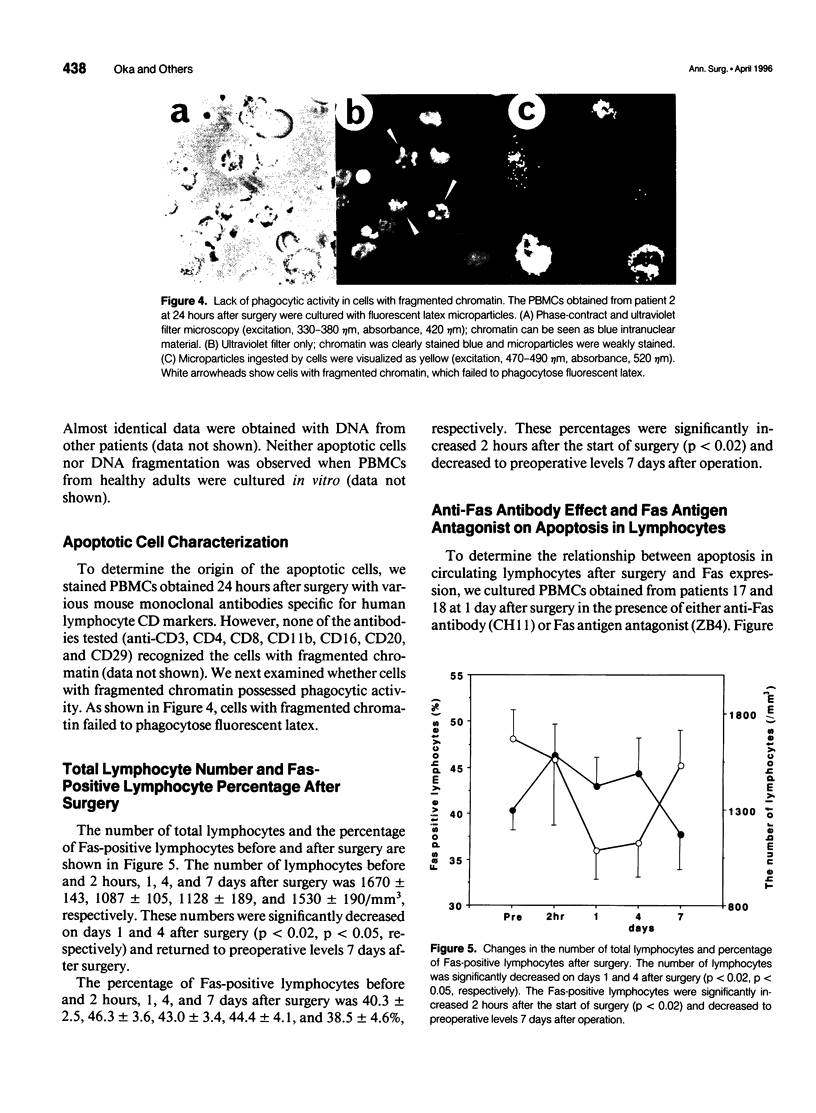
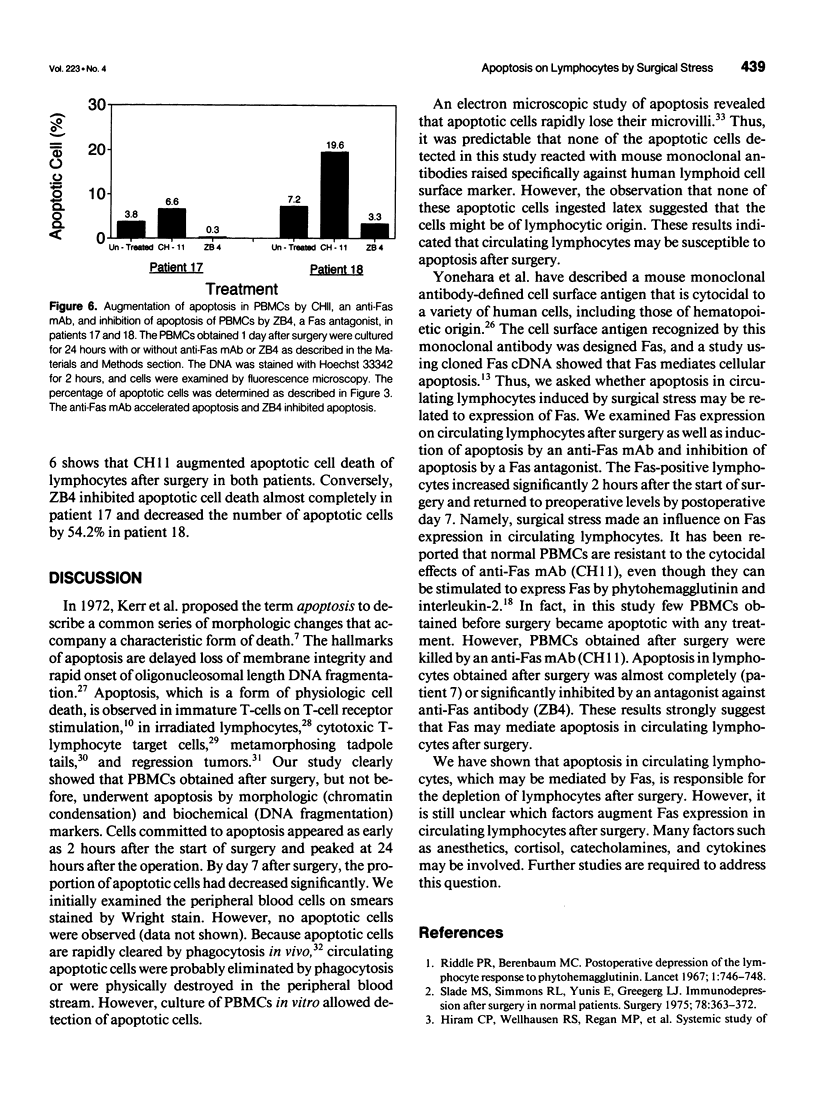

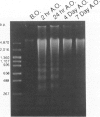
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham E. Immunologic mechanisms underlying sepsis in the critically ill surgical patient. Surg Clin North Am. 1985 Aug;65(4):991–1003. doi: 10.1016/s0039-6109(16)43690-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debatin K. M., Goldman C. K., Waldmann T. A., Krammer P. H. APO-1-induced apoptosis of leukemia cells from patients with adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 1993 Jun 1;81(11):2972–2977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhein J., Walczak H., Bäumler C., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Autocrine T-cell suicide mediated by APO-1/(Fas/CD95) Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):438–441. doi: 10.1038/373438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Don M. M., Ablett G., Bishop C. J., Bundesen P. G., Donald K. J., Searle J., Kerr J. F. Death of cells by apoptosis following attachment of specifically allergized lymphocytes in vitro. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1977 Aug;55(4):407–417. doi: 10.1038/icb.1977.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espanol T., Todd G. B., Soothill J. F. The effect of anaesthesia on the lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Sep;18(1):73–79. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk M. H., Trauth B. C., Debatin K. M., Klas C., Gregory C. D., Rickinson A. B., Calender A., Lenoir G. M., Ellwart J. W., Krammer P. H. Expression of the APO-1 antigen in Burkitt lymphoma cell lines correlates with a shift towards a lymphoblastoid phenotype. Blood. 1992 Jun 15;79(12):3300–3306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanabuchi S., Koyanagi M., Kawasaki A., Shinohara N., Matsuzawa A., Nishimura Y., Kobayashi Y., Yonehara S., Yagita H., Okumura K. Fas and its ligand in a general mechanism of T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):4930–4934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh N., Yonehara S., Ishii A., Yonehara M., Mizushima S., Sameshima M., Hase A., Seto Y., Nagata S. The polypeptide encoded by the cDNA for human cell surface antigen Fas can mediate apoptosis. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90614-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leithäuser F., Dhein J., Mechtersheimer G., Koretz K., Brüderlein S., Henne C., Schmidt A., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H., Möller P. Constitutive and induced expression of APO-1, a new member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, in normal and neoplastic cells. Lab Invest. 1993 Oct;69(4):415–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARKLEY K., BOCANEGRA M., EGO-AGUIRRE E., CHIAPPORI M., MORALES G. Adrenocortical function after major surgical operations and thermal trauma in man. Surgery. 1960 Mar;47:389–398. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mita E., Hayashi N., Iio S., Takehara T., Hijioka T., Kasahara A., Fusamoto H., Kamada T. Role of Fas ligand in apoptosis induced by hepatitis C virus infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Oct 28;204(2):468–474. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.2483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara J., Suda T., Nagata S. Selective apoptosis of CD4+CD8+ thymocytes by the anti-Fas antibody. J Exp Med. 1995 Feb 1;181(2):485–491. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Schaub L. B., Yonehara S., Crump W. L., 3rd, Grimm E. A. DNA fragmentation and cell death is selectively triggered in activated human lymphocytes by Fas antigen engagement. Cell Immunol. 1992 Mar;140(1):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(92)90187-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polk H. C., Jr, George C. D., Wellhausen S. R., Cost K., Davidson P. R., Regan M. P., Borzotta A. P. A systematic study of host defense processes in badly injured patients. Ann Surg. 1986 Sep;204(3):282–299. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle P. R., Berenbaum M. C. Postoperative depression of the lymphocyte response to phytohaemagglutinin. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):746–748. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91364-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross H., Johnston I. D., Welborn T. A., Wright A. D. Effect of abdominal operation on glucose tolerance and serum levels of insulin, growth hormone, and hydrocortisone. Lancet. 1966 Sep 10;2(7463):563–566. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)93036-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savill J., Fadok V., Henson P., Haslett C. Phagocyte recognition of cells undergoing apoptosis. Immunol Today. 1993 Mar;14(3):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. M., Osborne B. A. Programmed cell death, apoptosis and killer genes. Immunol Today. 1993 Dec;14(12):582–590. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(93)90197-S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellins K. S., Cohen J. J. Gene induction by gamma-irradiation leads to DNA fragmentation in lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Nov 15;139(10):3199–3206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slade M. S., Simmons R. L., Yunis E., Greenberg L. J. Immunodepression after major surgery in normal patients. Surgery. 1975 Sep;78(3):363–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strasser A. Apoptosis. Death of a T cell. Nature. 1995 Feb 2;373(6513):385–386. doi: 10.1038/373385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Takahashi T., Golstein P., Nagata S. Molecular cloning and expression of the Fas ligand, a novel member of the tumor necrosis factor family. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1169–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90326-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trauth B. C., Klas C., Peters A. M., Matzku S., Möller P., Falk W., Debatin K. M., Krammer P. H. Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science. 1989 Jul 21;245(4915):301–305. doi: 10.1126/science.2787530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonehara S., Ishii A., Yonehara M. A cell-killing monoclonal antibody (anti-Fas) to a cell surface antigen co-downregulated with the receptor of tumor necrosis factor. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1747–1756. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonehara S., Nishimura Y., Kishil S., Yonehara M., Takazawa K., Tamatani T., Ishii A. Involvement of apoptosis antigen Fas in clonal deletion of human thymocytes. Int Immunol. 1994 Dec;6(12):1849–1856. doi: 10.1093/intimm/6.12.1849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. The Caenorhabditis elegans genes ced-3 and ced-4 act cell autonomously to cause programmed cell death. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90174-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]