Full text
PDF

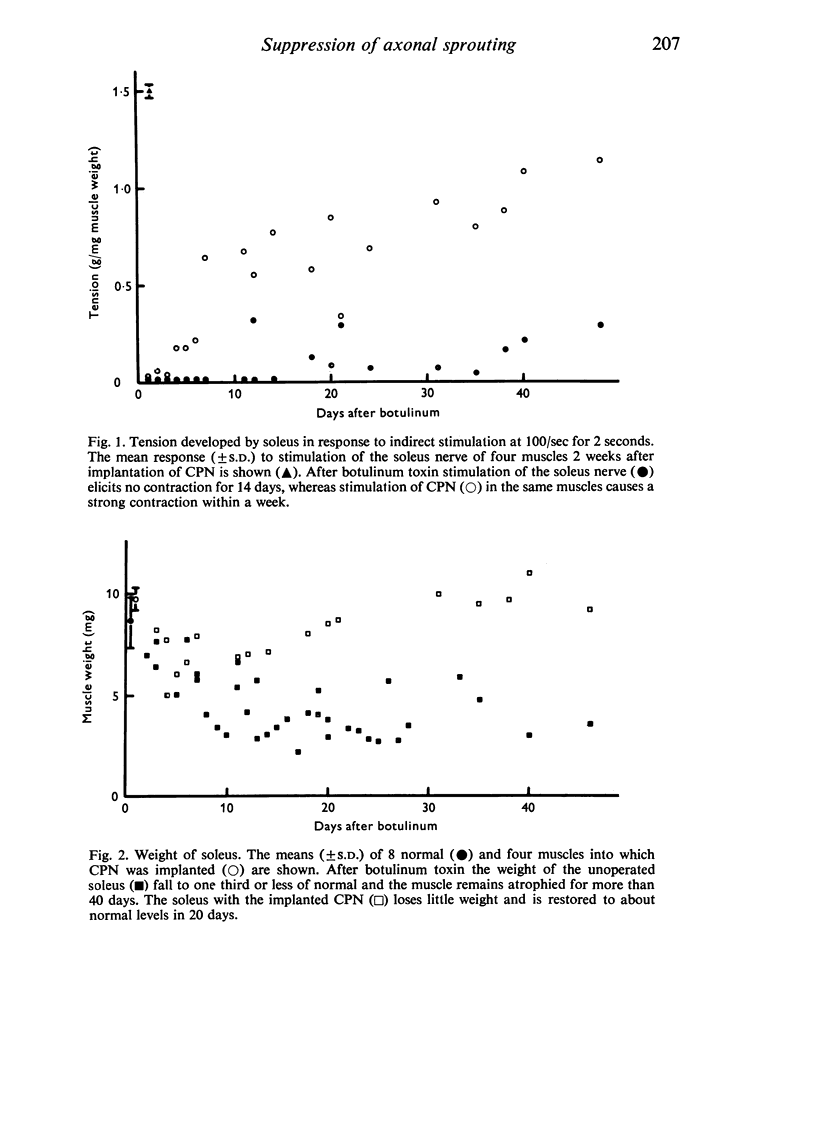



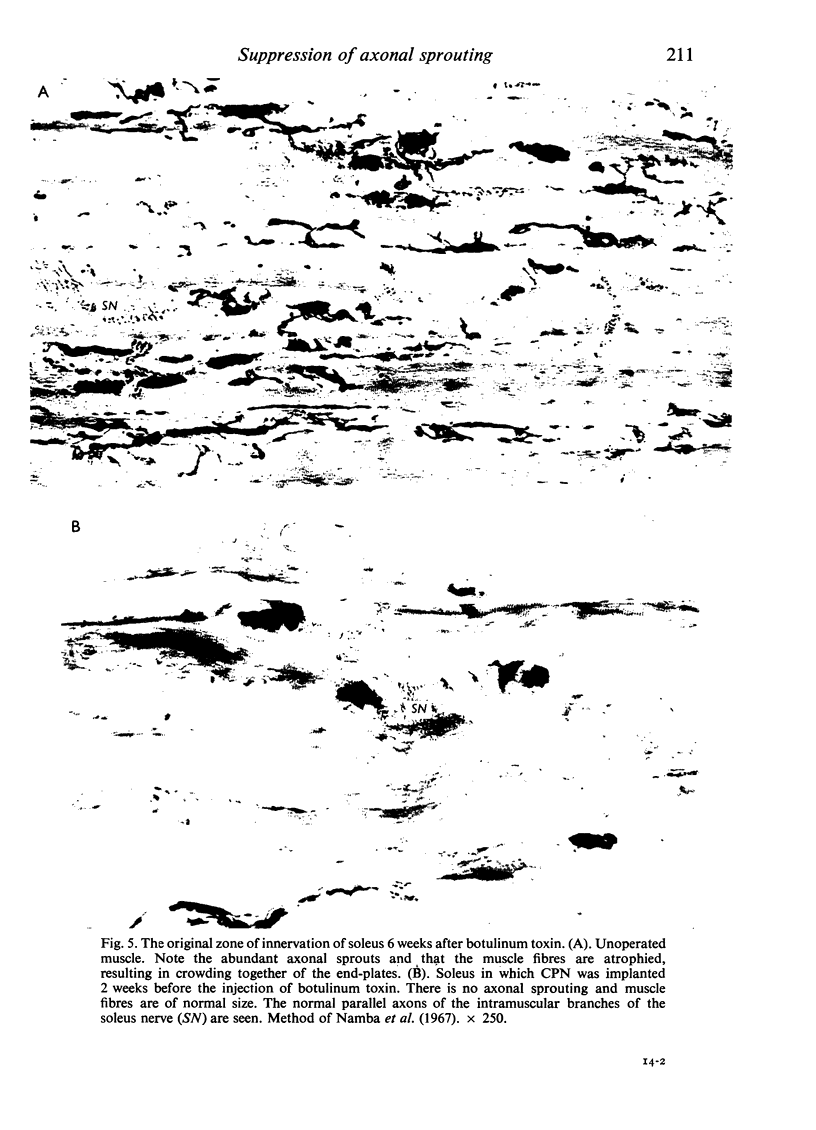




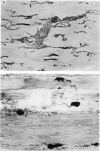
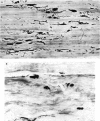
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURGEN A. S. V., DICKENS F., ZATMAN L. J. The action of botulinum toxin on the neuro-muscular junction. J Physiol. 1949 Aug;109(1-2):10–24. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coërs C. Structure and organization of the myoneural junction. Int Rev Cytol. 1967;22:239–267. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61837-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W. An electron microscopic comparison of motor end-plates of slow and fast skeletal muscle fibres of the mouse. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Sep;14(1):37–45. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W. An electron microscopic study of the changes induced by botulinum toxin in the motor end-plates of slow and fast skeletal muscle fibres of the mouse. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Sep;14(1):47–60. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W. Changes in motor innervation and cholinesterase localization induced by botulinum toxin in skeletal muscle of the mouse: differences between fast and slow muscles. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;33(1):40–54. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.1.40. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W. Hereditary motor end-plate disease in the mouse: light and electron microscopic studies. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Apr;33(2):238–250. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.2.238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W., Rogers M., Stolkin C., Tonge D. A. Proceedings: Suppression of botulinum toxin-induced axonal sprouting in skeletal muscle by implantation of an extra nerve. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):1P–2P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W., Stefani E. Electrophysiological studies of neuromuscular transmission in hereditary 'motor end-plate disease' of the mouse. J Physiol. 1971 Jan;212(2):535–548. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1971.sp009340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W., Strich S. J. The effects of botulinum toxin on the pattern of innervation of skeletal muscle in the mouse. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1968 Jan;53(1):84–89. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1968.sp001948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duchen L. W., Tonge D. A. The effects of tetanus toxin on neuromuscular transmission and on the morphology of motor end-plates in slow and fast skeletal muscle of the mouse. J Physiol. 1973 Jan;228(1):157–172. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsberg C. A. EXPERIMENTS ON MOTOR NERVE REGENERATION AND THE DIRECT NEUROTIZATION OF PARALYZED MUSCLES BY THEIR OWN AND BY FOREIGN NERVES. Science. 1917 Mar 30;45(1161):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.45.1161.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex S., Sonesson B., Thesleff S., Zelená J. Nerve implants in botulinum poisoned mammalian muscle. J Physiol. 1966 Jun;184(4):872–882. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fex S., Thesleff S. The time required for innervation of denervated muscles by nerve implants. Life Sci. 1967 Mar 15;6(6):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwyn D. G., Aitken J. T. The formation of new motor endplates in mammalian skeletal muscle. J Anat. 1966 Jan;100(Pt 1):111–126. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Nakamura T., Grob D. Staining for nerve fiber and cholinesterase activity in fresh frozen sections. Am J Clin Pathol. 1967 Jan;47(1):74–77. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/47.1.74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spitzer N. Miniature end-plate potentials at mammalian neuromuscular junctions poisoned by botulinum toxin. Nat New Biol. 1972 May 3;237(70):26–27. doi: 10.1038/newbio237026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonge D. A. Chronic effects of botulinum toxin on neuromuscular transmission and sensitivity to acetylcholine in slow and fast skeletal muscle of the mouse. J Physiol. 1974 Aug;241(1):127–139. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1974.sp010644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]